SELLING AND SALES MANGEMENT Chapter One The Field of Sales
17 Slides995.67 KB

SELLING AND SALES MANGEMENT Chapter One The Field of Sales Force Management

Sales Management : Sales management is a business discipline which is focused on the practical application of sales techniques and the management of a firm's sales operations. It is an important business function as net sales through the sale of products and services and resulting profit drive most commercial business. These are also typically the goals and performance indicators of sales management Also known as Sales force Management and maybe also defined as the management of the personal selling component of an organization's marketing program.

Personal Selling: persuasive communication between a representative of the company and one or more prospective customers, designed to influence the person's or group's purchase decision. A personal presentation by the company’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationship

THE CHANGE.? The world of professional selling is changing dramatically. Much of this change is driven by shifts in the way customers , particularly business customers, buy products. Important changes: Customers have become more sophisticated and demanding Customers want solutions rather than products Companies are using fewer suppliers Purchases being made from foreign suppliers Rapid transfer of technology Large accounts require more sophisticated selling

We now understand ‘The Changes’, now what? The ‘KEY’ to success is that: The sales force must be able to identify and develop relationships with the high profit potential accounts. Successful companies will distinguish themselves by the relationships they develop with their clients/ customers What does all this lead us to? This means that managing the sales force becomes more important to the ultimate success of most companies. Sales management will be primarily responsible for what happens when salesperson or selling team meets the customer.

Along with changes in their approach to customers, sales people will change themselves. They will have more in depth customer knowledge and more sophisticated selling and service skills. As a result, salespeople will be highly paid, more highly trained, and more skilled professionals.
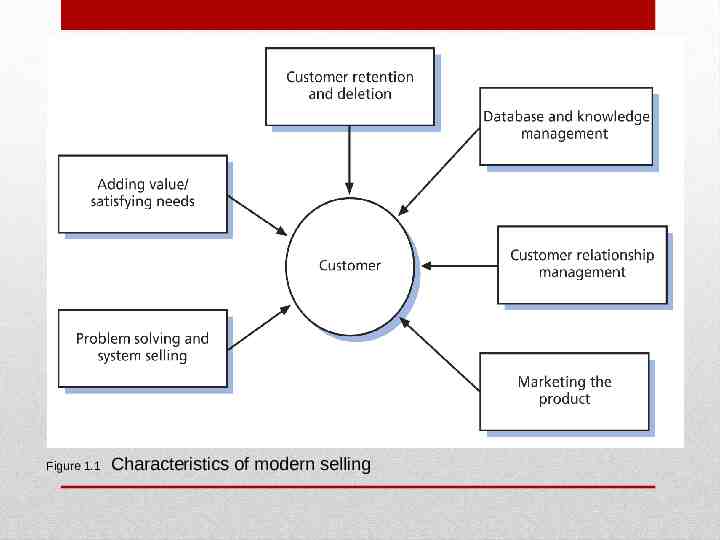
Figure 1.1 Characteristics of modern selling

Modern sales approaches: The shifts in the way customers buy in 21st century entails that sales function takes on a new robe and a novel sales approach. Some of the modern sales approaches include: Partnering Relationship selling Team selling Value added selling Consultative selling

Personal selling in the Marketing Mix Under the marketing concept, marketing research assumes the task of identifying customer needs and problems, while the firm’s marketing mix is used to deliver the solutions. The marketing mix is the set of strategies that a company utilizes to implement its marketing plan and pursue its marketing objectives. In line with the changes in the markets and marketing strategies, salespeople n sales managers are being asked to play a significant role in each component of the marketing mix.

The role of personal selling in product strategy: earlier limited input into product development decisions; but under marketing concept, sales personnel help specify desirable product features n benefits during product development phase. The role of personal selling in pricing strategy: they can ascertain competitive pricing and gauge market reaction to alternative price levels; advise senior management in pricing decisions; or granted some discretion in adjusting prices to market conditions. The role of personal selling in distribution strategy: be it direct, in which its the salesperson calling on ultimate customer, or indirect distribution, where salesperson works closely with intermediaries. The role of personal selling in promotion strategy: the presentation of informative and persuasive messages to the firm’s target market in an attempt to stimulate sales. Thus paving the way for the salesforce to sell the firm’s offerings.
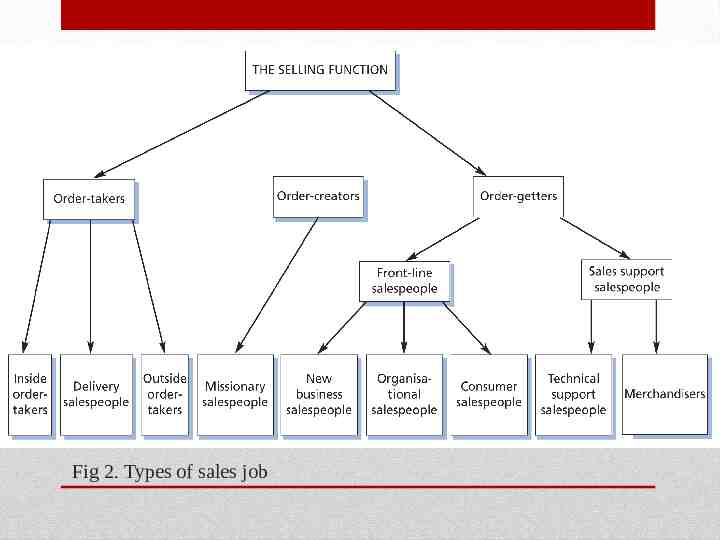
Fig 2. Types of sales job
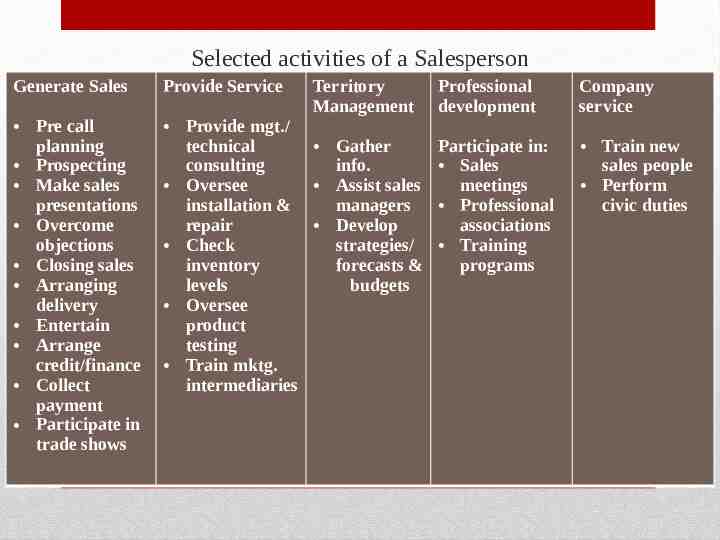
Selected activities of a Salesperson Generate Sales Provide Service Territory Management Professional development Pre call planning Prospecting Make sales presentations Overcome objections Closing sales Arranging delivery Entertain Arrange credit/finance Collect payment Participate in trade shows Provide mgt./ technical Participate in: Gather consulting info. Sales meetings Oversee Assist sales installation & managers Professional repair associations Develop strategies/ Training Check inventory forecasts & programs levels budgets Oversee product testing Train mktg. intermediaries Company service Train new sales people Perform civic duties
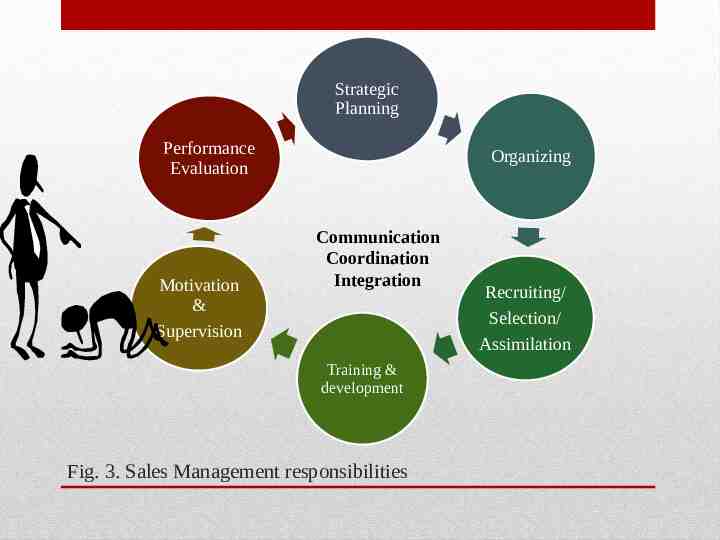
Strategic Planning Performance Evaluation Motivation & Supervision Organizing Communication Coordination Integration Training & development Fig. 3. Sales Management responsibilities Recruiting/ Selection/ Assimilation

Field Sales Manager’s Activities Analyze: the conditions of the selling situation 1.Review individual sales records n performance of salesperson 2.Assess specific market trends n conditions 3.Note relevant environmental factors n trends Plan: short run & long run 4.Establish sales objectives n develop strategies n procedures to attain these objectives 5.Transmit objectives, strategies n procedures to salesperson Organize: sales team to achieve the objectives 6.Break the selling tasks n supporting activities into operational jobs 7.Create specific job descriptions for these tasks n activities Direct: the operations of the sales team 8.Issue directions n delegate authority in order to get people do things 9.Motivate people (incentives), Train them and lead them. 10. Assure quality work and ethical behavior in conduct of business. Evaluate: sales performance 11. Create performance standards n measurement techniques 12. Analyze performance against standards 13. Take indicated remedial actions.

Crucial traits of a Sales manager 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Motivation – enthusiasm toward all major tasks with no strong aversion to any required tasks. Human relationship skills High energy levels Ambition – strong personal desire to achieve n advance Persuasiveness – interest in persuasive involvement rather than tendency to bully. Behavioral flexibility Intellectual ability Personal impact – charisma

Transaction oriented 1. 2. 3. 4. Get new accounts Get the order Cut the price to get the sale Manage all accounts to maximize short term sale. 5. Sell to anyone Relationship oriented 1. 2. 3. 4. Retain existing ones Become the preferred supplier Price for profit Manage each account for long term profit 5. Concentrate on high profit potential accounts Difference between Transaction – oriented selling and relationship – oriented selling

Important Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain how changes in purchasing patterns have changed the nature of the selling task? How does relationship oriented selling differ from transaction oriented selling? What activities a sales manager usually perform? Write down the general activities a salesperson has to perform?






