Quality System Structures for Industry 4.0 name Curriculum Development
23 Slides8.28 MB

Quality System Structures for Industry 4.0 name Curriculum Development of Master’s Degree Program in Industrial Engineering for Thailand Sustainable Smart Industry

Learning Objectives After completing this class, you should be able to: Understand approaches to Quality Management and how to select them Understand the differences between ISO 9000 and TQM and how to implement them Understand how Industry 4.0 impact Quality Management System and what Quality 4.0 is

Presentation Approaches to Quality

3 Approaches to Quality Management Consultancy approach Consultants help organizations to apply principles, methods and technical tools proposed by quality experts Standardization/ principle approach ISO 9001 Total Quality Management (TQM) Six Sigma Kaizen Juran Etc. Quality award approach Demin Prize Baldride Award European Quality Award
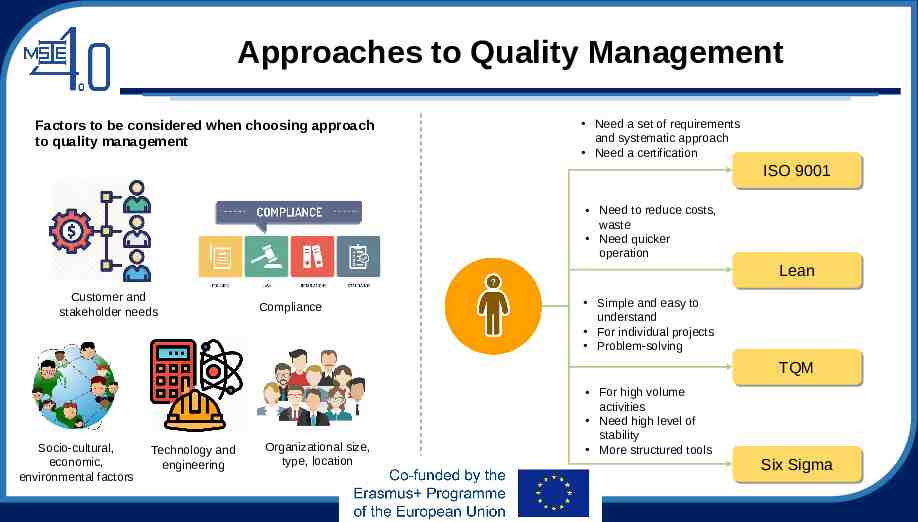
Approaches to Quality Management Factors to be considered when choosing approach to quality management Need a set of requirements and systematic approach Need a certification ISO ISO 9001 9001 Need to reduce costs, waste Need quicker operation Lean Lean Customer and stakeholder needs Compliance Simple and easy to understand For individual projects Problem-solving TQM TQM Socio-cultural, economic, environmental factors Technology and engineering Organizational size, type, location For high volume activities Need high level of stability More structured tools Six Six Sigma Sigma

ISO 9001 and TQM In this lessen, we will focus on 2 important quality approaches TQM and ISO 9000 were found to be the most prevalent quality approaches or strategies (Lee and Palmer, 1999) Lee, K.S. and Palmer, E. (1999), “An empirical examination of ISO 9000-registered companies in New Zealand”, Total Quality Management, Vol.10 No. 6, pp. 887-99

ISO 9001 Quality Management System (QMS) is a formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality polices and objectives. ISO 9001 is the world’s most popular and most commonly used standard for Quality Management System (QMS) Guidelines Why is QMS important? - Achieve customer satisfaction - Low cost of poor performance - Gain repeat business - Increase profitability - Increase effectiveness - Higher consistency ISO 9000 ISO 9001 Design Development Production Installation servicing ISO 9002 Production Installation ISO 9003 Inspection Testing

ISO 9001 Facts about ISO 9001 Generic – cover any organizational size, industry or culture – a standard for the whole wold An organization can only get a certification of ISO 9001 Identify what but not how requirements must be met Allow for flexibility Allow management to stay in the driving seat Provides the base level of a quality system, not a complete guarantee of quality Not a quality control tool Help facilitate international trade Registration process takes 12 – 18 months Can cost lots of money, time and paperwork Prone to failure when an organization focuses on certification not quality

ISO Standards ISO 31000 Risk management IATG 16949 Automotive Quality Management ISO 20000 IT service management. ISO/TS 29001:2010 Petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries ISO 13485 Medical Device AS 9100D Aviation, Space, and Defense Organizations ISO 9000: Quality Management ISO15378 and PS9000 Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials ISO 14000 Environmental management ISO 50001 ISO 22000 Food safety management Energy management
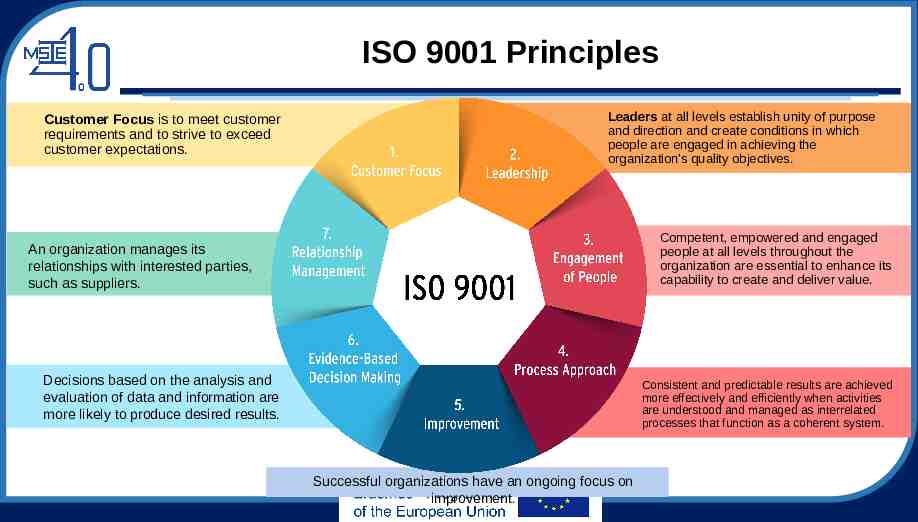
ISO 9001 Principles Customer Focus is to meet customer requirements and to strive to exceed customer expectations. Leaders at all levels establish unity of purpose and direction and create conditions in which people are engaged in achieving the organization’s quality objectives. Competent, empowered and engaged people at all levels throughout the organization are essential to enhance its capability to create and deliver value. An organization manages its relationships with interested parties, such as suppliers. Decisions based on the analysis and evaluation of data and information are more likely to produce desired results. Consistent and predictable results are achieved more effectively and efficiently when activities are understood and managed as interrelated processes that function as a coherent system. Successful organizations have an ongoing focus on improvement.
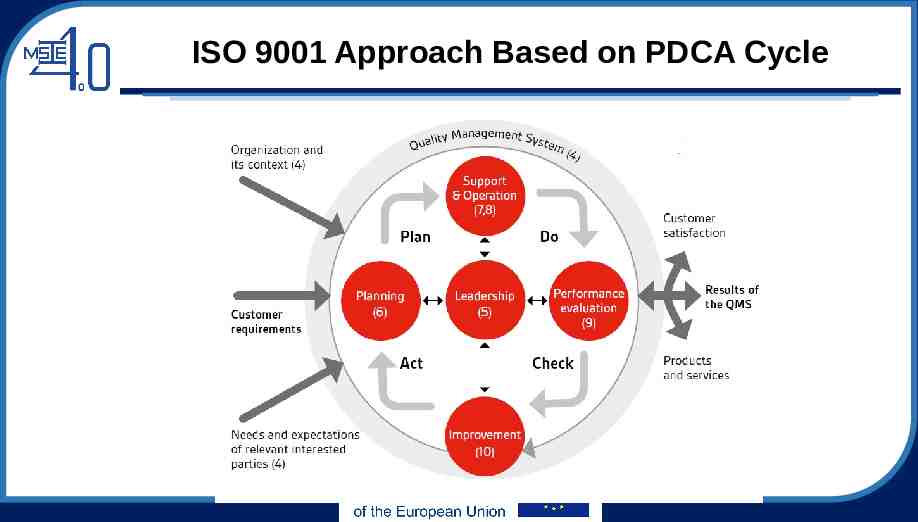
ISO 9001 Approach Based on PDCA Cycle
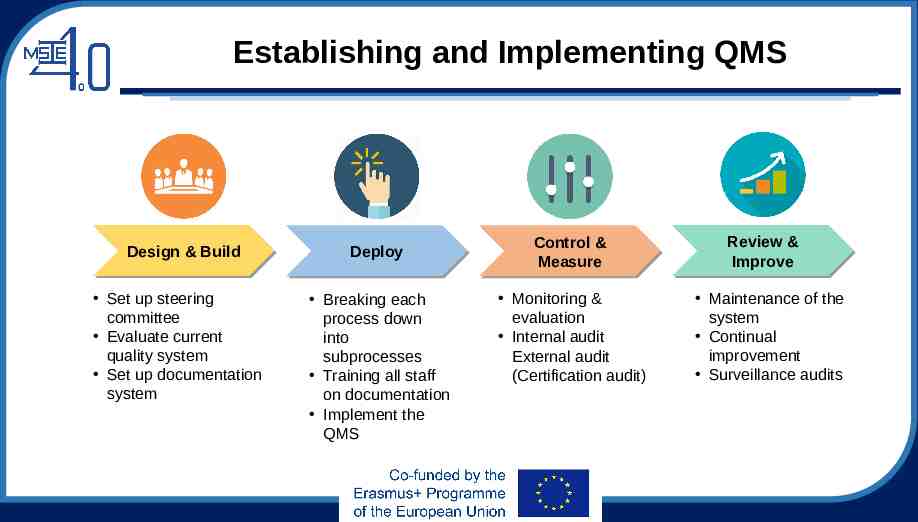
Establishing and Implementing QMS Design Design & & Build Build Set up steering committee Evaluate current quality system Set up documentation system Deploy Deploy Breaking each process down into subprocesses Training all staff on documentation Implement the QMS Control Control & & Measure Measure Monitoring & evaluation Internal audit External audit (Certification audit) Review Review & & Improve Improve Maintenance of the system Continual improvement Surveillance audits

Total Quality Management: TQM What is TQM? Total Quality Management (TQM) is “a management approach for an organization, centered on quality, based on the participation of all its members and aiming at long-term success through customer satisfaction and benefits to all members of the organization and to the society” T Total Q Quality M Involvement & input of everyone in the organization Fully meeting customer needs & requirements al the time Management ‘The way we act’ & operate policies, procedures including training and instruction to all employees Benefits of TQM Enhance competitive position Improve customer satisfaction Reduce waste and &work-over Greater organizational transparency Improve employee participation & satisfaction Improve productivity, market share, and profitability Enhance communication
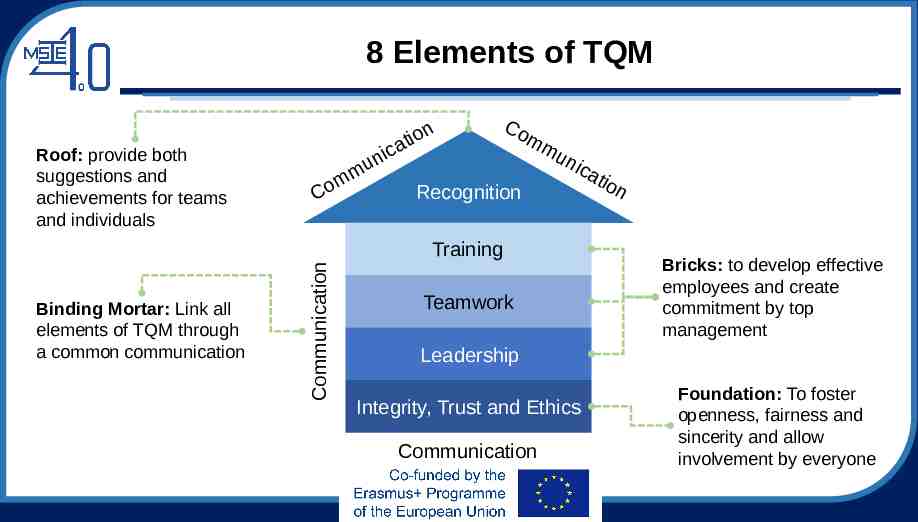
8 Elements of TQM Roof: provide both suggestions and achievements for teams and individuals Co nic u mm on i t a Co mm un Recognition ica Binding Mortar: Link all elements of TQM through a common communication Communication Training Teamwork ti o n Bricks: to develop effective employees and create commitment by top management Leadership Integrity, Trust and Ethics Communication Foundation: To foster openness, fairness and sincerity and allow involvement by everyone
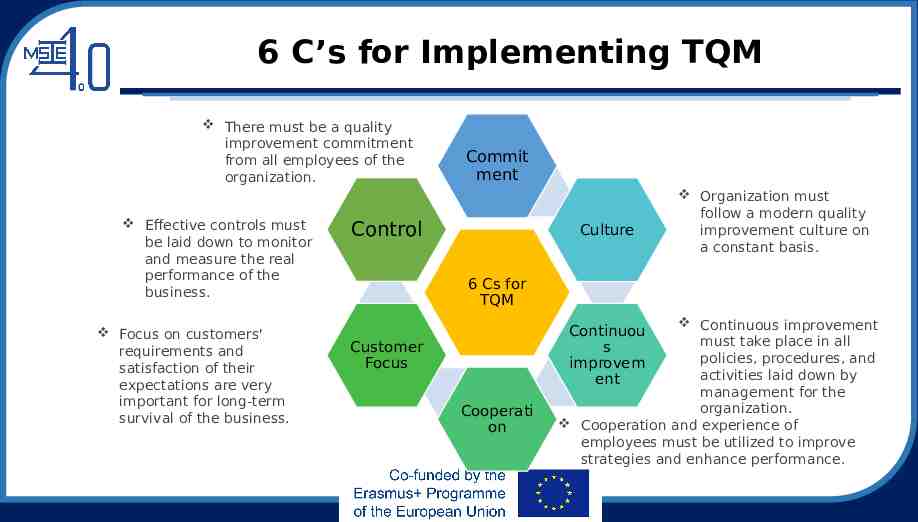
6 C’s for Implementing TQM There must be a quality improvement commitment from all employees of the organization. Effective controls must be laid down to monitor and measure the real performance of the business. Focus on customers' requirements and satisfaction of their expectations are very important for long-term survival of the business. Commit ment Control Culture Organization must follow a modern quality improvement culture on a constant basis. 6 Cs for TQM Continuous improvement must take place in all policies, procedures, and activities laid down by management for the organization. Cooperation and experience of employees must be utilized to improve strategies and enhance performance. Continuou s improvem ent Customer Focus Cooperati on
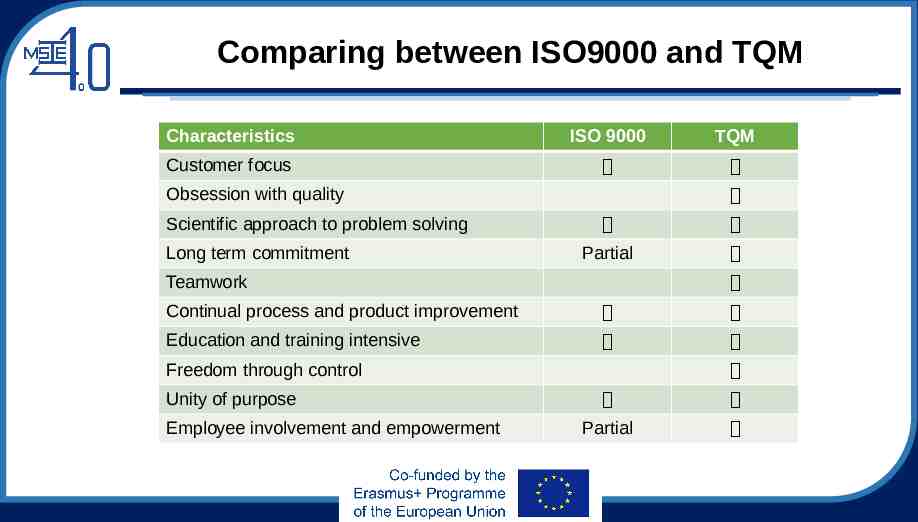
Comparing between ISO9000 and TQM Characteristics ISO 9000 TQM Customer focus Obsession with quality Scientific approach to problem solving Long term commitment Partial Teamwork Continual process and product improvement Education and training intensive Freedom through control Unity of purpose Employee involvement and empowerment Partial

ISO 9000 and TQM: Which One First? ISO 9000 & TQM are not interchangeable, but they are compatible with and complement each other The implementation of ISO 9000 & TQM together may lead to organisational success and competitive advantage. ISO 9000 First Recommend to implement in a traditional environment ISO 9000 is a foundation for TQM Implement TQM later to enhance employee motivation and operational efficiency, and achieve overall organisational success and performance TQM First Some companies might choose TQM first (Ex. Toyota) ISO 9000 is a subset of TQM ISO 9000 maybe redundant in a mature TQM environment For this case, the objective of implementing ISO is to obtain certification – for marketing purpose. Source: Magd, Hesham, and Adrienne Curry. "ISO 9000 and TQM: are they complementary or contradictory to each other?." The TQM magazine (2003).
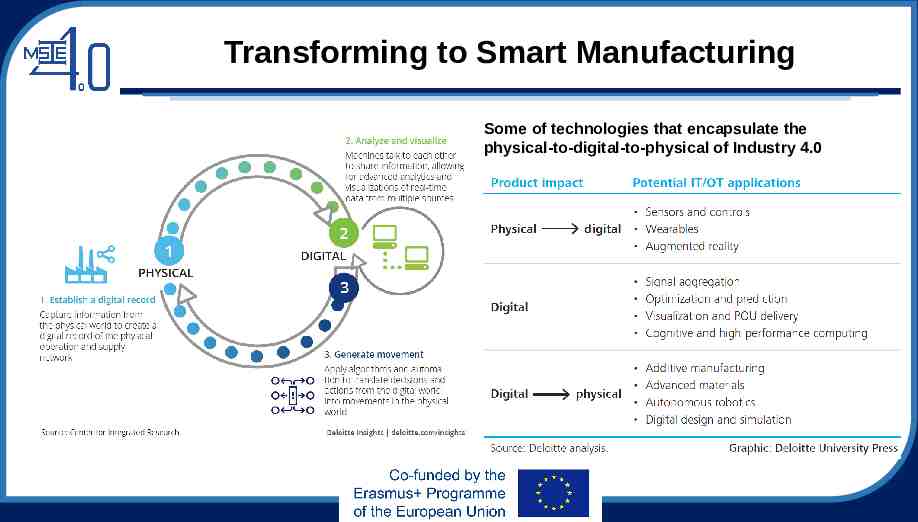
Transforming to Smart Manufacturing Some of technologies that encapsulate the physical-to-digital-to-physical of Industry 4.0
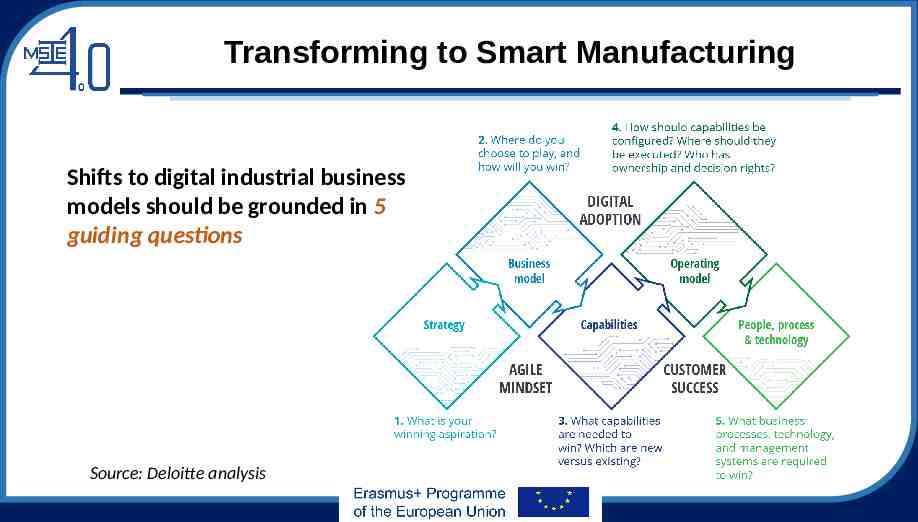
Transforming to Smart Manufacturing Shifts to digital industrial business models should be grounded in 5 guiding questions Source: Deloitte analysis
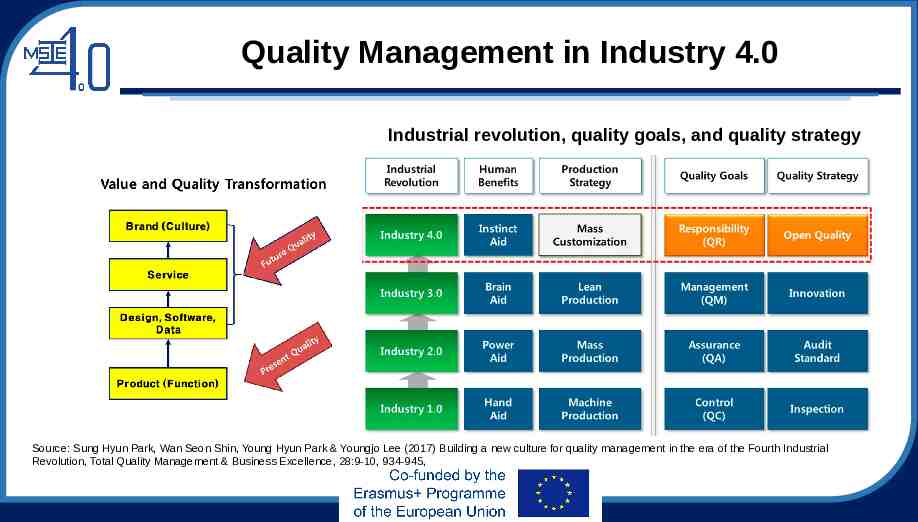
Quality Management in Industry 4.0 Industrial revolution, quality goals, and quality strategy Source: Sung Hyun Park, Wan Seon Shin, Young Hyun Park & Youngjo Lee (2017) Building a new culture for quality management in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 28:9-10, 934-945,
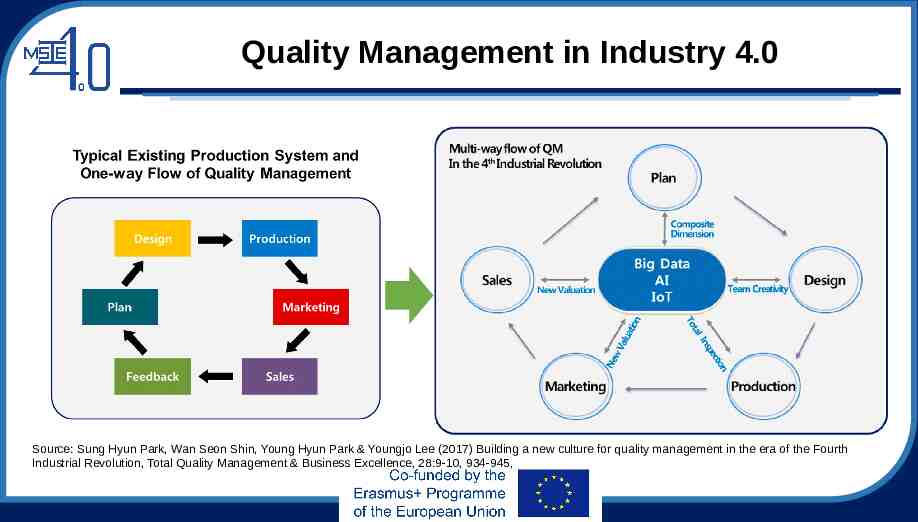
Quality Management in Industry 4.0 Source: Sung Hyun Park, Wan Seon Shin, Young Hyun Park & Youngjo Lee (2017) Building a new culture for quality management in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 28:9-10, 934-945,
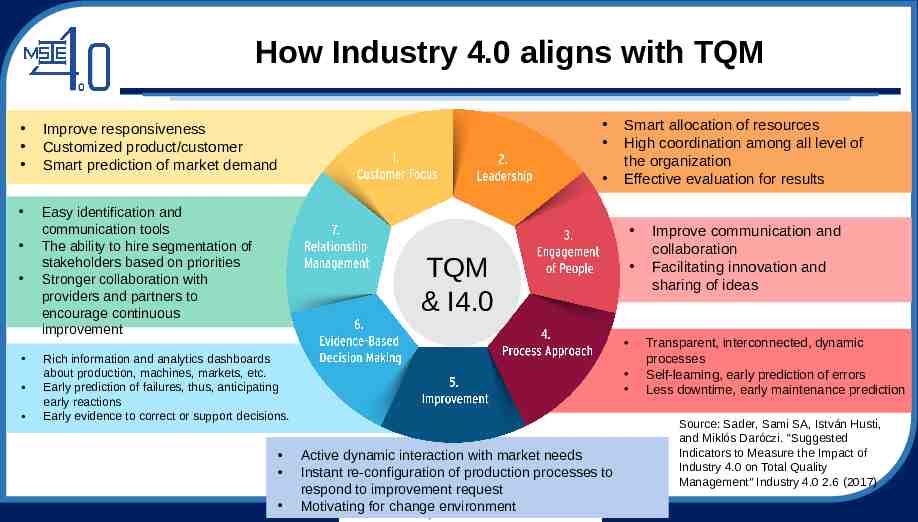
How Industry 4.0 aligns with TQM Improve responsiveness Customized product/customer Smart prediction of market demand Easy identification and communication tools The ability to hire segmentation of stakeholders based on priorities Stronger collaboration with providers and partners to encourage continuous improvement Smart allocation of resources High coordination among all level of the organization Effective evaluation for results TQM & I4.0 Rich information and analytics dashboards about production, machines, markets, etc. Early prediction of failures, thus, anticipating early reactions Early evidence to correct or support decisions. Active dynamic interaction with market needs Instant re-configuration of production processes to respond to improvement request Motivating for change environment Improve communication and collaboration Facilitating innovation and sharing of ideas Transparent, interconnected, dynamic processes Self-learning, early prediction of errors Less downtime, early maintenance prediction Source: Sader, Sami SA, István Husti, and Miklós Daróczi. “Suggested Indicators to Measure the Impact of Industry 4.0 on Total Quality Management" Industry 4.0 2.6 (2017)

Thank You https://msie4.ait.ac.th/ Together We Will Make Our Education Stronger @MSIE4Thailand MSIE 4.0 Channel Curriculum Development of Master’s Degree Program in Industrial Engineering for Thailand Sustainable Smart Industry






