Levels of Government “We cannot work or eat or drink; we cannot buy or
13 Slides297.00 KB

Levels of Government "We cannot work or eat or drink; we cannot buy or sell or own anything; we cannot go to a ball game or a hockey game or watch TV without feeling the effects of government. We cannot marry or educate our children, cannot be sick, born or buried without the hand of government somewhere intervening." - Canadian Senator Eugene Forsey

Canada is the second largest country in geographic area in the world today spanning 6 time zones population of approximately 31 million people very difficult for a single government to take care of all the responsibilities that exist throughout the nation In 1867, because Canada was physically such a large country with so many different needs, we adopted a federal system of government that had three levels BNA (British North America Act of 1867) outlined the system and separation of powers Federal, Provincial and Municipal

This style of government involves dividing the powers into national and various regional levels This allows the country to address the needs of various areas that may have specific expectations from their government There are certain aspects of Canadian society that simply could not be addressed by one level of government For instance, Nunavut (the newest territory) has completely different needs from a government than does Metropolitan Toronto Each level of government deals with different areas
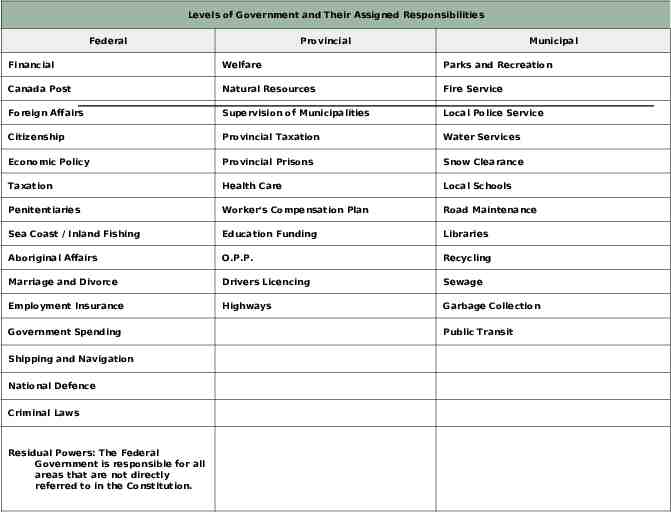
Levels of Government and Their Assigned Responsibilities Federal Provincial Municipal Financial Welfare Parks and Recreation Canada Post Natural Resources Fire Service Foreign Affairs Supervision of Municipalities Local Police Service Citizenship Provincial Taxation Water Services Economic Policy Provincial Prisons Snow Clearance Taxation Health Care Local Schools Penitentiaries Worker's Compensation Plan Road Maintenance Sea Coast / Inland Fishing Education Funding Libraries Aboriginal Affairs O.P.P. Recycling Marriage and Divorce Drivers Licencing Sewage Employment Insurance Highways Garbage Collection Government Spending Shipping and Navigation National Defence Criminal Laws Residual Powers: The Federal Government is responsible for all areas that are not directly referred to in the Constitution. Public Transit
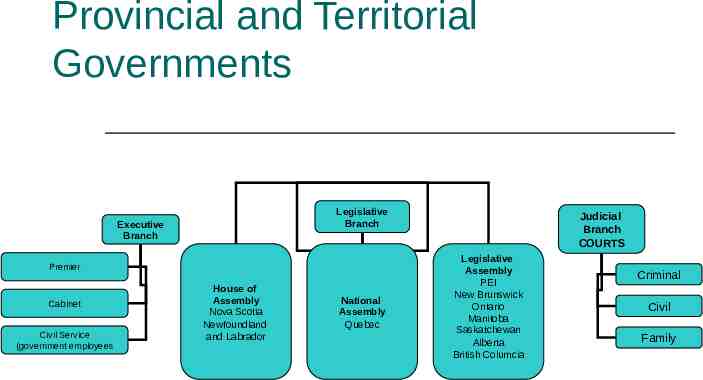
Provincial and Territorial Governments Legislative Branch Executive Branch Premier Cabinet Civil Service (government employees House of Assembly Nova Scotia Newfoundland and Labrador National Assembly Quebec Judicial Branch COURTS Legislative Assembly PEI New Brunswick Ontario Manitoba Saskatchewan Alberta British Columcia Criminal Civil Family

Executive Branch Premier: Leader of the party that wins the most seats becomes the premier of Premier Ministre (Quebec) Seats: the right to sit as a member of a legislature, based on winning a riding in an election

Lieutenant-Governor Representative of the crown Appointed by the Governor General on the advice of the premier Duties similar to Governor General but on a smaller scale Visits around provinces Opening of provincial legislature Swearing in cabinet ministres Signing bills and calling elections on the advice of the Premier

Lieutenant-Governor cont’d Tends to represent different cultural/ethnic groups that reflect the social and cultural make-up of their province

Legislative Branch Members in the provincial legislature are elected Called MLA’s (Members of Legislative Assembly) or MPP’s (Member of Provincial Parliament) Governing body introduces bills and has to answer to the opposition

Consensus Government Territories and Nunavut run by a consensus (do not belong to political parties) After election: elect a premier, Speaker and Cabinet from their own members Issues and bills are debated and passed with the agreement of all member Not adversarial but seeks compromise and benefits for all citizens

Relationship between the federal gov’t and the provincial/territorial gov’ts Often a love-hate relationship Provinces and territories that need help financially receive money from the fed gov’t in the form of transfer payments. Usually needed for hlth care or infrastructure Fed gov’t also administers the equalization program where richer provinces and territories contribute a higher share of taxes to help support less successful economies across Canada

Municipal or Local Governments “Think Globally, Act Locally”

Municipal/ Local Gov’t Has the greatest impact on you Provides leadership and governance for towns, cities, and regions Leaders are elected Responsible for: Local taxes -garbage collection By laws -public libraries Water inspection Maintenance of roads