System Requirements Specification Specifying the Specifications
24 Slides359.00 KB
System Requirements Specification Specifying the Specifications

Review from last class Requirements Engineering Tasks 1. Inception 2. Elicitation 3. Elaboration - next brief topic 4. Negotiation 5. Specification - main topic tonight 6. Validation 7. Management

Modeling What are the benefits of building a model? So, what needs to be modeled?

System Modeling Function & Information Flow Model what we will do with the data Data Model structure of the information Behavior Model how we interact with the system

Functional and Information Flow Modeling Data Flow Diagrams source code characters Syntax Analysis tokens characters Semantic Analysis machine compiler instructions yadda yadda object code machine instructions DFDs also require a Data Dictionary

Data Modeling Data Objects, Attributes, Relationships Formatted as Lists or Tables Entity Relationship Diagrams monitors security system enables/disables tests programs is programmed by sensor

Behavior Modeling State Transition Diagram done start 1 2 read msg send compose 4 file name save msg 3

Combining Info Flow & Behavior Use Cases http://www.evanetics.com/Articles/ar usecases/uc valueofucd.htm

Requirements Engineering Tasks 1. Inception 2. Elicitation 3. Elaboration 4. Negotiation 5. Specification 6. Validation 7. Management

Technically Speaking, "requirement" "specification" Requirement – understanding between customer and supplier Specification – what the software must do Requirements that are not in the SRS Costs Delivery dates Acceptance procedures etc

Uses of the SRS Design Validation Customer Contract – rarely

IEEE 830 Role of SRS 1. “The SRS must correctly define all of the software requirements, but no more.” 2. “The SRS should not describe design, verification, or project management details, except for required design constraints.”

IEEE 830 Characteristics of a Good SRS 1. Unambiguous 2. Complete 3. Verifiable 4. Consistent 5. Modifiable 6. Traceable 7. Usable during the Operation and Maintenance Phase

Desired SRS Characteristics Complete Consistent Changeable Traceable

Ambiguousness – example one The control total is taken from the last record. 1. The total is taken from the record at the end of the file. 2. The total is taken from the latest record. 3. The total is taken from the previous record. IEEE 830

Ambiguousness – example two All customers have the same control field. 1. All customers have the same value in their control field. 2. All control fields have the same format. 3. One control field is issued for all customers. IEEE 830

Ambiguousness – example three When a user fails to authenticate after a number of times, send a notification to IT. http://stackoverflow.com/questions/626737/how-do-you-resolve-ambiguities-in-specification

Clear, Complete Unclear Clearer The system shall be able to read updates from MedImg The system shall be able to provide historical reports The system shall be able to import new tumor patient data supplied by MedImg to the radiology management system, for evaluating the tumor to be malignant or benign The system shall be able to provide patient tumor data for the past five calendar years http://www.healthcareguy.com/

Expressing Requirements Through input/output specs aka IEEE 830 Format Use of Representative Examples Specification through Models IEEE 830

SRS Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2. General Description 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 3. Purpose Scope Definitions References Overview Product Perspective Product Functions User Characteristics General Constraints Assumptions and Dependencies Specific Requirements IEEE 830

3. Specific Requirements 3.1 Functional Requirements 3.1.1 Func Req 1 3.1.1.1 Introduction 3.1.1.2 Inputs 3.1.1.3 Processing 3.1.1.4 Outputs 3.1.2 Func Req 2 3.2 External Interface Requirements 3.2.1 User Interface 3.2.2 Hardware Interfaces 3.2.3 Software Interfaces 3.2.4 Communication Interfaces 3.3 Performance Requirements 3.4 Design Constraints 3.4.1 Standards Compliance 3.4.2 Hardware Limitations 3.5 Attributes 3.5.1 Security 3.5.2 Maintainability 3.6 Other Requirements 3.6.1 Database IEEE 830

Non-830-Style Requirements User stories encourage the team to defer collecting details. An initial place-holding goal-level story ("A Recruiter can post a new job opening") can be written and then replaced with more detailed stories once it becomes important to have the details. This technique makes user stories perfect for time-constrained projects. A team can very quickly write a few dozen stories to give them an overall feel for the system. They can then plunge into the details on a few of the stories and can be coding much sooner than a team that feels compelled to complete an IEEE 830–style software requirements specification. Quote from "Advantages of User Stories for Requirements" By Mike Cohn http://www.awprofessional.com/articles/article.asp?p 342885&seqNum 3
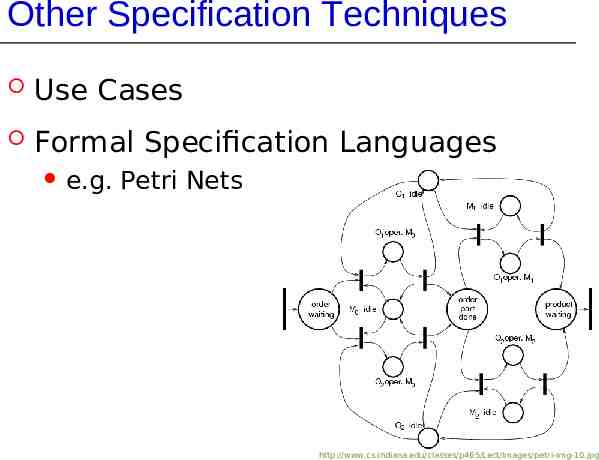
Other Specification Techniques Use Cases Formal Specification Languages e.g. Petri Nets http://www.cs.indiana.edu/classes/p465/Lect/Images/petri-img-10.jpg

Next Classes Agile Development Risk Analysis and Management Metrics Managing the Testing Process






