SAP MODULES BY ANAND KUMAR 1
38 Slides129.44 KB
SAP MODULES BY ANAND KUMAR 1
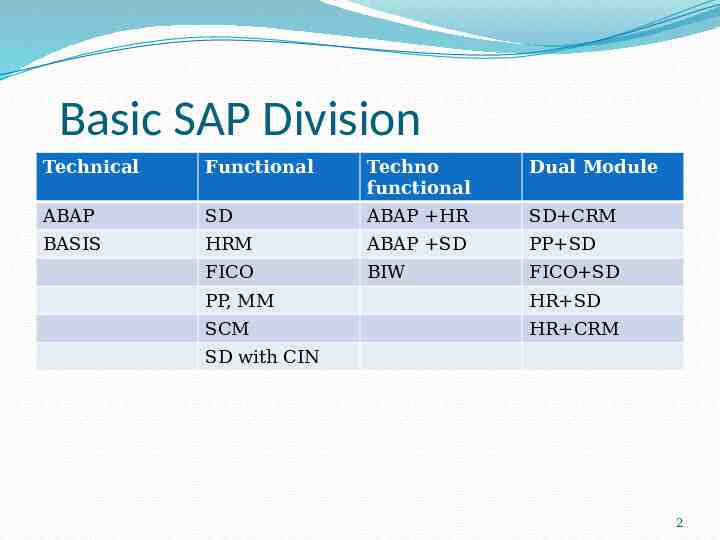
Basic SAP Division Technical Functional Techno functional Dual Module ABAP SD ABAP HR SD CRM BASIS HRM ABAP SD PP SD FICO BIW FICO SD PP, MM HR SD SCM HR CRM SD with CIN 2

3
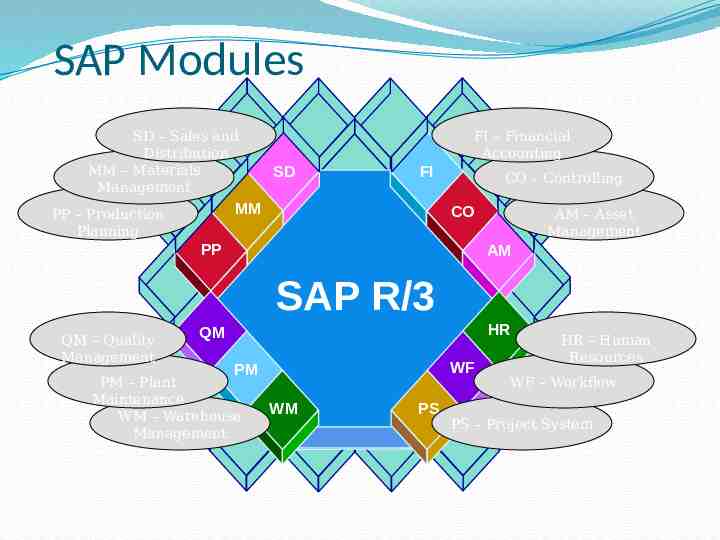
SAP Modules SD – Sales and Distribution MM – Materials Management FI – Financial Accounting SD FI MM PP – Production Planning CO – Controlling CO PP AM – Asset Management AM SAP R/3 QM – Quality Management HR QM WF PM PM – Plant Maintenance WM – Warehouse Management WM PS HR – Human Resources WF – Workflow PS – Project System

SAP are moving away from describing their system as a set of SAP Modules, now are using the term ‘solutions Financials Human Resources Customer Relationship Management Supplier Relationship Management Product Lifecycle Management Supply Chain Management Business Intelligence 5

SAP FI. FI means Financial accounting, it includes. General ledger Book close Tax Accounts receivable Accounts payable Asset Management (SAP AM) Consolidation Special ledgers 6

FI contd. SAP FI - which stands for Financial Accounting - is the SAP Module where regulatory or statutory data is tracked and managed. The SAP FI Module has the capability of meeting all the accounting and financial needs of an organization. It is within this SAP FI Module that Financial Managers as well as other Managers within your business can review the financial position of the company in real time as compared to legacy systems which often times require overnight updates before financial statements can be generated and run for management review. 7

SAP CO. CO stands for controlling, it includes. Cost elements Cost centers Profit centers Internal orders Activity based costing Product costing 8

SAP CO CONTD. The SAP CO (Controlling) Module provides supporting information to Management for the purpose of planning, reporting, as well as monitoring the operations of their business. Management decision-making can be achieved with the level of information provided by this module. 9

SAP PS Module PS is Project Systems – this SAP Module is where you can manage your projects, large and small, including Make to order Plant shut downs (as a project) Third party billing (on the back of a project) 10

SAP HR Module HR is for Human Resources . people are the important part of this SAP module, including Employment history Payroll Training Career management Succession planning SAP HR stands for Human Resources and this is the module which helps you optimize your HR processes to attract, develop and attain the right people including 11
SAP PM Module. Plant Maintenance is the PM – this SAP module is where you maintain your equipment (e.g. a machine, an oil rig, an aircraft etc), including Labour Material Down time and outages 12

SAP MM Module one of the most important SAP Modules where MM is Materials Management - underpins the supply chain, including Requisitions Purchase orders Goods receipts Accounts payable Inventory management BOM’s Master raw materials, finished goods etc 13

SAP MM Contd. AP MM stands for Materials Management and this is part of SAP Logistics which helps you manage end-to-end procurement and logistics business processes, from requisitioning to payment. Some of the main SAP MM transactions are: ME51N - Create Requisition ME21N - Create Purchase Order MIGO - Goods receipt a PO MIRO - Create Invoice 14

SAP QM QM stands for Quality Management This SAP module – improve the quality of your goods, including Planning Execution Inspections Certificates 15

SAP PP modules one of the really big SAP modules is Production Planning – manages your production process, including Capacity planning Master production scheduling Material requirements planning Shop floor 16

SAP SD Module one of the large SAP modules is Sales and Distribution – from order to delivery, including RFQ Sales orders Pricing Picking (and other warehouse processes) Packing Shipping 17

SAP BW Module BW stands for Business (Data) Warehouse which includes the following main functions: Data extraction from source systems Some technical and functional transformation of the data Storage of the data in what are called Info providers Reporting (which uses Info providers) 18

SAP ABAP It is not really a module, it stands for Advanced Business application Programming. This is the structured programming language for custom development including reports. ABAP is one of application specific fourth generation language. It was also intended to be used by SAP customers to enhance SAP applications – customers can develop custom reports and interfaces with ABAP programming. 19

Contd. The advanced way of programming in ABAP is using OOPS concept. What is oops? OOP is the common abbreviation for Object- Oriented Programming. Key Words: Objects', BAPI, BADI, 20

ABAP Webdynpro Pro This is the SAP standard UI technology for developing the web application in ABAP environment. Web Dynpro supports a structured design process. Automatic data transport using data binding Automatic input check The concept of Web Dynpro ABAP is identical with Web Dynpro Java and offers more or less the same functions. 21

SAP BASIS The ABAP language environment, including the syntax checking, code generation and runtime system, is part of the SAP Basis component. SAP Basis is the technological platform that supports the entire range of SAP applications, now typically implemented in the framework of the SAP Web Application Server. SAP Basis can be seen as the "operating system" on which SAP applications run. 22

Contd. SAP Basis currently runs on UNIX (AIX, HP-UX, Solaris, Linux), Microsoft Windows, i5/OS on IBM System i (formerly iSeries, AS/400) and z/OS on IBM System z (formerly zSeries, S/390). Supported databases are IBM DB2, Informix, MaxDB, Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server 23

SAP XI/PI SAP exchange infrastructure is SAP’s enterprise application integration software. used to facilitate the exchange of information among a company's internal software and systems and those of external parties. Like other NetWeaver components, SAP XI is compatible with software products of other companies. The central component of SAP XI is the SAP Integration Server, which facilitates interaction between diverse operating systems and applications across internal and external networked computer systems. 24

Component of SAP XI Integration building Integration Repository Integration directory Integration Server Business process engine Integration Engine Adapter engine. 25
SAP PI (process Integration) This section provides you with information about administration and maintenance tasks specific to the SAP Net Weaver usage type Process Integration (PI). Tasks: Monitoring Management Software logistics Troubleshooting 26

SAP CRM CRM is the acronym of Customer Relationship Management. CRM is a business system that consists of enterprise goals, business strategies, business processes and enterprise information systems. CRM software systems automate many customerrelated business tasks. 27

CRM vs. ERP and SCM ERP (Enterprise Relationship Management) and SCM (Supply Chain Management) are two other categories of enterprise software that are widely implemented in corporations and non-profit organizations. While CRM attempts to enhance the relationship with customers, the primary goal of ERP is to improve and streamline internal business processes, and SCM aims to facilitate the collaboration between the organization, its suppliers, the manufacturers, the distributors and the partners 28

CRM technical/ Functional CRM requirement will be either technical or functional. Technical candidates will be required to worked on GUI . 29

SAP MDM Master Data Management is an enabling foundation for enterprise information management – providing a single version of master data for supplier, product, customer, or user-defined data objects in heterogeneous environments. MDM ensures cross-system data consistency through interactive distribution. 30

SAP (ISU/CCS) The Customer Care and Service (ISU/CCS) Benchmark simulates typical processes in a utilities company. The core business processes can be divided into two main processes: consumption and revenue collection. For the consumption process, three batch jobs are utilized for collecting information – meter-reading orders have to be created and printed, and the results have to be uploaded into the system. To collect revenues, additional batch jobs – billing the customer, invoicing, and printing the bill – 31

SAP Retail overview SAP Retail is a completely integrated retailing system. It maps the complete set of business processes required for competitive assortment strategies, different retail formats, and ECR-driven logistics and distribution. It provides all the functions necessary for modeling business processes in a retail company. The business process area "Retailing" comprises the procurement, storage, 32 distribution, and sale of merchandise. SAP

The key retailing processes include: Assortment Management Sales Price Calculation Promotion Management Allocation Requirements Planning and Purchasing Goods Receipt Invoice Verification and Subsequent Settlement of End-Of-Period Arrangements Warehouse Management Picking and Delivery Billing Store Supply 33

SAP SCM SCM enables collaboration, planning, execution, and coordination of the entire supply network, empowering you to adapt your supply chain processes to an everchanging competitive environment. 34

SAP SCM Components SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization (SA P APO) SAP APO is composed of Demand Planning, Supply Network Planning, Multi-level Supply and Demand Matching, Production Planning and Detailed Scheduling, Transportation Management, and Global Available-to-Promise. 35

SCM Components Contd. SAP Forecasting and Replenishment (SAP F&R) SAP Event Management (SAP EM) EM enables the coordination of planning and activities within the business and with partners by exchanging information across systems and monitoring critical situations. Supply Network Collaboration (SNC) - formerly SAP I CH EM enables the coordination of planning and activities within the business and with partners by exchanging information across systems and monitoring critical situations. 36

Contd. SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) EWM offers flexible, automated support for processing various goods movements and for managing stocks in a warehouse complex. The system supports scheduled and efficient processing of all logistics processes within a warehouse. 37

SAP SRM Supplier relationship management is a comprehensive approach to managing an enterprise's interactions with the organizations that supply the goods and services it uses. 38






