HACKED, BREACHED, RANSOMED Why your entire org needs to care about
28 Slides1.16 MB

HACKED, BREACHED, RANSOMED Why your entire org needs to care about cybersecurity SEPTEMBER 27, 2021

Welcome!

MEET THE PRESENTER Adam Devereaux Digital Transformation Consultant @ Worksighted 11 years at Worksighted & 20 years helping Organizations with Security, Strategy, Planning and Technical consulting. 8 years clinical healthcare experience- 4 in LTC, 4 in ER

CYBER-CRIME? IT’S CRIME Ransomware Ransom (sometimes also extortion) Denial of Service attacks (DDOS) Extortion Phishing - Con jobs - scam artists Spear phishing - Sophisticated scam artists targeting you and your users Hacking - B&E

WHY THERE IS SO MUCH CYBER-CRIME? Full time job: FBI tracking over 100 active ransomware groups Cyber Warfare Nation state tolerance Training Spoils of Cyber-War Crime as a Service

WHY DO YOU CARE? Your Organization: Information Reputation Downtime Money Fines *Criminals can and will use this all against you. You Personally: Information Personal Reputation Money

HOW DO THEY GET YOUR PASSWORD? Phishing - users entering their credentials where they shouldn’t Dictionary attacks – Commonly Used Passwords Password re-use with other services Key Loggers Brute Force Attacks

WHAT HAPPENS IF MY EMAIL IS “BREACHED ”? WHY SHOULD I CARE? What’s happening now? What is data exfiltration? Why does this matter for healthcare orgs in particular? New tactics by attackers Direct deposit scams- can cause harm no matter who is breached

COMPUTER LICENSE?

Security vs Convenience What is the value of what you need to protect? Compliance requirements No Perfect Security – but what is right for you?

BREAKING DOWN AN ATTACK

EXAMPLE ATTACK PHISHING WITH BUSINESS CREDENTIAL RELEASE
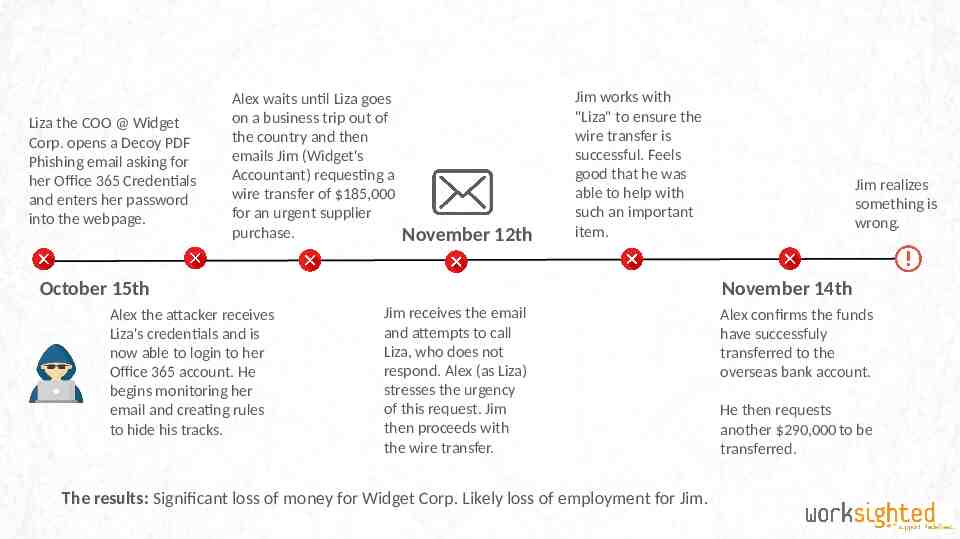
Liza the COO @ Widget Corp. opens a Decoy PDF Phishing email asking for her Office 365 Credentials and enters her password into the webpage. Alex waits until Liza goes on a business trip out of the country and then emails Jim (Widget's Accountant) requesting a wire transfer of 185,000 for an urgent supplier purchase. November 12th Jim works with "Liza" to ensure the wire transfer is successful. Feels good that he was able to help with such an important item. October 15th Alex the attacker receives Liza's credentials and is now able to login to her Office 365 account. He begins monitoring her email and creating rules to hide his tracks. Jim realizes something is wrong. November 14th Jim receives the email and attempts to call Liza, who does not respond. Alex (as Liza) stresses the urgency of this request. Jim then proceeds with the wire transfer. The results: Significant loss of money for Widget Corp. Likely loss of employment for Jim. Alex confirms the funds have successfuly transferred to the overseas bank account. He then requests another 290,000 to be transferred.
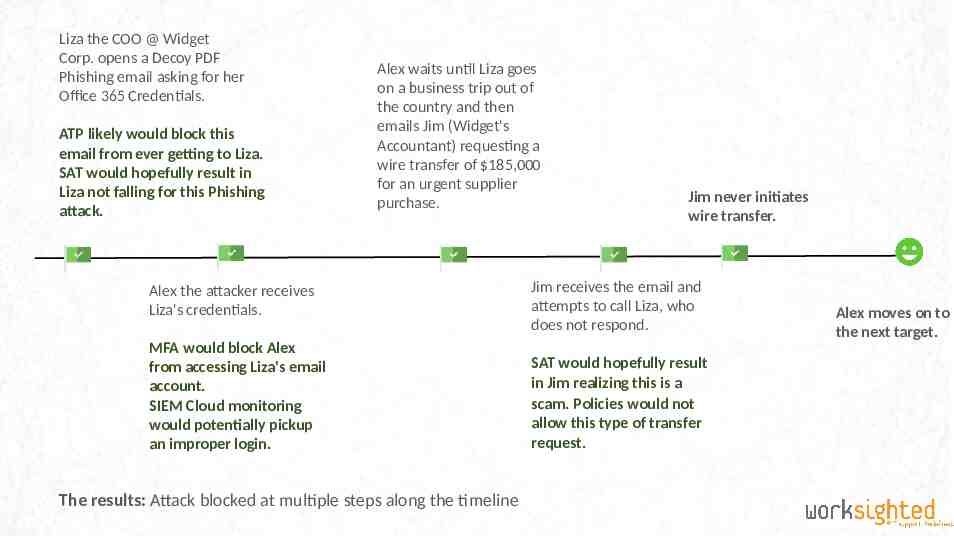
Liza the COO @ Widget Corp. opens a Decoy PDF Phishing email asking for her Office 365 Credentials. ATP likely would block this email from ever getting to Liza. SAT would hopefully result in Liza not falling for this Phishing attack. Alex waits until Liza goes on a business trip out of the country and then emails Jim (Widget's Accountant) requesting a wire transfer of 185,000 for an urgent supplier purchase. Jim never initiates wire transfer. Alex the attacker receives Liza's credentials. Jim receives the email and attempts to call Liza, who does not respond. MFA would block Alex from accessing Liza's email account. SIEM Cloud monitoring would potentially pickup an improper login. SAT would hopefully result in Jim realizing this is a scam. Policies would not allow this type of transfer request. The results: Attack blocked at multiple steps along the timeline Alex moves on to the next target.

EXAMPLE ATTACK RANSOMWARE
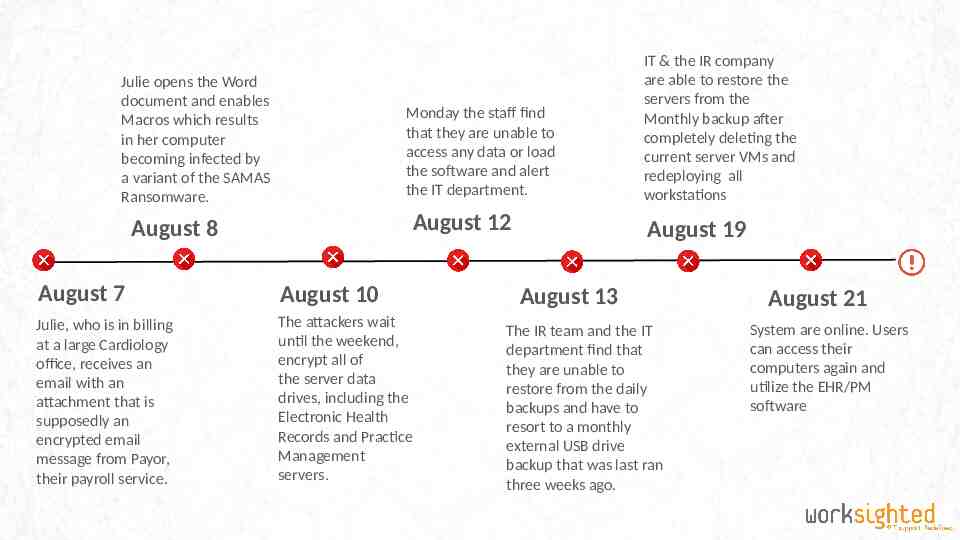
Julie opens the Word document and enables Macros which results in her computer becoming infected by a variant of the SAMAS Ransomware. Monday the staff find that they are unable to access any data or load the software and alert the IT department. August 12 August 8 August 7 August 10 Julie, who is in billing at a large Cardiology office, receives an email with an attachment that is supposedly an encrypted email message from Payor, their payroll service. The attackers wait until the weekend, encrypt all of the server data drives, including the Electronic Health Records and Practice Management servers. IT & the IR company are able to restore the servers from the Monthly backup after completely deleting the current server VMs and redeploying all workstations August 19 August 13 The IR team and the IT department find that they are unable to restore from the daily backups and have to resort to a monthly external USB drive backup that was last ran three weeks ago. August 21 System are online. Users can access their computers again and utilize the EHR/PM software
Julie Opens the Word document and enables Macros which results in her computer becoming infected SIEM/SOC would likely detect infection. Monday the staff find that they are unable to access any data or load the software and alert the IT department. Incident Response plan August 8 August 7 August 10 - AM August 9 Julie in billing at a large Cardiology office receives an email ATP would likely block the email. With SAT Julie would be wiser to the scam. The attackers wait until the weekend, encrypt all server data drives, including the Electronic Health Records and Practice Management servers. IT & the IR company are able to restore the servers from the nightly offsite backup. BC/DR planning and resources August 11 - AM August 10 - PM The IR team and the IT department find that they are unable to restore from the daily backups. Daily offsite backups that attackers are unable to access prevents massive data loss. The results: Ideally attack is not successful, but BC planning and DR plan saved August 11 - PM System are online. Users can access their computers again and full functionality restored.

OVERVIEW OF ATTACK DISSECTIONS Attack #1: Phishing What you can do: Training, Email Security, MFA, SIEM/SOC, Policies Attack #2: Ransomware What you can do: All of the above and always Business Continuity planning and resources

What does it look like to be attacked? Follow your response plan Engage your insurance company. Seek Legal Counsel Identify and Notify Parties Impacted Document Lessons Learned

CYBER SECURITY FRAMEWORKS Controls based: Program based: Risk based: Develop a basic strategy for security team Assess state of security program Build comprehensive security program Measure program security / competitive analysis Simplify communication between security team and business leaders Define key process steps to assess/manage risk Structure program for risk management Identify, measure, and quantify risk Prioritize security activities Examples: ISO/IEC 27001 NIST 800-53 Examples: NIST SP 800-39 NIST SP 800-37 Provide baseline set of controls Assess current technical state Prioritize control implementation Examples: NIST SP 800-53 CIS top 20 / 18

NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK Identify Risk planning Security posture Information mapping Protect SAT / MFA / IAM Detect SIEM/SOC Respond Recover Response BCP / DR Analysis Incident Response pla Communication Mitigation
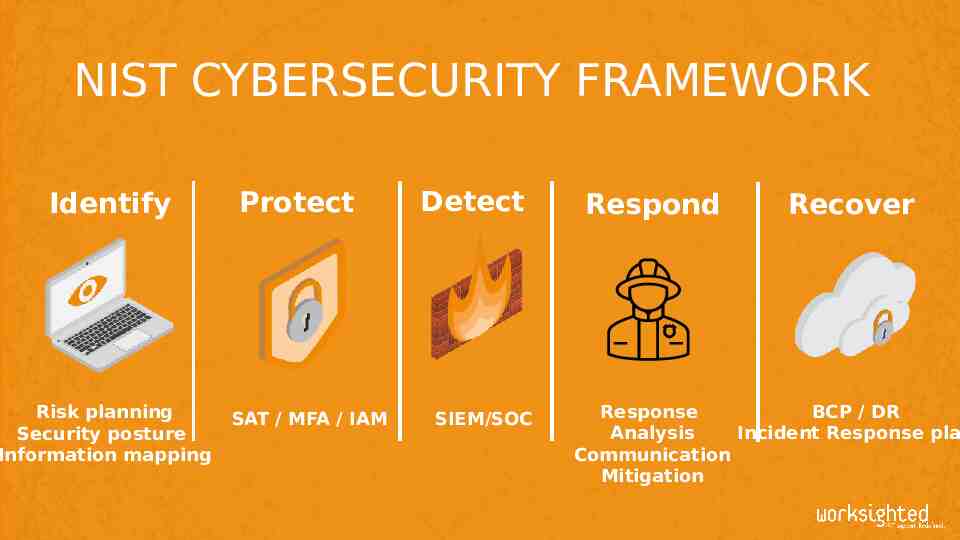
IDENTIFY Develop organizational understanding to manage cybersecurity risk to systems, people, assets, data, and capabilities.

PROTECT Develop and implement the appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical infrastructure services.

DETECT Develop and implement the appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event

RESPOND Develop and implement activities to take action: Analysis Response Communication Mitigation

RECOVER Develop and implement the appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident.

NEXT STEPS Learn, Connect, Grow.