The Progressive Era 1900-1917
59 Slides4.67 MB

The Progressive Era 1900-1917

What are the major problems in America today? What are you going to do about it?

What led to the rise of Progressivism? Immigration Industrialization Urbanization & urban slums Muckrakers Social Gospel

Muckrakers Writers who exposed the corrupt and illegal practices of big business and government

Jacob Riis Wrote How the Other Half Lives (1890), a novel which describes the urban slums and tenements Shocked the nation and created many reforms Quote in United States History textbook p. 418

Lincoln Steffens The “Father” of the Muckrakers Wrote The Shame Of The Cities (1904) Exposed corruption in St. Louis city politics

Ida Tarbell Wrote The History of Standard Oil Company (1904) Exposed the illegal business practices of Rockefeller’s company

Upton Sinclair Wrote The Jungle (1906), a novel which describes the foul conditions in Chicago’s meatpacking plants After President Theodore Roosevelt read it, he created the Meat Inspection Act and Pure Food and Drug Act

Chicago Stockyards & Meatpacking Plants

Social Gospel Belief that individuals could follow the Bible and make society “the kingdom of God” leads to reform Settlement houses – community center that provided services to the urban poor like English classes, nurseries, arts programs – Jane Addams created Hull House in Chicago (famous settlement house) – goal is to “Americanize” immigrants
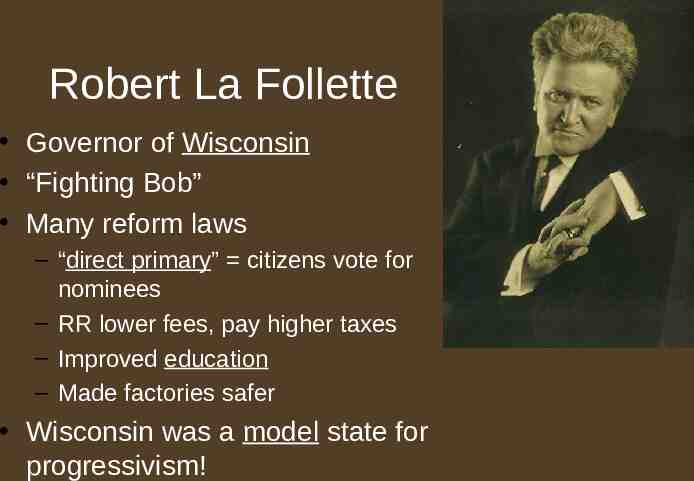
Robert La Follette Governor of Wisconsin “Fighting Bob” Many reform laws – “direct primary” citizens vote for nominees – RR lower fees, pay higher taxes – Improved education – Made factories safer Wisconsin was a model state for progressivism!

Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire New York City, 1911 Fire on the 8th, 9th, 10th floors 148 workers died-jumped from windows and down elevator shafts or smothered Showed the nation that workers needed greater safety

Progressive Goals End child labor Increased educational opportunities Provide services for urban poor Improve industrial working conditions End corruption in government Increase democratic opportunities for voters

Women Progressiv es

Prohibition To prohibit the sale of alcohol Led by Women’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) and Anti-Saloon League Cause: heavy drinking, domestic abuse and health problems Carrie A. Nation – entered saloons and attacked liquor bottles with her axe while people sang hymns at the door 18th Amendment – Prohibition Volstead Act – gave the detailed laws of Prohibition

Women’s Suffrage National American Women’s Suffrage Association (NAWSA) Susan B. Anthony was President, then Carrie Chapman Catt in 1900 Creation of National Women’s Party (NWP) by Alice Paul to push for an amendment

Three-Part Strategy 1. State Legislatures - wanted states to grant women’s suffrage 2. Court Cases - to make the 15th Amendment applicable to women 3. Constitutional Amendment -In 1913 the National Women’s Party pressured Congress to create an amendment to grant women’s suffrage In 1919, after World War I, the 19th Amendment was ratified, granting women the right to vote

Election and Political Reforms The Progressive Era Part 2

Direct Primary Elections Before: candidates chosen by a small group of party leaders and voters had no say Reform: “direct primaries” in which voters could choose which candidates they wanted to run

Secret Ballot Before: corrupted leaders often counterfeited ballots and cheated the voting system Reform: the secret (Australian) ballot was regulated by the government with a list of candidates and positions AND citizens vote in private!

17 Amendment th Before: U.S. Senators were chosen by state legislatures Reform: 17th Amendment creates the direct election in which voters choose the Senators

Initiative, Referendum, Recall Before: voters had no input on government actions Reform: voters have a greater voice in local government Initiative voters can introduce a specific bill into the legislature Referendum voters can express views on proposed measures Recall voters can remove a public official from office

Progressive Amendments 16th – Federal Income Tax 17th – Direct Election of Senators 18th – Prohibition enforced by Volstead Act 19th – Women’s Suffrage

Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909

Background aristocratic New York family sickly as a child, so he was determined to be physically fit and an outdoorsman Jobs: U.S. civil-service commissioner, governor of New York, Secretary of Navy, McKinley’s Vice-President On a hunting trip, he refused to shoot a bear cub and a toy-maker marketed a new product: the Teddy Bear VERY gregarious and boisterous

Outdoorsman

As President Becomes President when William McKinley is assassinated in 1901 Use of the “bully pulpit” used his position and power as president to shape public opinion and pursue his goals Progressive! Very loud and passionate about the issues Called for a “Square Deal” for Americans: keep the wealthy and powerful from taking advantage of small businesses and the poor; create a fair government

“Trustbuster” Enforces the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 U.S. v. E.C. Knight & Co. (1895) – Supreme Court ruled that the Sherman Antitrust Act doesn’t apply to manufacturing more trusts created Northern Securities v. U.S. (1904) –Supreme Court ruled that this RR company was an illegal trust Broke up beef industry and others Differentiated between “good trusts” (efficient, fair) and “bad trusts” (bullied, cheated consumers)

Anthracite Coal Mine Strike, 1902 Coal miners in PA went on strike for a raise and shorter workday Roosevelt summoned both sides to the White House because the nation needed coal to heat their houses in the winter Owners wouldn’t go, so TR threatened to send in federal soldiers to take over the mines The owners gave in; miners got a raise and shorter workday Success! TR is seen as pro-labor because he didn’t use force to end the strike.

Interstate Commerce Strengthens the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) Elkins Act (1903) – fined railroads that gave special rates to certain shippers Hepburn Act (1906) - allowed the ICC to set maximum railroad rates and fees

Health and Food Roosevelt was disgusted and revolted after reading The Jungle Meat Inspection Act (1906) – federal agents to inspect meat-processing plants and meat sold across state lines Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) – required correct and true labeling of food and drugs; today this is the job of the FDA

Environmental Conservation Creation of the U.S. Forest Service led by Gifford Pinchot Closed off 100 million acres of forestland Creation of national parks

End of Presidency Since Roosevelt had served most of McKinley’s second term, he had always promised to not run for reelection Handpicks Secretary of War William Howard Taft to be his successor and carry on his policies TR goes on an expedition

William Howard Taft 1909-1913

Presidential Decisions More antitrust cases than TR – Did not differentiate between “good” and “bad” trusts – American Tobacco v. U.S. (1911) – Duke family’s tobacco company was an illegal trust – Standard Oil & U.S. Steel were sued Payne-Aldrich Tariff (1909) – lowered the tariff Mann-Elkins Act (1910) – government control over telephone and telegraph rates Mann Act (1910) – prohibited white slavery (selling girls into prostitution) and transporting females across state lines for “immoral purposes”

End of Presidency TR was unhappy with him Unpopular with the public; didn’t like being president Lost reelection in 1912 After presidency served as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court

Progressive / Bull Moose Party Theodore Roosevelt called for a New Nationalism -- a program to restore the government as a trustbuster Said he was “strong as a bull moose” TR campaigned for a third term as president Split the Republican Party between himself and Taft

Candidates in Election of 1912 William H. Taft - Republican Woodrow Wilson - Democrat Theodore Roosevelt - Progressive Eugene V. Debs - Socialist
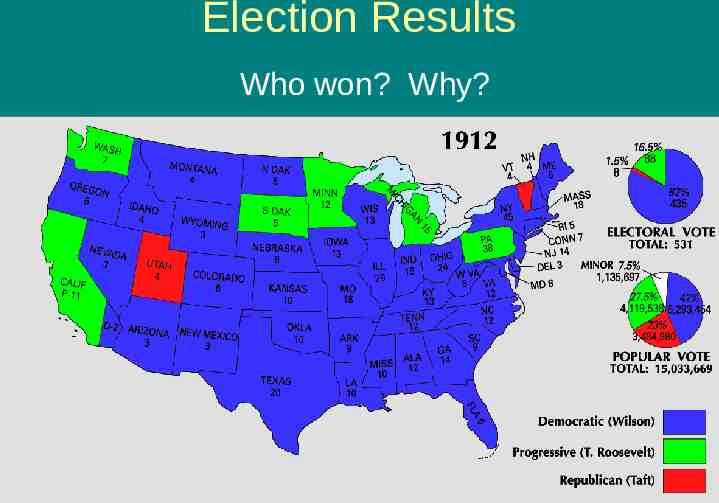
Election Results Who won? Why?

Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921

Background From a family of Presbyterian preachers Grew up in the South President of Princeton University Governor of New Jersey

New Freedom Called for strict government controls on corporations and create more opportunities for small businesses Attacked the tariffs, the banks, the trusts Tariffs – lowered tariffs (Underwood Tariff Act) – raised taxes (16th Amendment -- federal income tax)
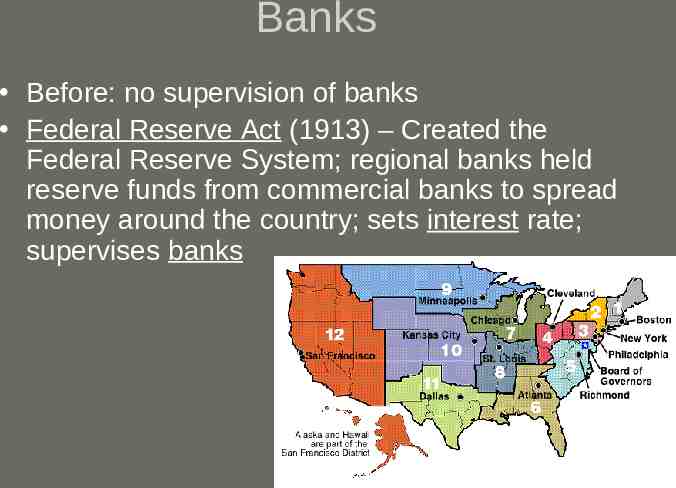
Banks Before: no supervision of banks Federal Reserve Act (1913) – Created the Federal Reserve System; regional banks held reserve funds from commercial banks to spread money around the country; sets interest rate; supervises banks

Trusts Before: TR and Taft were “trustbusters” Believed that there could be “good” and “bad” trusts Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) - strengthened other antitrust laws; detailed illegal business activities Federal Trade Commission (1914) – “watchdog agency;” monitored corporations to make sure they were using legal business practices; watched for false advertising and dishonest labeling

Other Info Encouraged the passage of the 19th Amendment Allowed segregation laws to be passed Eventually took us into World War I in 1917

How were African-Americans treated across the nation? Disenfranchisement – denied the right to vote – Literacy test – show that you are literate – Poll tax – pay to vote – Grandfather clause – if your grandfather voted, you can vote Segregation – – – – “separate but equal” De jure segregation - segregation by law De facto segregation - segregation by “choice” Jim Crow Laws

Jim Crow Laws State and local laws enacted in southern and border states Enforced between 1876 and 1965 Laws that segregated streetcars, schools, parks, and even cemeteries Black schools and other facilities became inferior

Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) Homer Plessy boarded an all white car, being 7/8th white and 1/8th black, and was arrested after refusing to change cars. Justices upheld a law requiring segregated railroad cars Segregation was constitutional as long as facilities were equal “separate but equal” Affected all minorities

Booker T. Washington Born a slave Believed blacks needed to acquire skills (ex. farming and carpentry) and be economically stable before seeking equality Wanted AfricanAmericans to wait patiently for change and earn the respect of white Americans
Washington’s Accomplishments Founded Tuskegee Institute - a vocational school in Alabama for African-Americans Wrote Up From Slavery, an autobiography Atlanta Compromise - speech given at the Atlanta Exposition – See quote on page 433 (“Comparing Viewpoints”)

W.E.B. DuBois First African-American to earn his Ph.D. from Harvard Demanded full, immediate, racial equality, including equal educational opportunities Wanted AfricanAmericans to resist all forms of racism

DuBois’s Accomplishments Niagara Movement (1905) - AfricanAmericans met to denounce gradual progress and vocational education Founder of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) -multiracial group that fought legal challenges to achieve political and social equality for blacks Editor of The Crisis (NAACP Newsletter) Wrote The Souls of Black Folk, a book which criticized Booker T. Washington

Ida B. Wells (Barnett) African-American journalist Moved to Chicago from Memphis in 1892 after a white mob destroyed her offices Led a national antilynching campaign Supported the NAACP

Wilmington Race Riot of 1898 Was an integrated city in the late 1800s after the Civil War In 1898 an AfricanAmerican journalist wrote an editorial about white women White mobs attacked his press African-Americans left Wilmington and the city became segregated with Jim Crow laws

How did technological changes redefine American culture? Electricity Skyscrapers Mail Order Catalogs Kodak Camera Movie Camera Wright Brothers Model T

Henry Ford Model-T affordable, basic car; 825, went about 30 mph Assembly Line faster, cheaper method of production Workers paid 5 a day - high wages!; wanted to have workers who could buy the product they made Great businessman

The End of the Progressive Era War erupts in Europe (WWI) in 1914 The U.S. enters the war in 1917 Decreased desire to reform society and push for governmental change

Recap! People – Muckrakers: – Progressives: – Presidents: – African-American Leaders: Issues

Accomplishments of the Progressive Era SOCIAL & ECONOMIC POLITICAL






