The Wendy Klag Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities
24 Slides9.29 MB

The Wendy Klag Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities

The Wendy Klag Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities is dedicated to the promotion of research and education regarding the origins, detection, measurement and prevention of conditions that affect behavioral, socioemotional and/or cognitive development, as well as evaluation of services and policies that support optimal development of affected children and their families.

The Wendy Klag Memorial Fund (2006)

Developmental Disabilities Task Force Recommendations, October 2007 “Considerable expertise at Hopkins and KKI exists across a wide array of autism- and autism-spectrum disorders and other developmental disabilities. A striking hallmark among these institutions is the obvious good will among the researchers, as well as the strong and long-standing collaborations among faculty across the SPH, SOM and KKI. However, there is no “locus” of organization or regularized communications about autism research activities across the institutions (e.g., there is a seminar series that several faculty publicize on their own, but no systematic way to reach out to others or to involve new researchers.) Instead, such communications tend to be haphazard, limiting the ability of existing researchers to attract new faculty to the field.” 4
Spring, 2012 5
6
7

CADDE: Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities Epidemiology Studies: – SEED: national case-control study of 2-5 year olds – EARLI: national pregnancy cohort of women at risk for another child with an ASD – ADDM: National surveillance of ASD prevalence – Ancillary projects: Epigenetic mechanisms in ASD GWAS GxE for ASD

CADDE: Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities Epidemiology Themes: – Both genes and environment play a role in ASD risk – Perinatal window may be important for assessing environmental risks and gene-environment interactions – Epigenetic mechanisms may interplay with genetic and environmental risks – Biomarkers may be important for risk or for better identification and treatment

National case-control study of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) 3 types of children enrolled: ASD Cases Other non-ASD developmental disorders Controls: births in time/area identified through vital statistics 5400 children aged 2-5 years parents 16200 participants Johns Hopkins University, Kennedy Krieger Institute, CARD MD St. Dept of Education, MD Dept of Health and Mental Hygiene

Research Areas in SEED: Examine broader ASD phenotype Genetic features Infection and immune function, including autoimmunity Reproductive and hormonal features Gastrointestinal features Sociodemographic characteristics Substance use, hospitalizations and injuries, sleep disorders, occupational exposures and mercury exposure
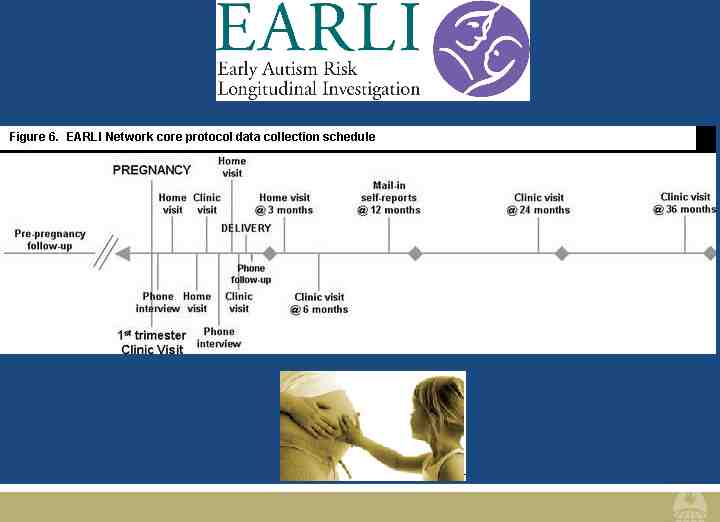
Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities Epidemiology (CADDE) Wendy Klag Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities (WKC) Broader scope of public health Build a community of investigators and students with a common purpose 13

WKC Activities Fund new and innovative faculty and student projects that will generate pilot data that can be leveraged into larger research projects (Due March 22, 2013) Enhance external funding competitiveness for new initiatives by, in addition to providing pilot funding support, coordinating resources and information regarding existing work and capacity at JHSPH and other Johns Hopkins University divisions, and KKI Promote educational opportunities through support of new courses, practicum experiences, and dissemination of research assistant positions to ultimately build a larger cadre of public health professionals with expertise in autism and developmental disabilities

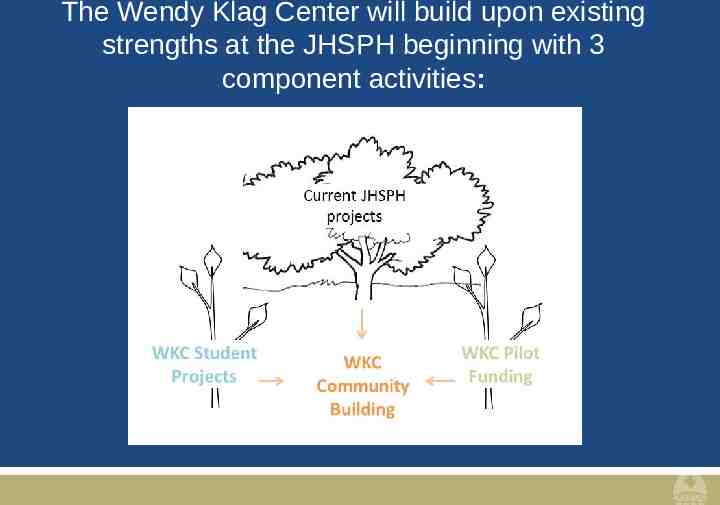
The Wendy Klag Center will build upon existing strengths at the JHSPH beginning with 3 component activities:
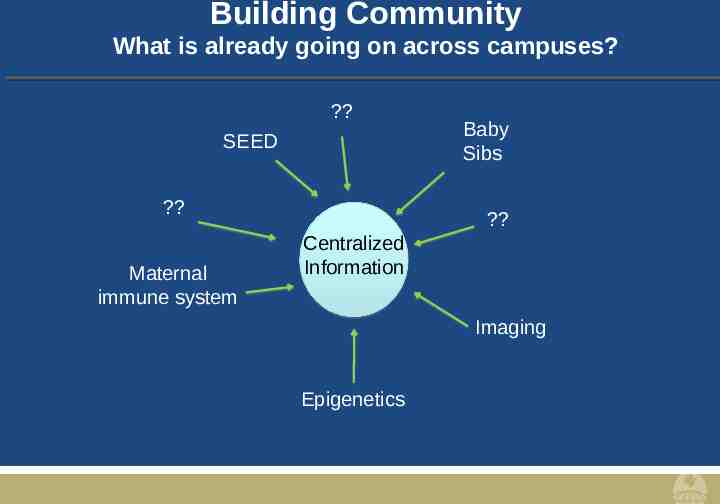
Building Community What is already going on across campuses? ? SEED ? Maternal immune system Baby Sibs ? Centralized Information Imaging Epigenetics
Building Community A centralized information resource can contribute to efficiency, facilitate new projects, more cross-fertilization ? SEED Maternal immune system Centralized Information Baby Sibs New initiatives Imaging Epigenetics
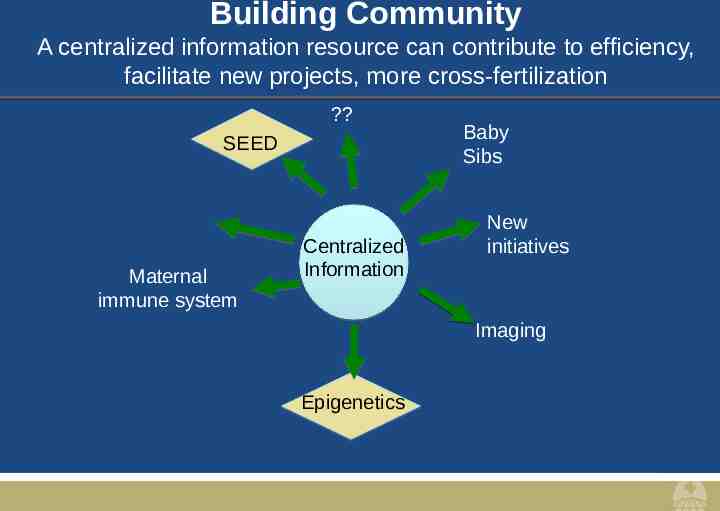
Advantages of a Centralized Resource Increase awareness of the impressive network of ASDand DD-related research already ongoing across campuses Facilitate resource and information sharing where possible – e.g.: Protocols; phlebotomy; biosamples; databasing; community / school contacts Initiate new collaborations – New projects / papers – New funding Centralized information will reduce burden on each investigator

WKC Activities (continued) Provide a forum for speakers and working groups focused on autism and developmental disabilities Serve as a liaison for intra-university, local, and state partnerships Stimulate and energize current faculty and students in the adoption of a multi-pronged approach that builds upon the school’s multidisciplinary strengths Attract new faculty and students with interest in ASD and DD to JHSPH 19

Identifying And Characterizing The Causes Of ASDs and DDs Requires Many Perspectives Psychiatry Epidemiology Biostatistics Psychology Neurology ASD & DD etiology Clinical genetics Genetics Epigenetics Bioinformatics Immunology Toxicology Environmental health Behavioral genetics Psychometrics

Understanding And Acting On ASDs and DDs From Cause, Prevention, Treatment, And Service Provision Requires Even More Perspectives Health Policy Sociology Psychiatry Epidemiology Biostatistics Psychology Behavioral Therapy Health Services Bioinformatics Neurology Immunology ASD & DD Clinical genetics Obstetrics Toxicology Health Economics Nursing Genetics Environmental health Education Behavioral genetics Epigenetics Pediatrics Psychometrics

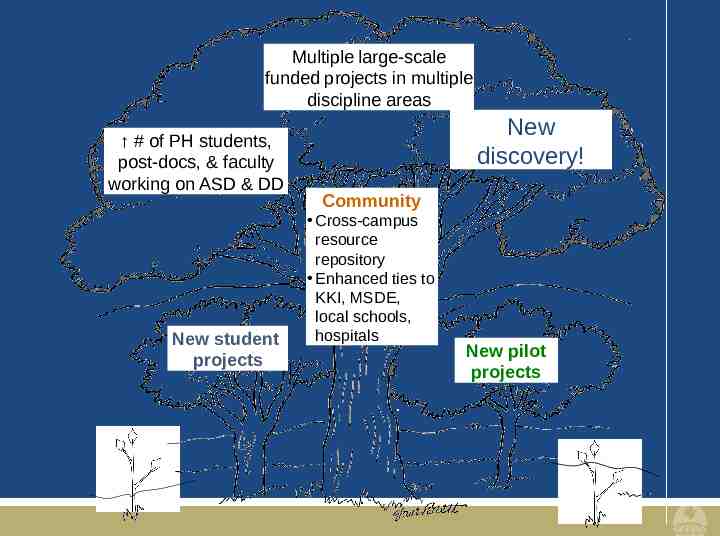
Multiple large-scale funded projects in multiple discipline areas # of PH students, post-docs, & faculty working on ASD & DD New student projects New discovery! Community Cross-campus resource repository Enhanced ties to KKI, MSDE, local schools, hospitals New pilot projects
Organization Director, Dani Fallin Associate Director, Janet DiPietro To be followed by: Additional Assoc Directors Core Faculty Affiliated Faculty 23

In conclusion Promote discovery, programs and policies that improve the lives of children and their families 24 Energize current faculty Benefit recruitment Guide student interest Stimulate intra-university, state and local liaisons Provide forum for internal and external speakers Enhance funding competitiveness Pilot data Expanded resources/environment 2009, Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved.







