Human Resources Management: Competencies for HR Professionals
33 Slides4.36 MB

Human Resources Management: Competencies for HR Professionals Chapter 2: HR Planning, Analytics, Finance/Accounting Unless otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) license. Feel free to use, modify, reuse or redistribute any portion of this presentation.

Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Discuss the importance of HR planning as it relates to strategy and the planning process. Describe the purpose of budgets. Discuss the methods companies use to estimate the supply and demand of human capital. Explain the components of a human resources information system (HRIS) and the impacts of technology. Describe how HRIS data, HR analytics and technology have increased the effectiveness of delivering HR services to employees. Explain how analytics can support decision-making in HR. Examine the importance of HR audits.

2.1 Human Resources Planning and Processes HR Planning is a strategic process that helps companies plan for future human resources that are needed to support the growth, or downsizing of production demands. It allows companies to predict the future, analyze the needs of the company, decide the market availability of candidates for specific jobs, and make decisions when and how to adapt and use human resources (people). HR departments begin an HR Plan by predicting or anticipating the number of employees they will need with the expansion, and what skills the new employees will need to possess.

2.1 Workforce Plan Development Competencies Maintain an understanding of the organization’s vision, mission, values, and goals. Create a future-focused workforce plan. Measure gaps in current talent needs. Assess future talent needs.
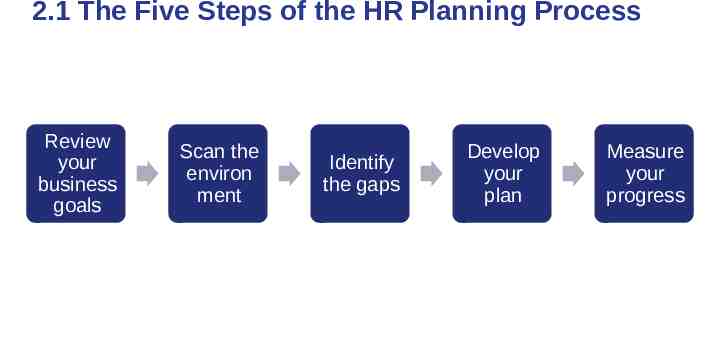
2.1 The Five Steps of the HR Planning Process Review your business goals Scan the environ ment Identify the gaps Develop your plan Measure your progress

2.1 Workforce Plan Execution Competencies Measure the impact of attraction initiatives. Measure employee retention. Measure gaps in current talent needs. Assess future talent needs. Identify the characteristics of desirable potential employees. Execute a workforce plan in accordance with sound project management principles. Determine the optimal methods for sourcing desirable potential employees. Identify potential employees using an appropriate mix of interviews, assessments, and reference checks. Select potential employees based on available evidence of fit with organizational strategic objectives. Orient new employees to the culture of the organization and the organization’s strategic objectives. Train new employees in a manner consistent with their competencies and the needs of the position. Create development plans for employees that are designed to fill gaps between current and future organizational skills needs. Implement measures to retain top talent.

2.2 HR Budgets An HR budget refers to the funds that HR allocates to all HR activities and processes across the organization. Before building a budget, managers need to understand costs. Costs can be classified in three ways: variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. There are many advantages to budgeting, including: communication, planning, collaboration, and evolution. Some of the disadvantages are that budgets can be inflexible, they are based on assumptions, and they can take a long time to create. The HR budget process include the following steps: Review past financial performance Choose a budgeting approach Analyze current data

2.2 Informed Business Decisions Competencies Align HR decisions with organizational strategy. Assess the organization’s financial and operating information for impact on HR strategy. This Photo by Meredith Snepp is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC

2.3 Forecasting Demand For Labour Forecast is an estimate of future human resources that a company needs to be successful. How companies forecast is weighted on several factors. Strategic Plan Legal Issues Competition Technology Turnover of employees Demographics This Photo by ResearchLeap is licensed under CC BY Budgets

2.3 External Trends Competencies Evaluate the credibility of sources of information. Keep current on business information and trends. Maintain awareness of broad economic, societal, technological, political, global, and demographic trends Identify HR opportunities and risks inherent in changes in economic, societal, technological, political, and demographic forces. Evaluate the applicability of new concepts and technology to the practice of HR within the organization.

2.4 HR Demand Forecasting Methods Nominal Group Method: a focus group of experts work face-to-face or virtually. Delphi Method: a group of experts predict specific future events through surveys and opinions. Trend Projections: Two methods are used with trend projections. Extrapolation uses past information related to change Once the information is gathered, the results need to be converted to staffing tables. HR departments are responsible for ensuring the right and most appropriate methods are used for reliability and validity.

2.5 Human Resources Supply There are two ways to solve staffing table needs: Internal supply are the existing employees who can be promoted to new positions, transferred to other departments or satellite offices, and could be demoted. External supply is hiring from outside the company. This Photo by PeopleMatters is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC

2.5 Estimating Internal Supply There are several methods HR departments use to track the supply of employees: Markov Analysis: future human resources needs that uses transitional probability matrices based on past data Human Resources Inventories: completed through HR audits of summaries of employees’ knowledge, skills and abilities (KSAs). Leadership and Management Inventories: similar to employee Human Resources Inventories. The KSAs are recorded. Replacement Charts: are like a “picture” that help to determine who can replace who when the need arises through a job opening.

2.5 Estimating External Supply: Labour Market Labour market analysis studies the companies labour market to assess the present and future availability of employees. Community Attitudes: The attitude of the local, national and international community affects the labour market. Demographics: Demographics affect the labour market in planning and trends for the future.

2.6 HR Response and Plan For Supply and Demand I HR departments should be prepared and have strategies in place to meet workforce supply and demand needs. The Response Plan needs to align with change within the organization, both short and long term. Change Management Competencies Establish understanding of the short- and long-term goals of planned organizational changes. Assess the HR implications of planned organizational changes. Evaluate the risks to success of an organizational change management strategy. Contribute to the development of an organizational change management strategy. Build an HR work plan to guide the necessary changes in concert with the organization’s change management strategy.
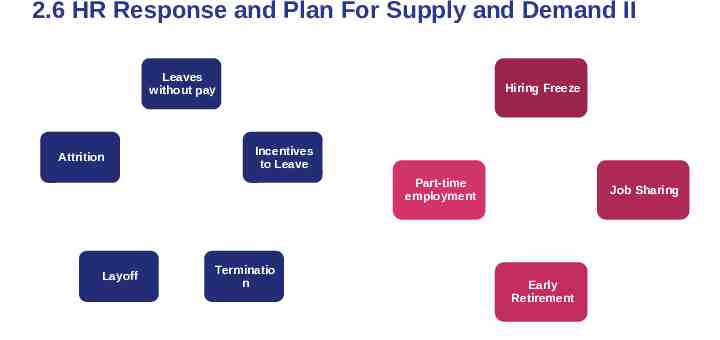
2.6 HR Response and Plan For Supply and Demand II Leaves without pay Attrition Hiring Freeze Incentives to Leave Part-time employment Layoff Terminatio n Job Sharing Early Retirement

2.6 Plan for Labour Shortages A labour shortage is not enough supply of employees to meet the demand for the company, and/or people do not have specific skills that company needs to operate the business. Good HR Planning through methods of tracking employees can avoid these situations. Hiring New Employees Contract Work Outsourcing Crowd-sourcing Overtime

2.7 Monitoring Performance Often, a great plan is written, taking lots of time, but isn’t put into practice for a variety of reasons. An excellent strategic and HR plan should discuss how “success” will be measured. It can be difficult to base an entire plan on forecasted numbers. As a result, an HRM department willing to change quickly to meet the organization’s needs proves its worthiness. By monitoring the changes constantly, you can be sure you can change your strategic plan as they come. Informed Business Decisions Competencies Align HR decisions with organizational strategy. Assess the organization’s financial and operating information for impact on HR strategy.

2.8 Human Resources and Technology, HRIS Today, every HR process has a technological element that enables it. A Human Resources Information System (HRIS) helps companies organize and manage people-related data. An HRIS system is an expensive and time-intensive commitment for any organization. The package selected should meet its current needs and have the flexibility to grow and expand with the organization into the foreseeable future. Human Resources Information Systems Competencies Maintain knowledge of developments in HR information systems. Create a list of specifications and requirements for the inputs and outputs of an HR information system. Use report templates to provide leaders with the necessary HR trend information to help achieve organizational objectives.
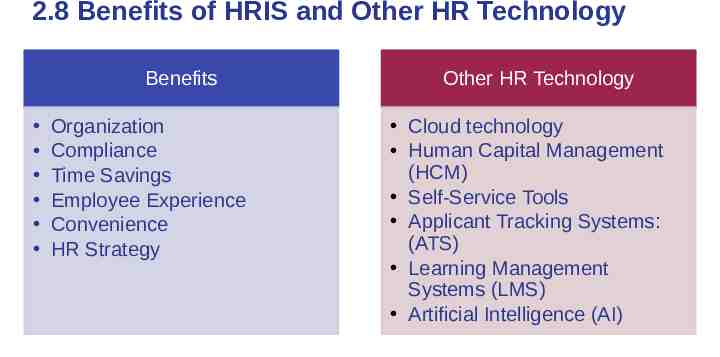
2.8 Benefits of HRIS and Other HR Technology Benefits Organization Compliance Time Savings Employee Experience Convenience HR Strategy Other HR Technology Cloud technology Human Capital Management (HCM) Self-Service Tools Applicant Tracking Systems: (ATS) Learning Management Systems (LMS) Artificial Intelligence (AI)

2.9 HR Analytics HR analytics is the process of analyzing this data in order to improve an organization’s workforce performance. The process can also be referred to as talent analytics, people analytics, or even workforce analytics. HR analytics: HR analytics specifically deals with the metrics of the HR function, such as time to hire, training expense per employee, and time until promotion. People analytics: People analytics, though often used as a synonym for HR analytics, is technically applicable to “people” in general. It can encompass any group of individuals even outside the organization.
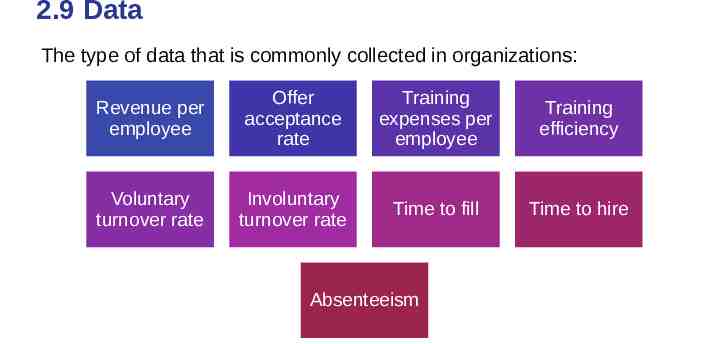
2.9 Data The type of data that is commonly collected in organizations: Revenue per employee Offer acceptance rate Training expenses per employee Training efficiency Voluntary turnover rate Involuntary turnover rate Time to fill Time to hire Absenteeism

2.9 Human Resources Information Competencies Maintain knowledge of the legal requirements regarding retention of HR information. Ensure that HR information is maintained in accordance with legal requirements. Identify the HR information that must be maintained to support organizational decision-making. Collect HR information that can be used to track progress towards meeting organizational objectives. Evaluate alternative tools for the maintenance of HR information. Use effective and efficient HR information retention tools.

2.9 Analytics and the Law Some legal considerations to keep in mind when implementing an HR analytics solution are: Employee privacy and anonymity Consent from employees about the amount and type of data collected Establishing the goal of data collection and informing employees accordingly IT security when using third-party software to run HR analytics Location of the HR analytics vendor – with whom the data will be stored – and their compliance with local laws

2.10 HR Analytics Application HR analytics is the process of analyzing and using data to make informed business decisions on the following: Job design Recruitment Talent Acquisition Training Compensation This Photo by Lukas is CC0 Public Domain Performance Management Health and Safety

2.11 HR Audits: An Interview Key insights about HR audits from the interview with Mike Haberman, SHRM-SCP, cofounder of Omega HR Solutions: An HR audit is a tool to help a company determine that the HR department is functioning as intended and covering all its designated areas. Types of HR audits include Organizational, Compliance, Functional, and Strategic. The choice between internal or external audits will depend on the audit's purpose. Legal sensitivity and efficient execution of time-consuming process requires external consultant. After completing an audit, correct identified problems. Additionally, collaborate with consultants for issue resolution and develop worklists for actionable findings. Organizational audits could be done periodically, while others should align with changes in the business world.

Summary Discuss the importance of HR planning as it relates to strategy. Describe the HR planning process. Explain the use of budgets to plan financial resources. Discuss the methods companies use to estimate supply and demand of human capital. Explain the components of a human resources information system (HRIS) Describe how HRIS data and HR analytics has increased effectiveness of delivering HR services to employees. Explain how analytics can support decision-making in HR. Examine the importance of HR audits.

End Chapter Review I 1. Review the HR Planning Process and the steps, individually. Discuss how you would create an HR plan for a company with 100 employees. Discuss how you would create an HR plan for a company of 2000 employees. What are the similarities? What are the differences? Discuss in a small group. 2. You are the HR Manager of a large company that is expanding. Presenting there are 5000 employees. The strategic plan mission is to expand to 8000 people over the next 3 years into difference markets, provide new products, and diversify into another country. It is your responsibility to create the HR Plan. Who do you speak to? Who do you get involved, and why? What is the first step you would take to create the HR Plan? Discuss in a small group.

End Chapter Review II 3. Why do companies align the HR Plan with the Strategic Plan? Discuss with a partner. 4. You work for a Canadian retail chain that has stores in Western Canada. The company wants to expand to Ontario and Nova Scotia. The goals is to open 10 new stores in each province within a year. The CEO asks you to complete an external and internal review. What factors would you consider and include in your review? Discuss in a small group. 5. You work for a digital music and 3-D company that sells it’s services to the movie industry. The job descriptions and the move customer’s needs are in constant flux, upgrading technology and developing new digital software. You need to complete some forecasting. Which ones would you consider? Why? Discuss with a partner.

End Chapter Review III 6. Review nominal group method and delphi method of forecasting, individually. What are the similarities? What are the differences? Do you have a preference you would use for a large electrical company that has 300 employees across Ontario? (The company is downsizing due to the slump in housing construction and sales). They expect to lay off about 100 employees. Discuss in a small group. 7. Why are staffing tables important to Human Resources? President? Brainstorm in large group. 8. Discuss an approach you would use if your company had “too many employees” and needed to cut back on staff by 30%? Why is this approach the most beneficial? Discussion in small group.

End Chapter Review IV 9. Discuss an approach you would use if your company was expanding by 40% over the next year. You now have 1000 employees and it is expected you will have 1400 employees within a year. Why is this approach the most beneficial? Discuss in small group. 10. What is the purpose of replacement charts? And, who would use them in the company? What would they use them for? Discuss with a partner. 11. Review the Conference Board of Canada website, individually. Share with a partner something that you learned that could b useful to an HR Manager. 12. Do you believe crowdsourcing is a good idea? Why? Why not? Brainstorm with the large group.

End Chapter Review V 13. Have you ever had to complete an application online through a database? What are the advantages for HR? Did you think the process was a good experience, as an applicant? A bad experience, as an applicant? Discuss with a partner. 14. Think about security as it relates to HR analytics. Do so research on security online, individually. What are the risks? Discuss with a partner. 15. What are the challenges facing companies that want to invest in an HRIS? Brainstorm in large group. 16. In your own words, describe HR analytics. Write a one-minute paper. Share with a partner. 17. Research “analytics and the law”, individually. Find something interesting about the search. Share with a partner.

End Chapter Review VI 18. How do HR analytics impact job design? Recruitment? Training? Compensation? Discuss in a small group. 19. Teacher will research a budget for a small company. Teacher will direct students to the weblink. Students will find and review the budget (annual) in a small group; and discuss variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. 20. In a small group, each group will decide on research for one company. The group will locate an income statement, balance sheet and statement of cash flow for the company. The group will share what they learned in the larger group. 21. In pairs, students will review horizontal analysis and vertical analysis. Each student chooses one topic. Explain to the fellow student, in your own words, what the topic means and its importance to businesses.






