Capability Maturity Model (CMM) in SW design Process Harri Reiman
30 Slides402.50 KB

Capability Maturity Model (CMM) in SW design Process Harri Reiman Section manager, IP Solutions Ericsson, Finland Email: [email protected] Phone: 358-9-2992254 CMM in SW design 1 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
Outline Basic rules in improvements Problems in SW projects - CMM as a helper CMM backround – – – – The SW crisis Increasing SW complexity Success factors Mature organisations Process - an important element – Role of a process – process as an organisational asset – Improving the process capability CMM as a model – – – – – Process maturity framework Role of CMM CMM structure, version 1.1 Maturity steps Key practices Characteristics on each CMM level – Levels 1- 5 CMM usage in process improvements CMM assessment – What is an an assessment – How an assessment is conducted – What results are produced in an assessment SEI’s maturity survey CMM in SW design 2 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Basic rules in improvements (1) “If you don’t know where you are, a map won’t help” Watts Humprey CMM in SW design 3 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Basic rules in improvements (2) “You need to know where you are, before you can decide where to go!” Grosby CMM in SW design 4 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Common problems in SW projects Project having always resource problems Quality criterias not always met Not enough competence in all projects Unexpected surprises in projects (technical & administrative) Unstabile input documents/products Improvements not meeting the real work . CMM in SW design 5 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

CMM as a helper There is NO silver bullet ! CMM CMM in SW design 6 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
SW crisis Factors leading to the establishment of the SEI (Software Engineering institute) and later on creation of CMM: Increasing cost of SW Quality problems in SW products Cost of SW maintenance US government put billions of dollars in SW acquisition USA’s competitiveness increasingly dependent on SW Increasing rate of change in technology and SW environment Typical SW project was a year late and exceeded two times the budget Increasing SW complexity CMM in SW design 7 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Increasing SW complexity Lines of Code Development structure 1,000 - 5,000 Individual programmer 5,000 - 25,000 25,000 - 100,000 100,000 - 1,000,000 1,000,000 - 10,000,000 10,000,000 - 100,000,000 CMM in SW design 8 Small team Large subdivided team Several teams or division Several companies National undertaking Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Mature organisations Processes are defined, documented and controlled Roles and responsibilities are clear Products and processes are measured Quality, costs and schedules are measured and followed-up Management is committed to continuous improvement Technology is effectively used within organisation’s SW process(es) Preventive quality work is a fact CMM in SW design 9 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
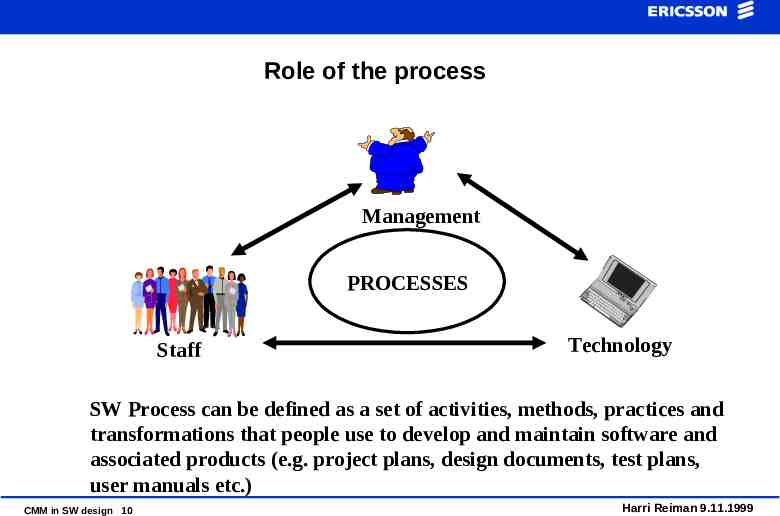
Role of the process Management PROCESSES Staff Technology SW Process can be defined as a set of activities, methods, practices and transformations that people use to develop and maintain software and associated products (e.g. project plans, design documents, test plans, user manuals etc.) CMM in SW design 10 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
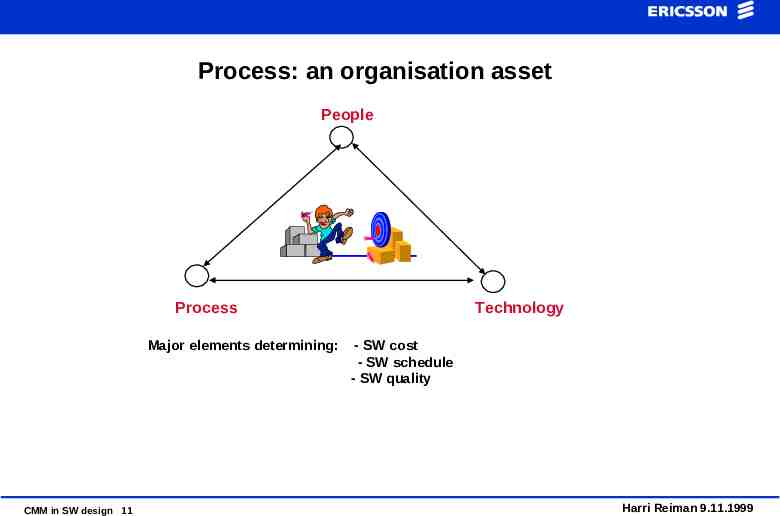
Process: an organisation asset People Process Major elements determining: CMM in SW design 11 Technology - SW cost - SW schedule - SW quality Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
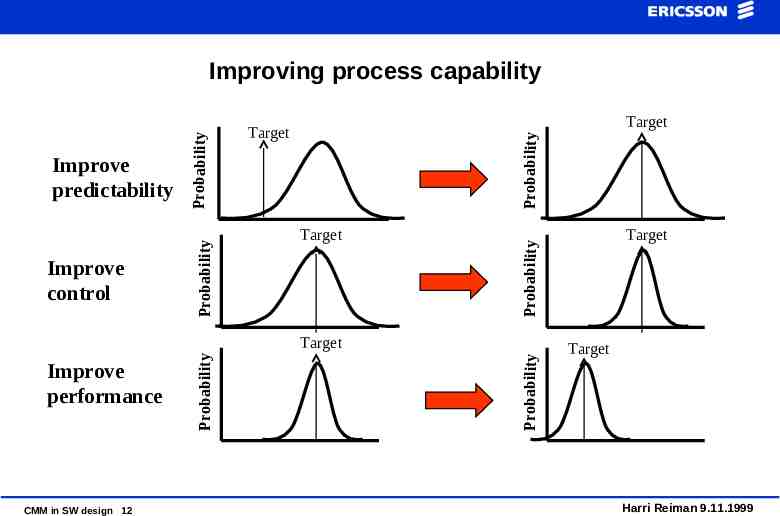
Target Probability Target Target CMM in SW design 12 Probability Probability Target Improve performance Target Probability Improve control Probability Improve predictability Probability Improving process capability Target Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
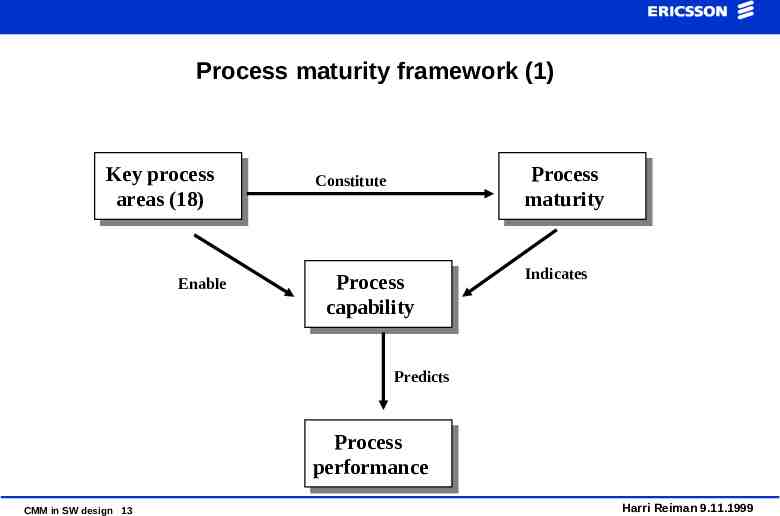
Process maturity framework (1) Key process areas (18) Enable Process maturity Constitute Process capability Indicates Predicts Process performance CMM in SW design 13 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
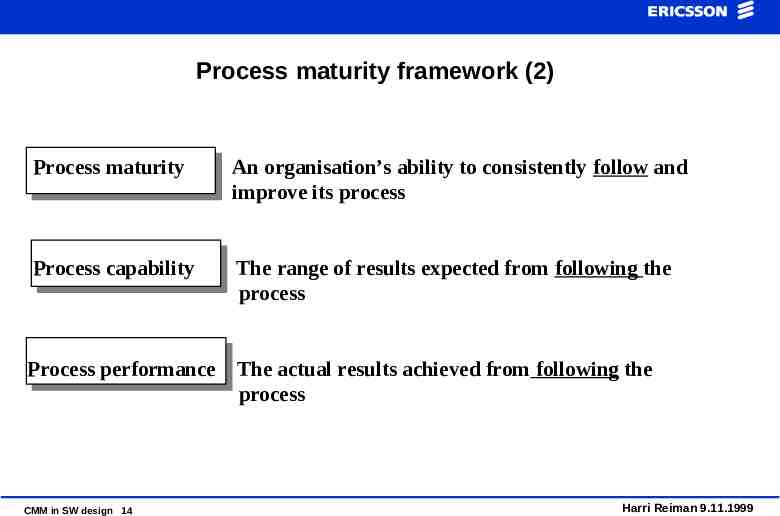
Process maturity framework (2) Process maturity An organisation’s ability to consistently follow and improve its process Process capability The range of results expected from following the process Process performance The actual results achieved from following the process CMM in SW design 14 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Role of CMM Provides a guide for measuring an organisation’s SW process capability Sets goals and priorities for SW process improvements Assists improvement action planning Outlines a method for applying process management and quality improvement concepts to SW development and maintenance Guides an organisation from ad hoc working environment to software “engineering excellence” CMM in SW design 15 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
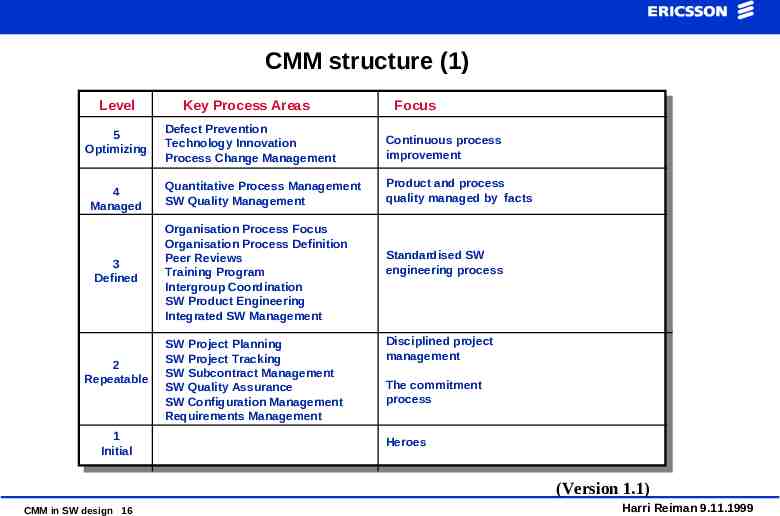
CMM structure (1) Level 5 Optimizing 4 Managed 3 Defined 2 Repeatable 1 Initial Key Process Areas Focus Defect Prevention Technology Innovation Process Change Management Continuous process improvement Quantitative Process Management SW Quality Management Product and process quality managed by facts Organisation Process Focus Organisation Process Definition Peer Reviews Training Program Intergroup Coordination SW Product Engineering Integrated SW Management SW Project Planning SW Project Tracking SW Subcontract Management SW Quality Assurance SW Configuration Management Requirements Management Standardised SW engineering process Disciplined project management The commitment process Heroes (Version 1.1) CMM in SW design 16 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
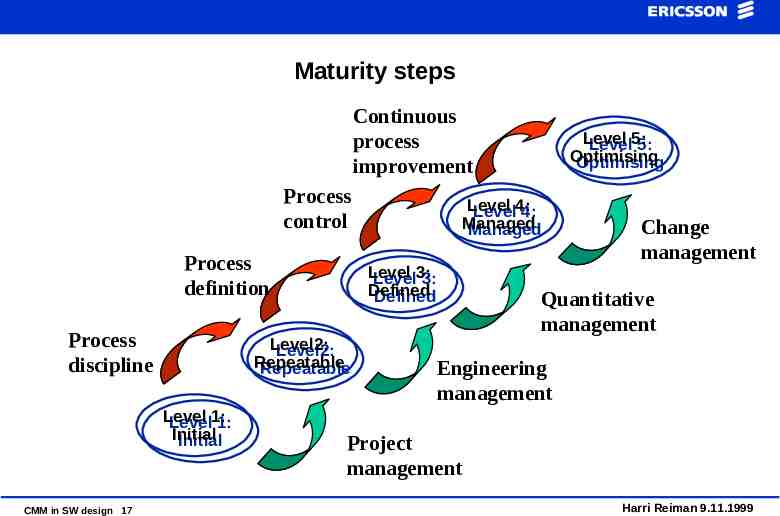
Maturity steps Continuous process improvement Process control Process definition Process discipline Level Level1: 1: Initial Initial CMM in SW design 17 Level Level4: 4: Managed Managed Level Level3: 3: Defined Defined Level2: Level2: Repeatable Repeatable Level Level5: 5: Optimising Optimising Change management Quantitative management Engineering management Project management Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
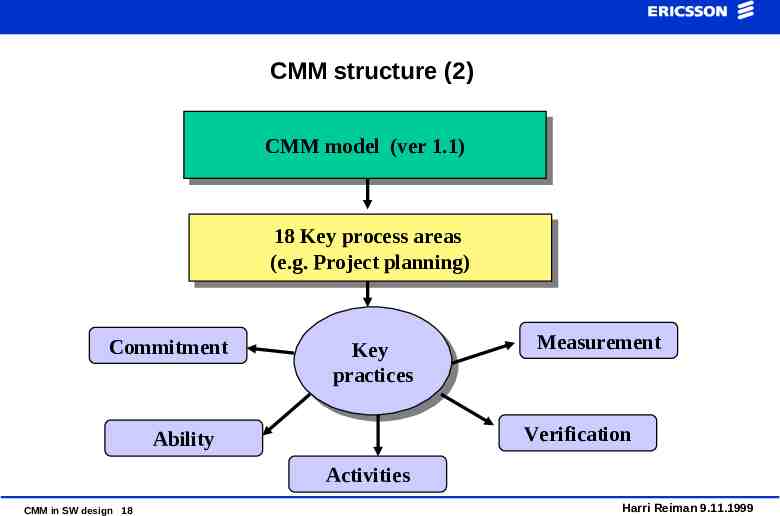
CMM structure (2) CMM CMMmodel model (ver (ver1.1) 1.1) 18 18Key Keyprocess processareas areas (e.g. (e.g.Project Projectplanning) planning) Commitment Key Key practices practices Measurement Verification Ability Activities CMM in SW design 18 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
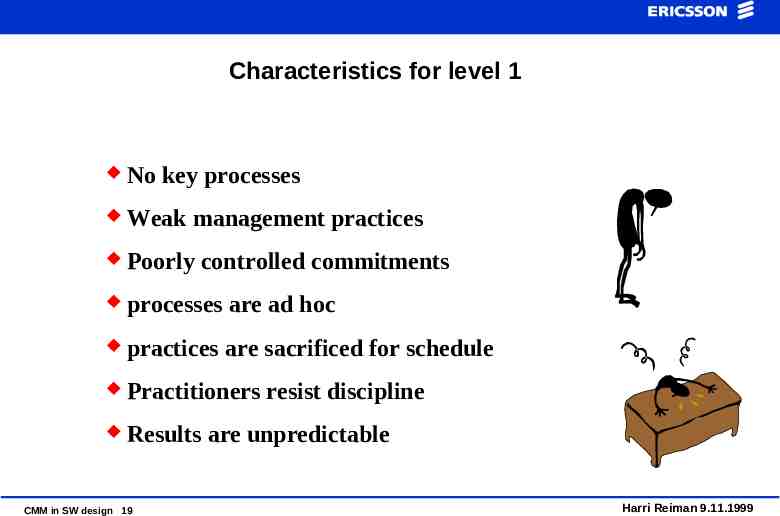
Characteristics for level 1 No key processes Weak management practices Poorly controlled commitments processes are ad hoc practices are sacrificed for schedule Practitioners resist discipline Results are unpredictable CMM in SW design 19 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Characteristics for level 2 Project management is strong and lays foundation for process discipline Project activities are planned and followed Project ensures that practices are performed Corrective actions are made when necessary Project “own” its commitments Commitments are clear and communicated Necessary baselines are build and controlled CMM in SW design 20 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
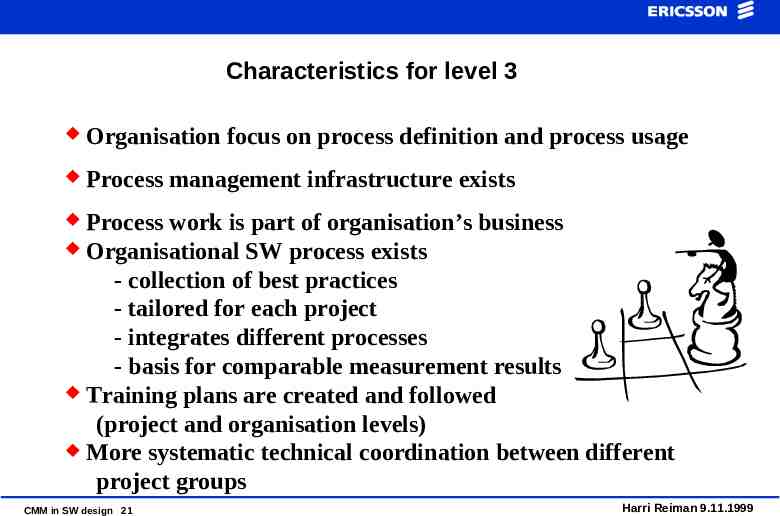
Characteristics for level 3 Organisation focus on process definition and process usage Process management infrastructure exists Process work is part of organisation’s business Organisational SW process exists - collection of best practices - tailored for each project - integrates different processes - basis for comparable measurement results Training plans are created and followed (project and organisation levels) More systematic technical coordination between different project groups CMM in SW design 21 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

Characteristics for level 4 Processes and products are on statistical control Quantitative limits are established for process performance Process performance is managed (I.e quantitatively controlled) Predictability is improved Data is actively used as a base in decision making Process capability baseline is established CMM in SW design 22 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
Characteristics for level 5 Continuous process improvement in place Processes and technology are continuously evaluated Individuals are empowered to improve their processes The causes of defects are eliminated as part of preventive quality work New technologies can be utilised effectively to improve process capability CMM in SW design 23 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
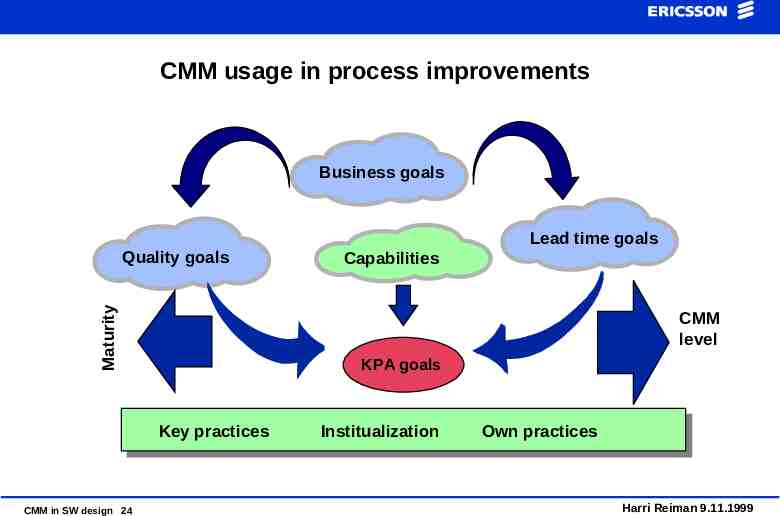
CMM usage in process improvements Business goals Lead time goals Maturity Quality goals CMM level KPA goals Key practices CMM in SW design 24 Capabilities Institualization Own practices Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
CMM assessment - What is an assessment Small number of high potential improvements are identified Consensus of improvement areas and needs is developed Motivation is created for improvement needs CMM model is used as á framework and reference to identify weaknesses Maturity questionnaires are used to define assessment scope Organisation’s goals are essential part of an assessment process GOAL: Most benefit for organisation s improvement planning and execution CMM in SW design 25 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999

CMM assessment - How an assessment is conducted An appraisal made by 4-8 experienced SW professionals Organisations maturity is assessed through 3-5 projects In-depth discussions with project leaders and practitioners to collect facts about the organisation’s practices Running time 5 -10 days Both documentation and practices are evaluated Strict confidentiality rules apply CMM in SW design 26 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
CMM assessment - What are produced in an assessment Findings on different Key Process areas weaknesses strengths observations (non-CMM related) Recommendations for addressing the findings M CM l 2 e Lev CMM in SW design 27 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
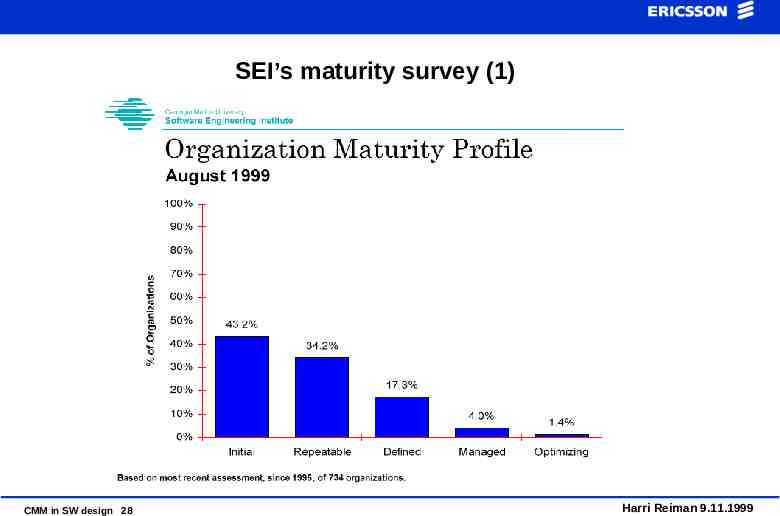
SEI’s maturity survey (1) CMM in SW design 28 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
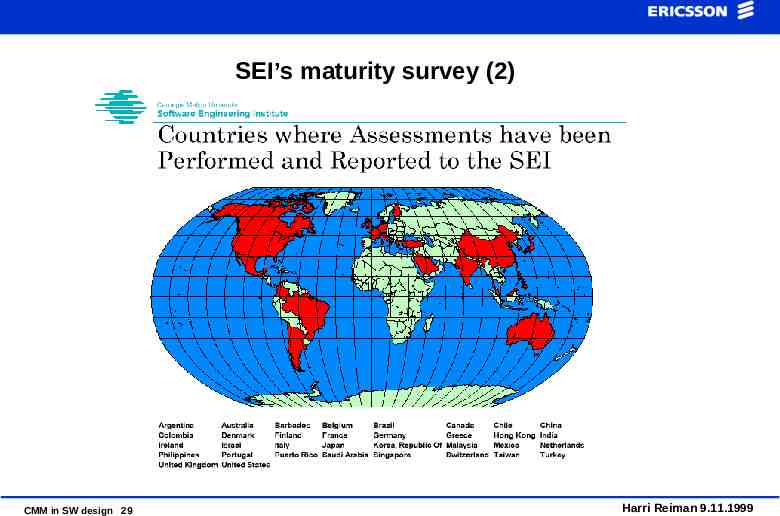
SEI’s maturity survey (2) CMM in SW design 29 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999
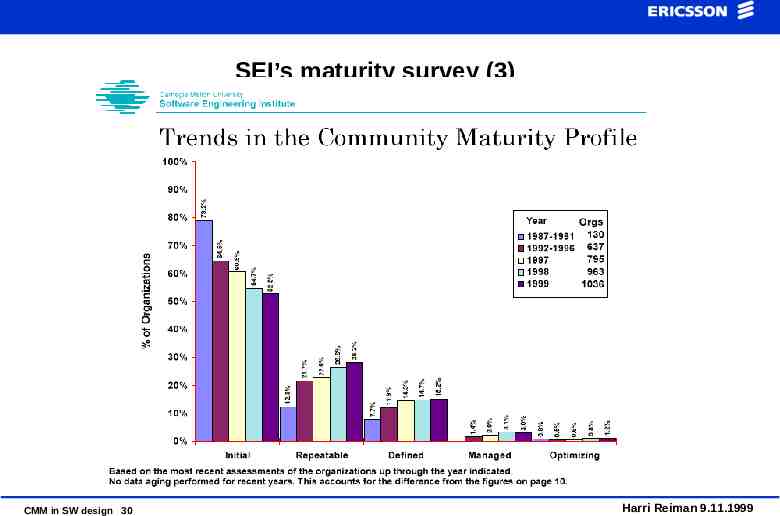
SEI’s maturity survey (3) CMM in SW design 30 Harri Reiman 9.11.1999






