Deputy State Veterinarian Seminar Montana Department of Livestock
72 Slides7.80 MB

Deputy State Veterinarian Seminar Montana Department of Livestock

MDOL Divisions Governor appointed Board comprised of 7 members: 1 each of dairy, sheep, swine and 4 beef producers. Animal Health And Food Safety Division Animal Health Diagnostic Laboratory Meat Inspection Milk and Egg Brands Enforcement

MDOL Divisions Animal Health And Food Safety Division Animal Health Diagnostic Laboratory Meat Inspection Milk and Egg Brands Enforcement Rule writing Import regulations Disease reporting Disease control programs Brucellosis Trichomoniasis Rabies Others Alternative Livestock

MDOL Divisions Animal Health and Food Safety Division Brands Enforcem ent Brands administrator 2 Area supervisors 16 District investigators 13 Markets Brand inspection required on cattle, horses, & sheep to cross county lines

32.3.138 DEPUTY STATE VETERINARIAN "Deputy State Veterinarian" means a veterinarian licensed in the state of Montana and deputized to perform state functions pursuant to ARM 32.3.139 of this subchapter who is not a current employee of the department or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

32.3.140 DUTIES a) Be aware of and follow all applicable regulations and instructions as outlined on the Deputy State Veterinarians section of the department's website; b) Be aware of and follow all applicable regulations and instructions as outlined in 9CFR; c) Quarantine in writing all animals exposed to a quarantinable disease upon suspicion of diagnosis in the absence of, or on the order of the state veterinarian. Immediate notification of quarantine must be made to the Montana State Veterinarian's office by phone, fax, or mail; d) Report immediately all cases of quarantinable diseases (ARM 32.3.104 and 32.3.105) to the state veterinarian in Helena, by telephone or fax; e) Release quarantine upon the direction of the state veterinarian and ARM 32.3.106 through 32.3.108;

32.3.140 DUTIES (cont.) f) Be responsible for proper use of all official certificates, forms, records, reports, tags, or other official identification used in the work as a deputy state veterinarian and take proper precautions to prevent misuse thereof; g) Immediately report the loss, theft, deliberate or accidental misuse of any official document or materials as listed above in (1)(d), and must keep these materials in only his/her custody prior to official use; h) File a monthly form regarding other reportable diseases; i) Email weekly, all required inspection forms, test charts, certificates of veterinary inspection, and vaccination certificates made during the week.

Duties of a Deputy State Veterinarian Email weekly all interstate certificates of veterinary inspection (ICVI)’s, test charts, inspection forms and vaccination certificates. CFR 86.5 (b)(1) the accredited veterinarian issuing an ICVI must forward a copy of the ICVI or other documentation to the state animal health official of the state of origin within 7 calendar days of the date of issuance. CFR 86.5 (b)(2) must keep a copy of the ICVI or alternate documentation For poultry and swine, for at least 2 years For cattle and bison, sheep and goats, cervids, and equines; for at least 5 years.

A Right or a Privilege? Not all licensed veterinarians are deputized. Non-deputized veterinarians cannot: Issue interstate certificates of veterinary inspection or use other official MDOL forms. Perform official trichomoniasis testing. Quarantine animals within the state of Montana. Deputization can be revoked.

Disease Reporting 81-2-107 Duty to Report - A person, including the owner or custodian, who has reason to suspect the existence of a dangerous, infectious, contagious, or communicable disease in livestock or the presence of animals exposed to the disease in this state shall immediately give notice to the department.

Diseases requiring IMMEDIATE reporting! May be reported to either the state or federal office. A verbal quarantine should be placed on premises. Quarantine should include all susceptible species.

3 Types of Quarantines: 1. Epidemiologic investigation by MDOL Conducted by MDOL/USDA on entire herd when an animal tests positive for select quarantinable diseases 2. Post- entry/illegal import Quaranti nes Issued when import requirements are not met before importing animals into MT Can be issued by deputy state veterinarian or Brands Enforcement Officers 3. Import exemption quarantine Requested by issuing veterinarian or MT producer One of the MT state veterinarians authorize animals to enter state prior to meeting import requirements
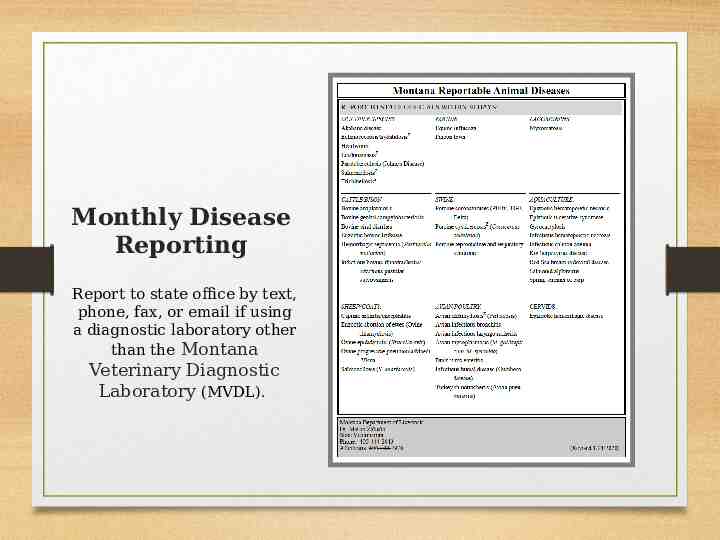
Monthly Disease Reporting Report to state office by text, phone, fax, or email if using a diagnostic laboratory other than the Montana Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory (MVDL).

Please remember Only submissions through the MVDL are automatically reported to our office. If you are using an alternate laboratory or are doing in house diagnostics, you must notify our office when a reportable disease is diagnosed. The reportable disease list is dynamic. Additions/removals based on feedback.

In the Past 24 months Brucellosis Brucella canis Johne’s Strangles West Nile virus Chronic Wasting Disease Rabies EHV-1 CAE Avian Influenza Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Tuberculosis EEE

Rabies Montana law references the Compendium of Animal Rabies Prevention and Control (2016).

Management of rabies 10 days Quarantine for dogs, cats, and ferrets that expose humans. 28 days Protective immune response following initial vaccination. 45 days Observation period for vaccinate exposed to a rabies positive animal. 60 days Length of county quarantine following positive terrestrial rabies case. 120 days Quarantine for non-vaccinates exposed to a positive, unsuitable, or unavailable animal.
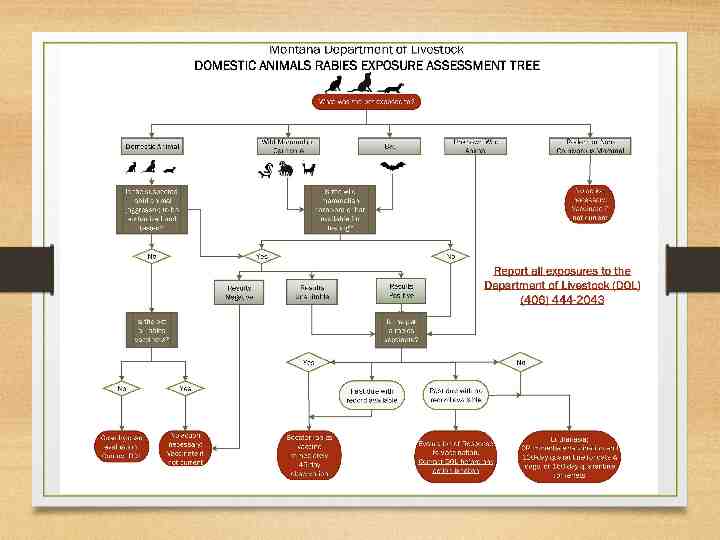
What is the veterinarian’s role? Education 45-day observation period 60-day county quarantine Vaccination 4-month quarantine Contact DOL Vaccination of animal at beginning of quarantine period Mid and Final examination of animals under quarantine Communication with and education of client Mandatory Reporter 37.114.201 any person, including, but not limited to a physician, dentist, nurse, medical examiner, other health care practitioner, administrator of a health care facility or laboratory, public or private school administrator, or laboratory professional who knows or has reason to believe that a case exists of a reportable disease or condition defined in ARM 37.114.203 must immediately report to the local health officer the information specified in ARM 37.114.205(1) and (2).

Human Exposure MDOL and DPHHS will work with the individual, the local veterinarian, animal control, and local public health officials to determine case management. Human bitten by animal: Contact public health /- animal control 37.114.203 Reportable Diseases and Conditions (at) Rabies in a human or animal; exposure to a human by a species susceptible to rabies infection 10-day quarantine regardless of vaccination status Do not vaccinate during 10-day quarantine Do not euthanize animal without permission & without testing!

Vaccination No state law requiring rabies vaccination Vaccination requirements are set by city and county ordinances Vaccination certificates should be consistent with the vaccine label

Can someone other than you administer the rabies vaccination? 32.3.2301 CONTROL OF BIOLOGICS (5) The sale of any rabies biologic except to a licensed veterinarian or public health agency is prohibited. Compendium of Animal Rabies Prevention and Control, 2016 Preexposure vaccination and management. Adherence to a regular rabies vaccination schedule is critical to protect animals against recognized and unrecognized rabies exposures. Parenteral animal rabies vaccines should be administered only by or under the direct supervision of a licensed veterinarian on premises. Rabies vaccines may be administered under the supervision of a licensed veterinarian to animals held in animal shelters before release.33,34 The veterinarian signing a rabies vaccination certificate must ensure that the person who administered the vaccine is identified on the certificate and has been appropriately trained in vaccine storage, handling, and administration and in the management of adverse events. This ensures that a qualified and responsible person can be held accountable for properly vaccinating the animal

Certificate of Veterinary Inspection (CVI) Health Certificate

Certificate of Veterinary Inspection ICVIs MUST INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Species covered Number of animals in shipment Purpose for movement Physical address from which animals originated Physical address that animal are destined to PO Boxes are not an acceptable address Name and address of consignor and consignee (if different) Official identification must be recorded for animals required to be officially identified

Certificate of Veterinary Inspection Examination/inspection of animals MUST be performed within 10 days prior to date of issuance unless monthly visits conducted. Valid for 30 days from the date of inspection. Required for out of state travel and some in-state exhibitions/shows. Must meet state of destinations import requirements. Animals returning to MT must meet our import requirements – potential impact to sporting bovine movements.

Certificate of Veterinary Inspection Fill out CVI completely and legibly, this is a legal document. Document all exemptions or special instructions including the name of person giving information. Accurately describe the age, gender, species, color and official ID of all animals on shipment. Verify test results. Do NOT re-tag animals with existing official ID (Bangs tags, silver USDA tags, Scrapie or RFID tags). Obtain all required permits: State of destination import permit if applicable. Montana re-entry permit if applicable. Sign and date the form.

Interstate Movement Prohibited Equine/ bovine piroplasmosis Anthrax Cattle scabies Pseudorabies Acute swine erysipelas TB See 9CFR 71.3 Johne’s Disease Brucellosis Scrapie Bluetongue Chlamydiosis Salmonella enteritidis serotype enteritidis Newcastle Disease

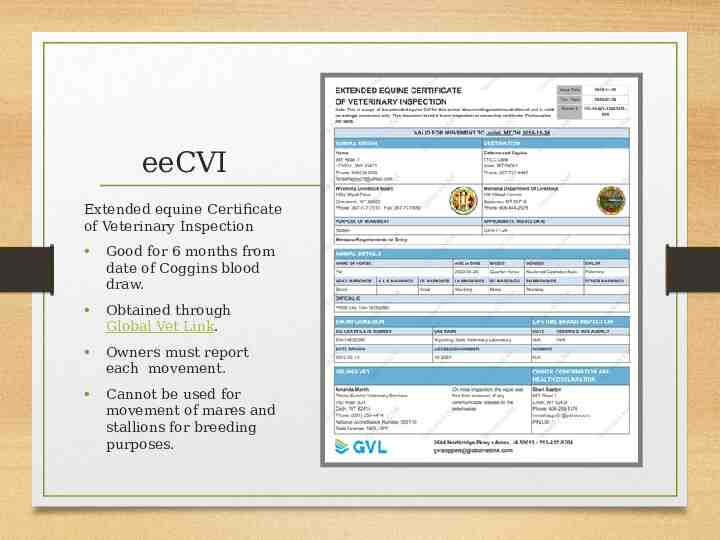
eeCVI Extended equine Certificate of Veterinary Inspection Good for 6 months from date of Coggins blood draw. Obtained through Global Vet Link. Owners must report each movement. Cannot be used for movement of mares and stallions for breeding purposes.

As a DSV you have quarantine authority in MT for animals who have entered without meeting import requirements. Verbal or written. Information must be relayed to Illegal Impor ts MDOL. Quarantine animals until requirements have been met and/or post illegal permit number is obtained from MDOL. Complete: Required testing/vaccination Call MDOL for post illegal permit number with the following information: 1. origin address 2. destination address 3. animal details (species, sex, breed, age, identification)
Traceability

Traceability - The Basics Official individual identification required* for interstate movement: All sexually intact cattle and bison 18 months of age and older All dairy cattle All animals for exhibition/sporting M branded cattle* Unless moving 1. To an approved tagging site 2. Between two states that have agreed upon alternate form of identification 3. Direct to slaughter. 4. To an approved livestock facility and then direct to slaughter. *Please note, cattle and domestic bison originating from Montana's DSA have additional identification requirements.

The Basics (cont.) All cattle and bison moved interstate require a certificate of veterinary inspection (CVI). Unless moving Direct to slaughter To approved livestock facility and then direct to slaughter Farm of origin to approved livestock facility For animals required to be officially identified, ID must be listed on the CVI, unless: Montana requires that 90% of listed tag numbers represent animals included in the shipment.

The Basics (cont.) Double tagging is not allowed, except: Second ear tag with same official identification number In specific cases when the need to maintain the identity of an animal is intensified (international export, quarantined herds, experiments ) Application of an 840 tag to an animal with an existing NUES tag, with both tags being initially recorded Brucellosis vaccination tag to an animal previously identified, with both tags being initially recorded If multiple forms of identification are present, they must all be recorded.

Sheep and Goat Identification Requirements When required: Importation Entry into interstate marketing channels Change of ownership Exhibition For which classes: Sexually intact sheep and goats, regardless of age All sheep and goats over 18 months of age All scrapie-suspect and test positive All scrapie-exposed and high-risk

Responsibilities Accredited Veterinarian Knowledge of and compliance with regulations Records retention Tag application CVIs Timely submission of documents Vaccination certificates CVIs Animal Health Official Education Realistic expectations Facilitation Records management Ability to trace animals

Records Management AKA Those pesky silver metal clips!!!

Records Management Tags What is required: Don’t lose Report if lost/transferred Record sufficient contact information, including: Owner Address Tag range applied Date of application 5 years What we expect:
Records Management Tags Electronic templates available Potential exists for reporting to MDOL

Brucellosis
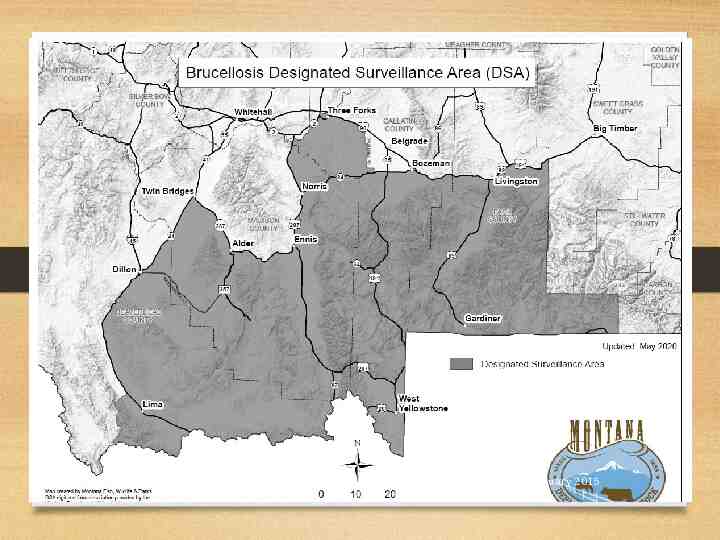
January 2015

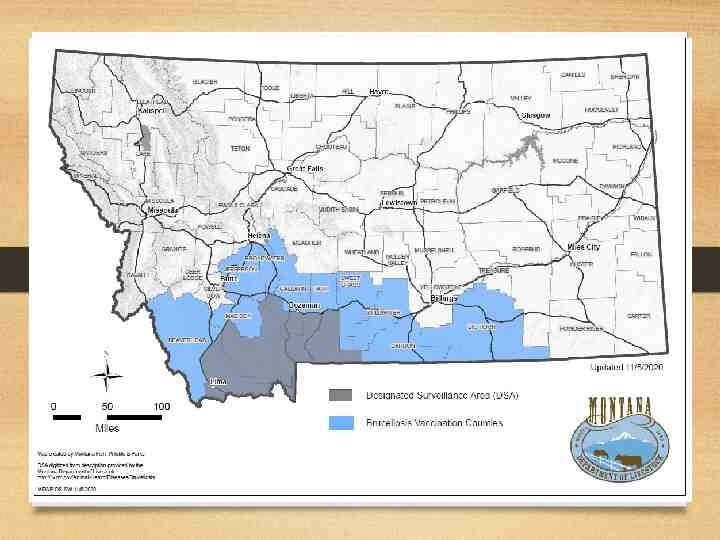
DSA/brucellosis regulations Movemen Bulls and females 12 months of age and older t testing Change of Bulls and females 12 months of age and older or ownershi any age if sold for breeding purposes p testing Brucellosi s vaccinatio n required -All females 12 months of age and older -Official Calfhood Vaccination (OCV) or Adult Vaccination (AV) -10 Counties that contain or border on the DSA or Wyoming’s Brucellosis Area of Concern Traceabili All bulls and ty-official females (includes feeder heifers 12 months of I.D. age) required
32.3.435 1. ALL test eligible animals and cattle or domestic bison of any age if intended to be used for breeding purposes that are or have been within the DSA: a) 2. TESTING A test within 30 days prior to movement out of the DSA or change of ownership, unless going to an approved Montana livestock market or directly to a slaughter. A test July 16th or after is acceptable for movement out of the DSA or change of ownership through February 15 of the following year.

32.3.436 VACCINATION Within the entirety of counties in which the DSA is located-all sexually intact female cattle and domestic bison that are four months of age or older as of January 1 of any year must be Official Calfhood Vaccinates (OCV).

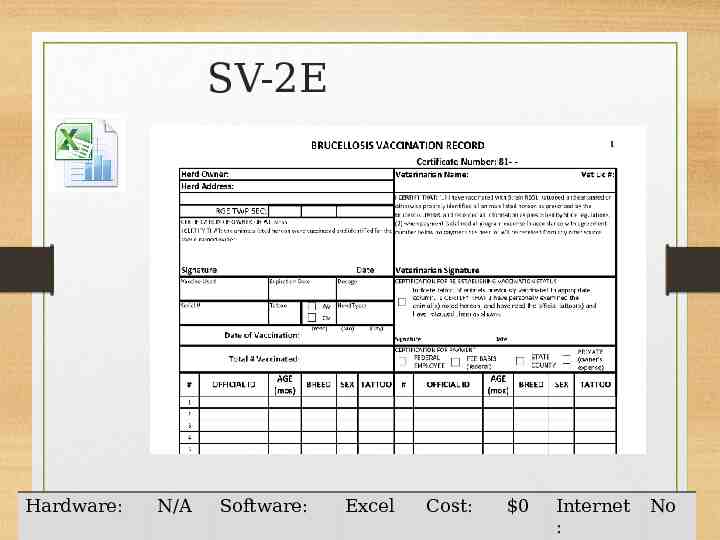
SV-2E Hardware: N/A Software: Excel Cost: 0 Internet : No
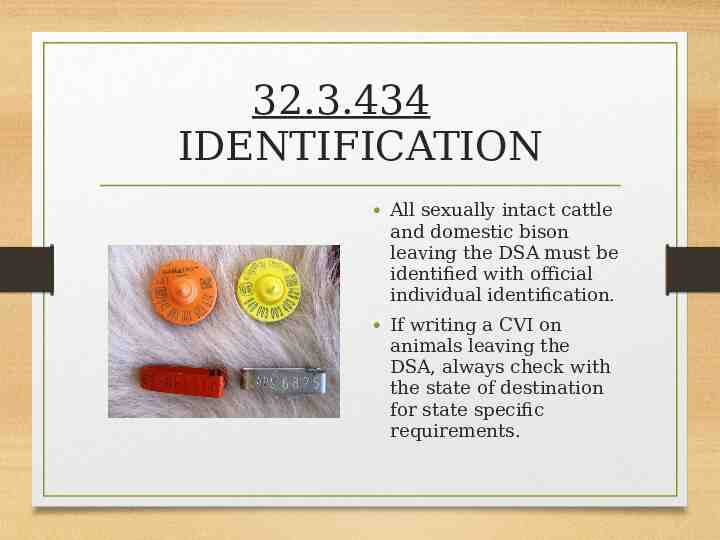
32.3.434 IDENTIFICATION All sexually intact cattle and domestic bison leaving the DSA must be identified with official individual identification. If writing a CVI on animals leaving the DSA, always check with the state of destination for state specific requirements.
Wildlife Surveillance
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis in MT: Reportable and Quarantinable Program outlines: Trichomoniasis Epizootic Area (Trich EA) Testing requirements Management of positive animals and herds Import requirements Penalties
Trichomoniasis Epizootic Area (EA): Negative test required for: All non-virgin bulls sold, loaned, or leased within or from the EA. All non-virgin bulls inspected out of the EA, including animals for change of pasture.

Statewide Test Requirements: Non-virgin bulls from multiple sources going to a common pasture for breeding Exception: Herds with an approved herd health plan on file with MDOL. Herd health plan must include: Best management practices A base line negative test of all non virgin bulls grazing in common A negative test of all newly acquired non-virgin bulls Non-virgin bulls imported into Montana. Exceptions: Sporting bovine, CAN origin exhibition, animals imported into CSS certified Bull Semen Collection facilities.

Virgin Bull: 12 months of age 12-24 months of age with an owner signed affidavit of virginity If you are testing bulls for out of state movement, please check state of destination requirements!

Official Testing: Deputy state veterinarian ONLY Minimum 2 weeks sexual rest prior to test. Minimum 1 week interval between multiple tests. Test good for 60 days or immediately upon commingling with female cattle Must be performed at an AAVLD accredited laboratory. Preferred labs for PCR testing include: MDOL Veterinary Diagnostic Lab CSU Veterinary Diagnostic Lab Wyoming State Veterinary Lab

Official Testing: Preputial scraping ONLY 3 negative weekly cultures 95% sensitivity NOT Specific for T. foetus PCR (DNA test) Specific for T. foetus 97% sensitive and specific if sample is properly collected on positive samples. Pooling of samples is now acceptable except for: Known positive herds Epidemiological investigation testing Some interstate movements

Identification Requirements: At the time of a bull’s first trich test, a MT trich tag or other approved official individual id tag must be applied.

Montana Johne’s Control Program

Program Background and Goals DOL has received inquiries from buyers of MT cattle for a “list of producers” who have tested for Johne’s Disease Cases of MT seedstock producers selling Johne’s positive cattle DOL looking for participation from seedstock, commercial and dairy herds Not focused on herds known to have had a positive animal in the past Producers can advertise/market their participation Will require industry buy-in “A positive, managed herd is lower risk than a herd with an unknown status”

Program Components 1.Education 2.Herd Management Plan 3. /- testing

Education Herd veterinarian will educate the producer, using information provided by DOL Basic disease information Management strategies Testing options Different ways to participate in the program

Herd Management Plan Classification Levels 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

0-Unmanaged Risk No actions taken towards management of Johne’s risk or spread No herd management plan in place 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

1-Evaluated Risk Herd management plan completed Clinical /- test positive cases removed or separated from high-risk group cattle /- testing on high-risk group cattle Animals showing clinical signs Offspring of positive dams 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

2-Managed Risk Completed all requirements of Level 1 including: Herd Management Plan Testing completed on all cattle 2 years of age Clinical and positive test cases removed 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

3-Assurance Completed all requirements of Level 2 including: Herd management Plan Annual testing on all cattle 2 yrs. of age Clinical and positive cases removed Two years since clinical or positive test case 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

4-High Assurance Completed all requirements of Level 3 including: Herd management Plan Annual testing on all cattle 2 yrs. of age Clinical and positive cases removed Five years since clinical or positive test case 0- Unmanaged Risk 1- Evaluated Risk 2- Managed Risk 3- Assurance 4- High Assurance

Testing Please note, all samples must be collected by or under the supervision of an accredited veterinarian, an animal health official, or authorized testing agent (employee of the DOL)

Additional Information Purchasing a classified herd Appealing the status of a test-positive animal Use of embryo transfer Herd additions Herd additions from other states

Renewal Owner and veterinarian must review and update the Herd Management Plan annually A copy of test results must also accompany the herd management plan

Reminder: Johne’s Regulations Johne’s is a reportable disease in Montana per Administrative Rule of Montana (ARM) 32.3.104 Johne’s positive animals are not subject to quarantine There are federal restrictions on the movement of positive animals across state lines Title 9, Code of Federal Regulations (9 CFR), part 71 Animals that are positive to an official Johne’s test may generally be moved interstate only to a recognized slaughtering establishment or to an approved livestock facility for sale to such an establishment The animals must bear an official ear tag and be shipped with an owner-shipper statement

Miscellaneous Biologics Tuberculin Anthrax Autogenous vaccines NPIP Avian Influenza Surveillance Form orders

Any Questions? Tahnee Szymanski Assistant State Veterinarian 406-444-5214









