Data Science and Analytics Curriculum development at Rensselaer (and
22 Slides5.93 MB

Data Science and Analytics Curriculum development at Rensselaer (and the Tetherless World Constellation) NRC BigData Education Workshop April 11-12, 2014, Washington DC Peter Fox (RPI and WHOI/AOP&E) [email protected], @taswegian Tetherless World Constellation, http://tw.rpi.edu #twcrpi Earth and Environmental Science, Computer Science, Cognitive Science, and IT and Web Science

Data is a 1st class citizen omsonreuters.com/content/press room/science/686112 2
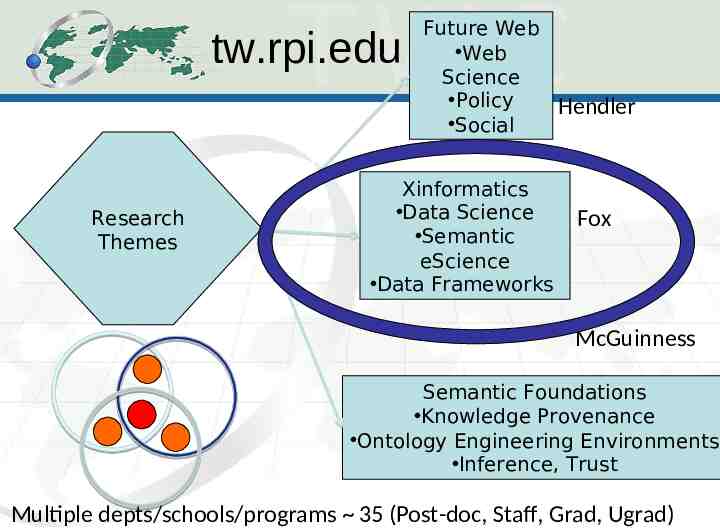
tw.rpi.edu Research Themes Future Web Web Science Policy Hendler Social Xinformatics Data Science Semantic eScience Data Frameworks Fox McGuinness Semantic Foundations Knowledge Provenance Ontology Engineering Environments Inference, Trust Multiple depts/schools/programs 35 (Post-doc, Staff, Grad, Ugrad)
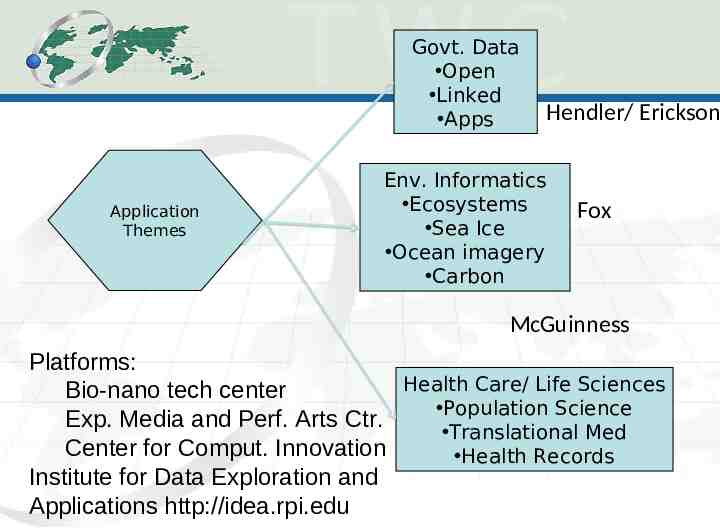
Govt. Data Open Linked Apps Application Themes Hendler/ Erickson Env. Informatics Ecosystems Sea Ice Ocean imagery Carbon Fox McGuinness Platforms: Health Care/ Life Sciences Bio-nano tech center Population Science Exp. Media and Perf. Arts Ctr. Translational Med Center for Comput. Innovation Health Records Institute for Data Exploration and Applications http://idea.rpi.edu
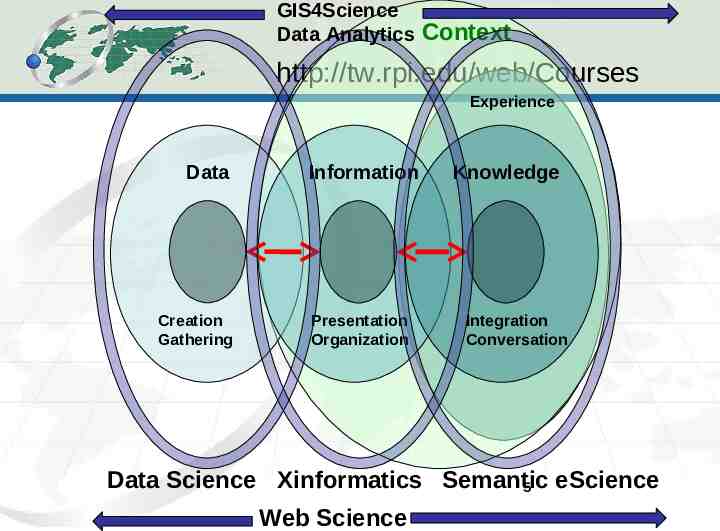
GIS4Science Data Analytics Context http://tw.rpi.edu/web/Courses Experience Data Creation Gathering Information Presentation Organization Knowledge Integration Conversation Data Science Xinformatics Semantic eScience 5 Web Science

I teach and am involved: Data Science*, Xinformatics*, GIS for the Sciences*, Semantic eScience*, Data Analytics*, Sematic Technologies** School of Science – ITWS and E&ES curriculum committees, SoS CC – E&ES international student advisor – Institute Faculty Fellow Institute-wide – New Digital Humanities program Institute for Data Exploration and Applications

Data Science/ Xinformatics Science has fully entered a new mode of operation. Data science is advancing inductive conduct of science driven by the greater volumes, complexity and heterogeneity of data being made available over the Internet. Data science combines of aspects of data management, library science, computer science, and physical science using supporting cyberinfrastructure and information technology. As such it is changing the way all of these disciplines do both their individual and collaborative work. Data science is helping scientists face new global problems of a magnitude, complexity and interdisciplinary nature whose progress is presently limited by lack of available tools and a fully trained and agile workforce. At present, there is a lack formal training in the key cognitive and skill areas that would enable graduates to become key participants in e-science collaborations. The need is to teach key methodologies in application areas based on real research experience and build a skill-set. At the heart of this new way of doing science, especially experimental and observational science but also increasingly computational science, is the generation of data. In the last 2-3 years, Informatics has attained greater visibility across a broad range of disciplines, especially in light of great successes in bio- and biomedical-informatics and significant challenges in the explosion of data and information resources. Xinformatics is intended to provide both the common informatics knowledge as well as how it is implemented in specific disciplines, e.g. X astro, geo, chem, etc. Informatics' theoretical basis arises from information science, cognitive science, social science, library science as well as computer science. As such, it aggregates these studies and adds both the practice of information processing, and the engineering of information systems. This course will introduce informatics, each of its components and ground the material that students will learn in discipline areas by coursework and project assignments.
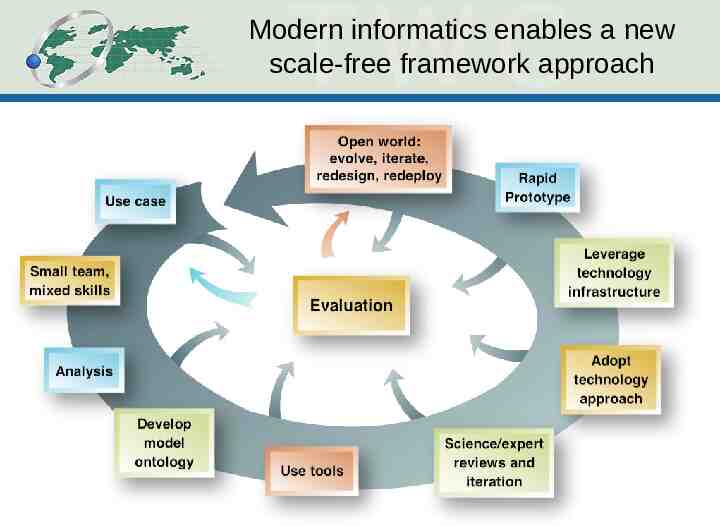
Modern informatics enables a new scale-free framework approach
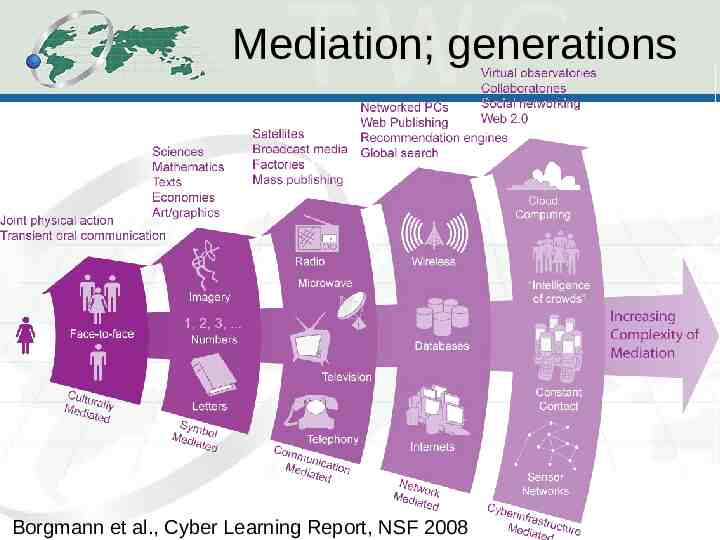
Mediation; generations Borgmann et al., Cyber Learning Report, NSF 2008
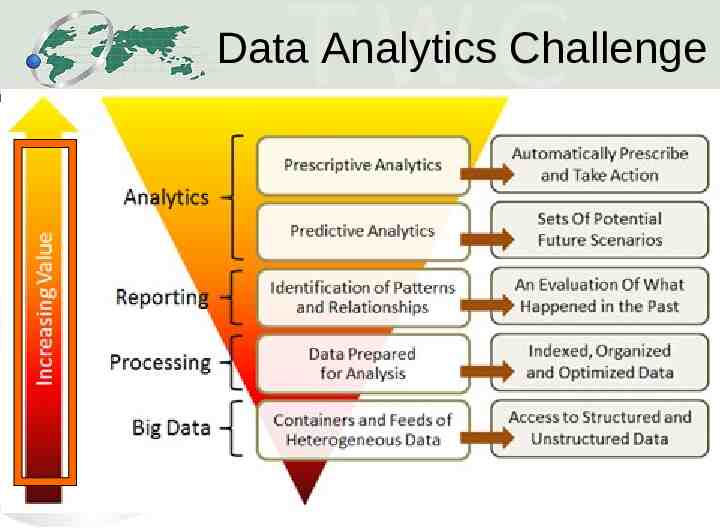
Data Analytics Challenge 10

IT and Web Science First IT academic program in U.S. First web science degree program in U.S. BS in ITWS (20 concentrations) and MS in IT (10 concentrations) PhD in Multi-Disciplinary Sciences http://itws.rpi.edu
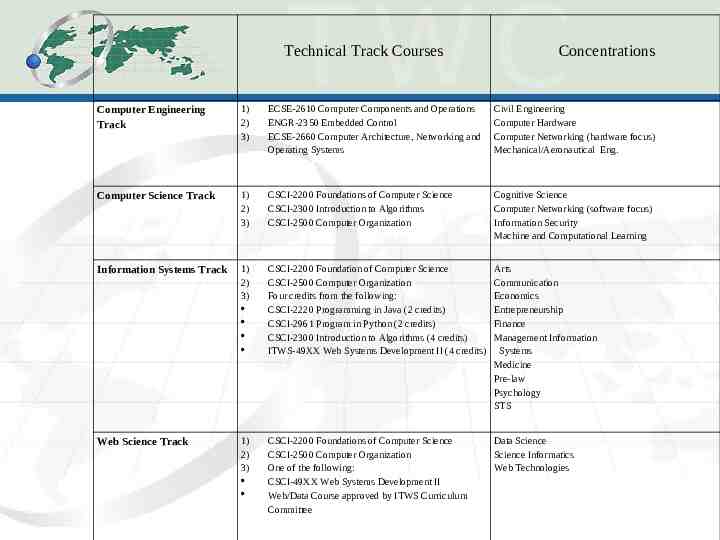
Technical Track Courses Concentrations Computer Engineering Track 1) 2) 3) ECSE-2610 Computer Components and Operations ENGR-2350 Embedded Control ECSE-2660 Computer Architecture, Networking and Operating Systems Civil Engineering Computer Hardware Computer Networking (hardware focus) Mechanical/Aeronautical Eng. Computer Science Track 1) 2) 3) CSCI-2200 Foundations of Computer Science CSCI-2300 Introduction to Algorithms CSCI-2500 Computer Organization Cognitive Science Computer Networking (software focus) Information Security Machine and Computational Learning Information Systems Track 1) 2) 3) CSCI-2200 Foundation of Computer Science CSCI-2500 Computer Organization Four credits from the following: CSCI-2220 Programming in Java (2 credits) CSCI-2961 Program in Python (2 credits) CSCI-2300 Introduction to Algorithms (4 credits) ITWS-49XX Web Systems Development II (4 credits) Arts Communication Economics Entrepreneurship Finance Management Information Systems Medicine Pre-law Psychology STS Web Science Track 1) 2) 3) CSCI-2200 Foundations of Computer Science CSCI-2500 Computer Organization One of the following: CSCI-49XX Web Systems Development II Web/Data Course approved by ITWS Curriculum Committee Data Science Science Informatics Web Technologies

CHANGES TO THE MASTER’S IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM In Spring 2013 the MS in IT core curriculum was revised to include Data Analytics. Networking core classes were replaced with Data Analytics core classes: Data Science, Database Mining, X-informatics, and Data Analytics (a new class offered in Spring 2014). The MS in IT program also added two new concentrations: Data Science and Analytics and Information Dominance. The Information Dominance concentration was developed for a new Navy program that will be educating a select group of 5-10 naval officers a year with the skills needed for military cyberspace operations. Two officers started in Fall 2013 and three began in Spring 2014.
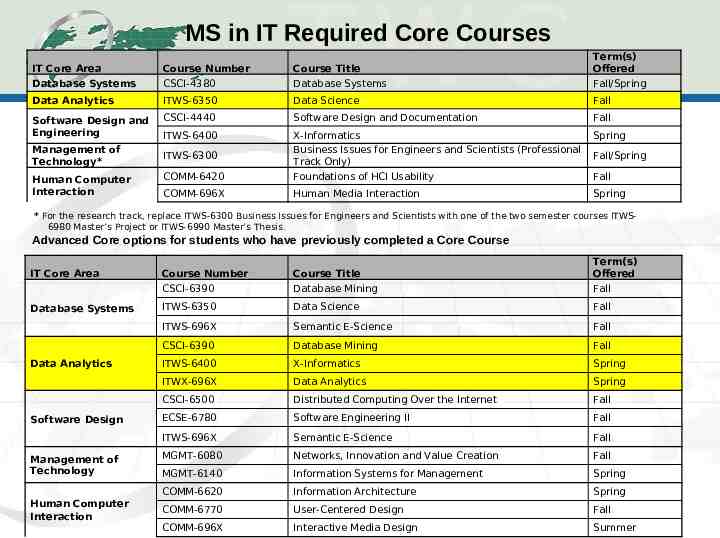
MS in IT Required Core Courses IT Core Area Database Systems Course Number CSCI-4380 Course Title Database Systems Term(s) Offered Fall/Spring Data Analytics ITWS-6350 Data Science Fall Software Design and Engineering CSCI-4440 Software Design and Documentation Fall ITWS-6400 Spring COMM-6420 X-Informatics Business Issues for Engineers and Scientists (Professional Track Only) Foundations of HCI Usability COMM-696X Human Media Interaction Spring Management of Technology* Human Computer Interaction ITWS-6300 Fall/Spring Fall * For the research track, replace ITWS-6300 Business Issues for Engineers and Scientists with one of the two semester courses ITWS6980 Master’s Project or ITWS-6990 Master’s Thesis. Advanced Core options for students who have previously completed a Core Course IT Core Area Course Number CSCI-6390 Course Title Database Mining Term(s) Offered Fall Database Systems ITWS-6350 Data Science Fall ITWS-696X Semantic E-Science Fall CSCI-6390 Database Mining Fall ITWS-6400 X-Informatics Spring ITWX-696X Data Analytics Spring CSCI-6500 Distributed Computing Over the Internet Fall ECSE-6780 Software Engineering II Fall ITWS-696X Semantic E-Science Fall MGMT-6080 Networks, Innovation and Value Creation Fall MGMT-6140 Information Systems for Management Spring COMM-6620 Information Architecture Spring COMM-6770 User-Centered Design Fall COMM-696X Interactive Media Design Summer Data Analytics Software Design Management of Technology Human Computer Interaction
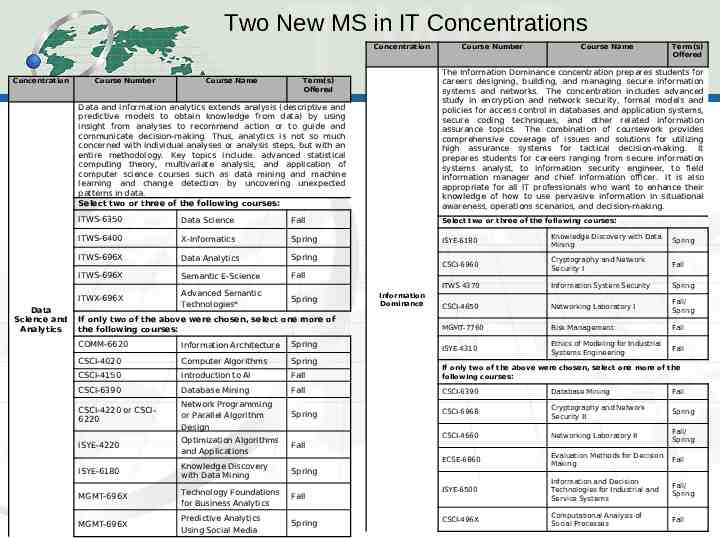
Two New MS in IT Concentrations Concentration Concentration Data Science and Analytics Course Number Course Name Term(s) Offered Data and Information analytics extends analysis (descriptive and predictive models to obtain knowledge from data) by using insight from analyses to recommend action or to guide and communicate decision-making. Thus, analytics is not so much concerned with individual analyses or analysis steps, but with an entire methodology. Key topics include: advanced statistical computing theory, multivariate analysis, and application of computer science courses such as data mining and machine learning and change detection by uncovering unexpected patterns in data. Select two or three of the following courses: The Information Dominance concentration prepares students for careers designing, building, and managing secure information systems and networks. The concentration includes advanced study in encryption and network security, formal models and policies for access control in databases and application systems, secure coding techniques, and other related information assurance topics. The combination of coursework provides comprehensive coverage of issues and solutions for utilizing high assurance systems for tactical decision-making. It prepares students for careers ranging from secure information systems analyst, to information security engineer, to field information manager and chief information officer. It is also appropriate for all IT professionals who want to enhance their knowledge of how to use pervasive information in situational awareness, operations scenarios, and decision-making. ITWS-6350 Data Science Fall Select two or three of the following courses: ITWS-6400 X-Informatics Spring ISYE-6180 Knowledge Discovery with Data Mining Spring ITWS-696X Data Analytics Spring CSCI-6960 Fall ITWS-696X Semantic E-Science Fall Cryptography and Network Security I ITWS-4370 Information System Security Spring ITWX-696X Advanced Semantic Technologies* CSCI-4650 Networking Laboratory I Fall/ Spring If only two of the above were chosen, select one more of the following courses: MGMT-7760 Risk Management Fall COMM-6620 Information Architecture Spring ISYE-4310 Fall CSCI-4020 Computer Algorithms Spring Ethics of Modeling for Industrial Systems Engineering CSCI-4150 Introduction to AI Fall If only two of the above were chosen, select one more of the following courses: CSCI-6390 Database Mining Fall CSCI-6390 Database Mining Fall CSCI-4220 or CSCI6220 Network Programming or Parallel Algorithm Design Spring CSCI-6968 Cryptography and Network Security II Spring Optimization Algorithms and Applications CSCI-4660 Networking Laboratory II ISYE-4220 Fall Fall/ Spring ECSE-6860 Spring Evaluation Methods for Decision Making Fall ISYE-6180 Knowledge Discovery with Data Mining MGMT-696X Technology Foundations for Business Analytics Fall ISYE-6500 Information and Decision Technologies for Industrial and Service Systems Fall/ Spring MGMT-696X Predictive Analytics Using Social Media Spring CSCI-496X Computational Analysis of Social Processes Fall Course Number Course Name Term(s) Offered Spring Information Dominance

Also at RPI Data Science Research Center and Data Science Education Center (dsrc.rpi.edu, 2009) http://www.rpi.edu/about/inside/issue/v4n17/ datacenter.html – Over 45: research faculty, post-docs, grad students, staff, undergraduates Data is one of the Rensselaer Plan’s five thrusts Other key faculty – Fran Berman (Center for Digital Society and RDA) – Bulent Yener (DSRC Director) – Jin Hendler (IDEA Director)
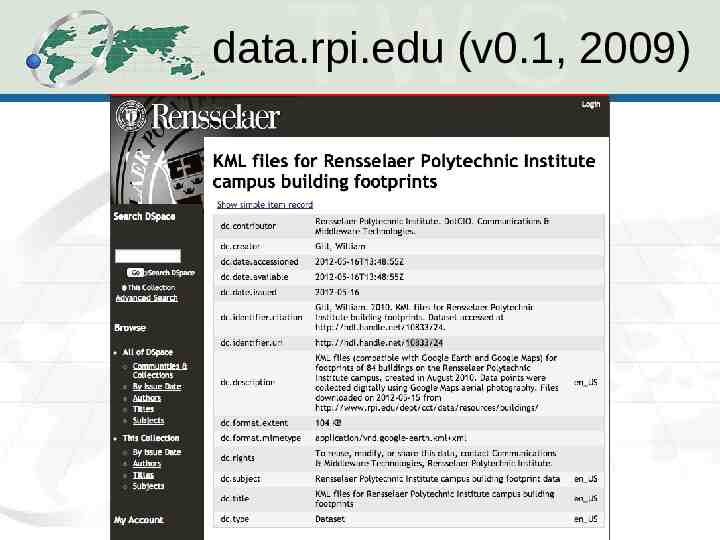
data.rpi.edu (v0.1, 2009)
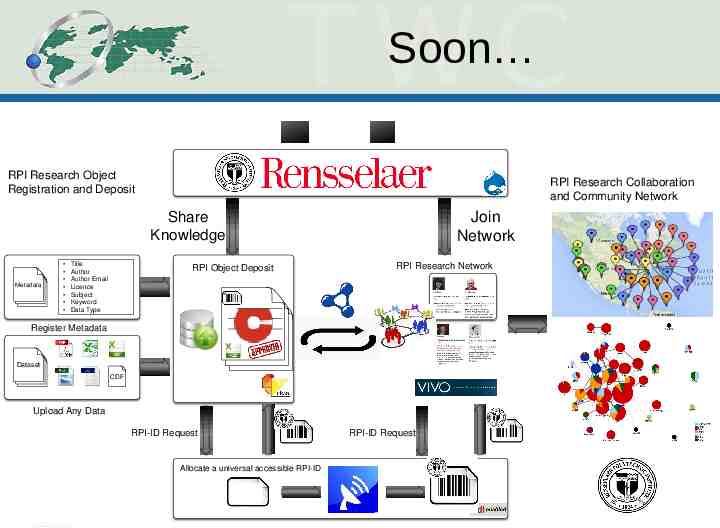
Soon RPI Research Object Registration and Deposit RPI Research Collaboration and Community Network Join Network Share Knowledge Metadata Title Author Author Email Licence Subject Keyword Data Type RPI Object Deposit RPI Research Network Register Metadata Dataset CDF Upload Any Data RPI-ID Request Allocate a universal accessible RPI-ID RPI-ID Request

More RPI Curriculua Environmental Science with Geoinformatics concentration Bio, geo, chem, astro, materials - informatics GIS for Science Master of Science – Data Science? (pending) Multi-disciplinary science program - PhD in Data and Web Science DATUM: Data in Undergraduate Math! (Bennett) Missing – intermediate statistics Graphs – significant potential here – must teach!

5-6 years in Science and interdisciplinary from the start! – Not a question of: do we train scientists to be technical/data people, or do we train technical people to learn the science – It’s a skill/ course level approach that is needed We teach methodology and principles over technology * Data science must be a skill, and natural like using instruments, writing/using codes Team/ collaboration aspects are key ** Foundations and theory must be taught ***
Challenging the “Heroic” Science Paradigm This national and international has drawn attention to the need for a reassessment of priorities to recognize that, in the new data era, the burden of making data and information usable shifts from the user to the provider.

And thus in 10 years






