Leadership in Nursing Preceptorship Name Class Professor October
17 Slides113.09 KB

Leadership in Nursing Preceptorship Name Class Professor October 15, 2013
The Role of the Preceptor Role Model Demonstrate ability and competence as a nurse Provide appropriate examples of how nurses should behave Act ethically and professionally Stress the importance of learning from one another and from mistakes Socializer Introduce the students to the field and to each other Educator Determine the needs of each student and help them reach their goals Provide student with feedback and help lessons transition into practice

Definitions of Leadership (noun) the action of leading a group of people or an organization. "different styles of leadership“ a position as a leader of a group, organization, etc. the power or ability to lead other people

What defines leadership? The ability to define a vision and guide individuals and groups toward that vision while maintaining group-promoting teamwork, commitment, and effectiveness Self awareness and self management abilities Although most people who we see as leaders fall naturally into these positions, these skills can occasionally be learned with careful attention to behaviors of both self and others Not all leaders are good leaders; the ability to “take charge” should not be considered leadership

Characteristics of an Effective Preceptor Communication Skills Ability to explain the reasons for clinical decisions A wealth of knowledge and experience Explains information clearly Evaluation of the Learner Providing positive feedback rather than punishment Motivation Promotes making mistakes as part of the learning process Emphasizes problem solving

Educational Techniques in Preceptorship Committed Teaching Asking for Evidence Reinforcement of Correct Responses and Actions Guidance About Mistakes Relate New Knowledge to Old Knowledge Provide a Summary

Problems Preceptors Face The clinical setting is at a rapid pace which places demands on the preceptor Preceptors have difficulty recognizing their students learning style and their own leadership style Most nurses act as preceptor because they feel obligated to rather then for their love of teaching (Burns et al., 2006)

Solutions The student, preceptor, and faculty must work together to overcome barriers Good preceptors are usually “empathic, warm, respectful, and humorous” (Burns et al., 2006) Preceptors must be aware of how to alter their teaching styles based on what is working for his or her unique group of students Preceptors should become familiar with different kinds of learners, especially adult learners Determining ways to include adult learner’s experience in activities is helpful Preceptors should encourage learning through participation

Educating nurses for leadership roles Heller et al. (2004) proposed that it may be useful to have leadership programs in order to educate preceptors on how to be good educators It is important to understand that people aren’t inherently born with leadership skills and it may be useful to incorporate this kind of a plan to ensure that nursing students are being taught effectively In this study, Heller et al. implemented an “action-learning” course to guide preceptors A majority of the students believed that this course was useful
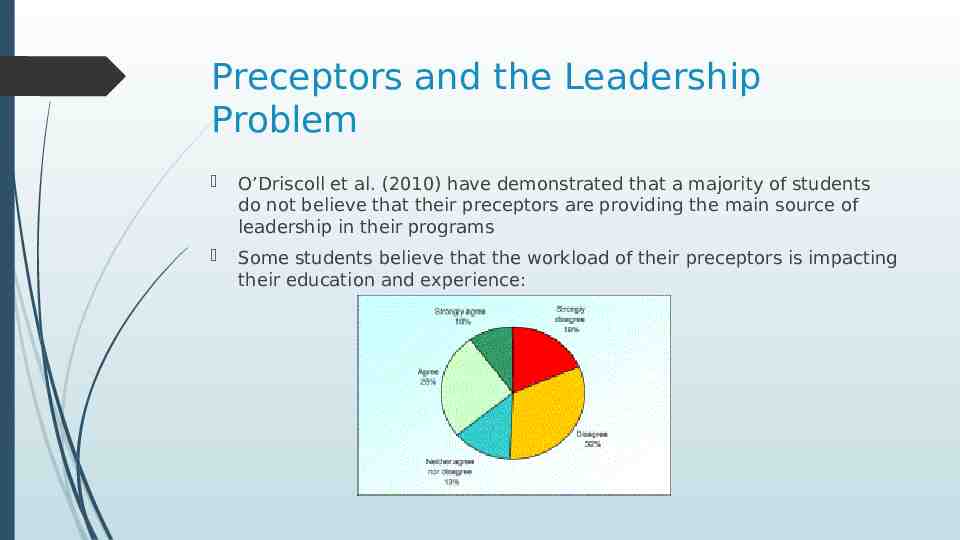
Preceptors and the Leadership Problem O’Driscoll et al. (2010) have demonstrated that a majority of students do not believe that their preceptors are providing the main source of leadership in their programs Some students believe that the workload of their preceptors is impacting their education and experience:

Leadership Problem Cont’d This study also demonstrated that: Lecturers’ presence in clinical areas are decreasing Practice nurses are becoming less involved with pre-registration students Ward managers are usually responsible for leading learning in the wards but that are likely to change their roles to avoid this As a consequence, mentors are primarily teaching the students, although they don’t usually have adequate time for this task because they must see patients

Nursing Leadership and Patient Outcomes Wong et al. (2007) have shown that certain nursing leadership styles lead to better patient outcomes It has also been hypothesized that certain preceptor leadership styles lead to nursing students’ overall success as nurses Psychologists have developed several categories of leadership styles that can describe preceptors and other educators Each individual leadership style is useful in its own situation

Types of Leadership Autocratic Bureaucratic Emphasizes safety and following rules “by the book” Charismatic The preceptor will mainly bark commands at students Enthusiastic and motivation leadership; usually does not lead to change Democratic The leader makes the final decision but the team is involved in decision making (Mind Tools, n.d.)

Types of Leadership (Cont’d) Laissez-Faire People-Oriented Focuses on the team to make decisions Servant Allows people to do work on their own Leads based on the needs of the team Task-Oriented Only focuses on getting the job done

Types of Leadership (Cont’d) Transactional Clear roles and responsibilities but punishment can occur for bad work Transformational Inspiring leadership

Conclusions A major problem with preceptor leadership is that many simply don’t want to teach It may be useful to provide preceptors with a workshop that will help them overcome the problems that they usually face and provide them with useful instructional methods Democratic and servant leadership should be adapted by almost all preceptors because it will enable them to be more effective teachers

References Burns C, Beauchesne M, Ryan-Krause P, Sawin K. (2006). Mastering the Preceptor Role: Challenges of Clinical Teaching. J Pediatr Health Care. Retrieved from http:// www.medscape.com/viewarticle/532189 Heller BR, Drenkard K, Esposito-Herr MB, Romano C, Tom S, Valentine N. Journal Continuing Education in Nursing. Retrieved http:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15481400 Mind Tools. (n.d.). Leadership Styles. Retrieved from http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newLDR 84.htm O’Driscoll MF, Allan HT, Smith PA. (2010). Still looking for leadership – Who is responsible for student nurses’ learning in practice? Nurse Education Today. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0260691709002445 Wong C, Cummings G. (2007). The relationship between nursing leadership and patient outcomes: a systematic review. Nursing Management. Retrieved from http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2007.00723.x/full (2004).