Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management chapter 12 Chapter 12
60 Slides950.00 KB

Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management chapter 12 Chapter 12 Version 6e Prepared by Deborah Baker Texas Christian University 2002 South-Western 1

Learning Objectives 1. Explain what a marketing channel is and why intermediaries are needed. 2. Define the types of channel intermediaries and describe their functions and activities. chapter 12 Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 2

Learning Objectives (continued) chapter 12 3. Describe the channel structures for consumer and business-to-business products and discuss alternative channel arrangements. 4. Define supply chain management and discuss its benefits. 5. Discuss the issues that influence channel strategy. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 3

Learning Objectives (continued) 6. Explain channel leadership, conflict, and partnering. chapter 12 7. Describe the logistical components of the supply chain. 8. Discuss the concept of balancing logistics service and cost. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 4

Learning Objectives (continued) 12 10. Discuss channels and distribution decisions in global markets. chapter 9. Discuss new technology and emerging trends in supply chain management. 11. Identify the special problems and opportunities associated with distribution in service organizations. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 5

Learning Objective 1 Explain what a marketing channel is and why intermediaries are needed. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 6
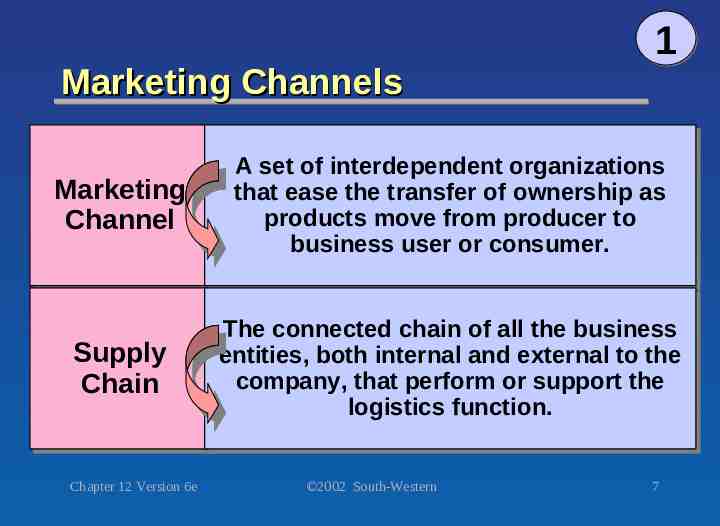
Marketing Channels 1 Marketing Marketing Channel Channel A A set set of of interdependent interdependent organizations organizations that that ease ease the the transfer transfer of of ownership ownership as as products products move move from from producer producer to to business business user user or or consumer. consumer. Supply Supply Chain Chain The The connected connected chain chain of of all all the the business business entities, entities, both both internal internal and and external external to to the the company, company, that that perform perform or or support support the the logistics logistics function. function. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 7
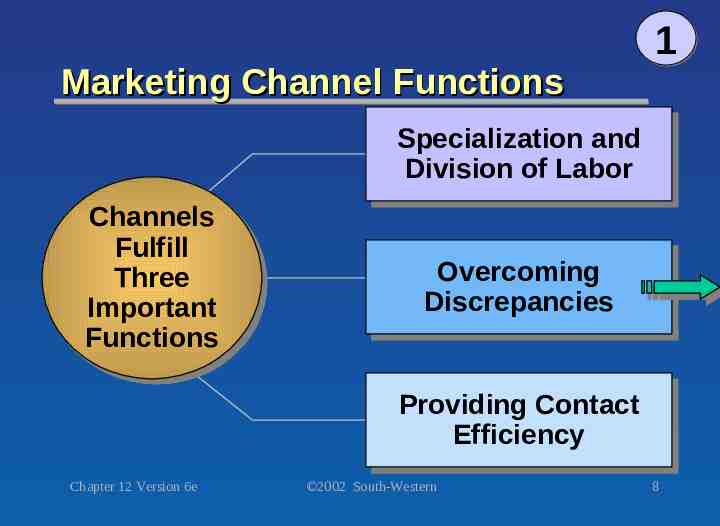
Marketing Channel Functions 1 Specialization Specialization and and Division Division of of Labor Labor Channels Channels Fulfill Fulfill Three Three Important Important Functions Functions Overcoming Overcoming Discrepancies Discrepancies Providing Providing Contact Contact Efficiency Efficiency Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 8

Specialization and Division of Labor 1 Provides economies of scale Aids producers who lack resources to market directly Builds good relationships with customers Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 9

Overcoming Discrepancies Discrepancy Discrepancy of of Quantity Quantity Discrepancy Discrepancy of of Assortment Assortment Chapter 12 Version 6e 1 The The difference difference between between the the amount amount of of product product produced produced and and the the amount amount an an end end user user wants wants to to buy. buy. The The lack lack of of all all the the items items aa customer customer needs needs to to receive receive full full satisfaction satisfaction from from aa product product or or products. products. 2002 South-Western 10

Overcoming Discrepancies 1 Temporal Temporal Discrepancy Discrepancy A A situation situation that that occurs occurs when when aa product product is is produced produced but but aa customer customer is is not not ready ready to to buy buy it. it. Spatial Spatial Discrepancy Discrepancy The The difference difference between between the the location location of of aa producer producer and and the the location location of of widely widely scattered scattered markets. markets. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 11
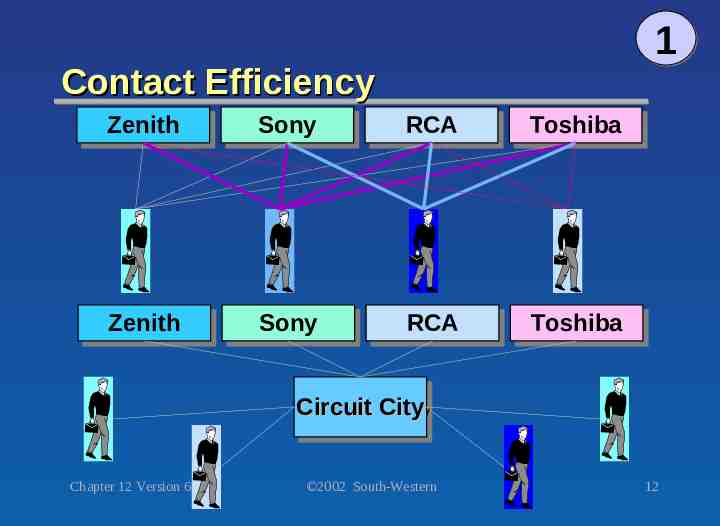
1 Contact Efficiency Zenith Zenith Sony Sony RCA RCA Toshiba Toshiba Zenith Zenith Sony Sony RCA RCA Toshiba Toshiba Circuit Circuit City City Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 12

Learning Objective 2 Define the types of channel intermediaries and describe their functions and activities. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 13
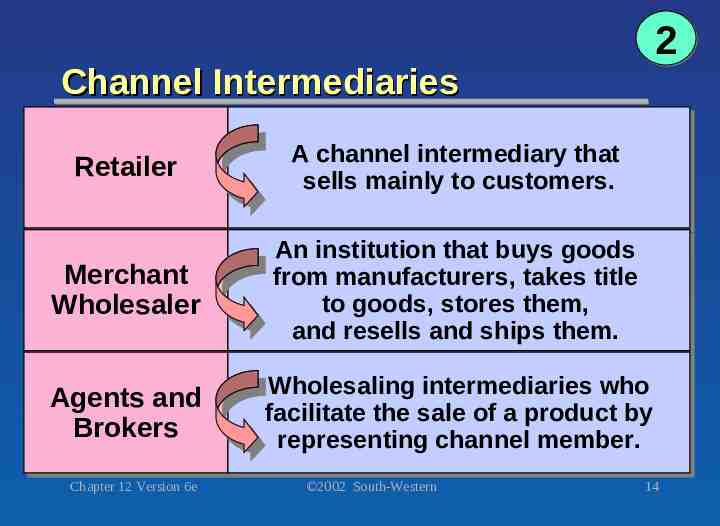
Channel Intermediaries 2 Retailer Retailer A A channel channel intermediary intermediary that that sells sells mainly mainly to to customers. customers. Merchant Merchant Wholesaler Wholesaler An An institution institution that that buys buys goods goods from from manufacturers, manufacturers, takes takes title title to to goods, goods, stores stores them, them, and and resells resells and and ships ships them. them. Agents Agents and and Brokers Brokers Wholesaling Wholesaling intermediaries intermediaries who who facilitate facilitate the the sale sale of of aa product product by by representing representing channel channel member. member. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 14
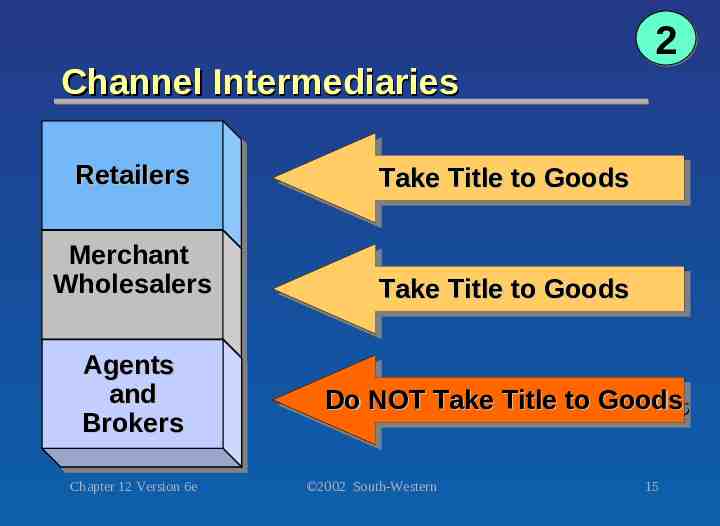
Channel Intermediaries Retailers Retailers Take Take Title Title to to Goods Goods Merchant Merchant Wholesalers Wholesalers Take Take Title Title to to Goods Goods Agents Agents and and Brokers Brokers Chapter 12 Version 6e 2 Do Do NOT NOT Take Take Title Title to to Goods Goods 2002 South-Western 15
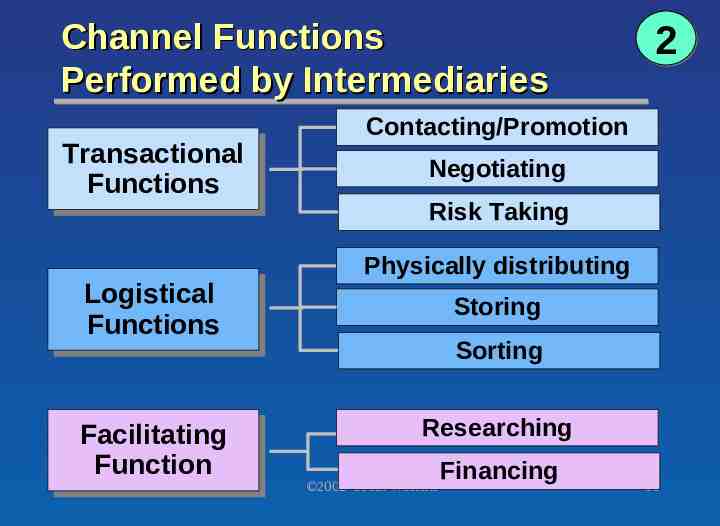
Channel Functions Performed by Intermediaries Transactional Transactional Functions Functions Logistical Logistical Functions Functions Facilitating Facilitating Function Function Chapter 12 Version 6e 2 Contacting/Promotion Negotiating Risk Taking Physically distributing Storing Sorting Researching 2002 South-Western Financing 16

2 Logistics The process of strategically managing the efficient flow and storage of raw materials, in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 17

3 Learning Objective Describe the channel structures for consumer and business-to-business products and discuss alternative channel arrangements. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 18

3 Direct Channel A distribution channel in which producers sell directly to consumers. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 19
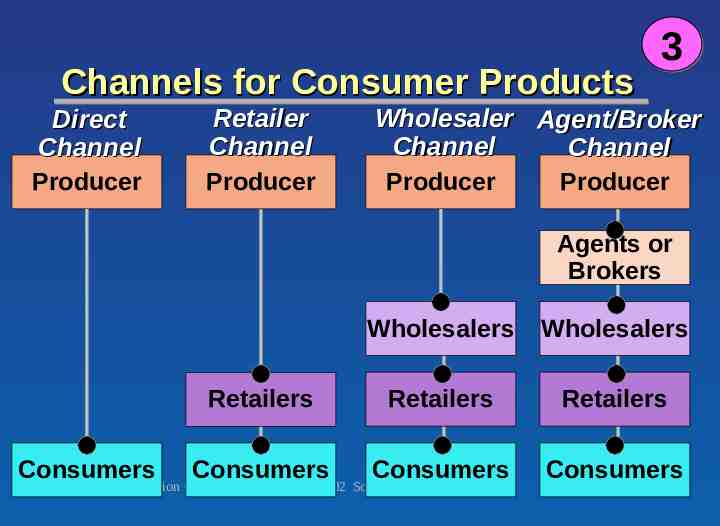
3 Channels for Consumer Products Retailer Channel Producer Direct Channel Producer Wholesaler Agent/Broker Channel Channel Producer Producer Agents or Brokers Consumers Wholesalers Wholesalers Retailers Retailers Retailers Consumers Consumers Consumers Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 20
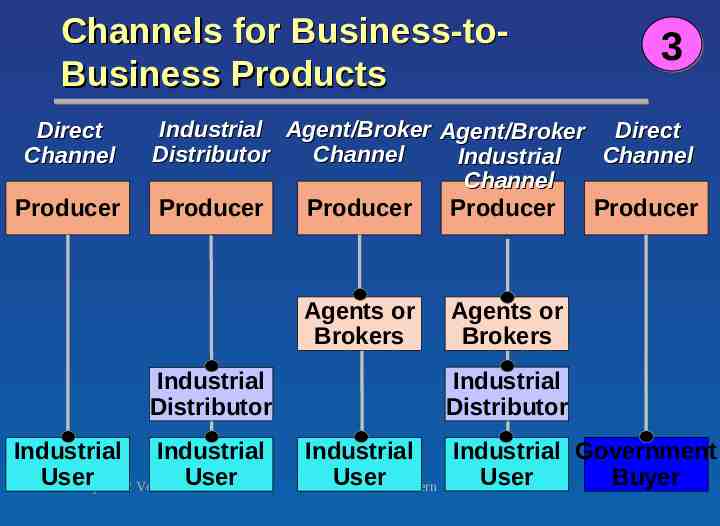
Channels for Business-toBusiness Products Direct Channel Producer 3 Industrial Agent/Broker Agent/Broker Direct Distributor Channel Channel Industrial Channel Producer Producer Producer Producer Agents or Brokers Industrial Distributor Industrial Industrial User User Chapter 12 Version 6e Agents or Brokers Industrial Distributor Industrial Government Industrial User User Buyer 2002 South-Western 21
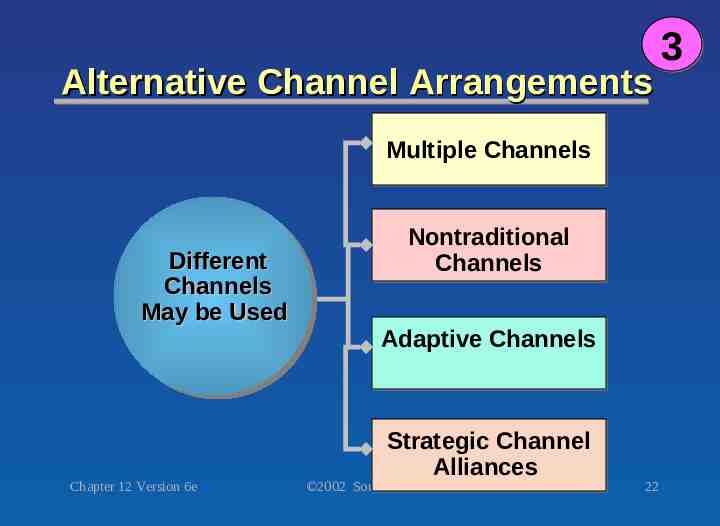
Alternative Channel Arrangements Multiple Channels Different Channels May be Used Chapter 12 Version 6e Nontraditional Channels Adaptive Channels Strategic Channel Alliances 2002 South-Western 22 3

4 Learning Objective Define supply chain management and discuss its benefits. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 23

4 Supply Chain Management A management system that coordinates and integrates all of the activities performed by supply chain members into a seamless process, from the source to the point of consumption. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 24
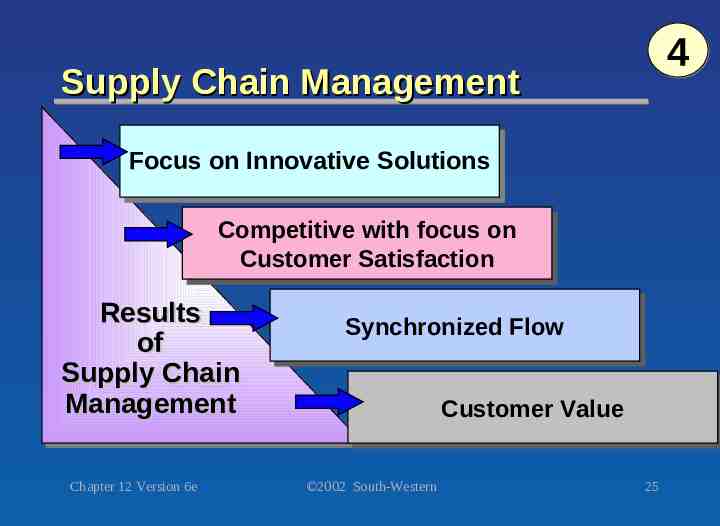
4 Supply Chain Management Focus Focus on on Innovative Innovative Solutions Solutions Competitive Competitive with with focus focus on on Customer Customer Satisfaction Satisfaction Results Results of of Supply Supply Chain Chain Management Management Chapter 12 Version 6e Synchronized Synchronized Flow Flow Customer Customer Value Value 2002 South-Western 25
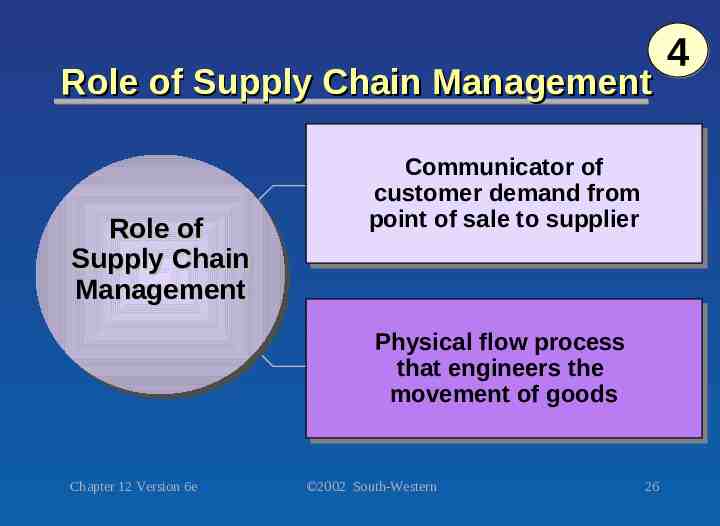
Role of Supply Chain Management Role Role of of Supply Supply Chain Chain Management Management Communicator Communicator of of customer customer demand demand from from point point of of sale sale to to supplier supplier Physical Physical flow flow process process that that engineers engineers the the movement movement of of goods goods Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 26 4
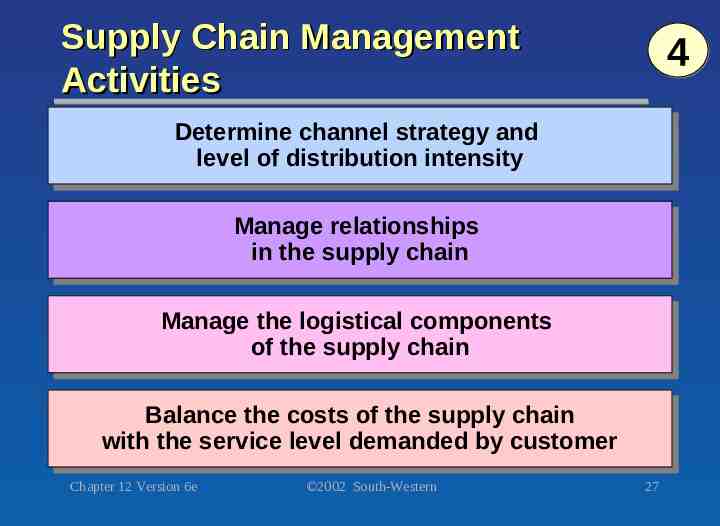
Supply Chain Management Activities 4 Determine Determinechannel channelstrategy strategyand and level level of of distribution distributionintensity intensity Manage Managerelationships relationships in inthe thesupply supplychain chain Manage Managethe thelogistical logisticalcomponents components of ofthe the supply supplychain chain Balance Balancethe thecosts costsof of the thesupply supplychain chain with withthe theservice servicelevel leveldemanded demandedby bycustomer customer Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 27
Benefits of Supply Chain Management 4 Reduced Reduced Costs Costs Improved Improved Service Service Common Common Benefits Benefits of of Supply Supply Chain Chain Management Management Chapter 12 Version 6e Enhanced Enhanced Revenues Revenues 2002 South-Western 28

5 Learning Objective Discuss the issues that influence channel strategy. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 29
5 Channel Strategy Decisions Issues Issues that that Influence Influence Channel Channel Strategy Strategy Factors Factors Affecting Affecting Channel Channel Choice Choice Levels Levels of of Distribution Distribution Intensity Intensity Market Market Factors Factors Intensive Intensive Distribution Distribution Product Product Factors Factors Selective Selective Distribution Distribution Producer Producer Factors Factors Exclusive Exclusive Distribution Distribution Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 30
5 Market Factors Customer Customer Profiles Profiles Consumer Consumer or or Industrial Industrial Customer Customer Market Market Factors Factors That That Affect Affect Channel Channel Choices Choices Chapter 12 Version 6e Size Size of of Market Market Geographic Location 2002 South-Western 31
5 Product Factors Product Product Complexity Complexity Product Product Price Price Product Product Factors Factors That That Affect Affect Channel Channel Choices Choices Chapter 12 Version 6e Product Product Life Life Cycle Cycle Product Product Delicacy Delicacy 2002 South-Western 32
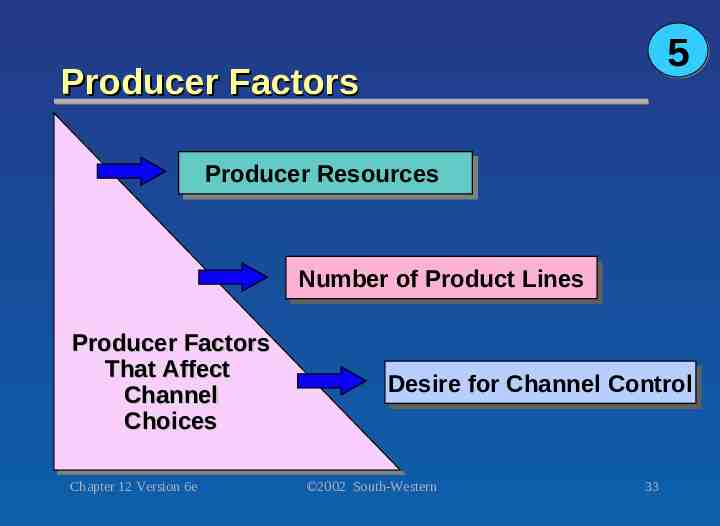
5 Producer Factors Producer Producer Resources Resources Number Number of of Product Product Lines Lines Producer Producer Factors Factors That That Affect Affect Channel Channel Choices Choices Chapter 12 Version 6e Desire Desire for for Channel Channel Control Control 2002 South-Western 33
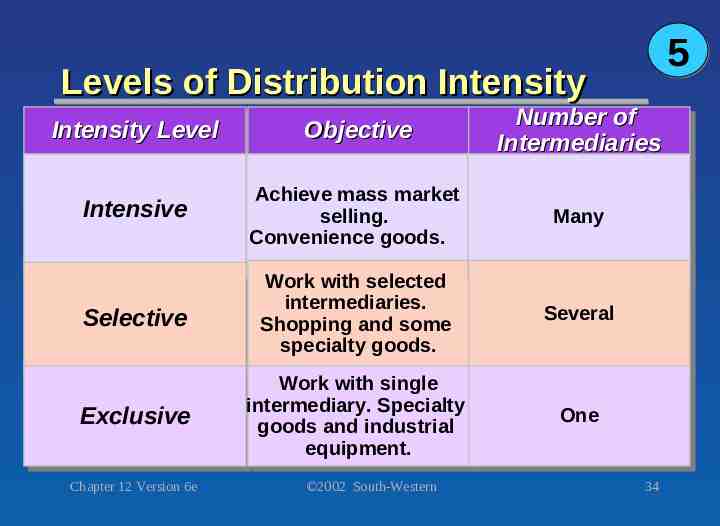
5 Levels of Distribution Intensity Intensity Intensity Level Level Objective Objective Number Number of of Intermediaries Intermediaries Intensive Intensive Achieve Achievemass massmarket market selling. selling. Convenience Conveniencegoods. goods. Many Many Selective Selective Work Workwith withselected selected intermediaries. intermediaries. Shopping Shoppingand andsome some specialty specialty goods. goods. Several Several Exclusive Exclusive Work Workwith withsingle single intermediary. intermediary.Specialty Specialty goods goods and and industrial industrial equipment. equipment. One One Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 34

6 Learning Objective Explain channel leadership, conflict, and partnering. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 35
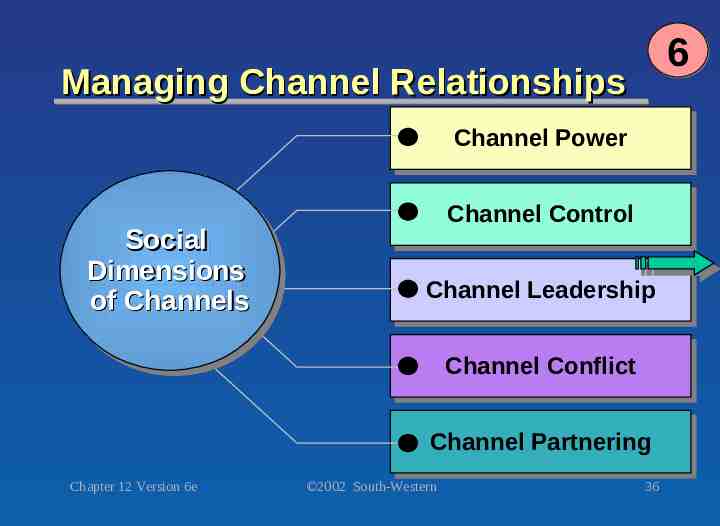
6 Managing Channel Relationships Channel Channel Power Power Social Social Dimensions Dimensions of of Channels Channels Channel Channel Control Control Channel Channel Leadership Leadership Channel Channel Conflict Conflict Channel Channel Partnering Partnering Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 36

Channel Power, Control, and Leadership Channel Channel Power Power 6 A A channel channel member’s member’s capacity capacity to to control control or or influence influence the the behavior behavior of of other other channel channel members members Channel Channel Control Control A A situation situation that that occurs occurs when when one one marketing marketing channel channel member member intentionally intentionally affects affects another another member’s member’s behavior. behavior. Channel Channel Leader Leader A A member member of of aa marketing marketing channel channel that that exercises exercises authority/power authority/power over over the the activities activities of of other other members. members. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 37
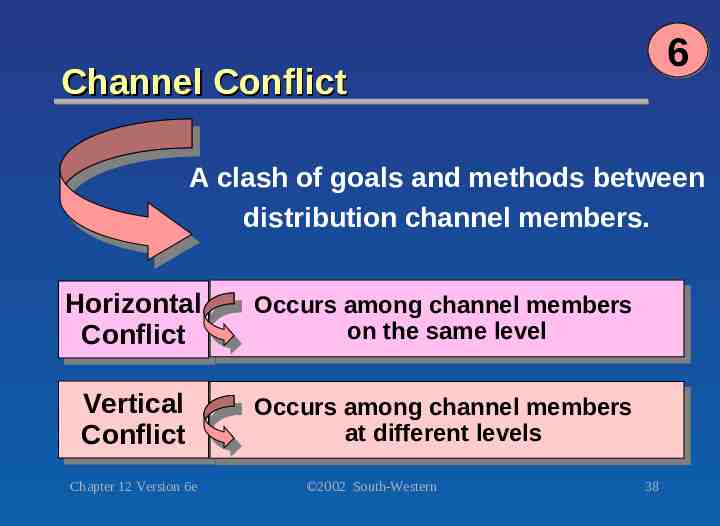
6 Channel Conflict A clash of goals and methods between distribution channel members. Horizontal Horizontal Conflict Conflict Occurs Occursamong amongchannel channelmembers members on onthe thesame samelevel level Vertical Vertical Conflict Conflict Occurs Occursamong amongchannel channelmembers members at atdifferent different levels levels Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 38
6 Channel Partnering The joint effort of all channel members to create a supply chain that serves customers and creates a competitive advantage. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 39
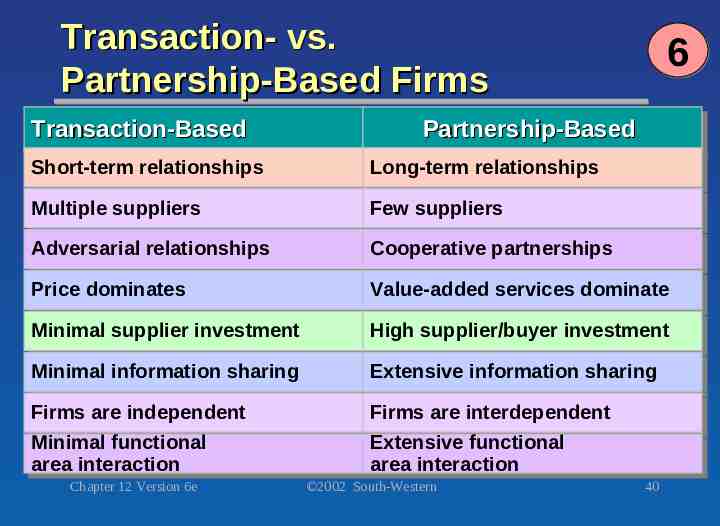
Transaction- vs. Partnership-Based Firms Transaction-Based Transaction-Based 6 Partnership-Based Partnership-Based Short-term Short-termrelationships relationships Long-term Long-termrelationships relationships Multiple Multiple suppliers suppliers Few Fewsuppliers suppliers Adversarial Adversarialrelationships relationships Cooperative Cooperativepartnerships partnerships Price Pricedominates dominates Value-added Value-addedservices servicesdominate dominate Minimal Minimalsupplier supplierinvestment investment High Highsupplier/buyer supplier/buyerinvestment investment Minimal Minimalinformation informationsharing sharing Extensive Extensiveinformation informationsharing sharing Firms Firmsare areindependent independent Minimal Minimalfunctional functional area areainteraction interaction Firms Firmsare areinterdependent interdependent Extensive Extensivefunctional functional area areainteraction interaction Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 40

7 Learning Objective Describe the logistical components of the supply chain. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 41
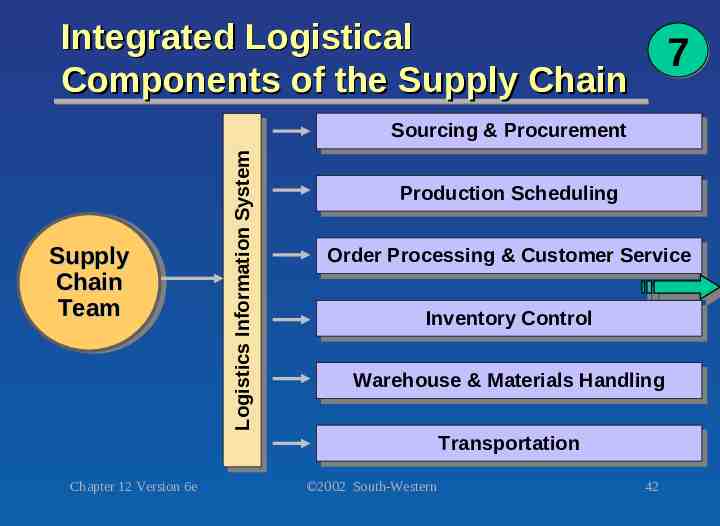
Integrated Logistical Components of the Supply Chain 7 Supply Supply Chain Chain Team Team Chapter 12 Version 6e LogisticsInformation Information System System Logistics Sourcing Sourcing&& Procurement Procurement Production Production Scheduling Scheduling Order OrderProcessing Processing&& Customer Customer Service Service Inventory InventoryControl Control Warehouse Warehouse&&Materials MaterialsHandling Handling Transportation Transportation 2002 South-Western 42
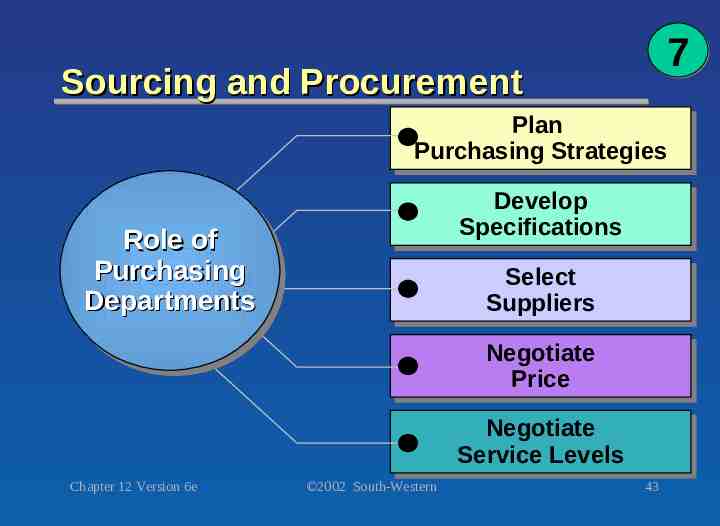
7 Sourcing and Procurement Plan Plan Purchasing Purchasing Strategies Strategies Develop Develop Specifications Specifications Role Role of of Purchasing Purchasing Departments Departments Select Select Suppliers Suppliers Negotiate Negotiate Price Price Negotiate Negotiate Service Service Levels Levels Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 43
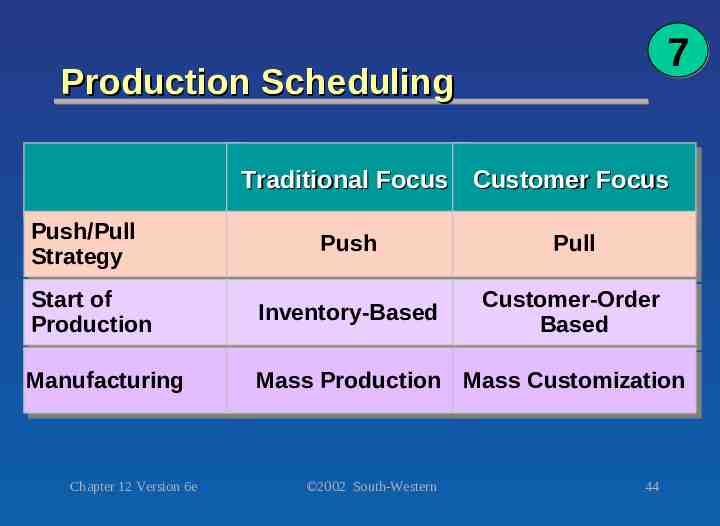
7 Production Scheduling Traditional Traditional Focus Focus Customer Customer Focus Focus Push/Pull Push/Pull Strategy Strategy Push Push Pull Pull Start Start of of Production Production Inventory-Based Inventory-Based Customer-Order Customer-Order Based Based Manufacturing Manufacturing Mass Mass Production Production Mass Mass Customization Customization Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 44

7 Just-in-Time Manufacturing A process that redefines and simplifies manufacturing by reducing inventory levels and delivering raw materials just when they are needed on the production line. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 45

7 Benefits of JIT Reduces raw material inventories Shortens lead times Creates better supplier relationships Reduces production and storeroom costs Reduces paperwork Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 46
7 Electronic Data Interchange Information technology that replaces paper documents that accompany business transactions. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 47
7 Inventory Control System A method of developing and maintaining an adequate assortment of materials or products to meet a manufacturer’s or a customer’s demand. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 48
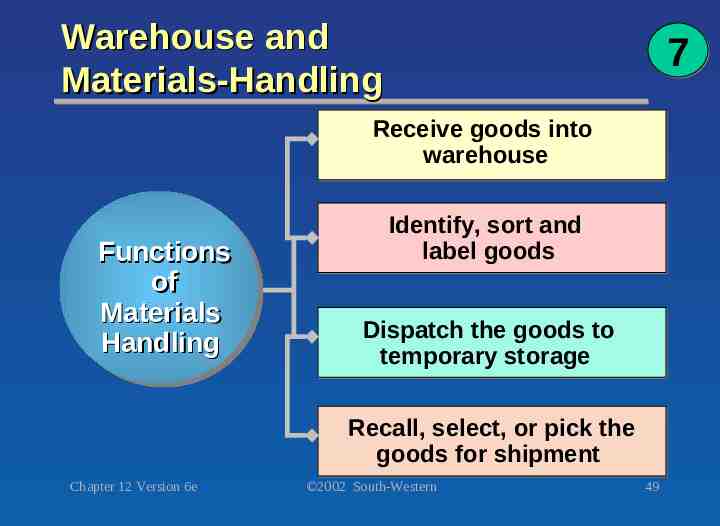
Warehouse and Materials-Handling 7 Receive goods into warehouse Functions of Materials Handling Identify, sort and label goods Dispatch the goods to temporary storage Recall, select, or pick the goods for shipment Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 49
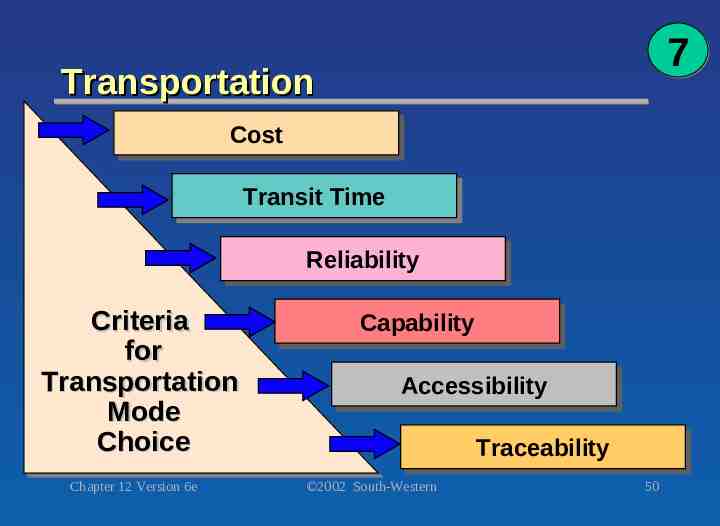
7 Transportation Cost Cost Transit Transit Time Time Reliability Reliability Criteria Criteria for for Transportation Transportation Mode Mode Choice Choice Chapter 12 Version 6e Capability Capability Accessibility Accessibility Traceability Traceability 2002 South-Western 50

Criteria for Ranking Modes of Transportation 7 Lowest Highest Relative Cost Air Truck Rail Pipe Water Transit Time Water Rail Pipe Truck Air Reliability Pipe Truck Rail Air Water Capability Water Rail Truck Air Pipe Accessibility Truck Rail Air Water Pipe Traceability Air Truck Rail Water Pipe Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 51

8 Learning Objective Discuss the concept of balancing logistics service and cost. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 52
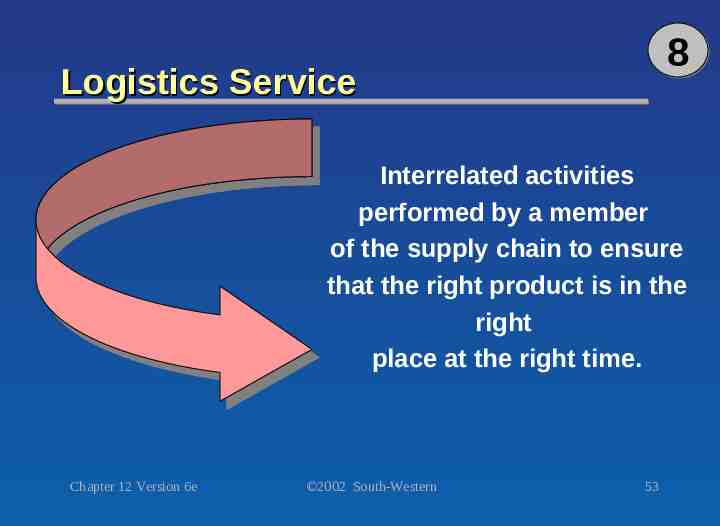
8 Logistics Service Interrelated activities performed by a member of the supply chain to ensure that the right product is in the right place at the right time. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 53

8 Logistical Competencies Devise logistics service strategies as a means of competitive differentiation Integrate members of supply chain to achieve operating excellence Respond quickly to changing logistical requirements Constantly monitor all aspects of the supply chain Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 54

9 Learning Objective Discuss new technology and emerging trends in supply chain management. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 55
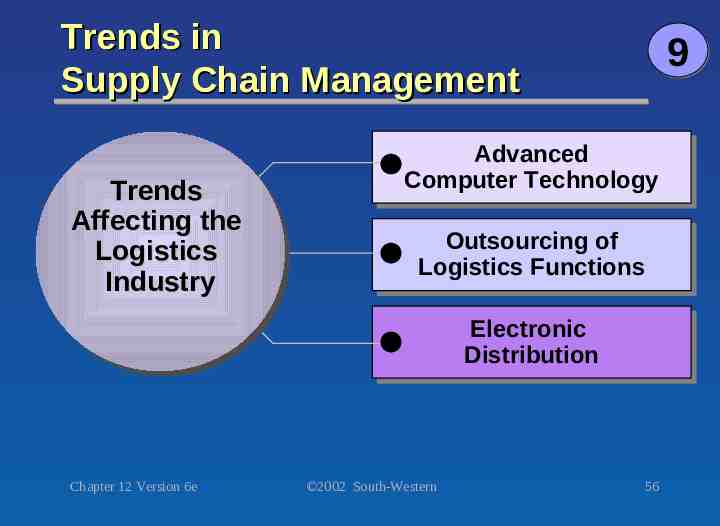
Trends in Supply Chain Management Trends Trends Affecting Affecting the the Logistics Logistics Industry Industry 9 Advanced Advanced Computer Computer Technology Technology Outsourcing Outsourcing of of Logistics Logistics Functions Functions Electronic Electronic Distribution Distribution Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 56

Learning Objective 10 Discuss channels and distribution decisions in global markets. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 57
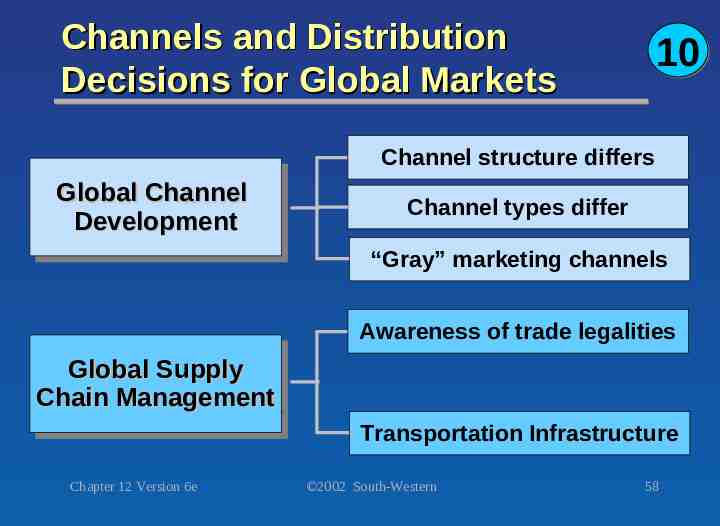
Channels and Distribution Decisions for Global Markets 10 Channel structure differs Global Global Channel Channel Development Development Channel types differ “Gray” marketing channels Awareness of trade legalities Global Global Supply Supply Chain Chain Management Management Transportation Infrastructure Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 58

Learning Objective 11 Identify the special problems and opportunities associated with distribution in service organizations. Chapter 12 Version 6e 2002 South-Western 59
Channels and Distribution Decisions for Services 11 Minimizing Minimizing wait wait times times Managing Managing service service capacity capacity Areas Areas of of Focus Focus for for Service Service Distribution Distribution Chapter 12 Version 6e Improving Improving delivery delivery through through new new channels channels 2002 South-Western 60






