Unit 1: Psychology’s History and Approaches
42 Slides6.41 MB

Unit 1: Psychology’s History and Approaches

Learning Targets Module 1: Psychology’s History 1-1 Explain why psychology is a science and why Module 1 the “rat is always right.” 1-2 Describe the three key elements of the scientific attitude and how they support scientific inquiry. 1-3 Explain how critical thinking feeds a scientific attitude and smarter thinking for everyday life. 1-4 Describe how psychology developed from early understandings of mind and body to the beginnings of modern science. Psychology’s History 1-5 Explain how critical thinking feeds a scientific attitude and smarter thinking for everyday life. 1-6 Explain how behaviorism, Freudian psychology and humanistic psychology furthered the development of psychological science.

How is psychology a science? Psychology uses the tools of science to describe explain predict control behavior and mental processes.

the “rat is always right”? Why isWhy theis“rat always right”? Facts speak for themselves Researchers have to accept the results of the study even if the hypothesis has been proven wrong.

TRY IT Can these questions be answered using science? Are the body and the soul separate entities? Does having a positive attitude improve outcomes for individuals with serious illness? What was the evolutionary benefit of depression?

What is one key element of the scientific attitude? Curiosity: asking questions

What is another key element of the scientific attitude? Skepticism: sifting reality from fantasy and demanding evidence

What is a third key element of the scientific attitude? Humility: accepting incorrect predictions
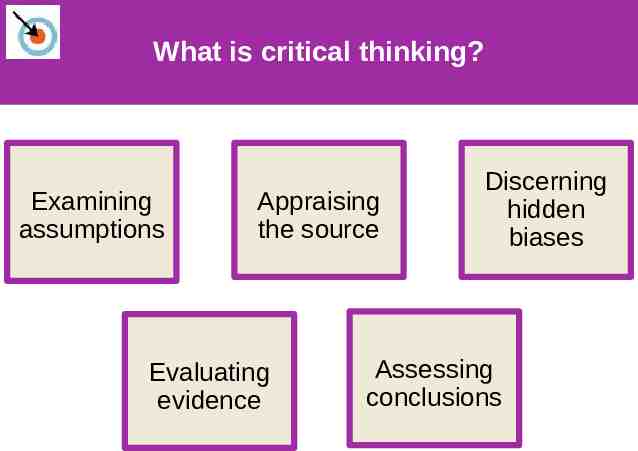
What is critical thinking? Examining assumptions Appraising the source Evaluating evidence Discerning hidden biases Assessing conclusions

TRY IT How would you think critically about the following statement? Climate change is a real and pressing danger. What is the assumption? What is the source of this statement? Are they reliable? Might the source have a reason to believe this? A bias? What evidence exists to support this statement? What evidence exists to refute it? What conclusions can I make about the information I gathered?

What did philosophers wonder about the mind? How does our mind work? How does our body relate to our mind? How much of what we know is innate? How much comes from our experiences?

The Greeks Socrates Plato Aristotle mind and body are separate mind continues after death knowledge is innate need data knowledge comes from observation knowledge is NOT innate
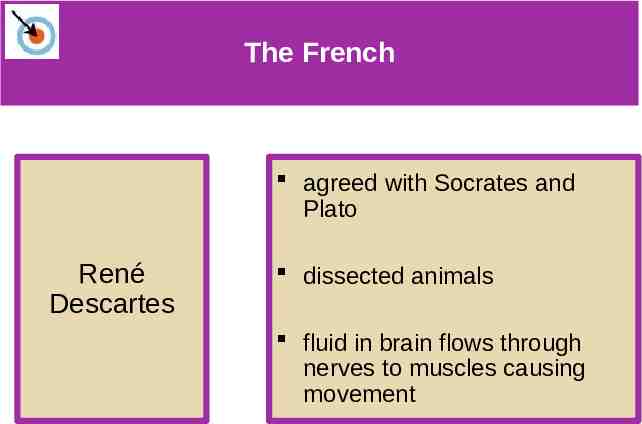
The French The French agreed with Socrates and Plato René Descartes dissected animals fluid in brain flows through nerves to muscles causing movement
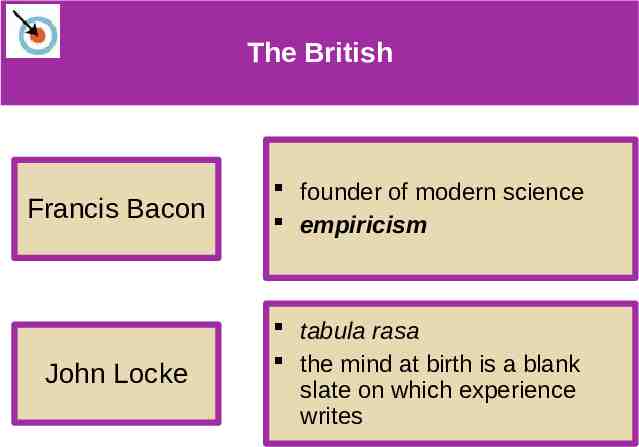
The British The British Francis Bacon founder of modern science empiricism John Locke tabula rasa the mind at birth is a blank slate on which experience writes

What is empiricism? What is empiricism? The idea that knowledge is the result of experience and that scientific knowledge is developed through observation and experimentation.

What were important milestones in psychology’s early development? established the first psychology lab wanted to measure the “atoms of the mind” the fastest mental processes Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)
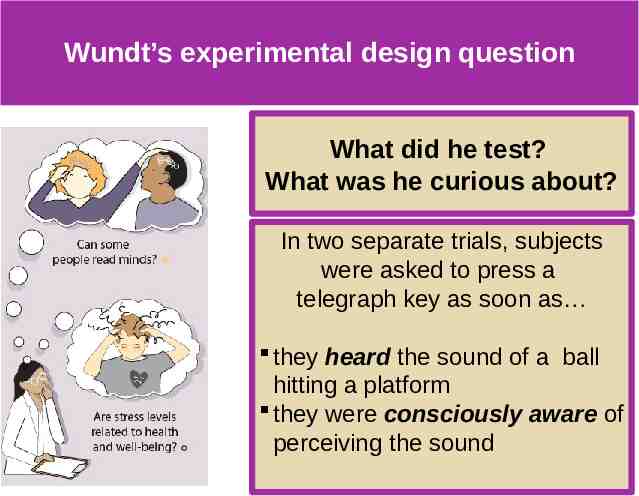
Wundt’s experimental design question What did he test? What was he curious about? In two separate trials, subjects were asked to press a telegraph key as soon as they heard the sound of a ball hitting a platform they were consciously aware of perceiving the sound

Wundt’s experimental design results What did he find? What were the results? In the first trial the subjects pressed the button in 1/10th of a second when they heard the sound of a ball hitting a platform But it took 2/10th of a second to wait until they were consciously aware of perceiving the sound

What were important milestones in psychology’s early development? Cont. introduced structuralism to study the elements of the mind used introspection Edward Bradford Titchener (1867-1927)
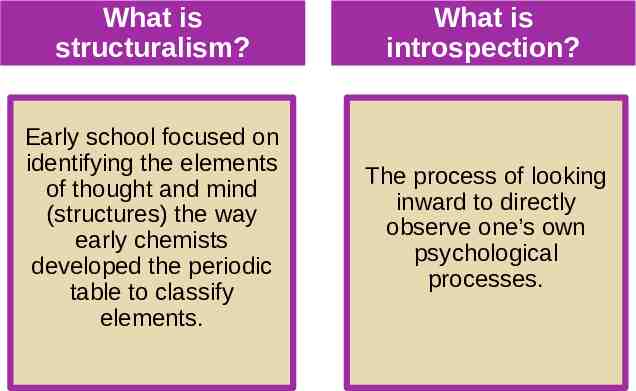
What is structuralism? What is What is What is introspection? structuralism? introspection? Early school focused on identifying the elements of thought and mind (structures) the way early chemists developed the periodic table to classify elements. The process of looking inward to directly observe one’s own psychological processes.

TRY IT Describe what you sense when you Chew a piece of spearmint gum. Smell the fries cooking in the cafeteria. Sit in the chair at your desk.

1. What Would You Answer? 1. What Would You Answer? Self-reflective introspection about the elements of experience best describes a technique used by which school of thought in psychology? A. B. C. D. E. functionalists empiricists structuralists behaviorists humanists

What were other important milestones in psychology’s early development? natural selection of mental and physical traits adaptive evolution influenced William James Charles Darwin (1809-1882)

What were some important milestones in psychology’s early development? introduced functionalism Principles of Psychology William James (1842-1910)

What is functionalism? Functionalism assumes a purpose smelling and thinking must have helped us evolve . structures of consciousness must serve a function. smelling is what the nose does thinking is what the brain does but WHY?

TRY IT structuralism or functionalism? Why do some people have strong willpower and others do not? Describe the characteristics of the pencil you are holding. How does eye color limit our ability to see in the dark?

What were additional important milestones in psychology’s early development? student of William James denied her Ph.D. due to gender memory researcher first female president of the APA Mary Whiton Calkins (1863-1930)

What were important contributions to psychology’s early development? student of Edward Titchener first female to earn Ph.D.in psychology The Animal Mind Margaret Floy Washburn (1871-1939)

2. What Would You Answer? 2. What Would You Answer? By seeking to measure “atoms of the mind”, who established the first psychology laboratory? A. B. C. D. E. Edward Bradford Titchener Margaret Floy Washburn Wilhelm Wundt G. Stanley Hall William James

How did behaviorism further the development of psychological science? B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) John B. Watson (1878-1958)

What is behaviorism? psychology should be an objective science observable behavior is important to study not the unseen mental processes

How did Freud further the development of psychological science? developed an influential treatment process called psychoanalysis personality theory Sigmund Freud (1856-1939)

What is Freudian (or psychoanalytic) psychology? Unconscious forces and childhood experiences affect our behavior and mental processes.

How did humanism further the development of psychological science? Abraham Maslow Carl Rogers Humans strive to reach their full potential Unconditional love Personal growth

What is humanism? “third force” in psychology rejected both behaviorism and psychoanalytic psychology the study of potential and personal growth

3. What Would You Answer? 3. What Would You Answer? With which of the following statements would John B. Watson most likely agree? A. Psychology should study the growth potential in all people. B. Psychology should study the unconscious mind. C. Psychology should focus on observable behavior. D. Psychology should study mental thought processes. E. Psychology should study how culture and beliefs impact an individual.

Learning Target 1-1 Review How is psychology a science, and why is it the “rat is always right”? Psychologists: think critically use the scientific method accept the results

Learning Target 1-2 Review What are the three key elements of the scientific attitude, and how do they support scientific inquiry? The scientific attitude encourages us to be: curious skeptical humble in testing ideas that don’t agree with ours.

Learning Target 1-3 Review How does critical thinking feed a scientific attitude and smarter thinking for everyday life? Critical thinking puts ideas to the test by: examining assumptions appraising the source discerning hidden biases evaluating evidence assessing conclusions

Learning Target 1-4 Review How did psychology develop from early understandings of mind and body to the beginnings of modern science? The Greeks wondered if ideas were innate or came from experience Locke thought we were tabula rasa Bacon gave us empiricism

Learning Target 1-5 Review What were some important milestones in psychology’s early development? Wundt established the first psych lab Wundt and Titchener: structuralism and introspection James: functionalism

Learning Target 1-6 Review How did behaviorism, Freudian psychology, and humanistic psychology further the development of psychological science? Watson: behaviorism focuses on studying behavior Freud: psychoanalysis focuses on unconscious influences Rogers and Maslow: humanism focuses on striving for growth






