Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William
35 Slides368.00 KB

Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 14 Computer Security Threats Patricia Roy Manatee Community College, Venice, FL 2008, Prentice Hall

Computer Security Confidentiality – Data confidentiality – Privacy Integrity – Data integrity – System integrity Availabilty
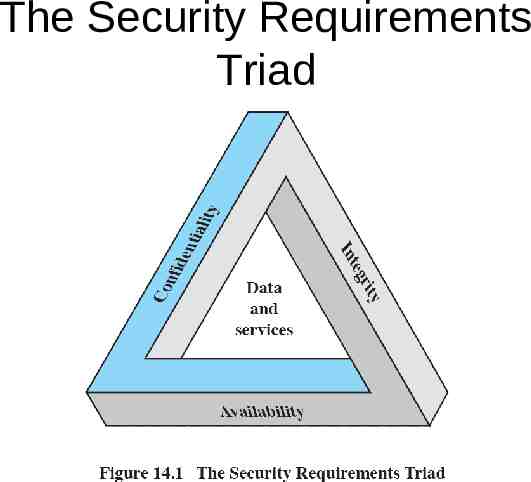
The Security Requirements Triad

Additional Concepts Authenticity Accountability
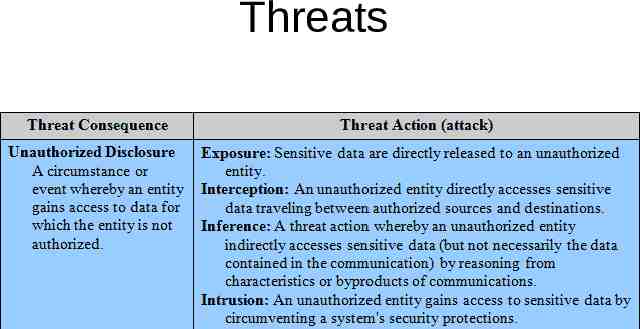
Threats

Threats

Threats

Threats
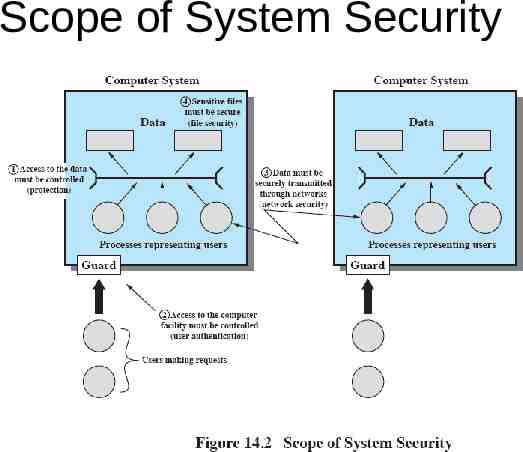
Scope of System Security
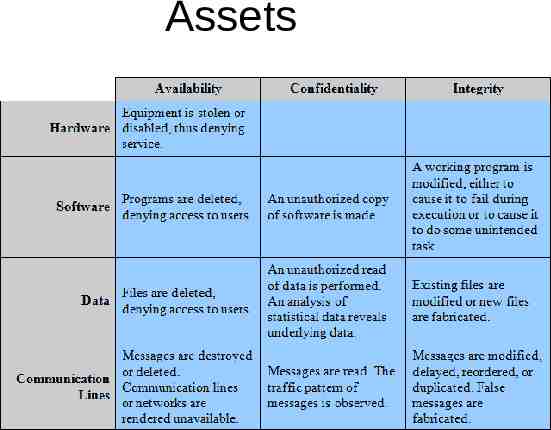
Assets

Intruders Masquerader Misfeasor Clandestine user

Intruders

Intruders

Intruders

Backdoor Trapdoor Secret entry point Useful for debugging tool for programmers

Logic Bomb Explodes when certain conditions are met – Presence or absence of certain files – Particular day of the week – Particular user running application

Trojan Horse Useful program that contains hidden code that when invoked performs some unwanted or harmful function Can be used to accomplish functions indirectly that an unauthorized user could not accomplish directly – User may set file permission so everyone has access

Mobile Code Transmitted from remote system to local system Executed on local system without the user’s explicit instruction

Multiple-Threat Malware Multipartite virus infects in multiple ways Blended attack uses multiple methods Ex: Nimda has worm, virus, and mobile code characteristics

Parts of Virus Infection mechanism Trigger Payload

Virus Stages Dormant phase – Virus is idle Propagation phase – Virus places an identical copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on the disk 21

Virus Stages Triggering phase – Virus is activated to perform the function for which it was intended – Caused by a variety of system events Execution phase – Function is performed 22

Simple Virus
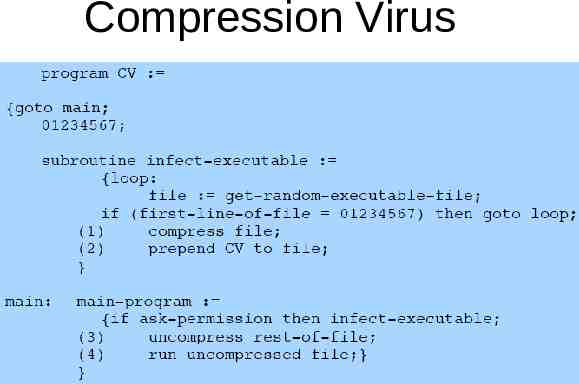
Compression Virus

Virus Classification by Target Boot sector infector File infector Macro virus

Virus Classification by Concealment Strategy Encrypted virus – Random encryption key encrypts remainder of virus Stealth virus – Hides itself from detection of antivirus software

Virus Classification by Concealment Strategy Polymorphic virus – Mutates with every infection Metamorphic virus – Mutates with every infection – Rewrites itself completely after every iteration

Macro Viruses Platform independent – Most infect Microsoft Word documents Infect documents, not executable portions of code Easily spread File system access controls are of limited use in preventing spread 28

E-Mail Viruses Attachment Open e-mail Uses e-mail software to replicate

Worms Use network connections to spread from system to system Electronic mail facility – A worm mails a copy of itself to other systems 30

Worms Remote execution capability – A worm executes a copy of itself on another system Remote log-in capability – A worm logs on to a remote system as a user and then uses commands to copy itself from one system to the other
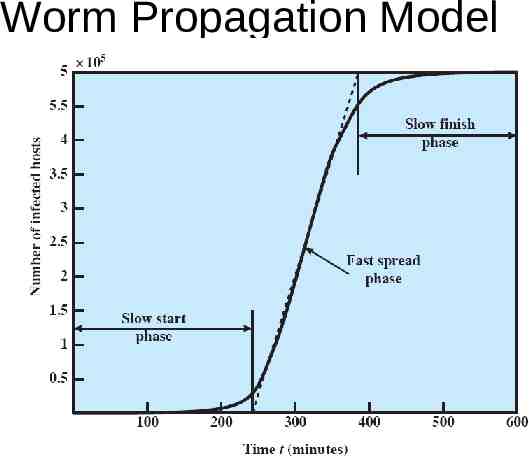
Worm Propagation Model

Bots Zombie or drone Program secretly takes of another Internet-attached computer Launch attacks that are difficult to trace to bot’s creator Collection of bots is a botnet

Rootkit Set of programs installed on a system to maintain administrator (or root) access to that system Hides its existence
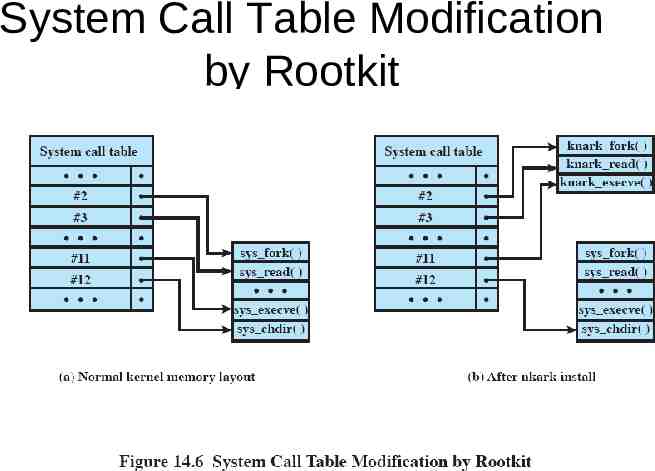
System Call Table Modification by Rootkit






