Human Resources Management Chapter 1 STRATEGIC HUMAN RESOURCE
31 Slides1.02 MB

Human Resources Management Chapter 1 STRATEGIC HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: AN OVERVIEW 1-1

1-2 Human Resource Management Utilization of individuals to achieve organizational objectives All managers at every level must concern themselves with human resource management Five functions

1-3 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS
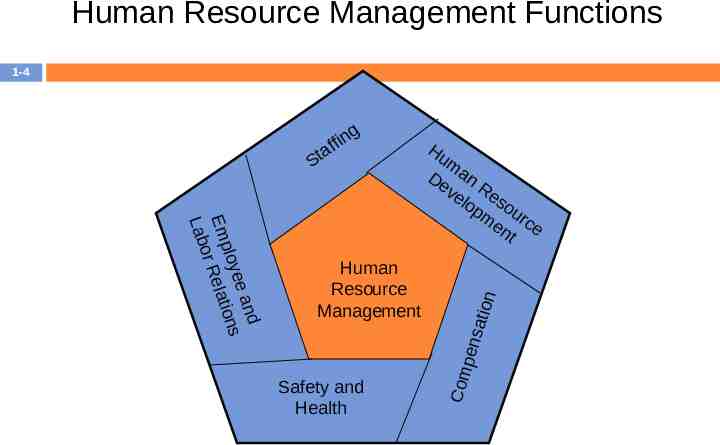
Human Resource Management Functions 1-4 g d e an s loye on Emp Relati or Lab Human Resource 1 Management Safety and Health Hu m De an ve Re lop so me urc nt e Com pens ation St in af f

Staffing Job Analysis Human Resource Planning Recruitment Selection 1-5

1-9 Human Resource Development Training Development Career Planning Career Development Organizational Development Performance Management Performance Appraisal

Compensation Compensation All rewards that individuals receive as a result of their employment 1-13

Compensation 1-14 Direct Financial Compensation - Pay that person receives in form of wages, salaries, bonuses, and commissions Indirect Financial Compensation (Benefits) All financial rewards not included in direct compensation such as paid vacations, sick leave, holidays, and medical insurance Nonfinancial Compensation - Satisfaction that person receives from job itself or from psychological and/or physical environment in which person works

Safety and Health Employees who work in safe environment and enjoy good health are more likely to be productive and yield long-term benefits to organization. 1-15

Legal Considerations Federal, state and local legislation Court decisions Presidential executive orders 1-17

HR’s Changing Role: Questions That Are Being Asked 1-18 Can some HR tasks be performed more efficiently by line managers or outside vendors? Can some HR tasks be centralized or eliminated altogether? Can technology perform tasks that were previously done by HR personnel? Many HR departments continue to get smaller.

1-19 HR’s Changing Role: Who Performs Human Resource Management Tasks? Human Resource Managers HR Outsourcing HR Shared Service Centers Professional Employer Organization (Employee Leasing) Line Managers Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall

Human Resource Manager 1-20 Historically, the human resource manager was responsible for each of the five HR functions Acts in advisory or staff capacity Works with other managers to help them deal with human resource matters Today HR departments continue to get smaller because others are accomplishing certain functions Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall

HR Outsourcing Transfers responsibility to an external provider Market for HR outsourcing is growing dramatically 1-21

1-22 HUMAN RESOURCE AS A STRATEGIC PARTNER
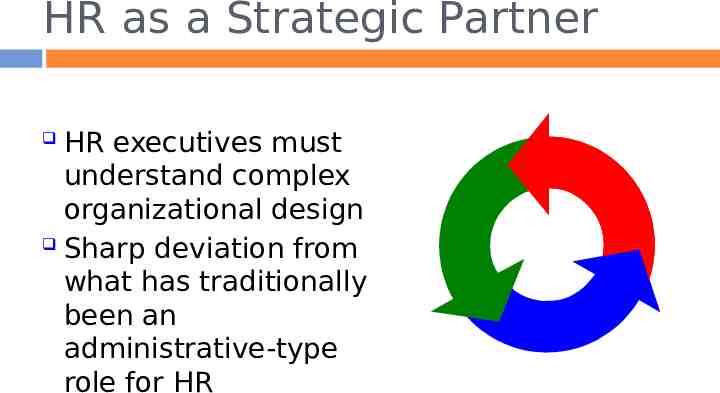
HR as a Strategic Partner HR executives must understand complex organizational design Sharp deviation from what has traditionally been an administrative-type role for HR 1-23

1-24 Strategic Activities CEOs Want from HR Make workforce strategies integral to company strategies and goals Leverage HR’s role in major change initiatives Earn the right to a seat at the corporate table Understand finance and profits Help line managers achieve their goals

Strategic Activities CEOs Want from HR (Cont.) 1-25 HR professionals must integrate goals of HR with goals of the organization Must focus on expanding its strategic and high-level corporate participation with an emphasis on adding value HR must demonstrate that it can produce a return on investment for its programs

1-26 Questions to Be Answered to Determine if HR Is Involved Strategically Is HR present at mergers and acquisitions planning meetings, strategy reviews, and restructuring discussions? Does HR provide an annual report on its ROI? Does HR lead the people strategy? Has it developed performance indicators for the success of that strategy?

1-27 Questions to Be Answered to Determine if HR Is Involved Strategically (Cont.) Is HR rated by its customers? Does the organization conduct strategic versus entitlement employee surveys? Are employee and other survey initiatives linked to customer and financial metrics? Is there an ROI process to evaluate HR initiatives connected to the business strategy?

Human Capital Metrics Measures of HR performance 1-28

Examples of HR Metrics 1-29 Time to fill open positions HR headcount ratios Administrative cost per employee Turnover cost Training return on investment Quality of hire

1-30 HUMAN RESOURCE DESIGNATIONS

1-31 Characteristics of an HR Executive Performs one or more HR functions A top-level manager Reports directly to CEO or head of major division

1-32 Characteristics of an HR Generalist Performs tasks in various HR-related areas Involved in several, or all, of the five HRM functions

1-33 Characteristics of an HR Specialist May be an HR executive, manager, or non-manager Typically concerned with only one of the five functional areas

1-34 EVOLUTION OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT

Traditional Human Resource Function in Large Firm 1-35 Separate sections were often created Placed under an HR Manager Each HR function may have a supervisor & staff HR Manager works closely with top management in formulating policy
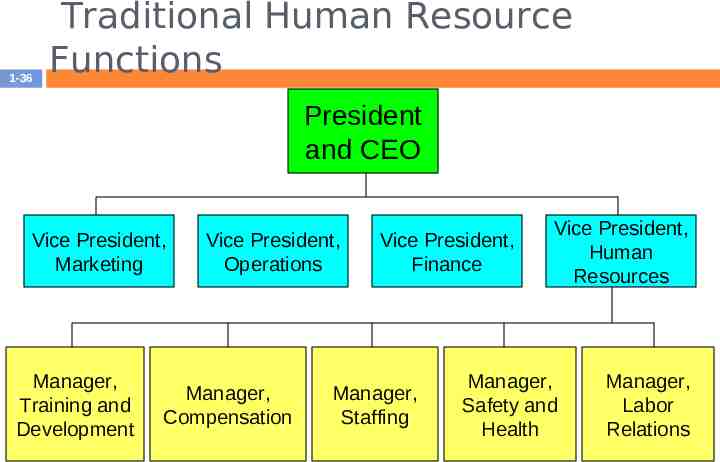
1-36 Traditional Human Resource Functions President and CEO Vice President, Marketing Manager, Training and Development Vice President, Operations Manager, Compensation Vice President, Finance Manager, Staffing Vice President, Human Resources Manager, Safety and Health Manager, Labor Relations
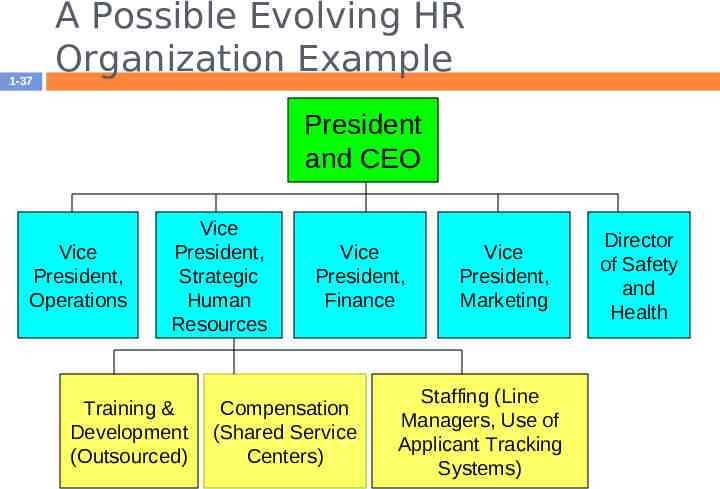
1-37 A Possible Evolving HR Organization Example President and CEO Vice President, Operations Vice President, Strategic Human Resources Training & Development (Outsourced) Vice President, Finance Compensation (Shared Service Centers) Vice President, Marketing Staffing (Line Managers, Use of Applicant Tracking Systems) Director of Safety and Health

Next 1-38 PART II. HR ETHICAL, LEGAL, AND SOCIAL CONSIDERATIONS Chapter 3: Workforce Diversity, Equal Employment Opportunity, and Affirmative Action






