EDUKNOWLEDGE A Framework for Educational Purposes Asst. Prof.
19 Slides217.43 KB

EDUKNOWLEDGE A Framework for Educational Purposes Asst. Prof. Dr. Thotsapon Sortrakul Aung Than Oo - ID: 5819455 IT6417 – Knowledge Management Faculty of Science & Technology Department of Information Technology

Intro “Managing Knowledge" means delivering the understanding of information and data people need to be effective in their jobs. Implementations of knowledge management focus on four main aspects: People: knowledge users, knowledge authors and knowledge analysts) Culture: create a culture where knowledge sharing is the norm Content: creating and managing data, information, and knowledge Technology: technical infrastructure that enables the capture, storage, and delivery of content In the view of modern constructivist learning theories – is not just transferring knowledge; it is a highly individualized task of construction

About E-Learning E-learning can be defined as learning using electronic technologies such as computer- and Internet-based courseware and local and wide area networks E-learning is essentially the network-enabled transfer of skills and knowledge. Content is delivered via the Internet, intranet/extranet, audio or video tape, satellite TV, and CD-ROM

E-Learning Process Learning process in an e-learning systems can be seen in two approach Technology driven development approach: Learning media Learning environment Categories of learning Learning objectives Learner Pedagogical driven development approach: Learner Learning objectives Categories of learning Learning environment Learning media

Eduknowledge A Framework for Educational Purposes Eduknowledge is mainly goal oriented, education tailored knowledge framework. Object like educational tailored knowledge Is a process of developing and adapting specific knowledge for educational purposes

Eduknowledge Components The main eduknowledge components are as below; The eduknowledge header: which gives details regarding the specific eduknowledge chunk and also acts as a user-friendly interface. The preliminary examples: which are introducing students in the specific domain of activity. The basic chunk of knowledge: that gives the ways to perform the specific task for which the eduknowledge was built.
Eduknowledge Components (Cont.) How to do (HTD) knowledge: which shows how to perform specific tasks related to the main task. Maintenance (M) knowledge: which has the role to help in solving specific problems that could appear during the task performance. Examples and case studies: are used in order to give the student the possibility to see in practice the applications of the knowledge.
Eduknowledge Components (Cont.) Dissemination mechanism: the tutorial mechanism used to train the student. Feedback mechanism: the mechanism used to take the feedback from the student and use it to adapt accordingly the tutorial process.
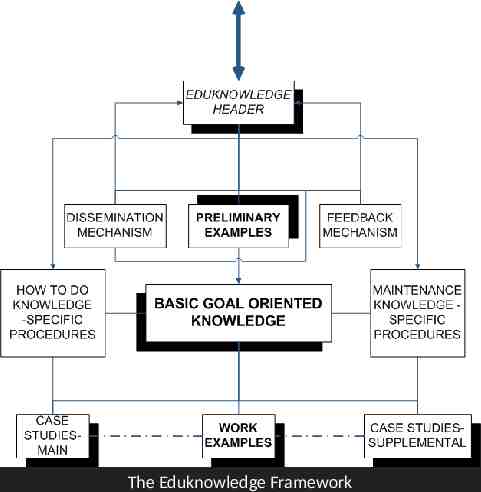
The Eduknowledge Framework

Eduknowledge Framework Design The team for the design phase must include minimal: Knowledge engineers Educational (instructional) designers Delivery designers [Landoni 2003]

Eduknowledge Framework Design (Cont.) The design team must perform the following main steps in order to optimally design the eduknowledge: Development of an optimal model of the task performance (regarding the task that will be the eduknowledge’s goal) Identification of the knowledge pool Identification of the specific knowledge chunks mapped on the logical steps for task performing Design the eduknowledge frame

Eduknowledge Framework Design (Cont.) Design the eduknowledge performance mechanisms Design the eduknowledge performance indicators Design of the eduknowledge delivery structure Development of the eduknowledge prototype [Landoni 1997] Testing the eduknowledge prototype
Eduknowledge Framework Design (Cont.) The design phase is based upon conceptual models, structured in two distinct structures: The model structure of education The model structure of actors the teacher [Yokohama 2006] the student the learning environment
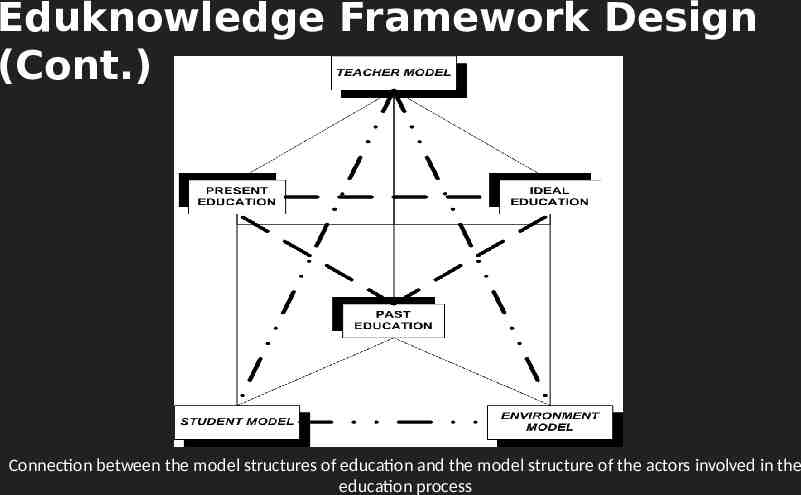
Eduknowledge Framework Design (Cont.) Connection between the model structures of education and the model structure of the actors involved in the education process

Interaction between Knowledge Management and ELearning The training is provided through 4 different\ media: User Guides: Users receive an email or announcements on the knowledge management newsletter regarding changes and upgrades and are encouraged to download the latest version of the guide. FAQ: FAQ documents are created based on questions received from users over time and sent to K-advisors and reflect user’s needs and feedback.

Interaction between Knowledge Management and ELearning The training is provided through 4 different media: Computer Based Training was developed by the knowledge management team and are stored on Learning Management System the knowledge management community of practice which is available to everyone and can be downloaded from there. Digital library: Digital library tools help users find the right information amidst a huge amount of digital material. Digital library features usually include search, browsing, and discovering special collections or exhibits. Search and browsing are used to locate resources and explore related topics.
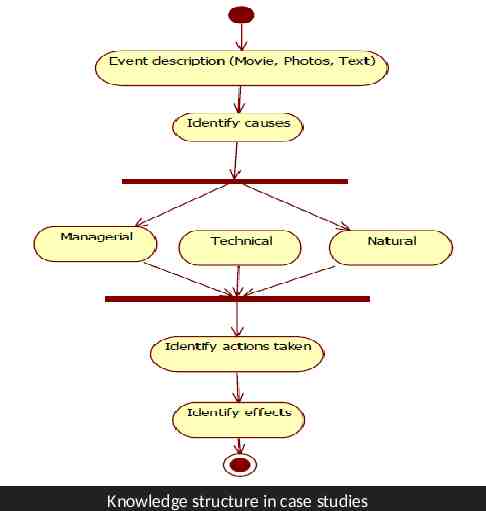
Knowledge structure in case studies

Conclusion The knowledge structure lead us to the conclusion that rules are appropriate for representing knowledge.

THANK YOU






