OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE 1 Scott Kettner Rahttiya Jinsirivanich Wongsuphan
76 Slides4.31 MB

OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE 1 Scott Kettner Rahttiya Jinsirivanich Wongsuphan Ketprathum Ekachai Juengjaroensuk Earl Mason Pajamas] Open Source Media Launch, Left to Right: Jeff Goldstein, Ed Driscoll, Glenn Reynolds, Larry Kudlow, Jane Hall, Roger L. Simon, Manuel L. Quezon, Michelle Malkin, Claudia Rosette, Charles Johnson, Clifford May, Michael Barone and Eugene Volokh. Source; http://www.allthingsbeautiful.com/all things beautiful/2005/11/blogging to dif.html
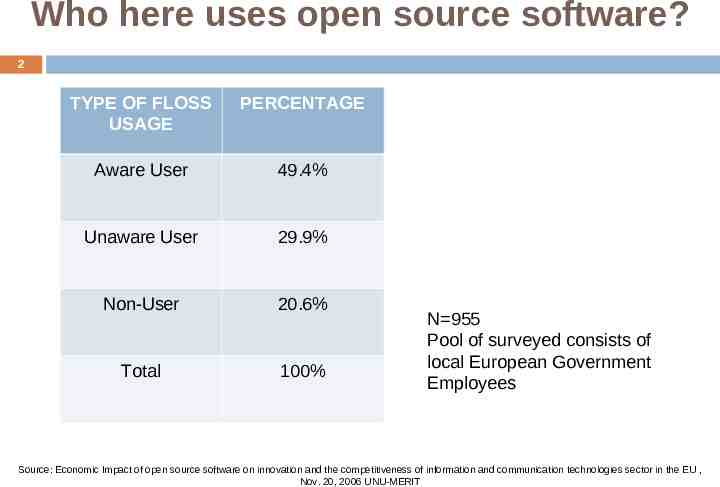
Who here uses open source software? 2 TYPE OF FLOSS USAGE PERCENTAGE Aware User 49.4% Unaware User 29.9% Non-User 20.6% Total 100% N 955 Pool of surveyed consists of local European Government Employees Source: Economic Impact of open source software on innovation and the competitiveness of information and communication technologies sector in the EU , Nov. 20, 2006 UNU-MERIT

Open Source Overview 3 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems

Open Source Overview 4 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems

What is Open Source Software? 5 “Open Source Software is computer software which source code is available under a license (or arrangement such as the public domain) that meets the Open source definition. This permits users to use, change, and improve the software, and to redistribute it in modified or unmodified form.” Source: Time Magazine, December 25, 2006, Viewed on March 13, 2008

Open Source Definition 6 Under the Open Source Definition, licenses must meet 10 conditions in order to be considered open source licenses. 1. Free Redistribution: The software can be freely given away or sold. 2. Source Code: The source code must either be included or freely obtainable. 3. Derived Works: Redistribution of modifications must be allowed. 4. Integrity of The Author's Source Code: Licenses may require that modifications are redistributed only as patches. 5. No Discrimination Against Persons or Groups: No one can be locked out. 6. No Discrimination Against Fields of Endeavor: Commercial users cannot be excluded. 7. Distribution of License: The rights attached to the program must apply to all to whom the program is redistributed without the need for execution of an additional license by those parties. 8. License Must Not Be Specific to a Product: The program cannot be licensed only as part of a larger distribution. 9. License Must Not Restrict Other Software: The license cannot insist that any other software it is distributed with must also be open source. 10. License Must Be Technology-Neutral: No click-wrap licenses or other medium-specific ways of accepting the license must be required. Source: http://opensource.org/docs/osd, viewed on March10, 2008

The History of Open Source Software 7 Late 1970's - Mid 1980's: UNIX A group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs originally developed UNIX, the most powerful operating system on a computer. 1980's: GNU Richard Stallman, a programmer at the Artificial Intelligence Lab (AI Lab), MIT, launched the GNU Project (free operating system) & the Free Software Foundation (FSF). “The GNU General Public License (GPL) was designed not only to ensure that the software produced by GNU will remain free, but to promote the production of more and more free software.” Source: http://www.netc.org/openoptions/background/history.html, Viewed on March 17, 2008
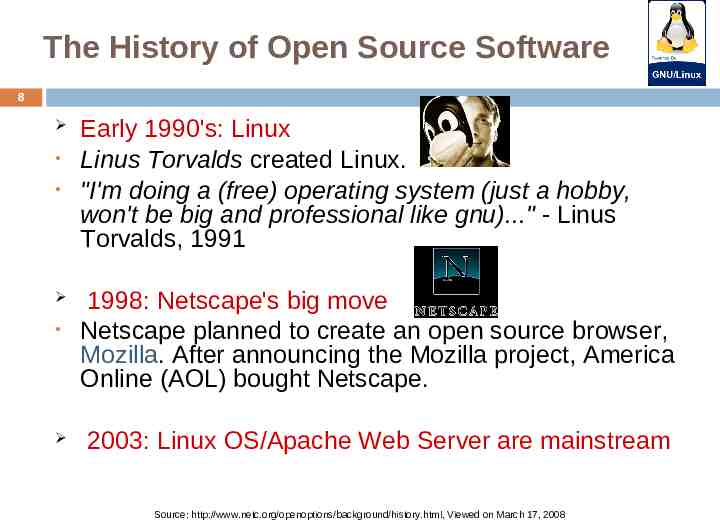
The History of Open Source Software 8 Early 1990's: Linux Linus Torvalds created Linux. "I'm doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won't be big and professional like gnu)." - Linus Torvalds, 1991 1998: Netscape's big move Netscape planned to create an open source browser, Mozilla. After announcing the Mozilla project, America Online (AOL) bought Netscape. 2003: Linux OS/Apache Web Server are mainstream Source: http://www.netc.org/openoptions/background/history.html, Viewed on March 17, 2008

Why Open Source is Important to Managers ? 9 New Technologies Drive down cost of doing business Custom Software Unknown uses of Open Source in Organization Source: www.ciozone.com/index.php/tool/50-top-open-source-resources-cios-should-know-and-maybe-love.html

Who is open source coming from? 10 Top 10 Companies Top 10 Academic Institutions 1. Regents Of The University Of California 4,955 Person-months 2 Massachusetts Institute Of Technology 4,774 Person-months 3 Carnegie Mellon University 1,687 Person-months 4 University Of Chicago 1,340 Person-months 5 INRIA 1,009 Person-months 6 University Of Amsterdam 982 Person-months 7 Stichting Mathematisch Centrum Amsterdam 870 Person-months 8 Ohio State University 551 Person-months 9 University Of Utah 518 Person-months 10 University Of Notre Dame 505 Person-months Source: http://www.businessreviewonline.com/os/archives/2007/01/where does open.html Economic Impact of open source software on innovation and the competitiveness of information and communication technologies sector in the EU , Nov. 20, 2006 UNU-MERIT
Where in the world does open source software come from? 11 Source: http://www.businessreviewonline.com/os/archives/2006/07/where in the wo.html
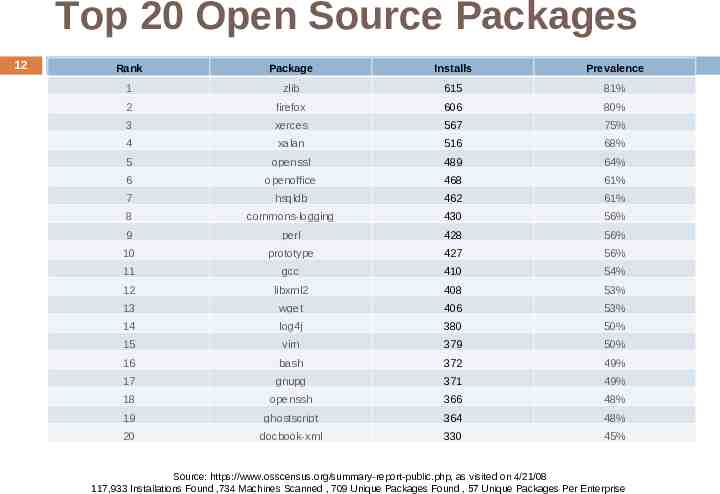
Top 20 Open Source Packages 12 Rank Package Installs Prevalence 1 zlib 615 81% 2 firefox 606 80% 3 xerces 567 75% 4 xalan 516 68% 5 openssl 489 64% 6 openoffice 468 61% 7 hsqldb 462 61% 8 commons-logging 430 56% 9 perl 428 56% 10 prototype 427 56% 11 gcc 410 54% 12 libxml2 408 53% 13 wget 406 53% 14 log4j 380 50% 15 vim 379 50% 16 bash 372 49% 17 gnupg 371 49% 18 openssh 366 48% 19 ghostscript 364 48% 20 docbook-xml 330 45% Source: https://www.osscensus.org/summary-report-public.php, as visited on 4/21/08 117,933 Installations Found ,734 Machines Scanned , 709 Unique Packages Found , 57 Unique Packages Per Enterprise

Open Source Overview 13 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems
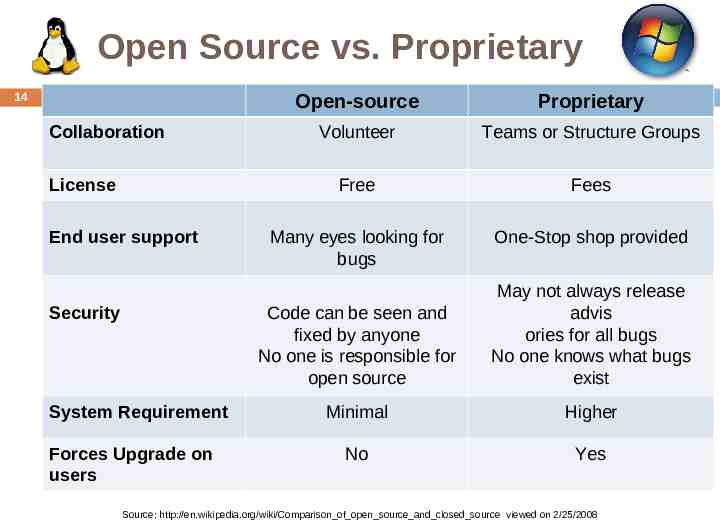
Open Source vs. Proprietary 14 Collaboration License End user support Security System Requirement Forces Upgrade on users Open-source Proprietary Volunteer Teams or Structure Groups Free Fees Many eyes looking for bugs One-Stop shop provided Code can be seen and fixed by anyone No one is responsible for open source May not always release advis ories for all bugs No one knows what bugs exist Minimal Higher No Yes Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison of open source and closed source viewed on 2/25/2008
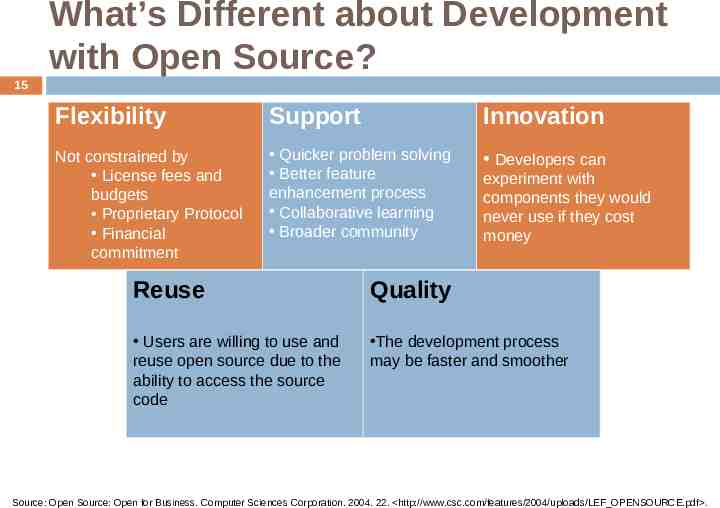
What’s Different about Development with Open Source? 15 Flexibility Support Innovation Not constrained by License fees and budgets Proprietary Protocol Financial commitment Quicker problem solving Better feature enhancement process Collaborative learning Broader community Developers can experiment with components they would never use if they cost money Reuse Quality Users are willing to use and reuse open source due to the ability to access the source code The development process may be faster and smoother Source: Open Source: Open for Business. Computer Sciences Corporation. 2004. 22. http://www.csc.com/features/2004/uploads/LEF OPENSOURCE.pdf .
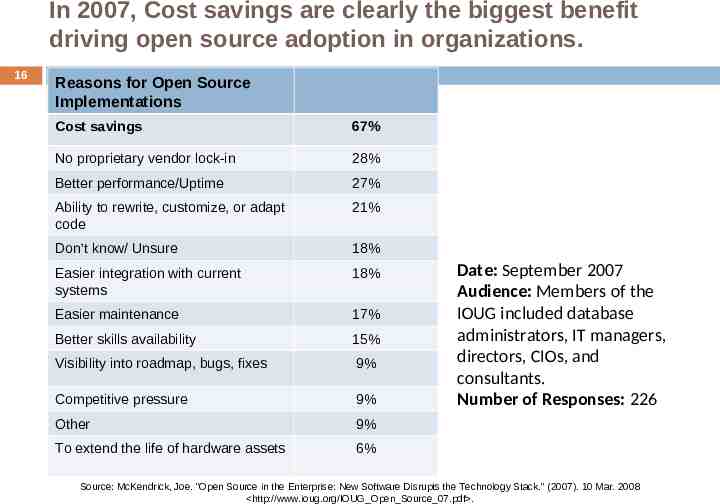
In 2007, Cost savings are clearly the biggest benefit driving open source adoption in organizations. 16 Reasons for Open Source Implementations Cost savings 67% No proprietary vendor lock-in 28% Better performance/Uptime 27% Ability to rewrite, customize, or adapt code 21% Don’t know/ Unsure 18% Easier integration with current systems 18% Easier maintenance 17% Better skills availability 15% Visibility into roadmap, bugs, fixes 9% Competitive pressure 9% Other 9% To extend the life of hardware assets 6% Date: September 2007 Audience: Members of the IOUG included database administrators, IT managers, directors, CIOs, and consultants. Number of Responses: 226 Source: McKendrick, Joe. "Open Source in the Enterprise: New Software Disrupts the Technology Stack." (2007). 10 Mar. 2008 http://www.ioug.org/IOUG Open Source 07.pdf .

The Dark Side of Open Source 17 ‘You Get What You Pay For’ The service and maintenance of open source software are not free. However, OS software support costs 20-30% less than commercial software. Source: "The Dark Side of Open Sauce" Leslie Kramer, Wall Street & Technology; Apr 2006 pg. 43

The Dark Side of Open Source 18 Another problem is the continued maintenance of software over long periods. “The community that develops this software is primarily a volunteer community, and they may get less interested in the product over time,” Michel Goulde Senior Analyst Forrester Research Source: "The Dark Side of Open Sauce" Leslie Kramer, Wall Street & Technology; Apr 2006 pg. 43
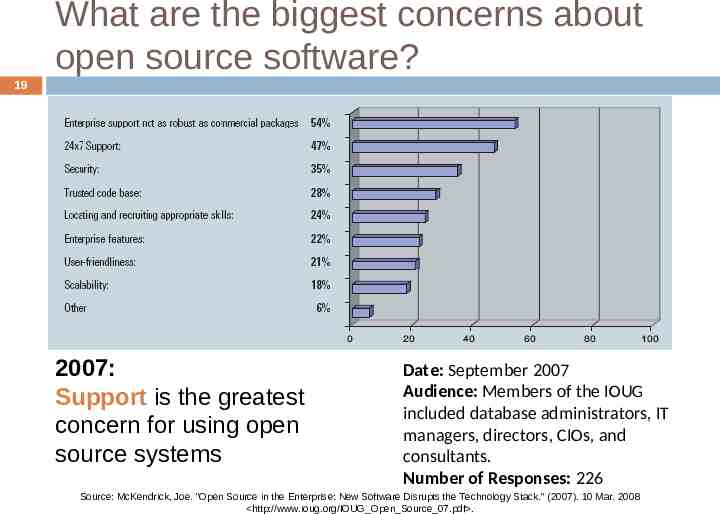
What are the biggest concerns about open source software? 19 2007: Support is the greatest concern for using open source systems Date: September 2007 Audience: Members of the IOUG included database administrators, IT managers, directors, CIOs, and consultants. Number of Responses: 226 Source: McKendrick, Joe. "Open Source in the Enterprise: New Software Disrupts the Technology Stack." (2007). 10 Mar. 2008 http://www.ioug.org/IOUG Open Source 07.pdf .

APACHE Story 20 APACHE WEBPAGE SERVERS RUN 50% OF THE WORLDS WEBSITES NONPROFIT APACHE SOFTWARE FOUNDATION DEVELOPS AND DISTRIBUTES APACHE HTTP SERVER 1ST DEVELOPED BY ROB MCCOOL IN 1995 APACHE LICENSE IS NOT PART OF GPL LICENSING ALTHOUGH FREE IT CAN BE USED AS PART OF CLOSED SOURCE DERIVATION Source: HTTP://EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG/WIKI/APACHE HTTP SERVER VIEWED 3\10\2008

APACHE Story 21 APACHE RE-DISTRIBUTED AS PART OF VARIOUS PROPRIETARY SOFTWARE PACKAGES ORACLE DATABASE IBM WEBSPHERE MAC OS (WEB OBJECTS) WEB SERVER COMPONENT OF THE LAMP APPLICATION STACK Source: HTTP://EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG/WIKI/APACHE HTTP SERVER VIEWED 3\10\2008

APACHE Story 22 APACHE FIRST WEBSERVER RELEASE WAS IN1995 DOWNLOAD, TWEAK IT, BURN IT, AND INSTALL ON AS MANY SERVERS AS YOU WANT Source: HTTP://HTTPD.APACHE.ORG VIEWED 3/10/2008
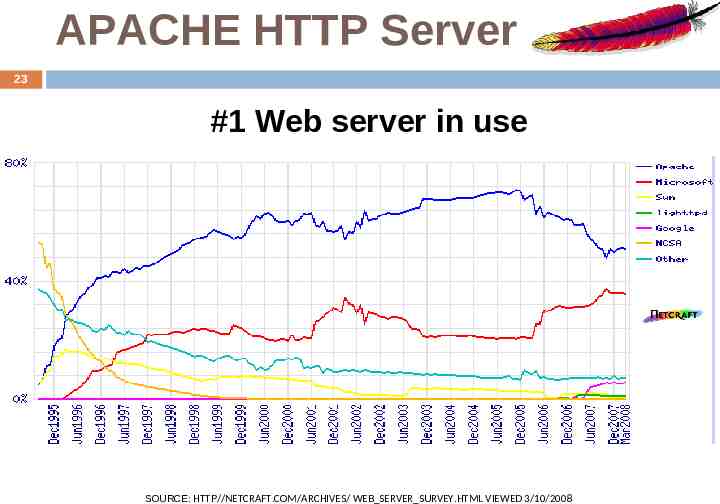
APACHE HTTP Server 23 #1 Web server in use SOURCE: HTTP//NETCRAFT.COM/ARCHIVES/ WEB SERVER SURVEY.HTML VIEWED 3/10/2008
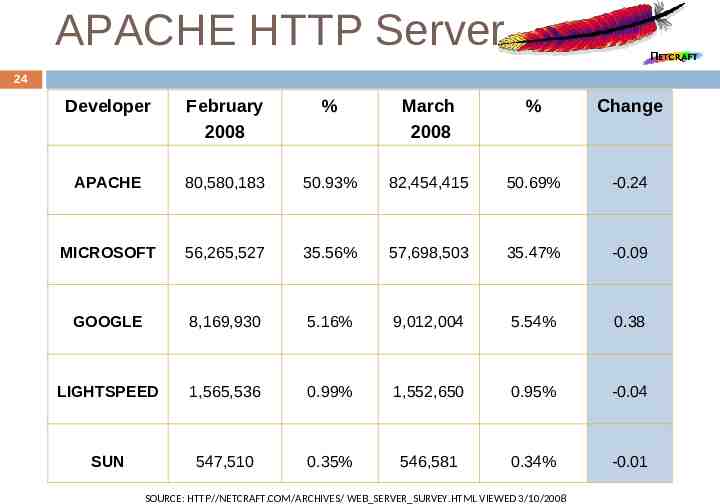
APACHE HTTP Server 24 Developer February 2008 % March 2008 % Change APACHE 80,580,183 50.93% 82,454,415 50.69% -0.24 MICROSOFT 56,265,527 35.56% 57,698,503 35.47% -0.09 GOOGLE 8,169,930 5.16% 9,012,004 5.54% 0.38 LIGHTSPEED 1,565,536 0.99% 1,552,650 0.95% -0.04 SUN 547,510 0.35% 546,581 0.34% -0.01 SOURCE: HTTP//NETCRAFT.COM/ARCHIVES/ WEB SERVER SURVEY.HTML VIEWED 3/10/2008

Open Source Overview 25 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems

What is HTML? 26 Hypertext mark up language Html is primarily a formatting language for web content The HTML documents are written in plain text, but with the addition of tags which describe or define the text they enclose Source: http://www.acad.bg/beginner/gnrt/appendix/glossary.html, viewed 3/8/2008

WHAT IS XML? 27 Extensible Markup language (Html formats data) Xml describes data structure XML is a markup language for documents containing structured information. XML not a fixed set of elements like HTML XML allows authors to define their own tags Source: http://www.acad.bg/beginner/gnrt/appendix/glossary.html, viewed 3\8\2008
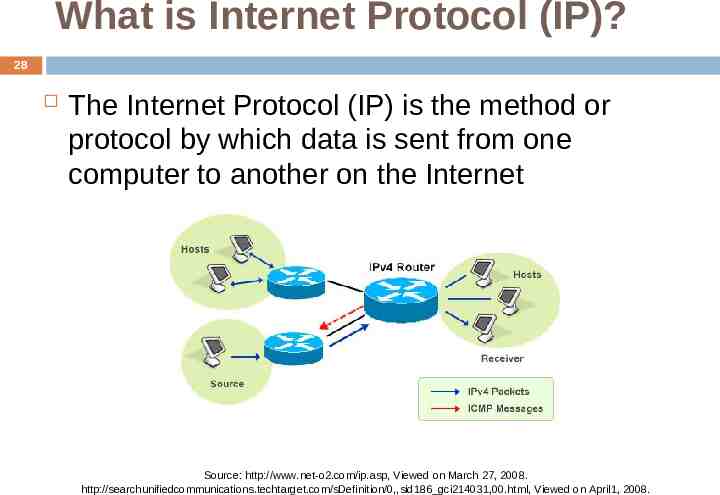
What is Internet Protocol (IP)? 28 The Internet Protocol (IP) is the method or protocol by which data is sent from one computer to another on the Internet Source: http://www.net-o2.com/ip.asp, Viewed on March 27, 2008. http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid186 gci214031,00.html, Viewed on April1, 2008.

Firefox at a Glance 29 Internet Browser sprang from Netscape (Phoenix 2002) 2nd most popular web browser (17%) Pop-up blockers, tabbed browsing, advanced privacy, and more Highly personalized by everyone Over 2000 add-on programs Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Firefox FREE SOFTWARE FOR YOUR PRACTICE, James Dom Dera; Family Practice Management; Feb 2006; 13,2; ABI/INFORM Global pg. 56
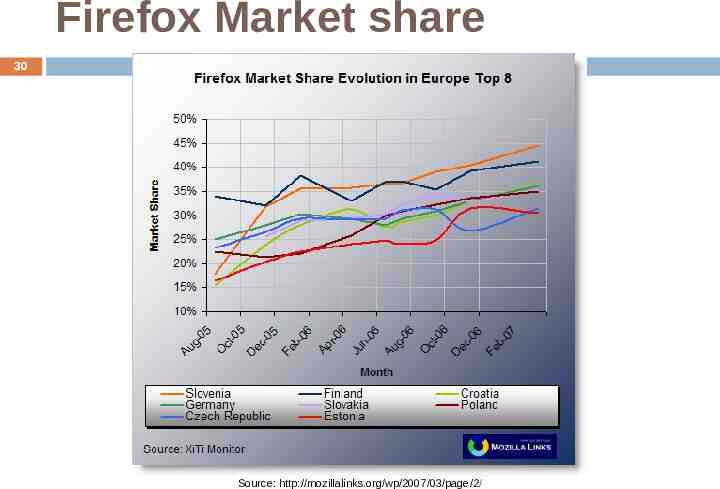
Firefox Market share 30 Source: http://mozillalinks.org/wp/2007/03/page/2/
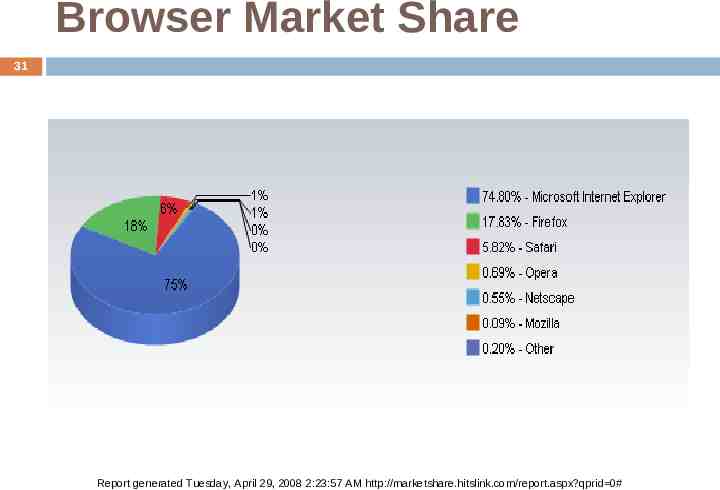
Browser Market Share 31 Report generated Tuesday, April 29, 2008 2:23:57 AM http://marketshare.hitslink.com/report.aspx?qprid 0#
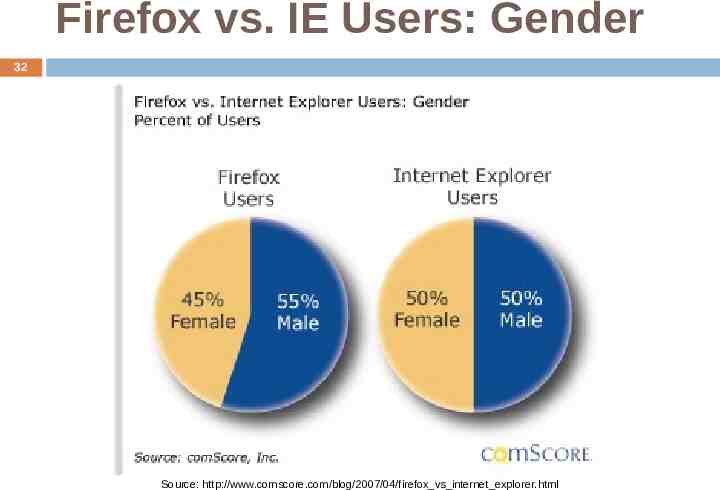
Firefox vs. IE Users: Gender 32 Source: http://www.comscore.com/blog/2007/04/firefox vs internet explorer.html
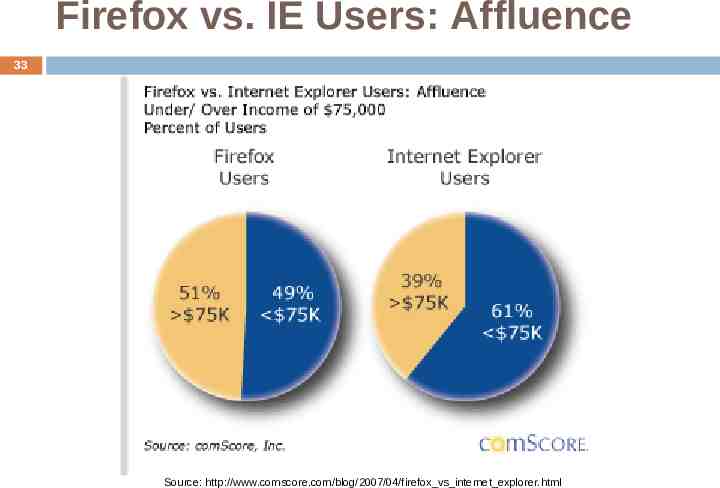
Firefox vs. IE Users: Affluence 33 Source: http://www.comscore.com/blog/2007/04/firefox vs internet explorer.html
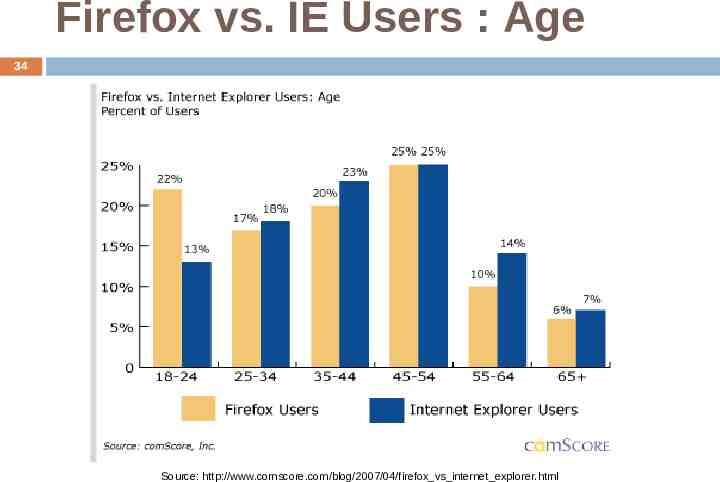
Firefox vs. IE Users : Age 34 Source: http://www.comscore.com/blog/2007/04/firefox vs internet explorer.html
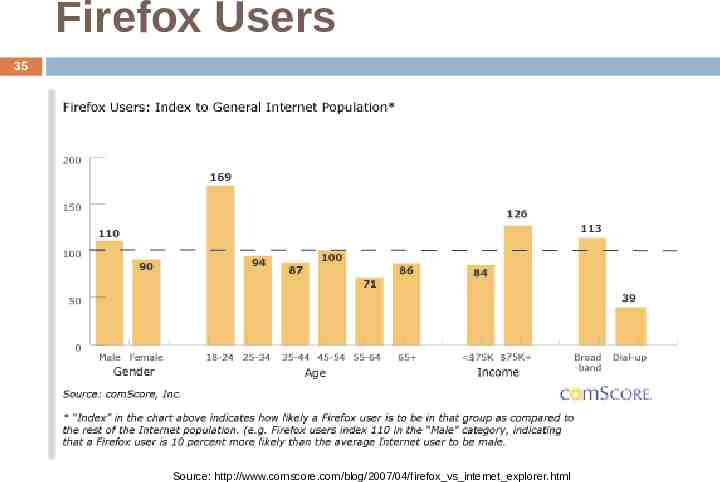
Firefox Users 35 Source: http://www.comscore.com/blog/2007/04/firefox vs internet explorer.html

The Mozilla Project 36 “The Mozilla project is a global community of people who have been working together since 1998 to create world-class open source software. Those involved in the community believe that openness, innovation, and opportunity are key to the continued health of the Internet. The projects on this page are just some examples of what the community is doing.” Source: http://www.mozilla.org/projects/
The Mozilla Family of Products 37 Camino Firefox SeaMonkey Sunbird and Lighting Thunderbird One Laptop Per Child Web Browser TomTom HOME Bonsai Bugzilla Tinderbox Tamarin, XPCOM, and XUL All logos taken from: http://www.mozilla.org/projects/

What is Linux? 38 Linux is a free Unix-type operating system originally created by Linus Torvalds with the assistance of developers around the world. Developed under the GNU General Public License, the source code for Linux is freely available to everyone. Source: http://www.linux.org/info/index.html, View on April 4, 2008.
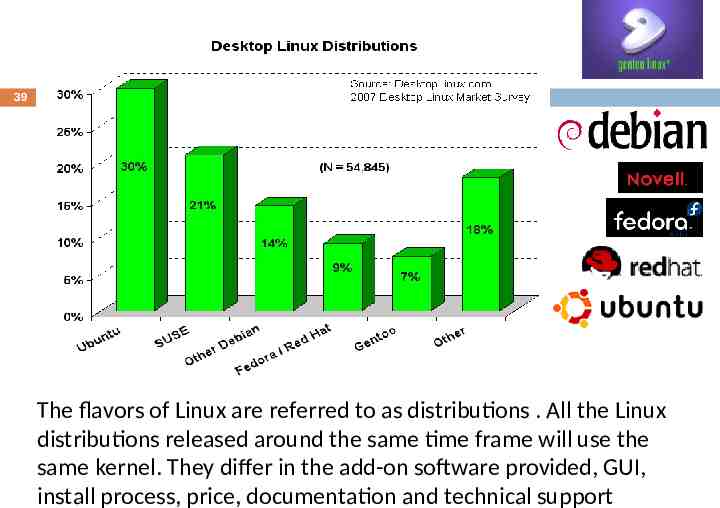
39 The flavors of Linux are referred to as distributions . All the Linux distributions released around the same time frame will use the same kernel. They differ in the add-on software provided, GUI, install process, price, documentation and technical support

13 reasons why Linux should be on your desktop 40 Kim Brebach a consultant with an Australian technology marketing group Source: “13 reasons why Linux should be on your desktop”, by Kim Brebach, http://www.desktoplinux.com/articles/AT5836989728.html, Viewed on March 20, 2008.

Can you make money from Linux? 41 YES!!! . Because “Linux is available for free, by download. It can be sold for profit as long as the seller adheres to certain criteria. A vendor may make modifications to the OS, as long as the source code is freely available. That means there is a bit of revenue to be made selling the commercial packages from companies like Red Hat or Caldera” Lynn Greiner; Computer Dealer News. Willowdale Source:” Computer Dealer News “, Lynn Greiner , http://proquest.umi.com/pqdweb?did 45047075&sid 6&Fmt 3&clientId 45249&RQT 309&VName PQD, Viewed on April 2, 2008.

LINUX vs. WINDOWS 42 Windows dominates in the desktops and personal computer markets with about 90% of the desktop market share, and in 2007 accounted for about 66% of all servers sold In server revenue market share (2007Q4) Windows achieved 36.3% and Linux achieved 12.7%. As of November 2007, Linux powered 85% of the world's most powerful supercomputers. In February 2008, Linux powered five of the ten most reliable internet hosting companies Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison of Windows and Linux , Viewed on April, 10, 2008
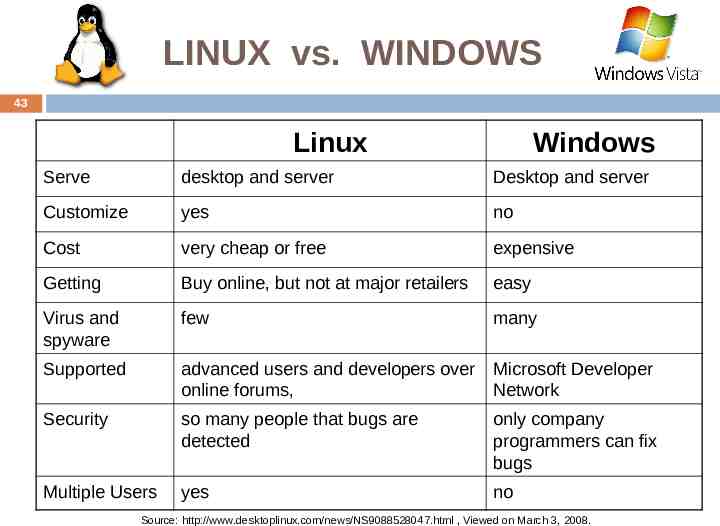
LINUX vs. WINDOWS 43 Linux Windows Serve desktop and server Desktop and server Customize yes no Cost very cheap or free expensive Getting Buy online, but not at major retailers easy Virus and spyware few many Supported advanced users and developers over Microsoft Developer online forums, Network Security so many people that bugs are detected only company programmers can fix bugs Multiple Users yes no Source: http://www.desktoplinux.com/news/NS9088528047.html , Viewed on March 3, 2008.

Why Wal-Mart will not have Linux desktops on its store shelves ? 44 On March 10, Wal-Mart spokesperson Melissa O'Brien told the Associated Press that Wal-Mart had decided not to restock its in-store gOS Linux powered Everex Green gPC TC2502."This really wasn't what our customers were looking for," O'Brien said Source: http://www.desktoplinux.com/news/NS9088528047.html , Viewed on March 3, 2008.

Why Windows wins and Linux loses ? 45 The installed base PC vendor support Hardware vendor support Software support Source: “Why Windows wins and Linux loses”, Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols, http://www.desktoplinux.com/news/NS6087894103.html , Viewed on April 3, 2008.

Java Language and Platforms 46 Language release in 1995 based on C and C Most JAVA technologies available free under the GNU General Public License Promised WORA Write Once, Run Anywhere Source: ALL THE FIXINGS, Jonathan Erickson, Dr. Dobb’s Journal; Aug 2006; 31, 8; ABI/IFORM Trade & Industry Page 6
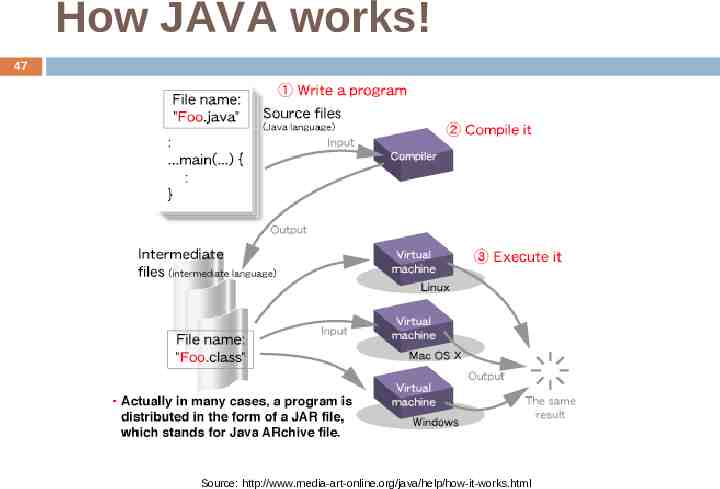
How JAVA works! 47 Source: http://www.media-art-online.org/java/help/how-it-works.html
The JAVA Family 48 SE (Standard Edition) EE (Enterprise Edition) Applets, Threads, Networking, RMI, Servlets, JDBC, JFC Swing, AWT, JFC 2D, Java Media API, JavaBeans and more Adds libraries which provide functionality to deploy fault-tolerant, distributed, multi-tier Java software, based largely on modular components running on an application server ME (Micro Edition) for small, resource-constrained devices such as cell phones, PDAs and set-top boxes Source: Nick Langley. "Mobile developers get to write once, run anywhere. " Computer Weekly 24 Jul 2007: 32. ABI/INFORM Trade & Industry. ProQuest. ***ABI/INFORM. 23 Apr. 2008 http://www.proquest.com.ezproxy.umsl.edu/
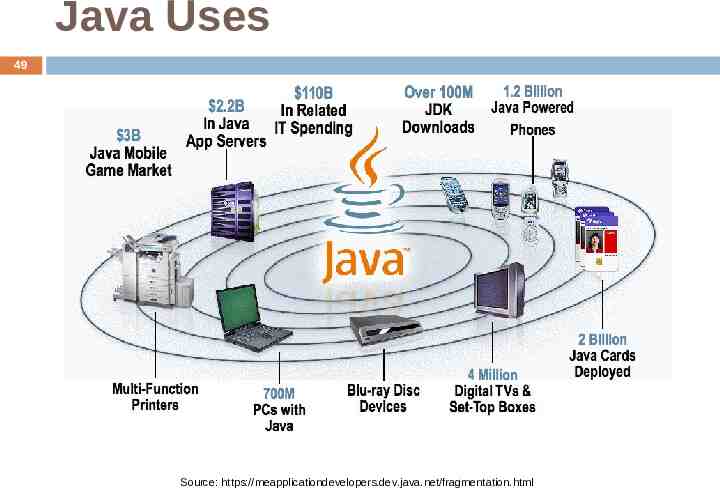
Java Uses 49 Source: https://meapplicationdevelopers.dev.java.net/fragmentation.html

Open Source Overview 50 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems

Sun Microsystems at a glance 51 Employees: 33,350 worldwide. Press Resources: sun.com/news Investor Resources: sun.com/investors Ranking: #187 on the Fortune 500 (2007) Fiscal Year 2008 Q2 Revenues: 3.615 billion. Locations: Sun conducts business in more than 100 countries around the globe. Source: http://www.sun.com/aboutsun/company/index.jsp

Sun Microsystems Strategy 52 According to Barton George, (the group manager for Sun Microsystems Inc.'s GNU/Linux strategy) Open Source is inevitable Sun will lead the way NetBeans, OpenOffice, MySQL and Glassfish If it’s not open source now it soon will be Q: How does Sun plan to make any money from Java? A: We don't make money from Java, the language. We make money doing things with, and that support the language. It's the same as a writer who makes money writing in English, but not by owning English. We have Java Enterprise System, Java Desktop System, the Solaris OS, workstations, servers, and services that all revolve around delivering Java Web services. Source: http://searchenterpriselinux.techtarget.com/news/interview/0,289202,sid39 gci1307014,00.html# http://www.sun.com/emrkt/boardroom/newsletter/1104feature.html

53 Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun’s open-source business strategy Jonathan Schwartz The current president and CEO of Sun Microsystems Interviewed on August 8, 2007 by Matt Asay Source: Asay, Matt. "Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun's Open-Source Business Strategy." 8 Aug. 2007. 25 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html .

Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun’s open-source business strategy 54 Q:At what point did he think open source was a capable to develop and distribute strategy for your company? A: The average start-up or corporate developer doesn't want to buy any software. Most don't care about the license--they care about the money Reach them through free distribution over the Net. 3 to 4 million copies of OpenOffice distribute to 100 million users worldwide every week. Free users of today are the corporate buyers of tomorrow Source: Asay, Matt. "Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun's Open-Source Business Strategy." 8 Aug. 2007. 25 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html .

Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun’s open-source business strategy 55 Q: How did he make the shift to open source go smoothly? A: It was no longer a democracy. Leading a company is about leading and making difficult decisions There was resistance There were serious questions Convince that it would improve, not degrade, security, performance, etc. The result has been fantastic. Source: Asay, Matt. "Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun's Open-Source Business Strategy." 8 Aug. 2007. 25 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html .

Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun’s open-source business strategy 56 Q: What do you hope to gain from contributions to communities like OpenOffice? A: Only 4,000 quota-bearing salespeople Beat competitors by leveraging the single-biggest sales channel that is the Internet Many Brazilian sees Sun’s logo everyday on OpenOffice, which their government or they downloaded for free. Customers find Sun. “When I see Sun's free software downloads in Western China or Siberia, where we have no sales presence at all, I have to ask how my competitors are going to survive when no one knows about them.” Source: Asay, Matt. "Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun's Open-Source Business Strategy." 8 Aug. 2007. 25 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html .

Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun’s open-source business strategy 57 Q: What advice would you give to the CEOs of proprietary software companies? 1. Revenue is a lagging indicator of developer adoption 2.Align your sales force's compensation to fit your model 3.Understand the demographics of your market Source: Asay, Matt. "Q&A: Jonathan Schwartz on Sun's Open-Source Business Strategy." 8 Aug. 2007. 25 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html .
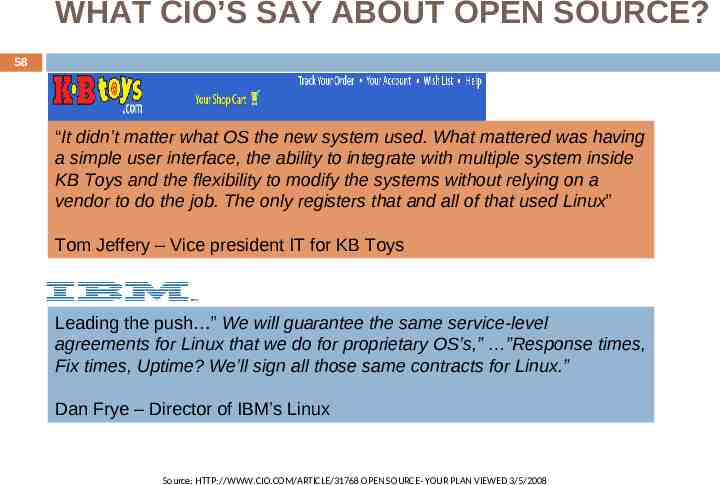
WHAT CIO’S SAY ABOUT OPEN SOURCE? 58 “It didn’t matter what OS the new system used. What mattered was having a simple user interface, the ability to integrate with multiple system inside KB Toys and the flexibility to modify the systems without relying on a vendor to do the job. The only registers that and all of that used Linux” Tom Jeffery – Vice president IT for KB Toys Leading the push ” We will guarantee the same service-level agreements for Linux that we do for proprietary OS’s,” ”Response times, Fix times, Uptime? We’ll sign all those same contracts for Linux.” Dan Frye – Director of IBM’s Linux Source: HTTP://WWW.CIO.COM/ARTICLE/31768 OPEN SOURCE- YOUR PLAN VIEWED 3/5/2008

E-TRADE 59 Josh Levine, first started shopping around in 1998 could he recalls having pun pitting Sun against other Unix vendors like IBM and HP E-Trade decided to go with 60 Sun boxes at 240,000 a pop and a 25,000 yearly maintenance fee on each ”the fun and Levine leverage was gone”, Levine speaking on Unix vendors says.”All there strategies are based on proprietary operating systems. Once you buy the hardware, you can’t move.”) Total cost for Sun boxes Total yearly maintenance fee 1,500,000 14,400,000 Source: HTTP://WWW.CIO.COM/ARTICLE/31768 OPEN SOURCE- YOUR PLAN VIEWED 3/5/2008

E-TRADE 60 What Levine did? He replaced those 60 sun boxes with 80 4,000 Intel servers (They already owned Linux which was the operating system used. Since Linux was based on Unix support, people easily made the transition). Total cost of 80 replacement boxes Total maintenance cost 320,000 0 Source: HTTP://WWW.CIO.COM/ARTICLE/31768 OPEN SOURCE- YOUR PLAN VIEWED 3/5/2008

Case Study: Rockin’ on without Microsoft 61 Sterling Ball CEO of ErnieBall World’s leading maker of guitar strings Product endorsed by:Artist ranging from Eric Clapton to Metallica Source:Becker, David. "Rockin' on Without Microsoft." 20 Aug. 2003. 27 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/2008-1082 3-5065859.html .

62 Case Study: Rockin’ on without Microsoft In 2000, Business Software Alliance conducted audit on the Ball Company Found 6 of 72 machines with unlicensed copies of programs Ball company settled 65,000, plus 35,000 in legal fees Company made evening news Source: Becker, David. "Rockin' on Without Microsoft." 20 Aug. 2003. 27 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/2008-1082 3-5065859.html .

63 Case Study: Rockin’ on without Microsoft Ball got rid of Microsoft products Ball IT crew cut the Ball comp. over to open source software Red Hat’s version of Linux, the OpenOffice office suite, and Mozilla’s web browser Claims he saved 80,000 right away with going to open source Source: Becker, David. "Rockin' on Without Microsoft." 20 Aug. 2003. 27 Feb. 2008 http://www.news.com/2008-1082 3-5065859.html .

Microsoft’s & IBM’s Strategy 64 &

Microsoft Open Source Strategy 65 “The Microsoft open source strategy is focused on helping customers and partners be successful in today’s heterogeneous technology world.” quoted from Microsoft Open Source Web site. Microsoft is signing technology agreements with other companies, Novell, BEA, Sun, XenSource, etc. because it wants to help their customers who are struggling with running open-source software alongside Microsoft software. Source: http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142, Viewed on April 2, 2008.
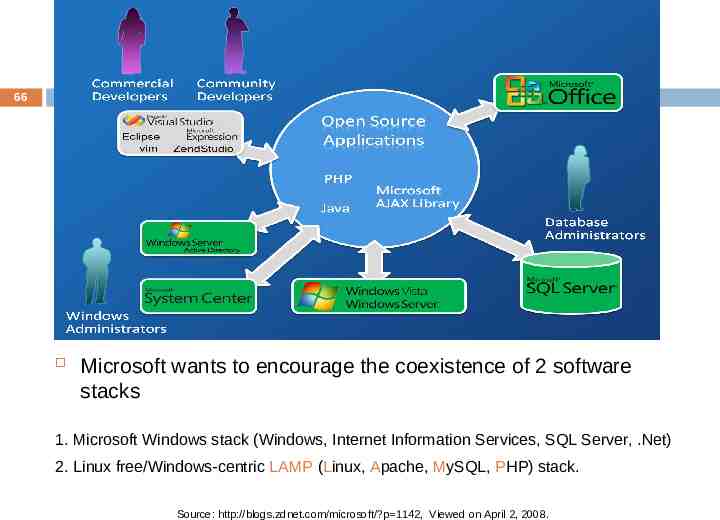
66 Microsoft wants to encourage the coexistence of 2 software stacks 1. Microsoft Windows stack (Windows, Internet Information Services, SQL Server, .Net) 2. Linux free/Windows-centric LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack. Source: http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142, Viewed on April 2, 2008.

Microsoft Open Source Strategy 67 Microsoft hires Open Source guy, Bill Hilf Hilf is appointed to General Manager of window server marketing & Platform strategy One of Hilf’s core issues is defining Microsoft’s role in open source Source: http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142

Microsoft Open Source Challenges 68 How to cooperate w/ OS initiatives and find value for Microsoft in that participation How to be in alliance with OS initiatives and at the same time compete against other proponents of OS such as Red Hat Linux systems and the software that goes in their boxes Understanding of how OS software from OS community developers will happen on their platform and the System of Accountability that will go along with that- Bill Hilf Source: http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142, viewed 3\7\2008

Why Open Source for Microsoft? 69 Reports from Microsoft’s Global Managers indicate that some of Microsoft’s biggest customers have ties to the OS software Increase interoperability between MS programs and some of the OS technologies Source: http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142 viewed 3\7\2008
IBM Open Source strategy 70 2 strategies for profiting from open source, from Linux: 1. “OSS is by some measures less expensive than proprietary software, so using it lowers the overall cost a customer pays for IBM’s computers, applications, and services. 2. OSS provides a common platform on top of which IBM can build and sell special applications and services.” IBM’s business model now focuses on selling high end hardware, proprietary software running on top of Linux, and integration and other customized services to enterprise customers. Source: http://people.ischool.berkeley.edu/ pam/papers/CACM%20IBM%20open%20source.pdf

71 University of Detroit Jesuit High School and Academy Approximately 100 older computers in need of upgrades Problem: To upgrade the computers software to Office 2000 they would have to upgrade the hardware Solution: Use Linux and OpenOffice on all old computers and continue using pre-loaded Microsoft software (Windows XP and office 2003) on the newer computers Details: 110 old computers 158 new computers Used (LTSP) Linux Terminal Server Project Purchased Linux servers to support LTSP clients but no pc replacements 21,000 to implement Linux/Openoffice option (more than 100,000 savings from Microsoft Plan) Source: http://www.linux.com/articles/45028

Open Source Overview 72 History Open Source vs. Proprietary Technical Components OS Effects on Business Strategy Best Practices for Open Systems

Best Practices for Open Systems 73 Get an understanding of the OS Technologies available Chose OS Tech. that best fits your business goals Understand Specific Licenses Research how you will support OS tech. and total cost of ownership Cost Reduction but keep in mind the long-term cost

Questions! 74

Citations 75 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. ALL THE FIXINGS, Jonathan Erickson, Dr. Dobb’s Journal; Aug 2006; 31, 8; ABI/IFORM Trade & Industry Page 6 Economic Impact of open source software on innovation and the competitiveness of information and communication technologies sector in the EU , Nov. 20, 2006 UNU-MERIT Open Source: Open for Business. Computer Sciences Corporation. 2004. 22. http://www.csc.com/features/2004/uploads/LEF OPENSOURCE.pdf "The Dark Side of Open Sauce" Leslie Kramer, Wall Street & Technology; Apr 2006 pg. 43 McKendrick, Joe. "Open Source in the Enterprise: New Software Disrupts the Technology Stack." (2007). 10 Mar. 2008 http://www.ioug.org/IOUG Open Source 07.pdf . "The Dark Side of Open Sauce" Leslie Kramer, Wall Street & Technology; Apr 2006 pg. 43 McKendrick, Joe. "Open Source in the Enterprise: New Software Disrupts the Technology Stack." (2007). 10 Mar. 2008 http://www.ioug.org/IOUG Open Source 07.pdf . Nick Langley. "Mobile developers get to write once, run anywhere. " Computer Weekly 24 Jul 2007: 32. ABI/INFORM Trade & Industry. ProQuest. ***ABI/INFORM. 23 Apr. 2008 http://www.proquest.com.ezproxy.umsl.edu/ 9. Time Magazine, December 25, 2006, Viewed on March 13, 2008 10. http://www.allthingsbeautiful.com/all things beautiful/2005/11/blogging to dif.html 11. http://opensource.org/docs/osd, viewed on March10, 2008 12. http://www.netc.org/openoptions/background/history.html, Viewed on March 17, 2008 13. ciozone.com/index.php/tool/50-top-open-source-resources-cios-should-know-and-maybe-love.html viewed 3/5/2008 14. http://www.businessreviewonline.com/os/archives/2007/01/where does open.html 15. http://www.businessreviewonline.com/os/archives/2006/07/where in the wo.html 16. https://www.osscensus.org/summary-report-public.php as visited on 4/21/08 17. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison of open source and closed source viewed on 2/25/2008 18. http://www.acad.bg/beginner/gnrt/appendix/glossary.html

Citations 76 18. http://www.net-o2.com/ip.asp, Viewed on March 27, 2008 19. http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid186 gci214031,00.html, Viewed on April1, 2008. 20. http://www.linux.org/info/index.html, View on April 4, 2008 21. http://www.Destoplinux.com 22. http://www.desktoplinux.com/articles/AT5836989728.html, Viewed on March 20, 2008 23. http://proquest.umi.com/pqdweb?did 45047075&sid 6&Fmt 3&clientId 45249&RQT 309&VName PQD, Viewed on April 2, 2008 24. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison of Windows and Linux , Viewed on April, 10, 2008 25. http://www.desktoplinux.com/news/NS9088528047.html , Viewed on March 3, 2008 26. http://www.mozilla.org/projects 27. http://www.media-art-online.org/java/help/how-it-works.html 28. https://meapplicationdevelopers.dev.java.net/fragmentation.html 29. http://www.sun.com/aboutsun/company/index.jsp 30. http://searchenterpriselinux.techtarget.com/news/interview/0,289202,sid39 gci1307014,00.html# 31. http://www.sun.com/emrkt/boardroom/newsletter/1104feature.html 32. http://www.news.com/8301-10784 3-9757417-7.html 33. http://blogs.zdnet.com/microsoft/?p 1142, Viewed on April 2, 2008 34. http://people.ischool.berkeley.edu/ pam/papers/CACM%20IBM%20open%20source.pdf 35. http:// www.opensource.motorola.com 4/10/2008 36. www.wallstreetandtech/goldbooks/showitem.jhtml?itemid 600010,viewed 4/23/2008 viewed on 2/25/08






