TopicΠ Financial Instruments and Markets 1
74 Slides555.50 KB

TopicΠ Financial Instruments and Markets 1

Financial Instruments 2
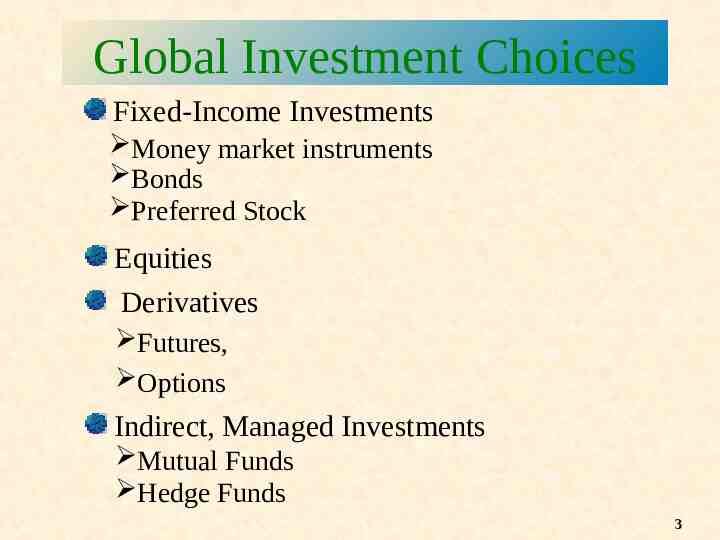
Global Investment Choices Fixed-Income Investments Money market instruments Bonds Preferred Stock Equities Derivatives Futures, Options Indirect, Managed Investments Mutual Funds Hedge Funds 3

Fixed Income Investments Most fixed income instruments specify a number of features including the following: The maturity date The coupon The par value 4

Money Market Instruments Treasury Bills Certificate of Deposits(CD) Commercial Paper(CP) Bankers’ Acceptances(BA) Eurodollars Repos and Reverses Repos Brokers’ Calls Federal Funds the LIBOR Market 5

Fixed Income Securities (I) Capital Market Government Bonds Treasury notes Treasury bonds Government agency bonds Municipal Bonds General obligation bonds (GOs) Revenue bonds 6

Fixed Income Securities (II) Capital Market Corporate Bonds Debentures Senior secured bonds Subordinated debentures Income bonds Convertible bonds Callable bonds Bonds with Warrants 7

Fixed Income Securities (Ш) Capital Market International Bond Investment Eurobond Yankee market bonds, Bulldog market, Samurai Market International domestic bonds Other Fixed Income Instruments Asset backed securities CMOs CARs Zero coupon bonds Preferred Stocks 8

Equity Securities Common Stock Foreign Equities American Depository Receipts(ADRs) American Shares Direct purchase International or global mutual funds 9

American Depository Receipts Easiest way to acquire foreign shares Certificates issued by a U.S. bank Buy and sell in U.S. dollars Dividends in U.S. dollars May represent multiple shares Very popular, over 1500 ADR programs available in 2002 10

Derivative Securities There are many types of derivative investments, including financial derivative securities whose payoffs are tied to various financial assets. Options Warrants Puts and calls Futures contracts 11

Derivatives: Options Warrants Puts and calls 12

Derivatives: Futures Standardized contracts to make or take delivery of some financial (or other) asset in exchange a specified payment at a future date. 13

Managed Investments Closed-end investment companies Open-end investment companies (Mutual funds) Hedge Funds: Venture capital pools: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): 14

Historic Return and Risk 15

Exhibit 3.1 Exhibit 3.2 16

Return/Risk: Characteristics Major classes of assets large company common stocks small capitalization common stocks long-term U.S. government bonds long-term corporate bonds Intermediate-term U.S. U.S. T-bonds T-bills consumer goods (measure inflation) 17

Return/Risk: focuses Consider: Exhibit 3.15 18

Summarizing the Historic Data Average premiums earned: Equity risk premium Small-stock premium Horizon premium Default premium 19

Exhibit3.3 Exhibit3.4 Exhibit3.6 Exhibit3.9 Exhibit3.7 Exhibit3.8 Exhibit3.10 20

World Portfolio Performance Exhibit3.16 Exhibit3.17 Exhibit3.18 Exhibit3.11 Exhibit3.12 21

Financial Markets and Market Structures 22

Types of markets Direct Search Markets Brokered Markets Dealer Markets Auction Markets 23

Characteristics of A Good Market Availability of info (timely & accurate) Liquidity Low TCs (Internal efficiency) External efficiency 24

Primary Capital Markets Underwriting Functions Relationships with Investment Bankers Negotiated Competitive bids Best-efforts Exhibit6.1 25

Primary Markets:Common Stock Types of new issues Forms of Underwriting Negotiated Competitive bids Best efforts Introduction of Rule 415 (Shelf Registration) Private Placement and Rule 144A 26

Rule 415: Shelf Regis tration Allows firms to register securities and sell them piecemeal over the next two years Pros: Cons: Used for straight debentures rather than CS or CB 27

Private Placements and Rule 144A Firms sells to a small group of institutional investors, with some assistance of an investment banker 28

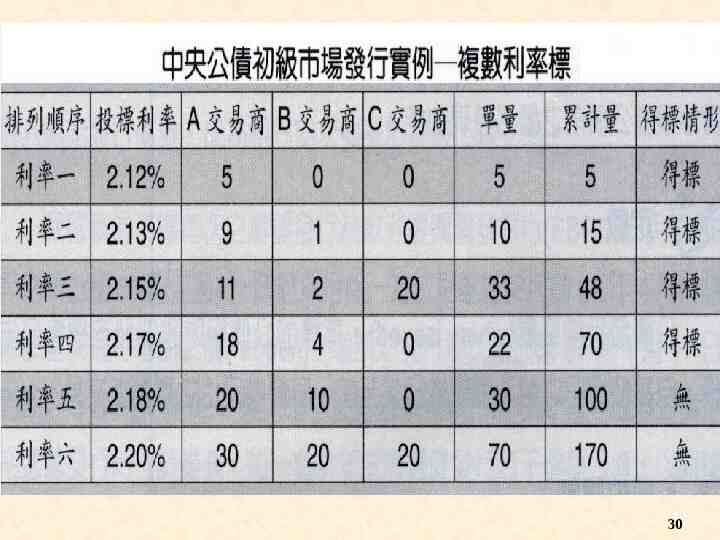
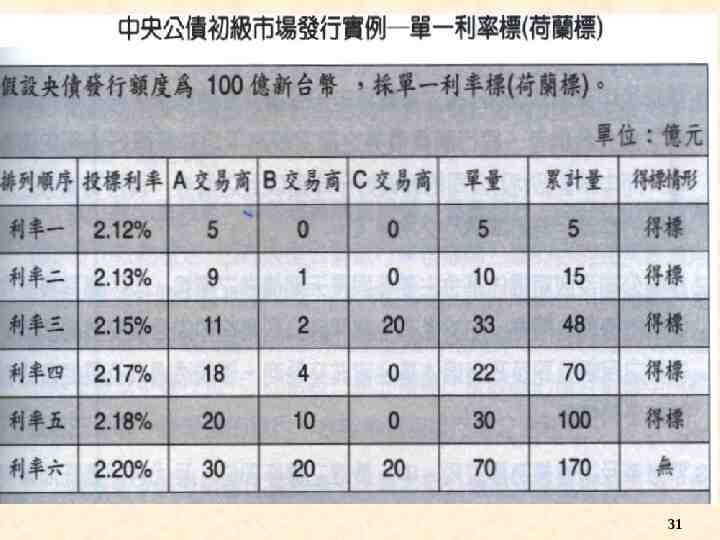
Primary Markets:Government Bond “Federal Reserve System” Auction Competitive bids vs. non-competitive bids 我國公債發行實務 中央公債原則採標售方式發行 標售方式 1. 複數利率 ( 價格 ) 標 2. 單一利率 ( 價格 ) 標,即荷蘭標 29
30
31

Primary Markets: Corporate Bond Negotiated arrangement 我國公司債發行實務 32
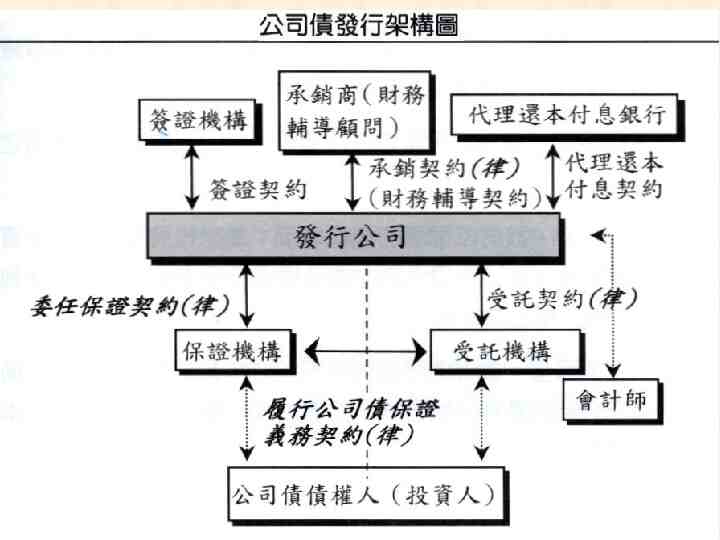
33

Secondary Markets Provide liquidity to investors who acquire securities in the primary market An active secondary market 34

Secondary Bond Markets Stock Exchanges (First Market) Over-the-counter market (Second Market) Third Market Fourth Market 35

Secondary Market Trading Systems Pure auction market Dealer market p.190 下表 Dealer Bid Ask 36

Call Versus Continuous Markets Call markets( 集合競價 ) Continuous markets( 連續競價 ) 37

Exchange Membership Four categories of membership: Specialists Commission brokers Floor brokers Registered traders 38

Major Types of Orders Market orders Limit orders Special Orders Stop loss MIT (Market-if-touched) 39

Margin Trading :Example (I) P0 50,#200 shares, IM 50% I0 5000 leverage factor 1/0.5 2 P1 R R( 100commission,6% on loan) 60 12000 5000 1 40% ( 20%) 5000 40 3000 ( 20%) 5000 1 40% 40

Margin Trading :Example (II) If MM 25% If P 30 6000 5000 16.67% Investor’s Margin 6000 Margin call for 41
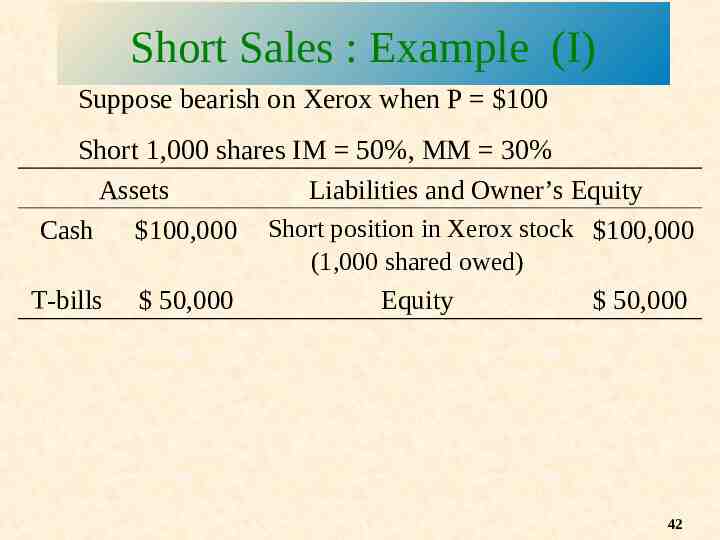
Short Sales : Example (I) Suppose bearish on Xerox when P 100 Short 1,000 shares IM 50%, MM 30% Assets Liabilities and Owner’s Equity Cash 100,000 Short position in Xerox stock 100,000 (1,000 shared owed) T-bills 50,000 Equity 50,000 42
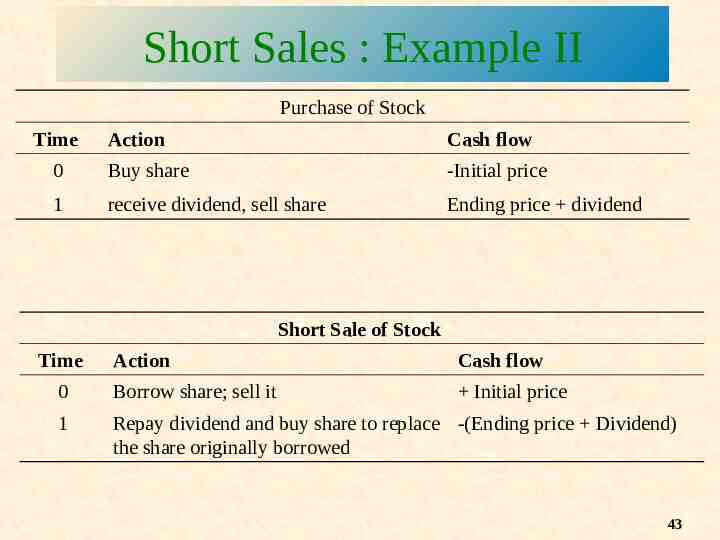
Short Sales : Example II Purchase of Stock Time Action Cash flow 0 Buy share -Initial price 1 receive dividend, sell share Ending price dividend Short Sale of Stock Time Action Cash flow 0 Borrow share; sell it Initial price 1 Repay dividend and buy share to replace -(Ending price Dividend) the share originally borrowed 43

擔保維持率 融資擔保品市值 原融券擔保品及保證 擔保維持率 金 原融資金額 融券標的證券市 價 44

Changes in the Securities Markets In recent years, major changes in securities markets have largely been driven by the influence of large financial (institutional) investors. Among the impacts: Negotiated (competitive) commission rates Influence of block trades Impact on stock price volatility Development of National Market System (NMS) 45

New Trading Systems Super DOT Display Book Opening Automated Report Service (OARS) Market Order Processing Limit Order Processing 46

Global Market Changes (I) NYSE Off-hours trading Listing foreign stocks on the NYSE 47

Global Market Changes (II) London Stock Exchange “Big Bang” Tokyo Stock Exchange “Big Bang” 48

Future Developments Creation and consolidation of stock exchanges More specialized investment companies Changes in the financial services industry Trading in Cybermarkets 49

SECURITY MARKET INDICATOR SERIES 50

What is an indicator series? It is an index that answers the question: What happened in the market today? 51

Uses of Security Market Index Performance benchmark Develop an index portfolio Measure(or examine factors of) market movements Technical Analysis,to predict future price move Proxy for mkt portfolio to compute j 52

Factors in Constructing Market Indicator Series Sample Weighting price weighted value-weighted unweighted Computational procedure 53

Stock-Market Indicator Series Price-Weighted Series Value-Weighted Series Equal-Weighted Series 54

DIJA: Computation 30 P it DJIAt i 1 股價總和 / 固定除數 Dadj Exhibit b7.2 Exhibit 7.1 55

Value Weighted Series It PQ P Q it it i0 i0 I 0 計算期市值總合 基期市值總合 ( 固定除數 ) Exhibit 7.3 Exhibit7.4 基期指 數 56

台灣發行量加權股價指數 It PQ P Q 基期: 55 年指數為 100 it it i0 it 100 採樣:所有上市普通股,但不含變更交易方式股票,基金受 益憑證,各類憑證、上市未滿月之股票。 固定權數隨採樣異動、現金增資、轉換公司債轉換為股票及 公司合併而調整 ( 無償配股除權則不調整 ) ,理論上除權前後 總市值無變化。 變動後總市值 新除固定除數 變動前指數 基期指數 57
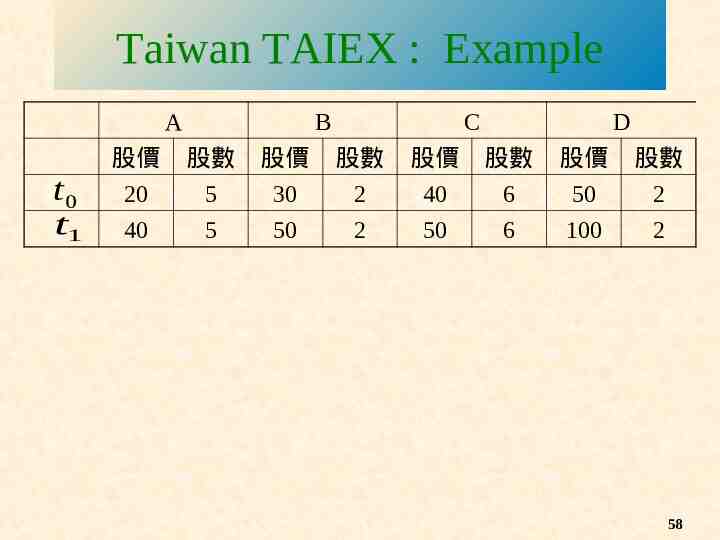
Taiwan TAIEX : Example A t0 t1 B C D 股價 股數 股價 股數 股價 股數 股價 股數 20 5 30 2 40 6 50 2 40 5 50 2 50 6 100 2 58
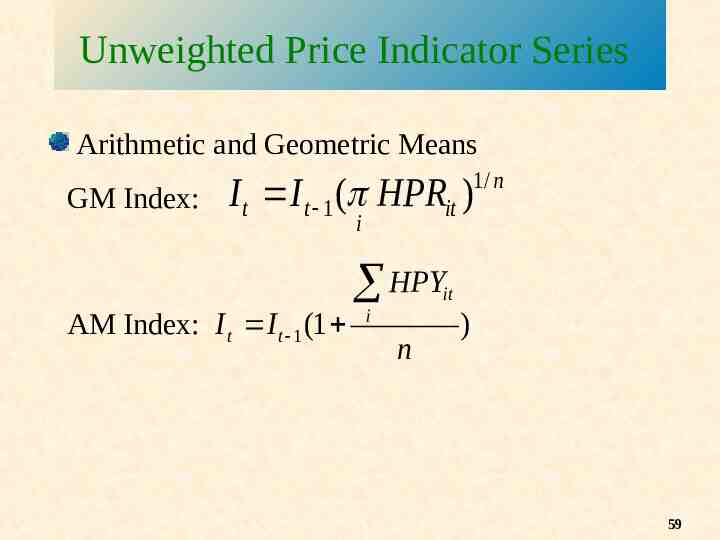
Unweighted Price Indicator Series Arithmetic and Geometric Means GM Index: 1/ n I t I t 1 ( HPRit ) i HPY it AM Index: I t I t 1 (1 i n ) 59

Exhibit7.8 60
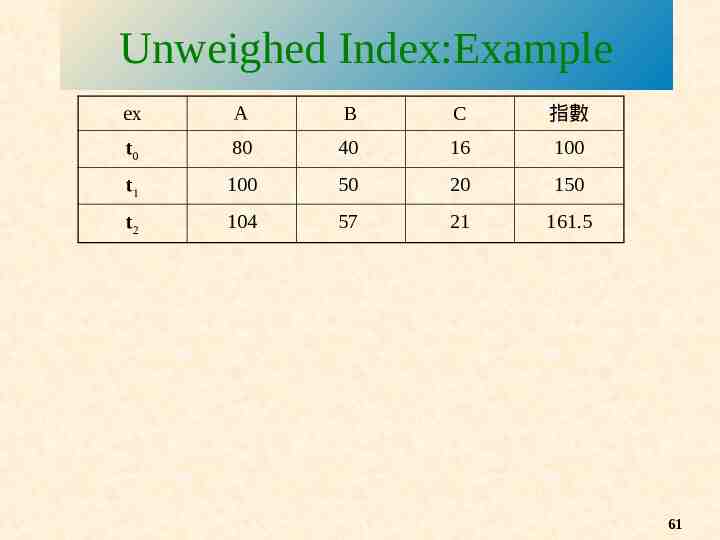
Unweighed Index:Example ex A B C 指數 t0 80 40 16 100 t1 100 50 20 150 t2 104 57 21 161.5 61
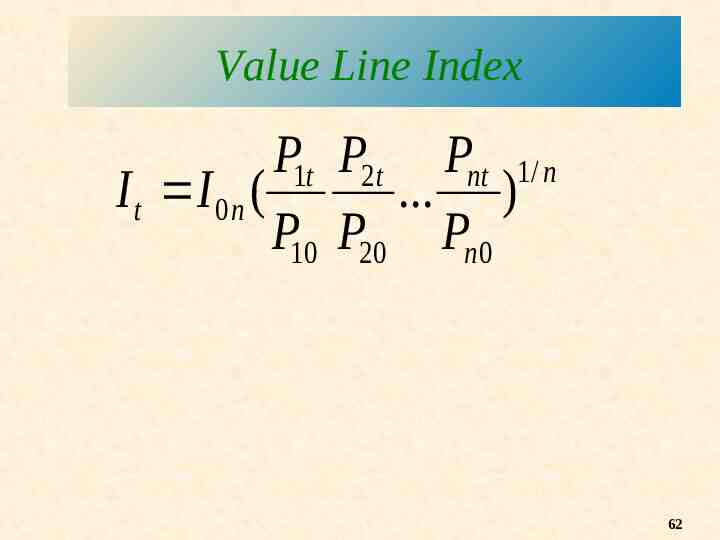
Value Line Index P1t P2t Pnt 1/ n I t I 0 n ( . ) P10 P20 Pn 0 62

Pi Xi Pi X i A 10 250 2500 (50%) B C 50 100 160 30 10 1500 1000 5000 (30%) (20%) 63
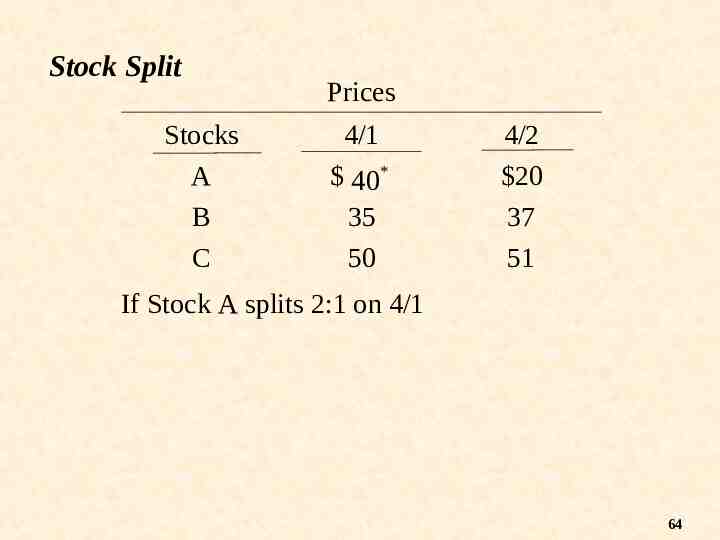
Stock Split Stocks A B C Prices 4/1 40* 35 50 4/2 20 37 51 If Stock A splits 2:1 on 4/1 64
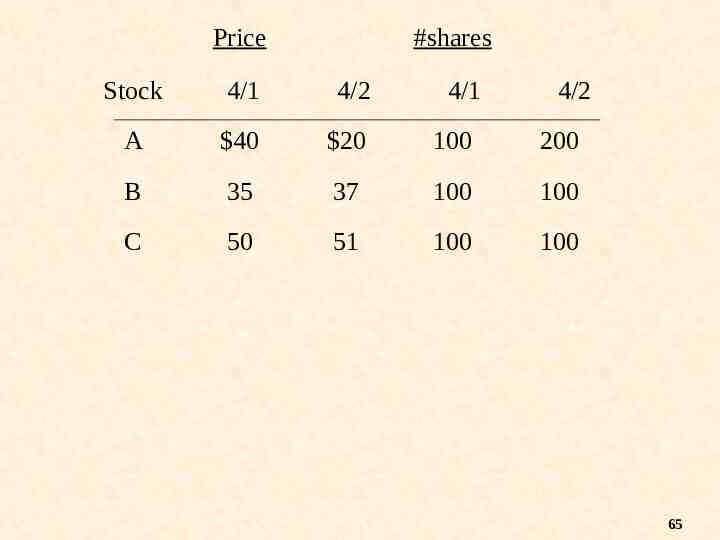
Price #shares Stock 4/1 4/2 4/1 4/2 A 40 20 100 200 B 35 37 100 100 C 50 51 100 100 65
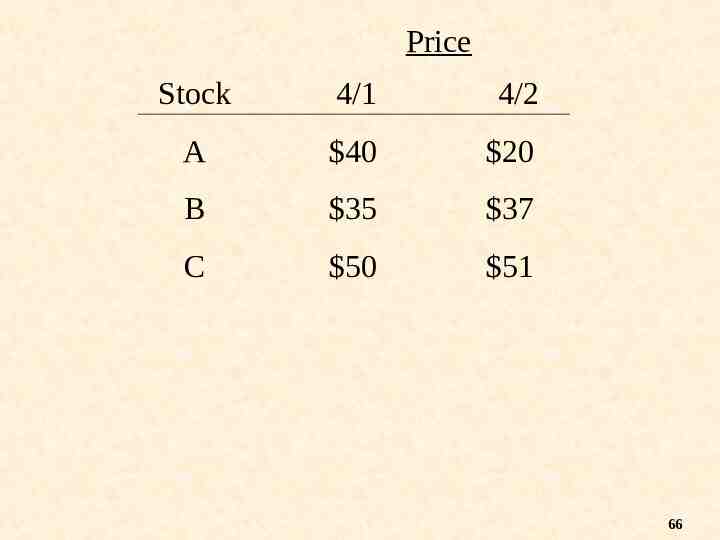
Price Stock 4/1 4/2 A 40 20 B 35 37 C 50 51 66

Style Indexes Measure the performance of various investment styles or sectors Size indexes type indexes Small-cap midcap Large-cap growth growth growth Small-cap midcap Large-cap value value value 67

Global Equity Indexes FT/S&P Actuaries World Indexes Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) World Indexes Dow Jones World Stock Index 68

Exhibit7.9 Exhibit7.10 Exhibit7.12 69

Comparison of World Stock Indexes Exhibit7.13 70

Bond-Market Indicator Series Relatively new and not widely published Growth in fixed-income mutual funds increase need for reliable benchmarks for evaluating performance Increasing interest in bond index funds, which requires an index to emulate 71

Difficulties in Creating a BondMarket Index bond quality Bond market changes Bond prices are affected differently without current and continuous transaction prices 72

Bond Market Index Series Investment-Grade Bond Indexes High-Yield Bond Indexes Global Government Bond Market Indexes Composite Stock-Bond Indexes Merrill Lynch-Wilshire U.S. Capital Markets Index (ML-WCMI) Brinson Partners Global Security Market Index (GSMI) 73

Comparison of Indexes Over Time Exhibit7.15 Exhibit7.16 74