South African culinary uniqueness and traditions 1. Significance
22 Slides227.84 KB
South African culinary uniqueness and traditions 1. Significance Traditional differences Sense of belonging and community Pride in their heritage Encourages patriotism Provides knowledge of tradition for future generations

2. Food is important for some religions 3. Cultural diversity Different groups Distinctive in ways Share common features Based on religion, ethnicity, gender, generation

Different Cultural needs in the South Africa Hospitality Industry 2.1 Vegetarians Eat products from plant origin with or without use of eggs dairy products No flesh of animals Several types according to how strictly they avoid animal products
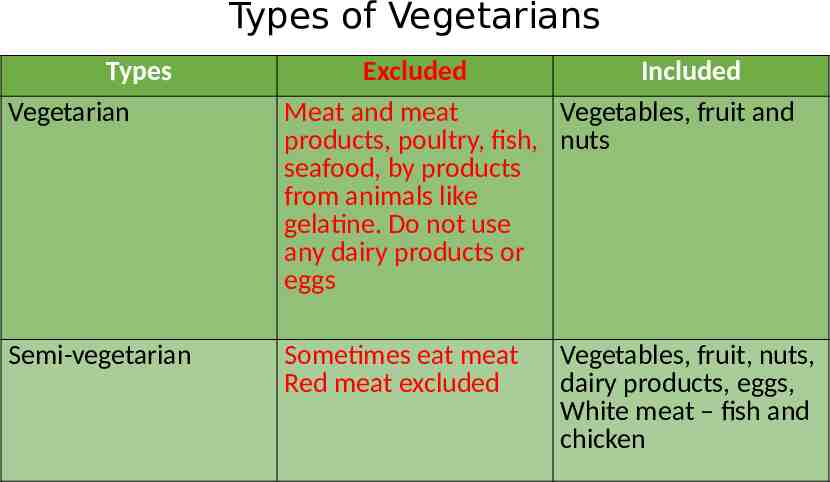
Types of Vegetarians Types Vegetarian Excluded Included Meat and meat Vegetables, fruit and products, poultry, fish, nuts seafood, by products from animals like gelatine. Do not use any dairy products or eggs Semi-vegetarian Sometimes eat meat Red meat excluded Vegetables, fruit, nuts, dairy products, eggs, White meat – fish and chicken
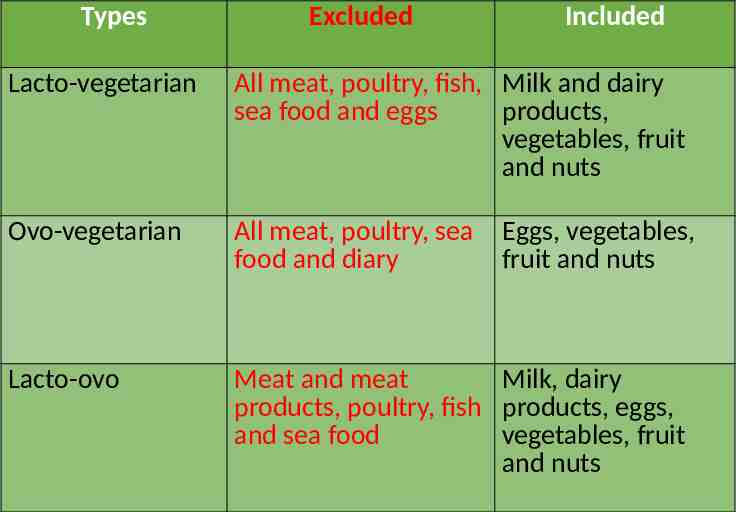
Types Excluded Included Lacto-vegetarian All meat, poultry, fish, Milk and dairy sea food and eggs products, vegetables, fruit and nuts Ovo-vegetarian All meat, poultry, sea food and diary Lacto-ovo Meat and meat Milk, dairy products, poultry, fish products, eggs, and sea food vegetables, fruit and nuts Eggs, vegetables, fruit and nuts
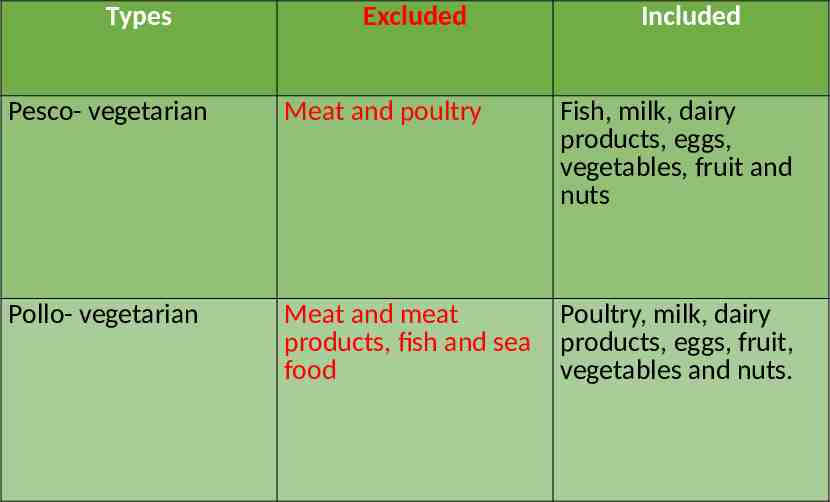
Types Excluded Included Pesco- vegetarian Meat and poultry Fish, milk, dairy products, eggs, vegetables, fruit and nuts Pollo- vegetarian Meat and meat products, fish and sea food Poultry, milk, dairy products, eggs, fruit, vegetables and nuts.
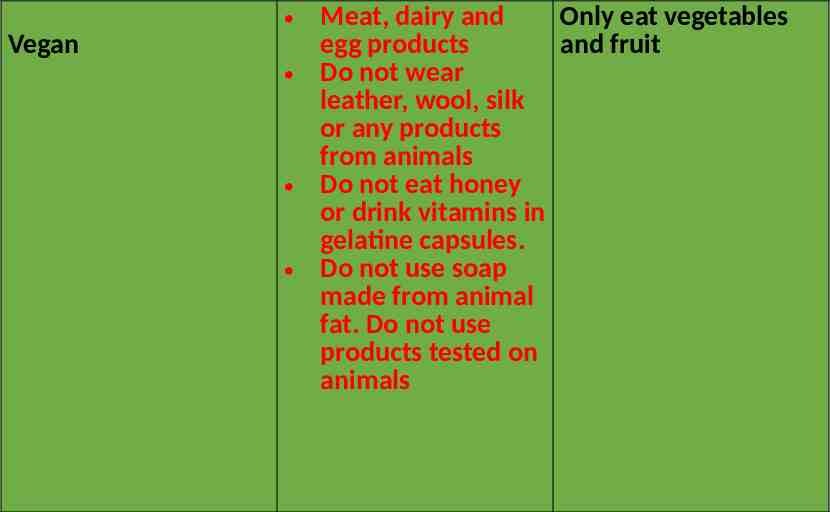
Vegan Only eat vegetables Meat, dairy and egg products and fruit Do not wear leather, wool, silk or any products from animals Do not eat honey or drink vitamins in gelatine capsules. Do not use soap made from animal fat. Do not use products tested on animals

Fruitarian All food from animals Only eat fruit from plants but not the plant. Raw and dried fruit, grains, nuts, honey and olive oil

2.2 Judaism (Kosher) 1. Dietary laws based on Old Testament Kosher Fit / acceptable Eaten by followers of Jewish faith Preparation is important Beth Din Jewish court approves food as kosher Paref not contain any dairy or meat ingredients neutral fruit and vegetables Milchik milk and dairy used in the food Meat contains kosher meat or derivatives

2. Guidelines Shoket do slaughter process on animals and birds that have been permitted by the Bible Kosher process No blood may be used 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Drain blood from meat Soak in water for 30 minutes 1 Hour in salt Can be grilled Some fat removed Within 72 hours after slaughtering

Continue 2 sets of utensils for preparation and cooking for preparation and cooking Meat Milchik Equipment used for non-kosher food may not be used for kosher foods Utensils and dishes may not be washed together If only 1 basin use plastic inserts Separate basins Separate dish towels May not eat meat and dairy together After eating meat, 6 hours should lapse before eating dairy products

Continue May eat meat after dairy after: Solid parev food Parev liquid Rinsing the mouth Eggs, fruit, vegetables and cereals Parev Fish with fins and scales Shellfish No insects Beth Din Kosher logo on processed food

2.3 Islam (Halaal) 1. Muslim - Believe in Allah SWT - Profet Mohammed brought laws to mankind - Laws is written in Holy Koraan 2. Halaal - According to Allah SWT - In Holy Koraan - Lawful and permitted - All ingredients must be Halaal

HALAAL Foods certified as Halaal by : - Muslim Judicial Council - Islamic Council of South Africa HARAM Prohibited food
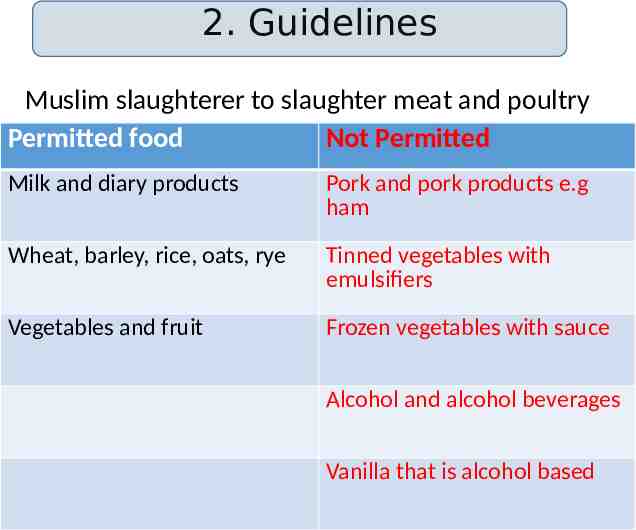
2. Guidelines Muslim slaughterer to slaughter meat and poultry Permitted food Not Permitted Milk and diary products Pork and pork products e.g ham Wheat, barley, rice, oats, rye Tinned vegetables with emulsifiers Vegetables and fruit Frozen vegetables with sauce Alcohol and alcohol beverages Vanilla that is alcohol based

2.4 Hinduism Many Indians Don’t always eat meat Eat meat only : No pain cause No violence Believe that pain and suffering will come back Conscientious Hindo Strict vegetarian Avoid meat, eggs, milk

2.5 Traditional African religions African diet is different from Western diet Culture, taste an tradition is important Proud of their tradition South Africa is a rainbow nation

Strandlopers Khoi people Lived on Cape shore from: Mussels, crayfish, abalone Seagulls, seals, penguins Edible seaweed Roots and fruit Eat sheep and cattle Enjoyed Pork fat Sail fat of sheep fried until crispy mixed with wild cabbage

San Good game hunters “Veldkos” Wild asparagus Sorrel Mustard leaves Waterblommetjies stew Mutton stew with creamy white waterblommetjies and sorrel for flavour

2.5 Traditional African Religion Game, goat, chicken and offal Wild greens, root vegetables, berries, maize and sorghum Insects ( protein rich) Locusts Termites Mopane worms

Xhosas, Zulu’s, Sotho’s, Tswana’s and Swazi’s Maize meal are used for Sour milk porridge Dumplings Crumbly phutu pap Fine-grained mieliepap Roasted green mealies, samp, maize meal

Beverages African beer / Umqombothi Maize sorghum yeast Mageu Fermented beverage maise meal water Sorghum beer / amabele / amazimba / luvhele brewed sorghum Other beer : Pineapple beer and sorghum beer






