1 Service Management (5e) Operations, Strategy, Information Technology
12 Slides536.00 KB

1 Service Management (5e) Operations, Strategy, Information Technology By Fitzsimmons and Fitzsimmons Chapter – 1 Role of Service in an Economy

1-2 Learning Objectives Describe the central role of services in an economy. Discuss the evolution of an economy from an agrarian society to a service society. Describe the features of preindustrial, industrial, and postindustrial societies. Describe the features of the new service economy

1-3 Service Definitions Services are deeds, processes, and performances. Valarie Zeithaml & Mary Jo Bitner A service is a time-perishable, intangible experience performed for a customer acting in the role of a co-producer. James Fitzsimmons

1-4 Definition of Service Firms Service enterprises are organizations that facilitate the production and distribution of goods, support other firms in meeting their goals, and add value to our personal lives. James Fitzsimmons
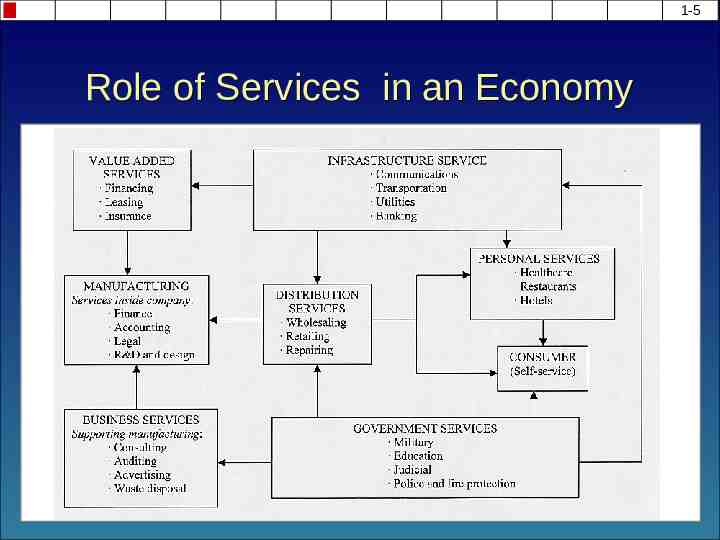
1-5 Role of Services in an Economy
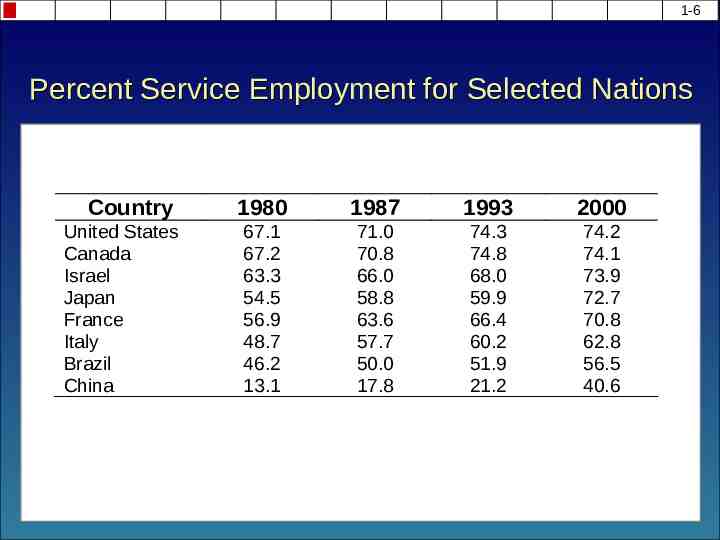
1-6 Percent Service Employment for Selected Nations Country United States Canada Israel Japan France Italy Brazil China 1980 1987 1993 2000 67.1 67.2 63.3 54.5 56.9 48.7 46.2 13.1 71.0 70.8 66.0 58.8 63.6 57.7 50.0 17.8 74.3 74.8 68.0 59.9 66.4 60.2 51.9 21.2 74.2 74.1 73.9 72.7 70.8 62.8 56.5 40.6
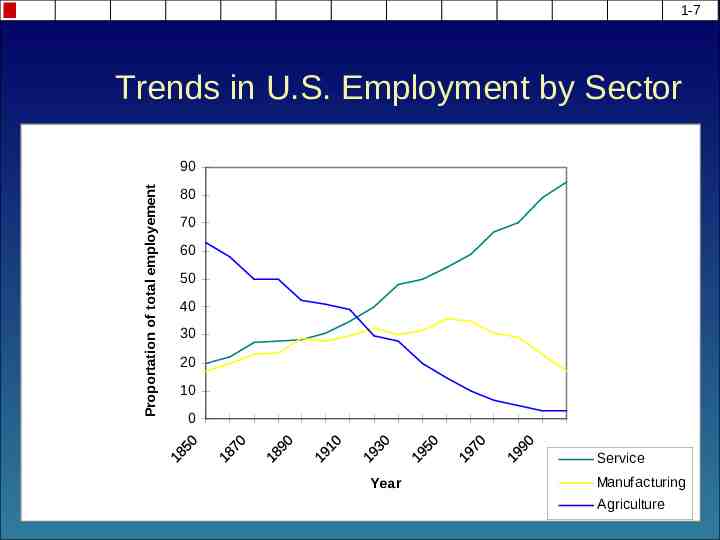
1-7 Trends in U.S. Employment by Sector Proportation of total employement 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Service Year Manufacturing Agriculture
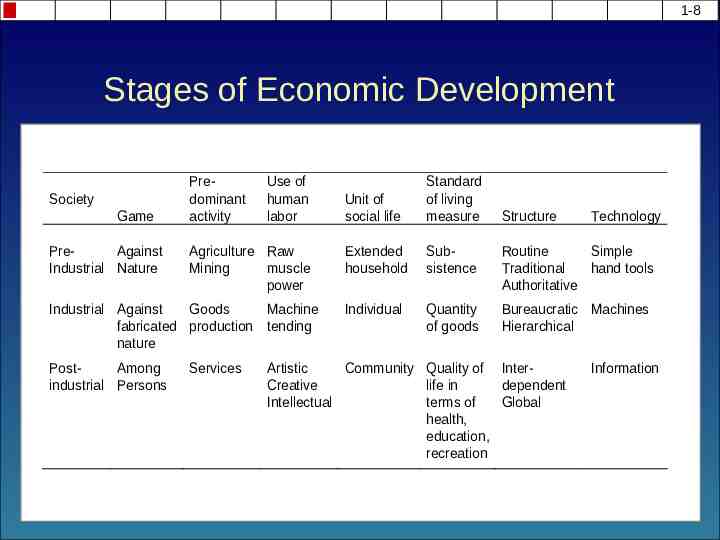
1-8 Stages of Economic Development Society Game PreAgainst Industrial Nature Predominant activity Use of human labor Agriculture Raw Mining muscle power Industrial Against Goods Machine fabricated production tending nature PostAmong industrial Persons Services Unit of social life Standard of living measure Extended household Subsistence Routine Simple Traditional hand tools Authoritative Individual Quantity of goods Bureaucratic Machines Hierarchical Structure Artistic Community Quality of InterCreative life in dependent Intellectual terms of Global health, education, recreation Technology Information
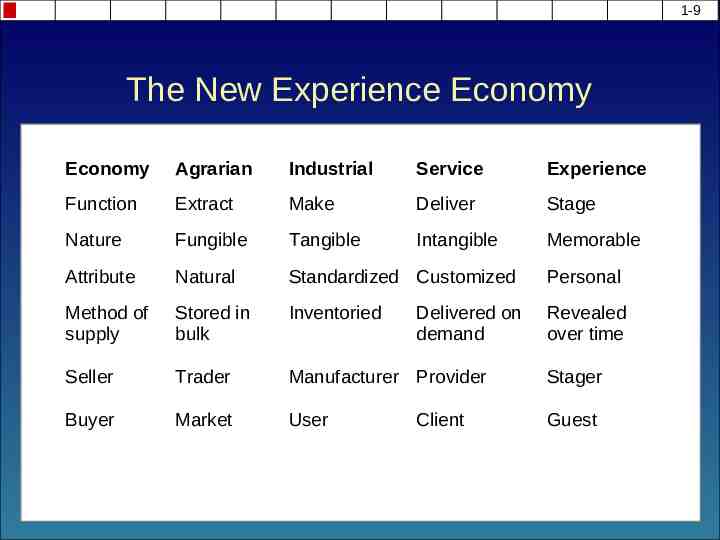
1-9 The New Experience Economy Economy Agrarian Industrial Service Experience Function Extract Make Deliver Stage Nature Fungible Tangible Intangible Memorable Attribute Natural Standardized Customized Personal Method of supply Stored in bulk Inventoried Revealed over time Seller Trader Manufacturer Provider Stager Buyer Market User Guest Delivered on demand Client
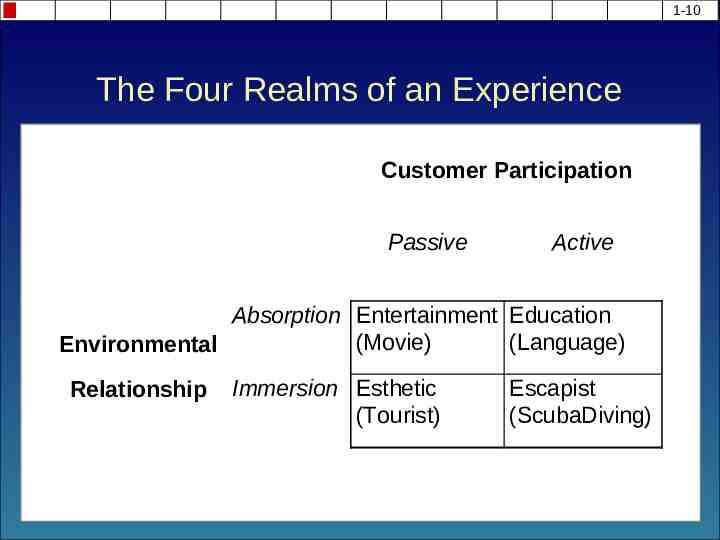
1-10 The Four Realms of an Experience Customer Participation Passive Active Absorption Entertainment Education (Movie) (Language) Environmental Relationship Immersion Esthetic (Tourist) Escapist (ScubaDiving)

1-11 Experience Design Principles Theme the Experience (Forum shops) Harmonize Impressions with Positive Cues (O’Hare airport parking garage) Eliminate Negative Cues (Cinemark talking trash containers) Mix in Memorabilia (Hard Rock T-shirts) Engage all Five Senses (Mist in Rainforest)

1-12 Source of Service Sector Growth Innovation Push theory (e.g. Post-it) Pull theory (e.g. Cash Management) Services derived from products (Video Rental) Information driven services Difficulty of testing service prototypes Social Trends Aging of the population Two-income families Growth in number of single people Home as sanctuary






