REVIEW QUESTIONS FOCUSED ON COMPETENCY #3 By: ALFIE P.
74 Slides989.80 KB

REVIEW QUESTIONS FOCUSED ON COMPETENCY #3 By: ALFIE P. SARMIENTO, Ph.D. 5th Placer 1998 FISPhil Founding Officer

In deriving the primary classification, the ten fingerprints are divided into five pairs. The first pair is composed of the A)right thumb and right index finger B)left thumb and left index finger C)right middle and right ring finger D)right little finger and left thumb A aps [email protected]

What Henry classification is derived by ridge counting the loop appearing in the right or left little finger? A)Major Classification B)Key Classification C)Final Classification D)Sub-secondary Classification C) Final Classification aps [email protected]

What Henry classification involves ridge counting the first loop in the ten print card starting from the right thumb except the little fingers? A)Final Classification B)Key Classification C)Major Classification D)Primary Classification B) Key Classification aps [email protected]

When there are 3 or more intervening ridges above the right delta, the tracing is called A)Meeting B)Inner C)Outer D)none of these B) Inner aps [email protected]

How do fingerprint examiners ridge count plain whorls? A)the left delta to the core in left hand. B) Treat it as ulnar loops C) the right delta to the core in right hand. D) Treat it as radial loops E) Perform ridge tracing B) Treat it as ulnar loops aps [email protected]

Which of the following is not represented by numerical symbol? A)Primary B)Key C)Major D)final C) Major aps [email protected]

If two index fingers were amputated, both will be classified as A)similar to their counterpart fingers. B) Plain whorls with meeting tracings. C)of whorls with no additional reference. D)identical to the opposite fingers. B) Plain whorls with meeting tracings. aps [email protected]

In a set of prints containing all whorl type patterns, the key classification is obtained by A)conducting ridge tracing on whorls B)putting a dash on the numerator C) ridge counting the first whorl appearing in the ten print D)leaving it blank C aps [email protected]

The little white lines that are found on a fingerprint that looks like scars of blisters and burns are referred to as A)Scars B)Warts C)Furrows D)creases D) creases aps [email protected]
It is defined as inner terminus of the fingerprint pattern. A)Core B)Delta C)Dermis D)Dot A) Core aps [email protected]

What is the probability ratio that two person might have identical fingerprints according to Francis Galton? a. b. c. d. 1 in 64 million 1 in 6 million 1 in 64 billion 1 in 6 billion aps [email protected]

What is the NCIC code of a fingerprint exhibiting a plain whorl with three intervening ridges above the right delta? a. b. c. d. WI WO PI PO aps [email protected]

The classification system icnofalangometrica of Juan Vucetich means a. b. c. d. finger description finger track measurement finger sorting finger analysis aps [email protected]

What NCIC code of shall be used if a finger shows the requisites of a radial loop with 15 ridge counts? a. b. c. d. 15 (I) for inner (O) for outer 65 aps [email protected]

Which of the following codes reflect Francis Galton’s elementary fingerprint classification system? a. b. c. d. WWWLLLWLLW AULSRSWUXXSRUCUPLSRS XXPIdIXOSRTTAA6049dM M 32 W MMM M 32 W MMM aps [email protected]

When two complementary strands of DNA are hybridized or bound together a ladder like structure is formed. Because of the three dimensional structure of the chemical components in the backbone, a spiral configuration results. This natural state of DNA is called a. b. c. d. Double coil Double spiral Double helix Double strands aps [email protected]

Which of the foregoing is a type of DNA that contains more unique features? a. b. c. d. Mitochondrial DNA DNA strand Nuclear DNA Molecular DNA aps [email protected]

Blood type is a form of class evidence whereby DNA is said to be a. b. c. d. Conclusive evidence individualistic Best evidence generic aps [email protected]
A type of fingerprint pattern that possesses an angle, an upthrust, or two of the three basic characteristics of the loop. A)ARCH – PLAIN B)ARCH –TENTED C)LOOP – ULNAR D)LOOP - RADIAL B) ARCH –TENTED aps [email protected]

Any distortion or alteration not in the original friction ridge impression, produced by an external agent or action. A)Compression B)Artifact C)Dermabrasion D)Discrepancy B) Artifact aps [email protected]
Two or more fingers connected along the sides by skin. A)PENTADACTYLY B)SYNDACTYLY C)BRACHYDACTYLY D)ECTRODACTYLY B) SYNDACTYLY aps [email protected]

A bifurcation with one short ridge branching off a longer ridge. A)BIFURCATION B)SPUR C)DELTA D)DOT B) SPUR aps [email protected]

A friction ridge not fully developed which may appear shorter and thinner in appearance than fully developed friction ridges (interstitial, nascent). A)INCIPIENT RIDGE B)INTERVENING RIDGE C)PAPILLARY RIDGE D)FRICTION RIDGE A) INCIPIENT RIDGE aps [email protected]

An alpha expression derived from the pattern of the index fingers. A)SUB SECONDARY B)SECONDARY C)MAJOR D)KEY B) SECONDARY aps [email protected]

The space between the shoulders of a loop, free of any appendages that abut upon the recurve at a right angle on the outside. A)SUFFICIENT RECURVE B)TYPE LINES C)BRIDGE D)DIVERGENCE A) SUFFICIENT RECURVE aps [email protected]

A type of pattern in which one or more ridges enter upon either side, recurve, touch or pass an imaginary line between delta and core and pass out, or tend to pass out, on the same side the ridges entered. The flow of the pattern runs toward the little finger. A)LOOP – ULNAR B)LOOP – RADIAL C)WHORL – PLAIN D)WHORL - DOUBLE LOOP A) LOOP – ULNAR aps [email protected]

Those areas that are enclosed within the pattern area of loops and whorls. They are also known as the core and the delta. A)FULCRUM AREA B)FRICTION RIDGE UNIT C)FOCAL POINTS D)FIBULAR AREA C) FOCAL POINTS aps [email protected]

A type of fingerprint pattern which has two deltas and at least one ridge which makes, or tends to make, one complete circuit, which may be spiral, oval, circular, or any variant of a circle. An imaginary line drawn between the two deltas must not touch or cross any recurving ridges within the inner pattern area. A)WHORL – ACCIDENTAL B)WHORL - DOUBLE LOOP C)WHORL - CENTRAL POCKET D)WHORL - PLAIN C) WHORL - CENTRAL POCKET aps [email protected]

A type of pattern in which one or more ridges enter upon either side, recurve, touch or pass an imaginary line between delta and core and pass out, or tend to pass out, on the same side the ridges entered. The flow of the pattern runs toward the thumb. A)LOOP – ULNAR B)LOOP – RADIAL C)WHORL – PLAIN D)WHORL - DOUBLE LOOP B) LOOP – RADIAL aps [email protected]

An alpha expression derived from the index, middle and ring fingers of both hands. A)KEY B)MAJOR C)FINAL D)SUB-SECONDARY D) SUB-SECONDARY aps [email protected]

Ridge detail is present, but is dissociated due to trauma or genetic causes. It lacks any continuous pattern flow. A)SCARF SKIN B)MOTTLED SKIN C)CREASE D)SPUR B) MOTTLED SKIN aps [email protected]

That point on a ridge at or nearest to the point of divergence of two type lines, and located at or directly in front of the point of divergence. A)CORE B)DOT C)FURROWS D)DELTA D) DELTA aps [email protected]

What is ALPS? A)Automated Latent Print System B)Authenticated Latent Print System C)Automated Latent Pattern System D)Authenticated Latent Pattern System A) Automated Latent Print System aps [email protected]

It is referred to as friction ridge flow and general morphological information. A)level 1 detail B)Level 2 detail C)Level 3 detail D)Level 4 detail A) Level 1 detail aps [email protected]

It is known as individual friction ridge paths and friction ridge events such as ending ridges, dots, enclosure etc. A)level 1 detail B)Level 2 detail C)Level 3 detail D)Level 4 detail B) Level 2 detail aps [email protected]

It is defined as friction ridge dimensional attributes. A)level 1 detail B)Level 2 detail C)Level 3 detail D)Level 4 detail C) Level 3 detail aps [email protected]

It is also known as ridge characteristics. A)minutiae B)typica C)Galton details D)All of the above D) All of the above aps [email protected]

Galton details are best described as A)level 1 detail B)Level 2 detail C)Level 3 detail D)Level 4 detail B) Level 2 detail aps [email protected]

It is the point at which one friction ridge divides into three friction ridges. A)trident B)webbing C)trifork D)None of the above D) None of the above aps [email protected]

Approximately 25% of the population falls into which primary classification? A) B) C) D) E) 0/0 25/25 1/1 20/20 50/50 aps [email protected]

The intrinsic or innate ridge formations are called A) B) C) D) Level 1 detail Level 2 detail Level 3 detail Level 4 detail aps [email protected]

When two bifurcations form on the same ridge facing each other and their branches join, the formation is called A)spur B)dot C)enclosure D)trifurcation aps [email protected]

A whorl in the right middle finger would be given the numerical value of in calculating the Primary Value of the Henry Classification System. A)2 B)4 C)8 D)16 aps [email protected]

Congenital absence of friction ridge skin is known as: A)ridge dysplasia B)ridge aplasia C)ridge dysphasia D)none of the above aps [email protected]

The core of a loop is placed upon or within . A)the innermost sufficient recurve B)the innermost ridge C)the innermost recurve D)any of the above aps [email protected]

Type lines may be defined as the two innermost ridges which start parallel, diverge, and surround or tend to surround . A) B) C) D) the core the delta the pattern area an upthrust aps [email protected]

An area comprised of the combination of ridge flow, ridge characteristics, and ridge structure. A)FRICTION RIDGE B)FRICTION RIDGE UNIT C)FRICTION RIDGE IDENTIFICATION D)FRICTION RIDGE DETAIL aps [email protected]

A sampling technique used to increase the size of an image file by creating more pixels and increasing the apparent resolution of an image. When used to decrease image size, interpolation is generally referred to as down sampling. A) INTERDIGITAL B) Image Retrieval System C) INTERPOLATION D) INDIVIDUALIZATION aps [email protected]

He was credited for his statistical model of fingerprint individuality, published in 1911. His model was very simplistic and ignored relevant information but was the foundation for others to develop improved statistical models. His work became the basis for Locard's Tripartite Rule. A) Balthazard, Dr. Victor B) Bayes, Rev. Thomas C) Bayes, Rev. Thomas D) Beck, Adolf aps [email protected]

In the distal phalange of the fingers, the configuration of friction ridges that are utilized in classification. A) PATTERN FORMATIONS B) PATTERNS C)PATTERN AREA D)PATTERN CLASSIFICATION aps [email protected]

Area located at the heel of the foot. A) B) C) D) Ball area Calcar area Calpar area Phalange area aps [email protected]

Underdeveloped ridges associated with an excess of creases. A) B) C) D) RIDGE DYSPLASIA RIDGE DISSOCIATION RIDGE FLOW RIDGE HYPOPLASIA aps [email protected]

End to end fusion of the phalanges of the fingers or toes. A) B) C) D) SURFACTANT SYMPHALANGY SYNDACTYLY SYNPERONIC aps [email protected]
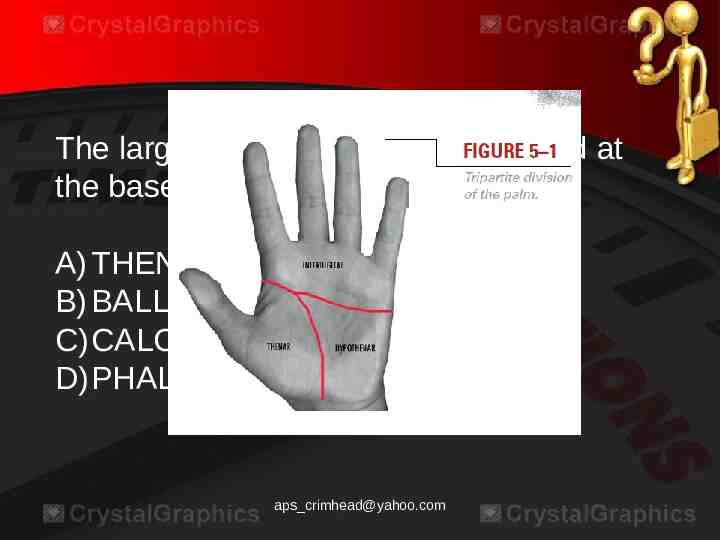
The large cushion of the palm located at the base of the thumb. A) THENAR AREA B) BALL AREA C)CALCAR AREA D)PHALANGE aps [email protected]

Term commonly used in the United Kingdom and some Commonwealth countries to designate a latent print. A) B) C) D) Mark Print Matrix Art aps [email protected]

A lighting technique used to visualize latent friction ridge impressions where the light is directed on an object in a sloping direction. A) Forensic Light Source B) Fluorescence C)Oblique Lighting D)Parallel Lighting aps [email protected]

Reagent used to detect/enhance bloody friction ridge detail. A) CYCLOHEXANE B) CROWLE'S DOUBLE STAIN C)CRYSTAL VIOLET D)DIAMINOBENZIDINE aps [email protected]

A recording of an individual's friction ridges with black ink, electronic imaging, photography, or other medium on a contrasting background. A) LATENT PRINT B) KNOWN PRINT C)PATENT PRINT D)TEN PRINT aps [email protected]

The designation of friction ridge skin into basic categories of general shapes. A) B) C) D) PATTERN AREA PATTERN FORMATIONS PATTERNS PATTERN CLASSIFICATION aps [email protected]

The larger of the two bones of the forearm, on the palmar side of the little finger. A) B) C) D) ULNA RADIUS FEMUR CARPAL aps [email protected]

Situated at the closest point of attachment; direction toward the body. A) B) C) D) PRIMARY PROXIMAL QUALITATIVE QUANTITATIVE aps [email protected]

Chaining together many simple molecules to form a more complex molecule with different physical properties. A) POLYMERIZATION B) REDOX C)RUBBING TECHNIQUE D)SEQUENTIAL PROCESSING aps [email protected]

Proximity of characteristics to each other. A) RELATIVE POSITION B) RELATIVITY C)FIXED POSITION D)PROXIMATE POSITION aps [email protected]

The smaller of the two bones of the forearm, on the same side as the thumb. A) B) C) D) ULNA RADIAL FEMUR CARPALS aps [email protected]

The friction ridge skin area on the side and underside of the hand. A) B) C) D) PALMAR AREA PALMAR ZONE PAPILLARY RIDGES PAPILLAE aps [email protected]

Palmar area below the fingers and above the thenar and hypothenar areas. A) B) C) D) INTERPOLATION INTERVENING RIDGES INTERDIGITAL DIGITAL aps [email protected]

Variances in the reproduction of friction skin caused by pressure, movement, force, contact surface, etc. A) B) C) D) DISSOCIATED RIDGES DOWN SAMPLING DISTORTION TRAUMA aps [email protected]

When the ridges of an image are a different color from the background and the furrows of an image are the same color as the background, as opposed to a negative image. A) NEGATIVE PRINT B) POSITIVE PRINT C)KNOWN PRINT D)INKED PRINT aps [email protected]

The outer edge of a palm print typically left on a document when people write. This includes the outer portion of the hypothenar and may include the outer edge of interdigital section and the outer edge of the little finger. A) Writer's Palm B) Palmar Zone C)Palm Print D)Papillary Layer aps [email protected]

This involves preparing photographic enlargements of the latent and inked fingerprints. A grid of equally-sized squares is then superimposed on each, with the squares of each grid occupying identical positions on each print. The forensic scientist examines both imprints square by square looking for identical characteristics. A) Osborn Grid Method B) James Grid Method C) Purkinje Grid Method D) West Grid Method aps [email protected]

A ridge break may be caused by: A) a dirt B) a failure in matrix deposition C)incorrect deposition pressure D)any of the above E) none of the above aps [email protected]

The NCIC code for missing/amputated fingers is: A) B) C) D) AA SR XX TT aps [email protected]

Thank you for your Patience! GOOD LUCK GOD BLESS!!! aps [email protected]






