Billing & Coding Emergency Department Procedures
41 Slides138.90 KB

Billing & Coding Emergency Department Procedures & Point-of-Care Ultrasound E L I Z AB E T H B AR RA L L W E R L E Y , M D P R O GRA M D I R E C T O R AS S I S TA N T P R O F E S S O R O F E M E R GE N CY M E D I C I N E P E N N S TAT E H E A LT H

Reimbursement Cognitive work Evaluation and Management (E/M) codes 99281 – 99285 Critical Care codes Procedures Reimbursement may be higher than E/M service

CPT Codes Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Maintained by the AMA Select few E/M codes in Emergency Medicine Specific codes for specific procedures

CPT vs CMS Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Differences between CPT and CMS for E/M Dependent upon group and payer mix CPT guidelines apply if non-participatory with a payer

RVUs Relative Value Unit Value assigned to E/M codes, CPT codes In 2019, 1 RVU 36.04 Total RVU components: Physician Work Practice Expense (facility) Liability Insurance (malpractice)

General Approach to Procedures In addition to E/M services Document each procedure individually “Remember, you do not get reimbursed for what you do, you get paid for what you document about what you do!” ACEP Coding and Reimbursement Pearls

General Approach to Procedures Document (when applicable): Procedure performed Indication Location Laterality Complexity Technique Supplies used

General Approach to Procedures Many procedures only have 1 CPT code Other procedures can have multiple options

Modifiers Special circumstance related to a procedure -22 Increased Procedural Services -50 Bilateral Procedure -51 Multiple Procedures -53 Discontinued Procedure

Modifiers Special circumstance related to a procedure -76 Repeat Procedure or Service by Same Physician or other qualified Health Care professional -77 Repeat Procedure by Another Physician or other qualified Health care Professional Anatomic Modifiers Performance Measurement Modifiers

Lacerations/Wound Repair RVU Complexity of wound Simple, intermediate, complex Length of repair Measure, don’t estimate Details matter 2.5 cm 12.6cm – 20.0cm 2.6cm – 7.5cm 20.1cm – 30.0cm 7.6cm – 12.5cm 30.0 cm
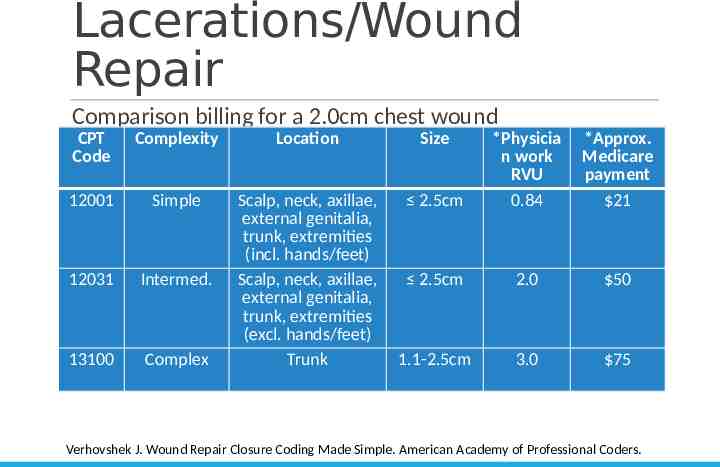
Lacerations/Wound Repair Comparison billing for a 2.0cm chest wound CPT Code Complexity Location Size 2.5cm *Physicia n work RVU 0.84 *Approx. Medicare payment 21 12001 Simple 12031 Intermed. 13100 Complex Scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk, extremities (incl. hands/feet) Scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk, extremities (excl. hands/feet) Trunk 2.5cm 2.0 50 1.1-2.5cm 3.0 75 Verhovshek J. Wound Repair Closure Coding Made Simple. American Academy of Professional Coders.

Lacerations/Wound Repair Grouped together (one CPT code) Same anatomic site Same complexity Coded individually Different anatomic groupings Varying complexity

Lacerations/Wound Repair Simple Superficial One-layer closure Anatomic groupings Scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands or feet) Face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes

Lacerations/Wound Repair Intermediate Layered closure (skin subcutaneous tissue) Single-layer closure but contaminated 3 different anatomic groupings Complex Multi-layer Extensive tissue damage and repair

Lacerations/Wound Repair Tissue Adhesive or Staples Use same CPT code for other wound repair Rare exception for Medicare subgroups

Lacerations/Wound Repair Priority in which wound repairs are coded Complexity Anatomic site Size

Lacerations/Wound Repair Factors that impact coding Complexity of closure Extent of cleaning Debridement Revision of wound edges Foreign body removal

Lacerations/Wound Repair Additional Diagnoses Do not increase E/M services themselves Do support the E/M service documented

Abscess I&D Simple Single Small collection of purulence

Abscess I&D Complex or Multiple (any of 3) Multiple Probing/loculations Packing Sub-fascial – more complicated to code

Fracture/Dislocation Care Fracture and/or Dislocation codes Defined as surgical “global care” procedures Closed treatment of fracture without manipulation Closed treatment of fracture with manipulation Closed treatment of dislocation with fracture with manipulation Closed treatment of dislocation without fracture, with manipulation Open vs closed fracture open vs closed treatment

Fracture/Dislocation Care Fracture-management services Restorative Care Definitive Care No splint code Splinted but not fracture-care services? Splint code

Fracture/Dislocation Care E/M service vs fracture/dislocation code Separate medical service Detailed history and exam Supports higher level E/M service

Fracture/Dislocation Care High RVUs Associated procedures? Procedural sedation X-ray interpretation

Procedural Sedation Solo completion or assisting others Only direct patient contact counts

Procedural Sedation Defined by time Initial code 0-30 minutes, met at 16 minutes Additional time 15 minute intervals, met at 8 minutes

Point-of-Care Ultrasound What is needed: Interpretation Medical necessity/Indication Images saved Diagnostic and procedural guidance

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Defined by body area, not procedure Limited vs Complete Exams Complete Limited Most c/w EM practice Exception: TV US No “limited” option

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Modifiers – common to ED POCUS -26: professional component Professional services only VS professional AND technical services -76: Repeat procedure by same person -77: Repeat procedure different different person -52: Service reduction

Point-of-Care Ultrasound FAST/E-FAST Limited abdominal US Limited transthoracic echocardiogram Limited thoracic US

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Pelvic US – based on pregnancy status Transabdominal Obstetric eval Non-obstetric eval Transvaginal Only “complete” option Must use modifier

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Procedural guidance Same rules apply for documentation Procedure US guidance – separate CPT codes

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Procedural guidance Select procedures – CPT code includes US Thoracentesis Paracentesis Arthrocentesis

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Procedural guidance CPT 76937 Vascular US guidance Static vs. dynamic Can only bill for dynamic Images obtained when available Post-procedure confirmation
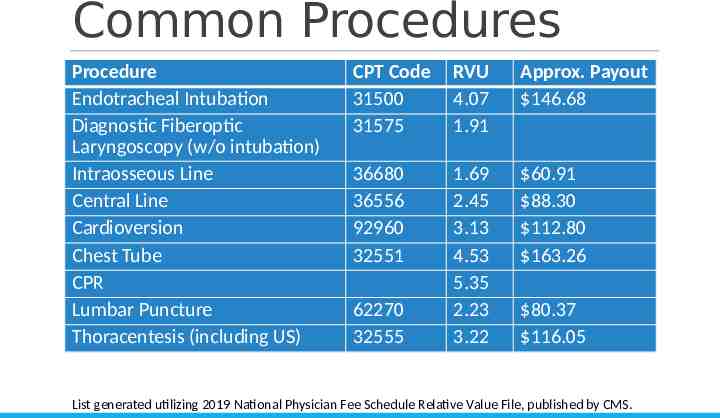
Common Procedures Procedure Endotracheal Intubation Diagnostic Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy (w/o intubation) Intraosseous Line Central Line Cardioversion Chest Tube CPR Lumbar Puncture Thoracentesis (including US) CPT Code 31500 31575 RVU 4.07 1.91 Approx. Payout 146.68 36680 36556 92960 32551 1.69 2.45 3.13 4.53 5.35 2.23 3.22 60.91 88.30 112.80 163.26 62270 32555 80.37 116.05 List generated utilizing 2019 National Physician Fee Schedule Relative Value File, published by CMS.
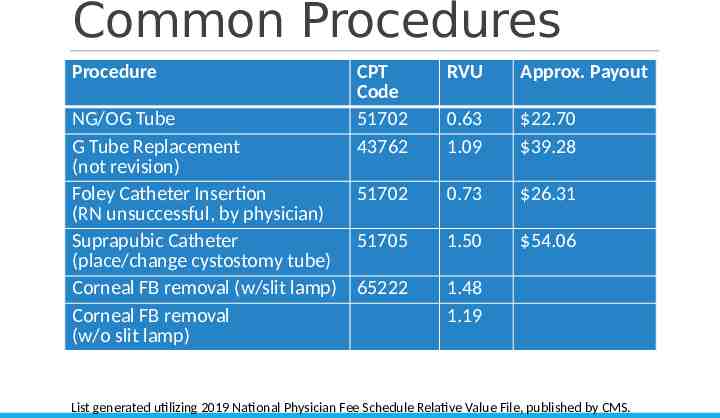
Common Procedures Procedure CPT Code 51702 43762 NG/OG Tube G Tube Replacement (not revision) Foley Catheter Insertion 51702 (RN unsuccessful, by physician) Suprapubic Catheter 51705 (place/change cystostomy tube) Corneal FB removal (w/slit lamp) 65222 Corneal FB removal (w/o slit lamp) RVU Approx. Payout 0.63 1.09 22.70 39.28 0.73 26.31 1.50 54.06 1.48 1.19 List generated utilizing 2019 National Physician Fee Schedule Relative Value File, published by CMS.
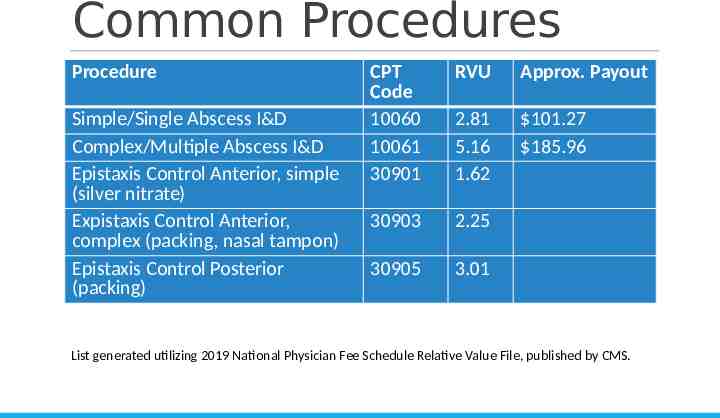
Common Procedures Procedure Simple/Single Abscess I&D Complex/Multiple Abscess I&D Epistaxis Control Anterior, simple (silver nitrate) Expistaxis Control Anterior, complex (packing, nasal tampon) Epistaxis Control Posterior (packing) CPT Code 10060 10061 30901 RVU Approx. Payout 2.81 5.16 1.62 101.27 185.96 30903 2.25 30905 3.01 List generated utilizing 2019 National Physician Fee Schedule Relative Value File, published by CMS.

References 1. Emergency department coding and reimbursement: a physician’s guide. LOGIX Health. 2. What every graduating resident needs to know about reimbursement. American College of Emergency Physicians. Updated March 2019. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/what-every-graduating-residentneeds-to-know-about-reimbursement/ 3. CPT codes, guidelines & additional resources. American Medical Association. https://www.ama-assn.org/amaone/cpt-current-procedural-terminology 4. Evaluation and management documentation requirements – CMS vs. CPT. American College of Emergency Physicians. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/documentation-guidelines/ evaluation-and-management-documentation-requirements--cms-vs.-cpt/ 5. Approach to emergency department coding FAQ. American College of Emergency Physicians. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/reimbursement-faqs/ approach-to-emergency-department-coding-faq/

References 6. Coding and reimbursement pearls. American College of Emergency Physicians. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/coding-and-reimbursementpearls/#laceration 7. Modifier dictionary FAQ. American College of Emergency Physicians. Updated April 12 2017. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/reimbursement-faqs/ modifier-dictionary-faq/ 8. Verhovshek J. Wound repair closure coding made simple. American Academy of Professional Coders. https://www.aapc.com/blog/26267-closure-coding-made-simple/ 9. Magdziarz D. Reimbursement 2019: a field-guide for physicians in the trenches. American College of Osteopathic Emergency Physicians. https://acoep.org/ss19/wpcontent/uploads/2019/03/Reimbursement-2019 -A-Field-Guide-for-Physicians-in-theTrenches Magdziarz.pdf 10. Verhovshek J. Coding abscess procedures. American Academy of Professional Coders. https://www.aapc.com/blog/37219-coding-abscess-procedures/

References 11. Orthopedic fracture/dislocation management FAQ. American College of Emergency Physicians. Updated May 16, 2015. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/reimbursement-faqs/orthopedicfracture--dislocation-management-faq/#question0 12. Verhovshek J. Proper coding for endotracheal intubation. American Academy of Professional Coders. https://www.aapc.com/blog/28116-proper-coding-for-endotrachealintubation/ 13. Ultrasound FAQ. American College of Emergency Physicians. Updated September 2019. https://www.acep.org/administration/reimbursement/reimbursement-faqs/ultrasoundfaqs/#question10