Quality Part 4 Indicators & Safety Initiatives Ferris State University
13 Slides2.48 MB

Quality Part 4 Indicators & Safety Initiatives Ferris State University - Nursing 541 Shannon Sharrar, Juline Lloyd, Leslie Peterson, Elizabeth Watson, and Rosilind Richardson

Nursing Hours per Patient Day/Patient-Staff Ratio What is a nursing hours per day? Number of nurses allocated according to the nursing hours per patient day What is Nurse – Patient Ratio? Number of nurses per number of patients or patient days determines staffing levels Who endorses the NSI nursing hours per patient day? American Nurses Association National Quality Forum (Montalvo, 2007) Complications associated with nursing hours per day/nurse-patient ratio: Budget Errors Quality of care Nursing burnout
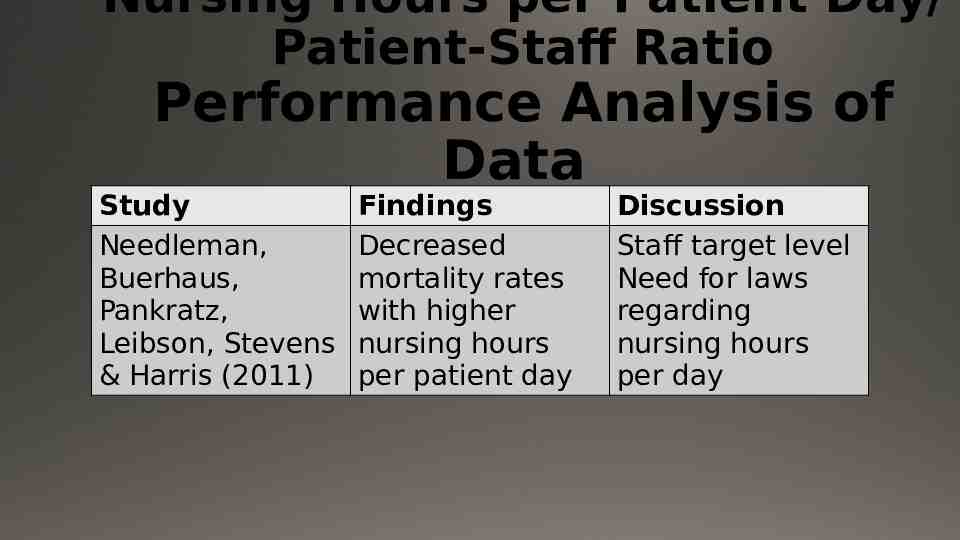
Nursing Hours per Patient Day/ Patient-Staff Ratio Performance Analysis of Data Study Needleman, Buerhaus, Pankratz, Leibson, Stevens & Harris (2011) Findings Decreased mortality rates with higher nursing hours per patient day Discussion Staff target level Need for laws regarding nursing hours per day

Nursing Hours per Patient Day/ Patient-Staff Ratio Performance Analysis of Data Study He, Staggs, BergquistBeringer, & Dunton (2016) Findings Increased staffing led to lower event rate with all outcomes Discussion RN staffing numbers affect NSIs – fall rate and pressure ulcer

NSI: Falls What is a fall: “An unplanned decent to the floor” (National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators, 2013). Who endorses the NSI falls? The Joint Commission The Institute of Medicine The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Complications associated with falls: Injuries Considered hospital acquired if injury (Centers for Medicare and Medicaid, 2015) Costly Decreased quality of life for patient

NSI: Falls Performance Analysis of Data Study Findings Discussion Barker, Morello, Ayton, Hill, Brand, Livingston & Botti (2017) Nurses are key players in falls prevention Practical benefits Fall risk tools are useful in preventing falls 6-PACK nurse led falls prevention program uses interventions known to decrease falls ease of use for nurses decrease noncompliance with nurses

NSI: Falls Performance Analysis of Data Study Findings Discussion Spoelstra, Given & Given (2012) Multifactorial fall prevention intervention programs decrease both falls and fall injuries in hospitalized patients Multifactorial fall prevention intervention programs include evidence based interventions

: Quality Improvement Identify areas for improveme nt Quality Improvement: a systematic approach that is driven by data and meant to improve systems within an organization (Shirey et al,. 2011) Purpose of Quality Improvement: Improve the quality and Evaluate response Analyze data safety of health care systems (Weston & Roberts, 2013) Quality improvement initiatives: falls, patient-staff ratios, medication errors, hospital acquired infections, hospital readmits (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2017) Implement Formulate goals/plan
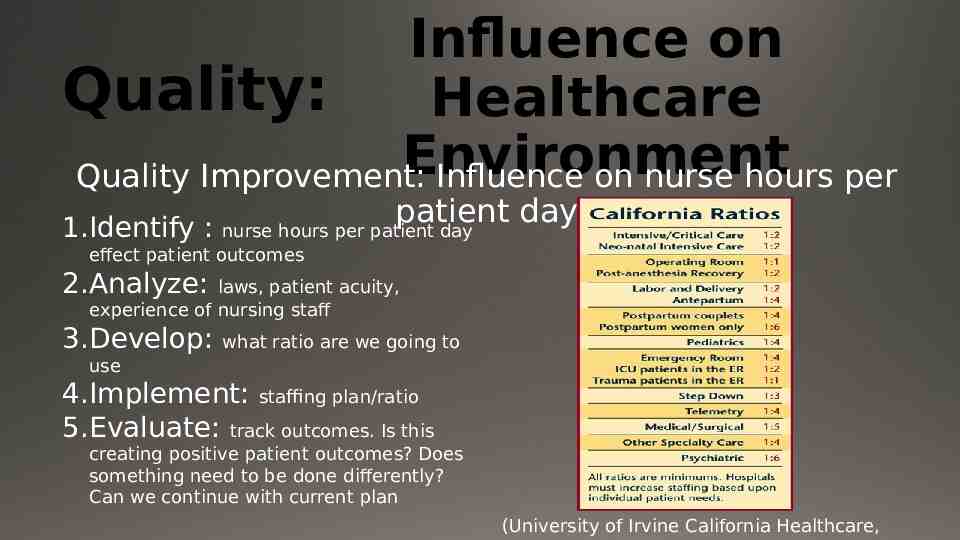
Influence on Quality: Healthcare Environment Quality Improvement: Influence on nurse hours per patient day 1.Identify : nurse hours per patient day effect patient outcomes 2.Analyze: laws, patient acuity, experience of nursing staff 3.Develop: what ratio are we going to use 4.Implement: staffing plan/ratio 5.Evaluate: track outcomes. Is this creating positive patient outcomes? Does something need to be done differently? Can we continue with current plan (University of Irvine California Healthcare,

Influence on Healthcare Quality: Environment Quality Improvement: Monitoring fall rates Spectrum Health, 2017 Quality Improvement Project: Silkworth, Gevaart, Morin, 2016) Baker, Ferrara, Wagner,

References American Nurses Association. (2017). Nursing staff measures . In Policy & Advocacy. Retrieved from http://www.nursingworld.o MainMenuCategories/Policy-Advocacy/Federal/Agencies/ANA-Leading-Patient-Safety/Nurse-Staffing-Measures Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2017, September). QI guide on improved nursing care. Retrieved October 5, 201 https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/systems/monahrq/myqi/nursing.html Barker, A. L., Morello, R. T., Ayton, D. R., Hill, K. D., Brand, C. A., Livingston, P. M., & Botti, M., (2017, February). Acceptability of PACK falls prevention program: A pre-implementation study in hospitals participating in a cluster randomized controlle ONE. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172005 Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2015). Hospital acquired conditions. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/Medicar Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/HospitalAcqCond/Hospital-Acquired Conditions.html He, J., Staggs, V., Bergquist-Beringer, S., & Dunton, N. (2016, October). Nurse staffing and patient outcomes: a longitudinal stu trend and seasonality. BMC Nursing, 15(60). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-016-0181-3

References Institute of Medicine. (2011). The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. Montalvo, I. (2007). The national database of Nursing Quality Indicators. Retrieved from http:/www.nursingworld MainMenuCatergories/ANAMarketplace/ANAPeriodicals/OJIN/TableofContents/Volume122007/No3Sept07/NursingQualityIndicators.asp Shirey, M., Hauck S., Embree, J., Kinner, T., Schaar, G., Phillips, L., Ashby, S., Swenty, C., McCool, I. (2011). Showcasing differences between quality improvement, evidence -based practice and research. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 42(2) , 57-68 Silkworth, A. L., Baker, J., Ferrara, J., Wagner, M., Gevaart, M., & Morin, K. (2016, January). Nursing staff develop a video to prevent falls: A quality improvement project. Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 31(1), 40-45. doi:10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000135 Spoelstra, S. L., Given, B. A., & Given, C. W. (2012, February 1). Fall prevention in hospitals. Clinical Nursing Research, 21(1), 92-112. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773811418106 The Joint Commission Center for Transforming Healthcare. (2017). Targeted solutions tool for preventing falls. Retrieved from http:// www.centerfortransforminghealthcare.org/tst pfi.aspx

References University of Irvine California Healthcare. (2012). Staffing, scheduling, and budgeting processes . In Exemplary Professional Practice . Retrieved from http://www1.ucirvinehealth.org/magnetnursing/clienthtml/69/exemplary-professional-practice/73/6885.htm Weston, M., & Roberts, D. W. (2013, September). The influence of quality improvement efforts on patient outcomes and nursing work: A perspective from chief nursing officers at three large health systems. The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, 18(13). doi:10.3912/ OJIN.Vol18No03Man02