SUBSTANCE USE AND ABUSE IN SOUTH AFRICA A presentation by the
54 Slides1.86 MB

SUBSTANCE USE AND ABUSE IN SOUTH AFRICA A presentation by the Central Drug Authority to the Portfolio Committee On Social Development 8 November 2011 1

SNAPSHOT SURVEY: JUNE 2010 TO MARCH 2011 A PICTURE OF THE DRUG SITUATION IN SOUTH AFRICA AS REFLECTED BY COMMUNITIES IN THE NINE PROVINCES 8 November 2011 2

CONTENTS National Statistics and Research on substance abuse Nature and type of substance abuse Effects of substance abuse on women and children Measures for preventing and combating substance abuse i.a.w. the NDMP 8 November 2011 3

OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY Create awareness regarding substance abuse . Assess community members’ knowledge of substance use and abuse. Identify the types of drugs used in communities. Establish awareness of substance abuse prevention and treatment services in their communities. Assess community members’ awareness of their roles and responsibilities regarding prevention of alcohol and drug abuse. Assess community members’ awareness regarding the law. Establish from the community members what the government and others should do to prevent alcohol and drug abuse. 8 November 2011 4

SURVEY METHOD Used triangulation to incorporate both quantitative and qualitative methods. 9 provinces participated with samples from the selected localities. Guidance and ethical issues taken into account. Training offered by CDA members to the research assistants on request. 8 November 2011 5

DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS Pilot study conducted in Gauteng June 2010 Mobilisation campaign launched in Northern Cape in October 2010. Theme: “No place for drugs in my community”. Questionnaires administered by trained volunteers and staff. Data from the questionnaires were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. 8 November 2011 6
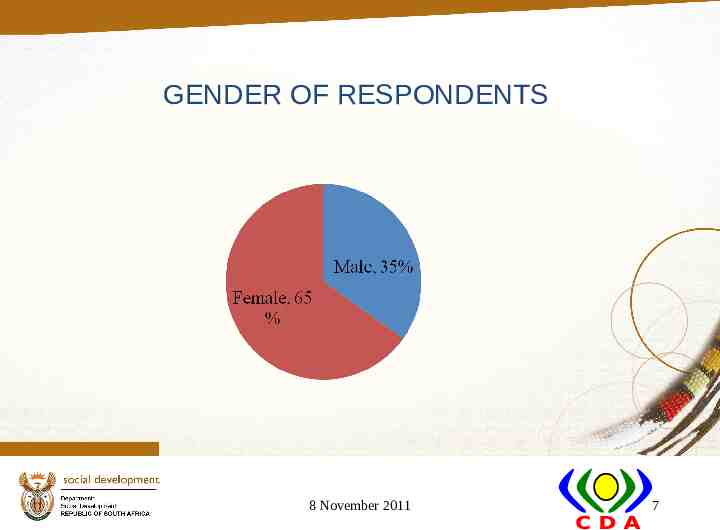
GENDER OF RESPONDENTS 8 November 2011 7
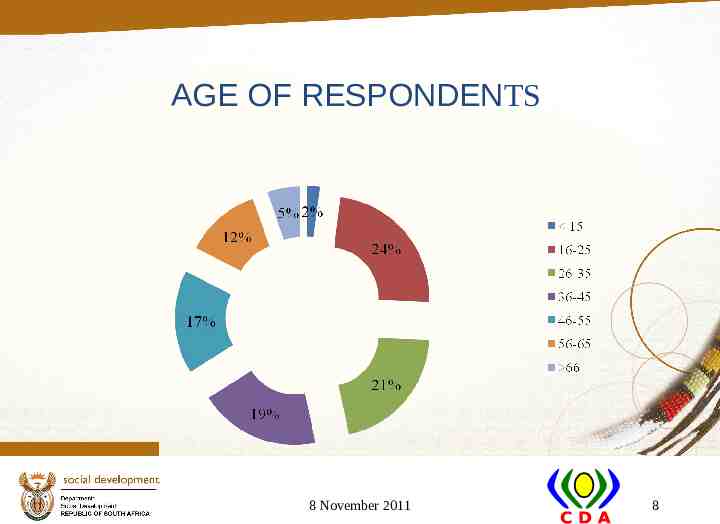
AGE OF RESPONDENTS 8 November 2011 8
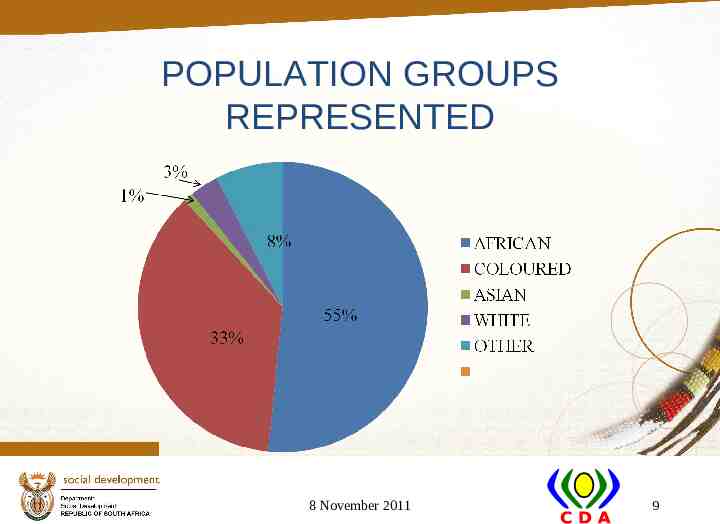
POPULATION GROUPS REPRESENTED 8 November 2011 9

RESIDENTIAL AREAS 8 November 2011 10
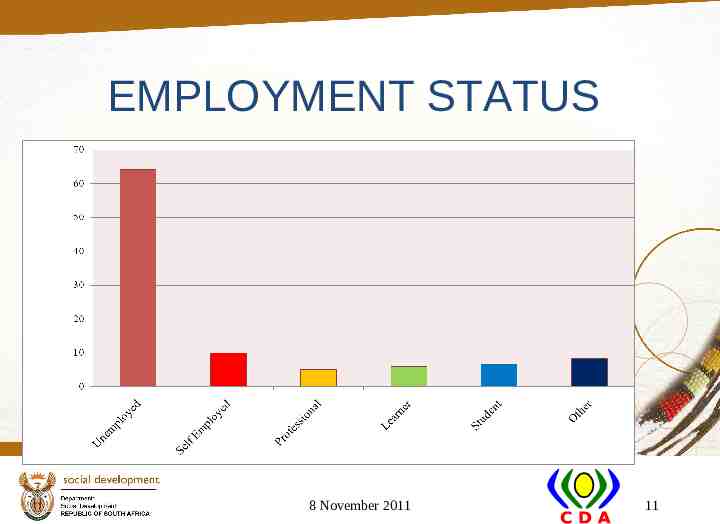
EMPLOYMENT STATUS 8 November 2011 11
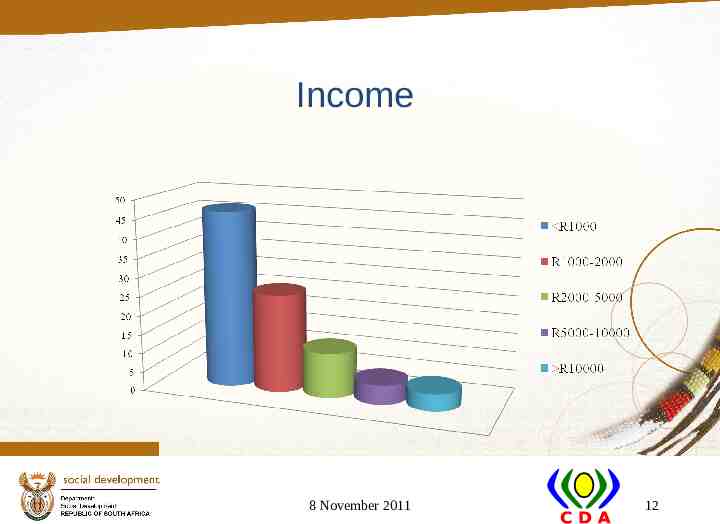
Income 8 November 2011 12

OTHER ISSUES ADDRESSED IN SNAPSHOT SURVEY AND SUMMIT Role of policy and legislative prescripts Substance abuse is everyone’s business South African Harm Reduction perspective Empowerment is the key to supply reduction Is substance abuse treatment and aftercare adequate? 8 November 2011 13
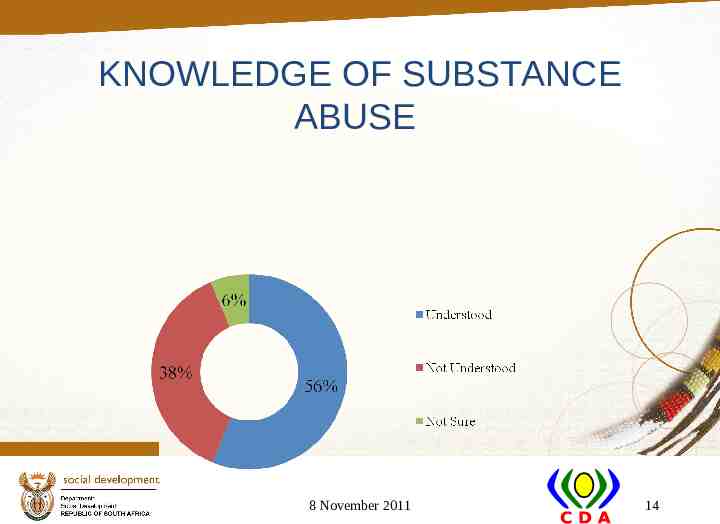
KNOWLEDGE OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE 8 November 2011 14
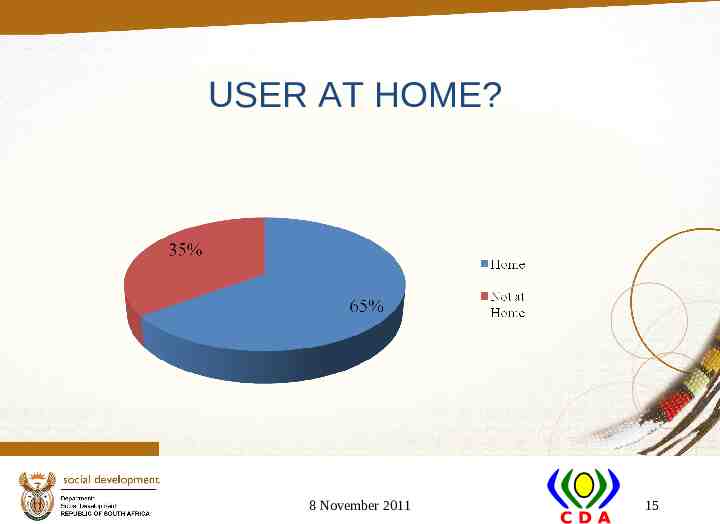
USER AT HOME? 8 November 2011 15
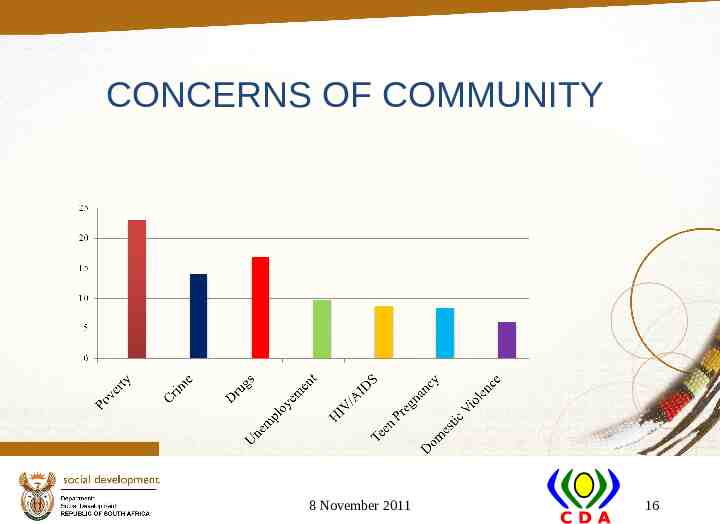
CONCERNS OF COMMUNITY 8 November 2011 16
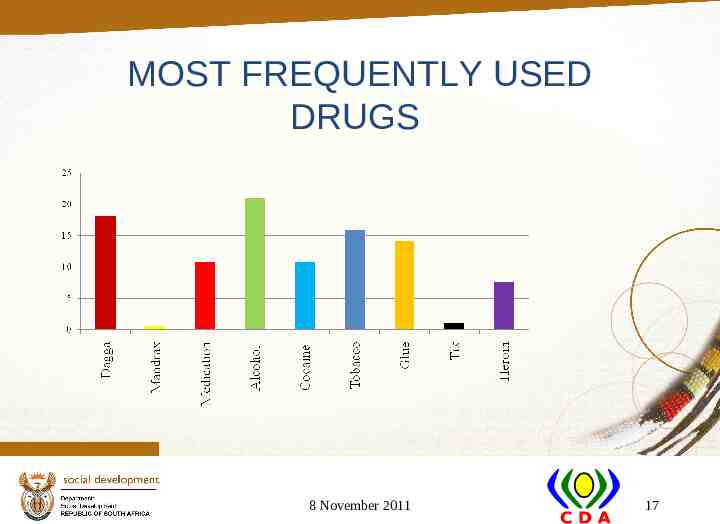
MOST FREQUENTLY USED DRUGS 8 November 2011 17
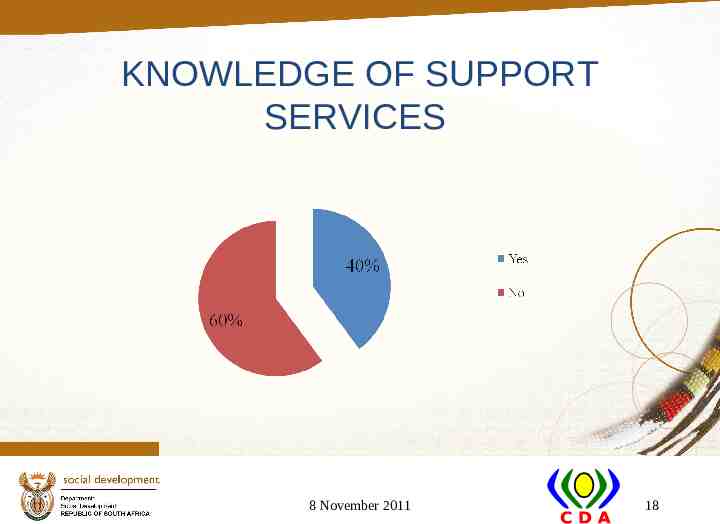
KNOWLEDGE OF SUPPORT SERVICES 8 November 2011 18
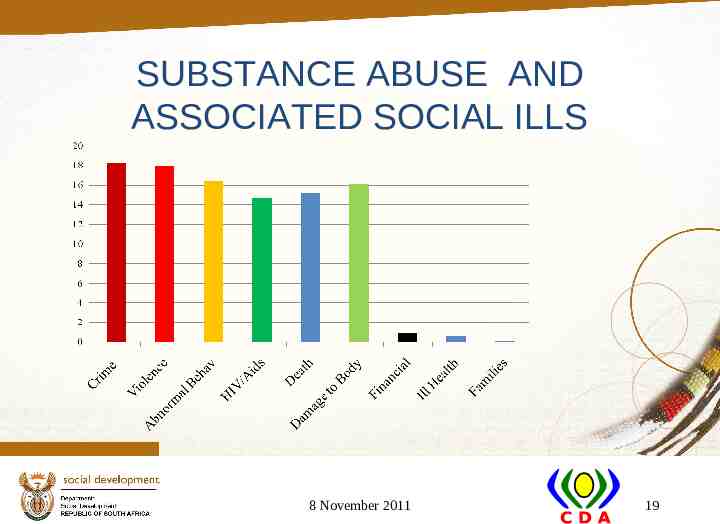
SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND ASSOCIATED SOCIAL ILLS 8 November 2011 19
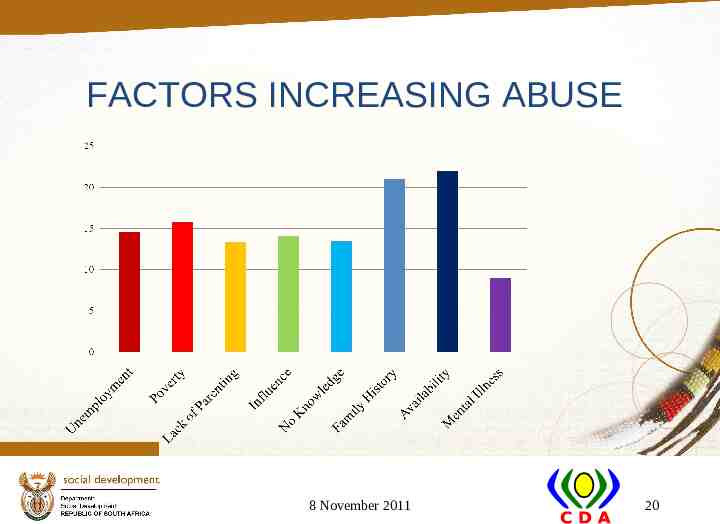
FACTORS INCREASING ABUSE 8 November 2011 20
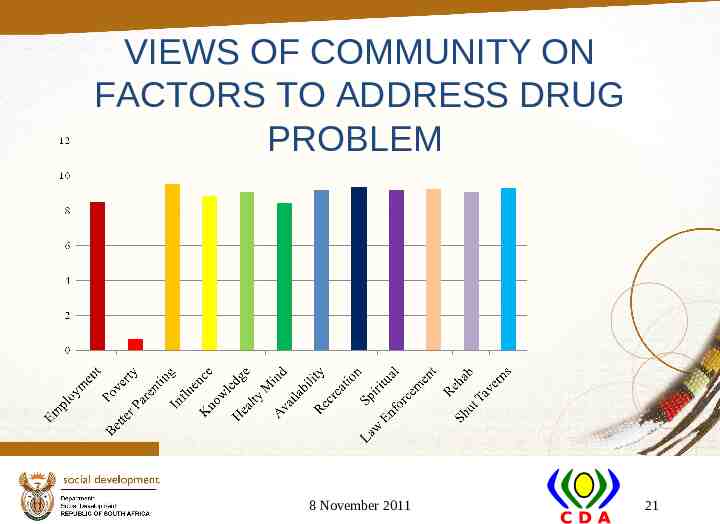
VIEWS OF COMMUNITY ON FACTORS TO ADDRESS DRUG PROBLEM 8 November 2011 21
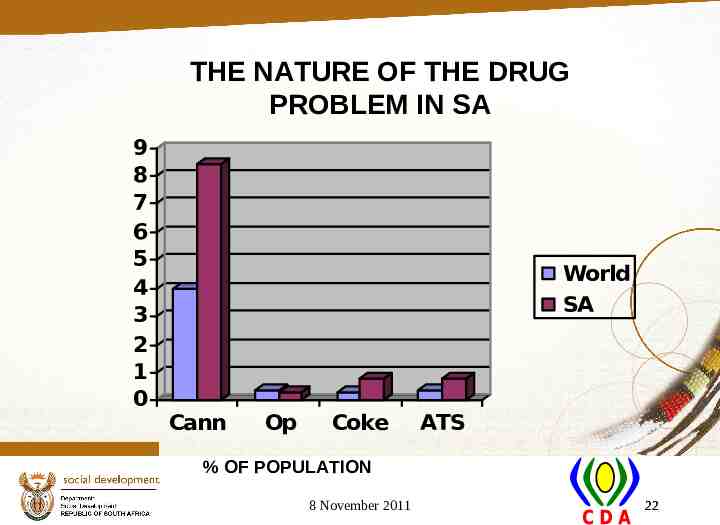
THE NATURE OF THE DRUG PROBLEM IN SA 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 World SA Cann Op Coke ATS % OF POPULATION 8 November 2011 22
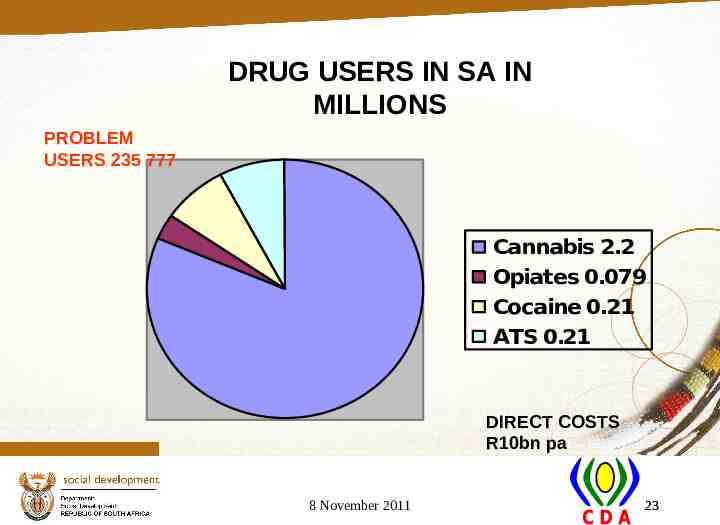
DRUG USERS IN SA IN MILLIONS PROBLEM USERS 235 777 Cannabis 2.2 Opiates 0.079 Cocaine 0.21 ATS 0.21 DIRECT COSTS R10bn pa 8 November 2011 23
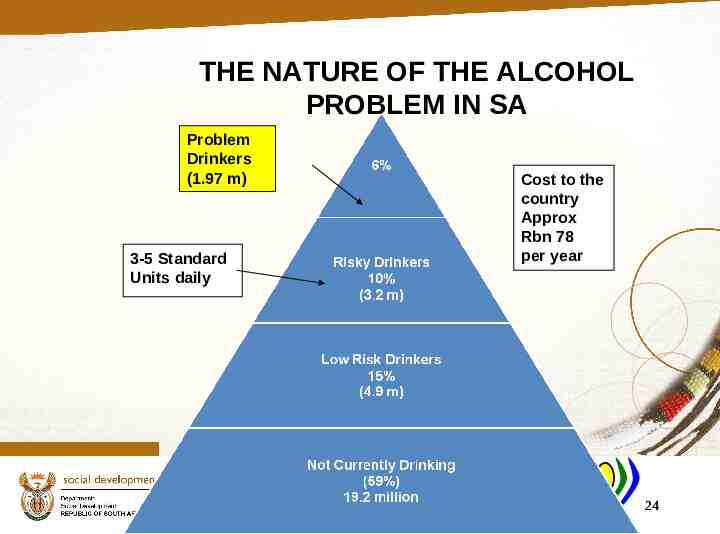
THE NATURE OF THE ALCOHOL PROBLEM IN SA Problem Drinkers (1.97 m) Cost to the country Approx Rbn 78 per year 3-5 Standard Units daily 8CDA: November May 2008 2011 24
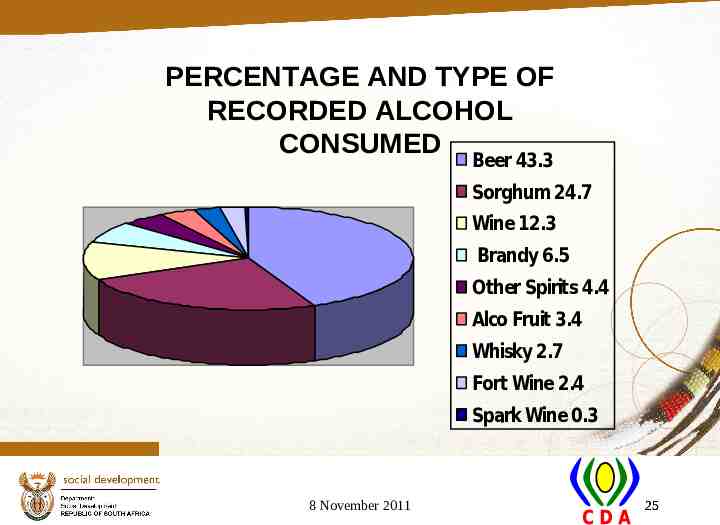
PERCENTAGE AND TYPE OF RECORDED ALCOHOL CONSUMED Beer 43.3 Sorghum 24.7 Wine 12.3 Brandy 6.5 Other Spirits 4.4 Alco Fruit 3.4 Whisky 2.7 Fort Wine 2.4 Spark Wine 0.3 8 November 2011 25

TOTAL CONSUMPTION OF ALCOHOL SA’s 10.1 m drinkers EACH drink per year: 196 six-packs of beer, or 62 bottles of spirits, or 20.1 L of pure alcohol per head Top Ten in the World! 220 bottles of wine, or 666 cartons of sorghum beer 8 November 2011 26

THE DRUG PROBLEM: ADULTS UP CLOSE AND PERSONAL THINK ABOUT: Binge Drinkers: 37% plus Monday drivers: 10% drunk DUI: 7000 deaths per annum Drug dealers of 18: R100k per day turnover Dependent of 24: R5000 per day Link between drug use, HIV/AIDS, TB, violence and crime Co-dependents: Bankrupt and destitute Heroin dependents: 2% recovery success All dependents: 47% plus bipolar 8 November 2011 27
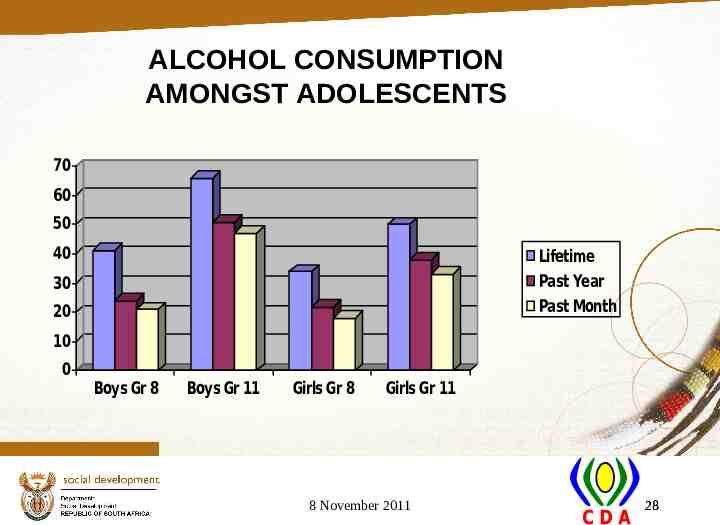
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION AMONGST ADOLESCENTS 70 60 50 40 Lifetime Past Year Past Month 30 20 10 0 Boys Gr 8 Boys Gr 11 Girls Gr 8 Girls Gr 11 8 November 2011 28
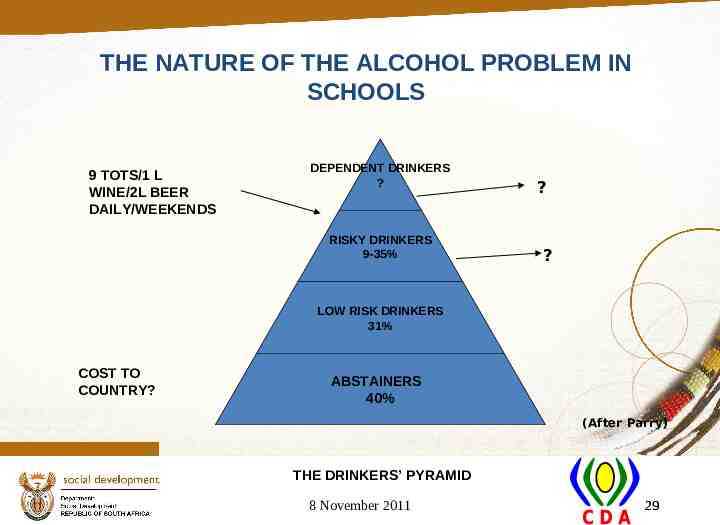
THE NATURE OF THE ALCOHOL PROBLEM IN SCHOOLS 9 TOTS/1 L WINE/2L BEER DAILY/WEEKENDS DEPENDENT DRINKERS ? RISKY DRINKERS 9-35% ? ? LOW RISK DRINKERS 31% COST TO COUNTRY? ABSTAINERS 40% (After Parry) THE DRINKERS’ PYRAMID 8 November 2011 29
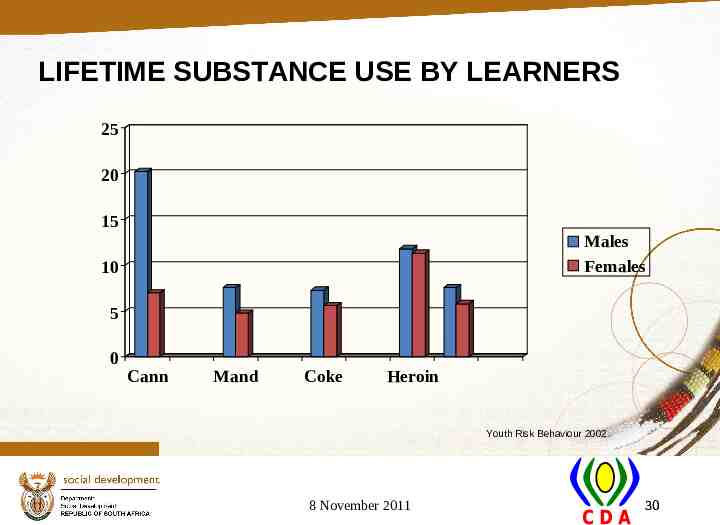
LIFETIME SUBSTANCE USE BY LEARNERS 25 20 15 Males Females 10 5 0 Cann Mand Coke Heroin Youth Risk Behaviour 2002 8 November 2011 30

YOUNG SUBSTANCE USERS AND POTENTIAL HARM Crime and violence Accidents and injuries Risky sexual behaviour/unplanned pregnancies/STI’s/HIV and AIDS Learning problems Mental and physical health problems 8 November 2011 31
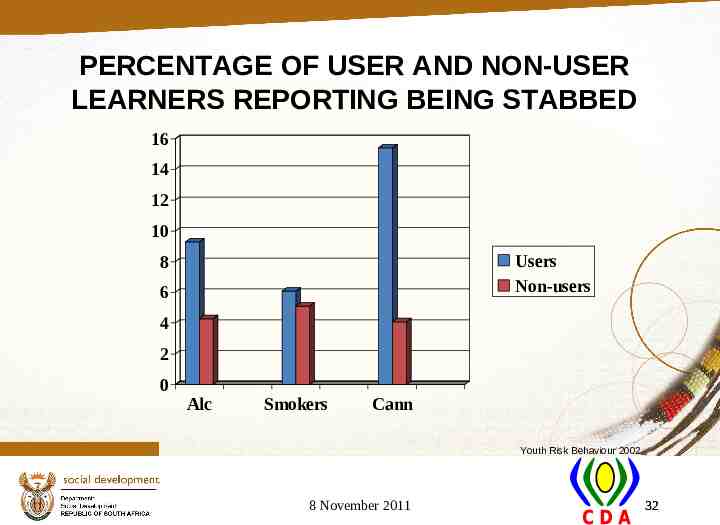
PERCENTAGE OF USER AND NON-USER LEARNERS REPORTING BEING STABBED 16 14 12 10 Users Non-users 8 6 4 2 0 Alc Smokers Cann Youth Risk Behaviour 2002 8 November 2011 32
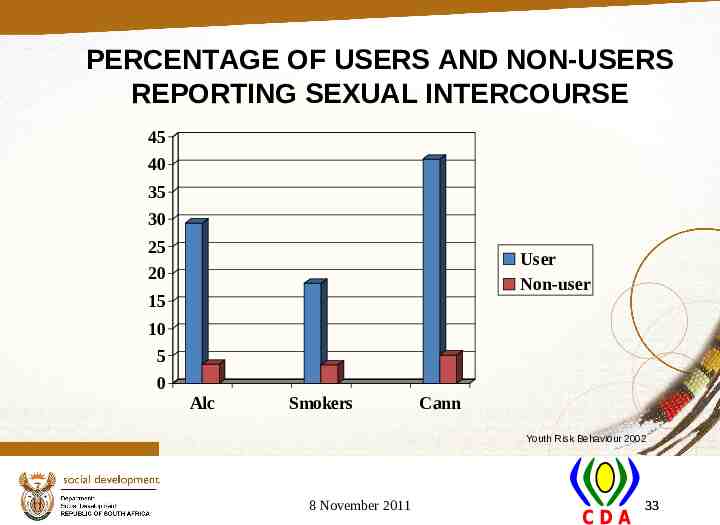
PERCENTAGE OF USERS AND NON-USERS REPORTING SEXUAL INTERCOURSE 45 40 35 30 25 20 User Non-user 15 10 5 0 Alc Smokers Cann Youth Risk Behaviour 2002 8 November 2011 33
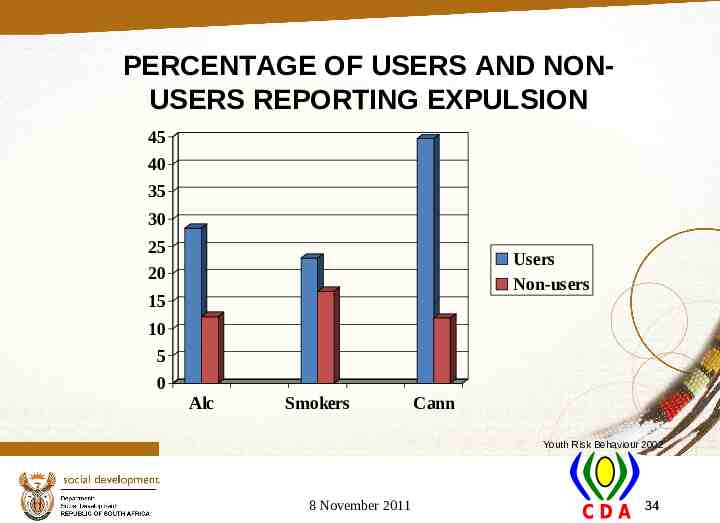
PERCENTAGE OF USERS AND NONUSERS REPORTING EXPULSION 45 40 35 30 25 20 Users Non-users 15 10 5 0 Alc Smokers Cann Youth Risk Behaviour 2002 8 November 2011 34

THE DRUG PROBLEM: THE YOUTH UP CLOSE AND MORE PERSONAL THINK ABOUT SCHOOLS & YOUNG OFFENDERS: Age of Dependence: 12 years and reducing. School children: 1 in 2 experimented Drug dealers in schools: Target schools Increase in injection drug use (IDU) HIV/AIDS in prisons linked to IDU Tik :42% to 98% level in Cape treatment centres SACENDU and ISS: Positive link between drugs and violence Drug Disguises: Peanuts; tattoos; sweets; cakes; lollipops 8 November 2011 35

Women’s substance abuse –The Basics Women’s substance abuse is different Addiction occurs more rapidly for women Frequently involves more than one mood-altering substance Produces serious medical consequences over a briefer period of time Women are more likely to have co-morbid psychiatric disorders 8 November 2011 36

What we know We know that Women respond differently to treatment than men, particularly to programmes designed initially for men (like the 12 steps) We know that Women abuse substances at different rates, and for different motivations than men We know that Women use different substances and for different reasons than men 8 November 2011 37

Women’s substance abuse –The Basics Women’s substance abuse is different Women are more likely to be victims of violence, physical abuse, domestic violence and rape According to Mondanaro et al. (1982) 46% of all drug-dependent women have been victims of rape 28% to 44% have been victims of incest Studies indicate these percentages are significantly higher for incarcerated women. (80% have experienced some form of abuse) 8 November 2011 38

What we know We know that: Gender responsiveness requires programmes specifically geared to meet the needs of women, who experience substance abuse differently than men on many levels We know that: These programmes must also be culturally sensitive Intersection of gender expectations within culture are important to consider when adapting treatment programme to different populations We know that Programme must take into account family and children 8 November 2011 39

What we know We know that: There are many risk factors and co-occurring disorders (e.g. a history of traumatic exposure) and consequences (interference with parenting) of substance abuse that are unique for women, giving rise to special treatment needs of substance-abusing women with children We know that: Service barriers exist for women differently than for men. Substance abusing mothers also experience unique barriers to receiving the services they need to recover, such as absence of child care and lack of gender-specific treatment in their communities 8 November 2011 40

CDA STRATEGIES FOR COMBATING ADDICTION DEMAND REDUCTION SUPPLY REDUCTION HARM REDUCTION 8 November 2011 41
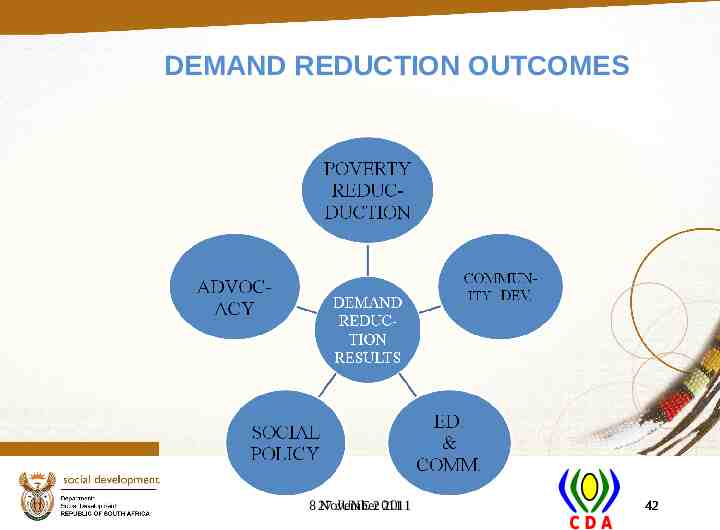
DEMAND REDUCTION OUTCOMES 8 27 November JUNE 2011 2011 42

SUPPLY REDUCTION OUTCOMES TRENDS LEGAL ACTION PRODUCTION SUPPLY REDUCTION RESULTS CONTROL TRAFFICKING PRICES PURITY CONSUMPTION 8 27 November JUNE 2011 2011 43

HARM REDUCTION OUTCOMES DETOX & REHAB LIMITING SPREAD OF IDU DISEASES AFTERCARE & REINTEGRATION HARM REDUCTION RESULTS CONTROL OF DISTRIBUTION AND ACCESS SUBSTITUTION THERAPY MEDICAL TREATMENT EDUCATION & COMMUNICATION 8 27 November JUNE 2011 2011 44

SUBSTANCE USE AND ABUSE IN SOUTH AFRICA The drug problem in South Africa is extremely serious, with drug usage at twice the world norm, and alcohol consumption among the Top 10. The socio-economic consequences of this cost the country more than Rbn 130 per year. The CDA integrated strategy is incorporated in the National Drug Master Plan. 8 November 2011 45

ANTI-SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESOLUTIONS AND THE COMMUNITY NEEDS There are 34 resolutions: remembering them all is a monumental task There are presently 12 factors/needs expressed by the communities For ease in remembering and reporting a grouping of resolutions into common factors is desirable. People remember alliterative terms more easily or terms that make a word that has meaning to them. 8 November 2011 46
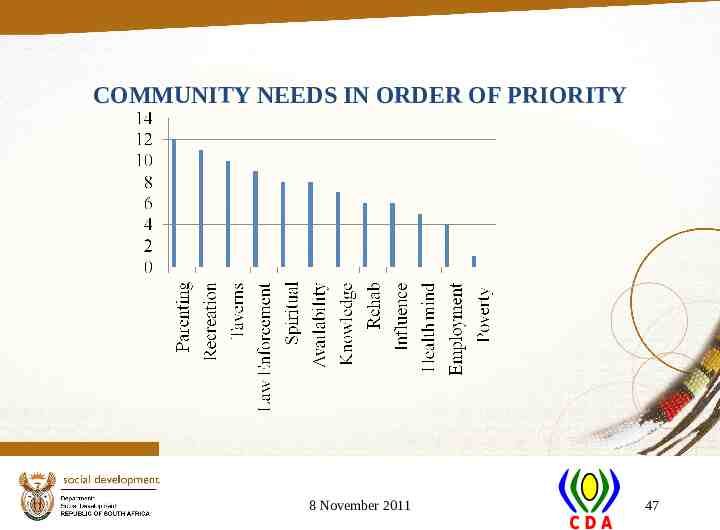
COMMUNITY NEEDS IN ORDER OF PRIORITY 8 November 2011 47

SOME COMMUNITY NEEDS GROUPED IN TERMS OF COMMONALITIES FACTOR COMMONALITY GROUP Parenting Family Education Re-education Spirituality Faith education Re-education Knowledge Substance/abuse Education Re-education Influence Life skills education Re-education Healthy mind Life skills education Re-education 8 November 2011 48

GROUPED COMMUNITY NEEDS AND INTEGRATED NDMP STRATEGY NEEDS Re-education Recreation EQUALS SUPPLY REDUCTION Reduction Re-enforcement Rehabilitation DEMAND REDUCTION HARM REDUCTION Re-employment 8 November 2011 49

EXAMPLE: SOME SUMMIT RESOLUTIONS GROUPED RES No. CONTENT POTENTIAL GROUP 1 Laws & policies on alcohol Re-enforcement 2 Structure and mandate of CDA Re-enforcement 3 Reducing accessibility of alcohol Reduction 4 Reductions on sales of alcohol Reduction 5 Reduce liquor outlets Reduction 6 Control of home brews and concoctions Reduction 7 Raising duties and taxes on alcohol Reduction 8 November 2011 50

DEMAND REDUCTION OUTCOMES 8 November 2011 51

SUPPLY REDUCTION OUTCOMES TRENDS LEGAL ACTION PRODUCTION SUPPLY REDUCTION RESULTS CONTROL TRAFFICKING PRICES PURITY CONSUMPTION 8 November 2011 52

HARM REDUCTION OUTCOMES DETOX & REHAB LIMITING SPREAD OF IDU DISEASES AFTERCARE & REINTEGRATION HARM REDUCTION RESULTS CONTROL OF DISTRIBUTION AND ACCESS SUBSTITUTION THERAPY MEDICAL TREATMENT EDUCATION & COMMUNICATION 8 November 2011 53

IN CONCLUSION: SUBSTANCE USE AND CONTROL IN SOUTH AFRICA Snapshot survey conducted to determine community needs on dependence-forming substances 2010-2011:12 key needs identified 2nd Biennial Anti-substance Abuse Summit developed 34 resolutions CDA mandated to review and revise NDMP to meet new requirements including community needs and resolutions to combat substance use, abuse and dependence Integrated and balanced strategy of demand-, supply- and harm reduction developed. Draft NDMP 2012-2016 drafted and now under review by stakeholders. 8 November 2011 54






