Proposed Maturity Model for IG FISMA Reporting Andy Patchan
21 Slides3.85 MB

Proposed Maturity Model for IG FISMA Reporting Andy Patchan Associate IG for Information Technology Federal Reserve Board & Consumer Financial Protection Bureau Chair, FAEC IT Committee Louis King Assistant Inspector General for Financial and IT Audits Department of Transportation Federal Audit Executive Council September 3 -4, 2014

Discussion Points Background on FISMA CIO and OIG FISMA reporting (limitations and inconsistencies) Increasing cybersecurity attacks Uses and advantages of maturity models Proposed maturity model for IGs assessment of agencies’ information security continuous monitoring (ISCM) programs Progress to date and next steps References for proposed maturity model 2

Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA) Requires agencies to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide information security program Requires IGs to conduct an annual independent evaluation of – Agencies’ information security program and practices – The effectiveness of security controls and techniques for select information systems – Compliance with FISMA and related policies and guidelines The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) also requires IGs to answer specific questions on the performance of agency information security programs in 11 areas 3
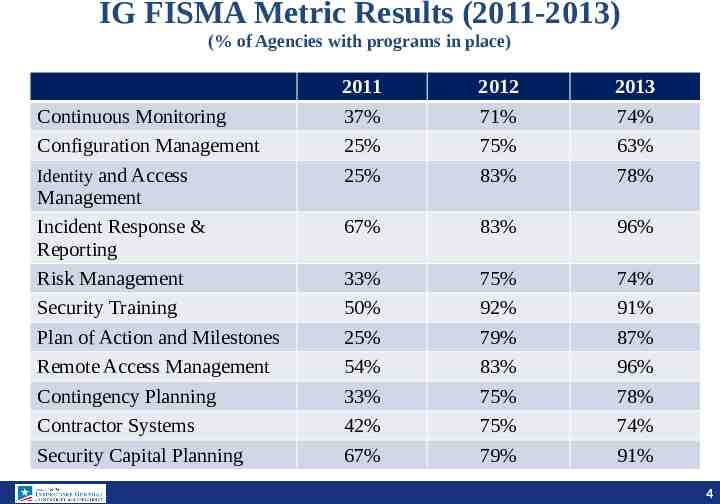
IG FISMA Metric Results (2011-2013) (% of Agencies with programs in place) Continuous Monitoring Configuration Management Identity and Access Management Incident Response & Reporting Risk Management Security Training Plan of Action and Milestones Remote Access Management Contingency Planning Contractor Systems Security Capital Planning 2011 37% 25% 25% 2012 71% 75% 83% 2013 74% 63% 78% 67% 83% 96% 33% 50% 25% 54% 33% 42% 67% 75% 92% 79% 83% 75% 75% 79% 74% 91% 87% 96% 78% 74% 91% 4 4 4
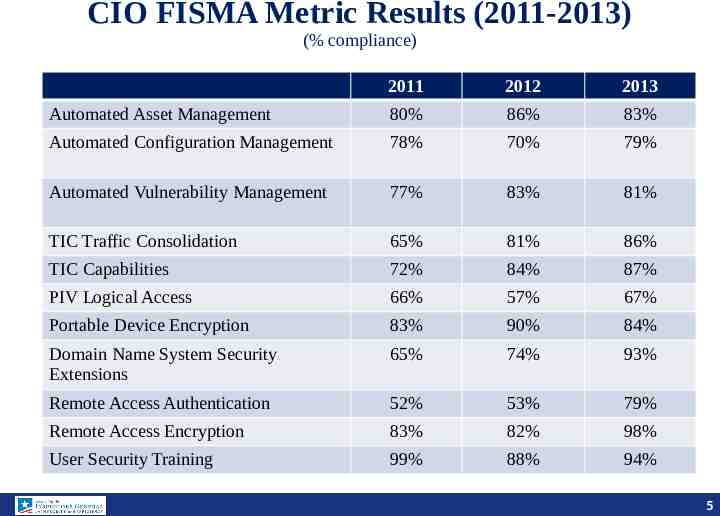
CIO FISMA Metric Results (2011-2013) (% compliance) 2011 2012 2013 Automated Asset Management 80% 86% 83% Automated Configuration Management 78% 70% 79% Automated Vulnerability Management 77% 83% 81% TIC Traffic Consolidation 65% 81% 86% TIC Capabilities 72% 84% 87% PIV Logical Access 66% 57% 67% Portable Device Encryption 83% 90% 84% Domain Name System Security Extensions 65% 74% 93% Remote Access Authentication 52% 53% 79% Remote Access Encryption 83% 82% 98% User Security Training 99% 88% 94% 5 5
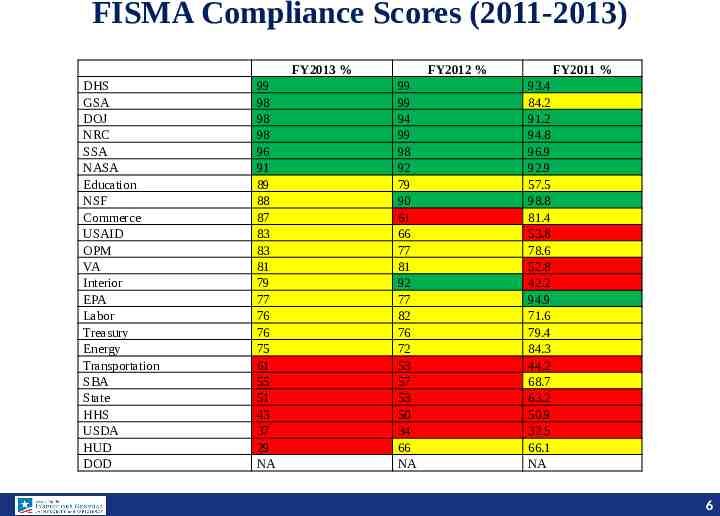
FISMA Compliance Scores (2011-2013) FY2013 % DHS GSA DOJ NRC SSA NASA Education NSF Commerce USAID OPM VA Interior EPA Labor Treasury Energy Transportation SBA State HHS USDA HUD DOD 99 98 98 98 96 91 89 88 87 83 83 81 79 77 76 76 75 61 55 51 43 37 29 NA FY2012 % 99 99 94 99 98 92 79 90 61 66 77 81 92 77 82 76 72 53 57 53 50 34 66 NA FY2011 % 93.4 84.2 91.2 94.8 96.9 92.9 57.5 98.8 81.4 53.8 78.6 52.8 42.2 94.9 71.6 79.4 84.3 44.2 68.7 63.2 50.9 32.5 66.1 NA 6 6 6
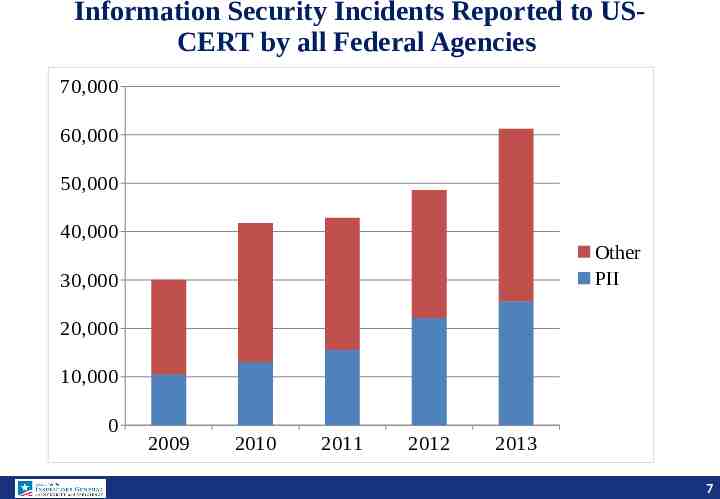
Information Security Incidents Reported to USCERT by all Federal Agencies 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 Other PII 30,000 20,000 10,000 0 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 7 7
What is the Status of Information Security? 8 8

Maturity Models A maturity model refers to a set of characteristics, attributes, indicators, or patterns that represent capability and progression in a certain discipline Can be used to identify current status of information security against set of requirements Cold reader can understand the status of an organization’s information security against specified requirements and in relation to other organizations NIST has developed approaches for information security maturity models Maturity models used in IT organizations and electric industry 9 9

OIG Approach for Development of a Maturity Model for Information Security Continuous Monitoring (ISCM) ISCM is defined as maintaining ongoing awareness of information security, vulnerabilities, and threats to support organizational risk management decisions ISCM is identified as an administration priority and a crossagency priority – OMB M-14-03, Enhancing the Security of Federal Information and Information Systems, provides guidance on ISCM and managing information security risks on a “continuous” basis 10 10

Current FY 2014 IG FISMA Metrics for ISCM Has the organization established an enterprise-wide continuous monitoring program that assesses the security state of information systems that is consistent with FISMA requirements, OMB policy, and applicable NIST guidelines? Besides the improvement opportunities that may have been identified by the OIG, does the program include the following attributes? Documented policies and procedures for continuous monitoring Documented strategy for information security continuous monitoring Implemented ISCM for information technology assets Evaluate risk assessments used to develop their ISCM strategy Conduct and report on ISCM results in accordance with their ISCM strategy Ongoing assessments of security controls (system-specific, hybrid, and common) that have been performed based on the approved continuous monitoring plans Provides authorizing officials and other key system officials with security status reports covering updates to security plans and security assessment reports, as well as a common and consistent POA&M program that is updated with the frequency defined in the strategy and/or plans 11 11
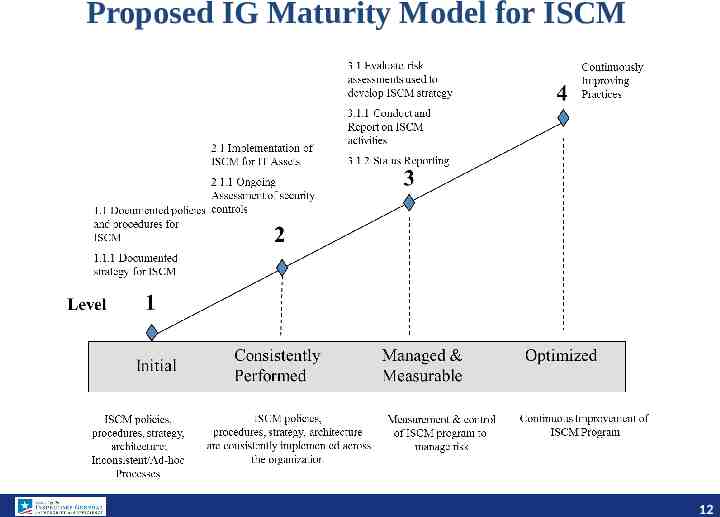
Proposed IG Maturity Model for ISCM 12
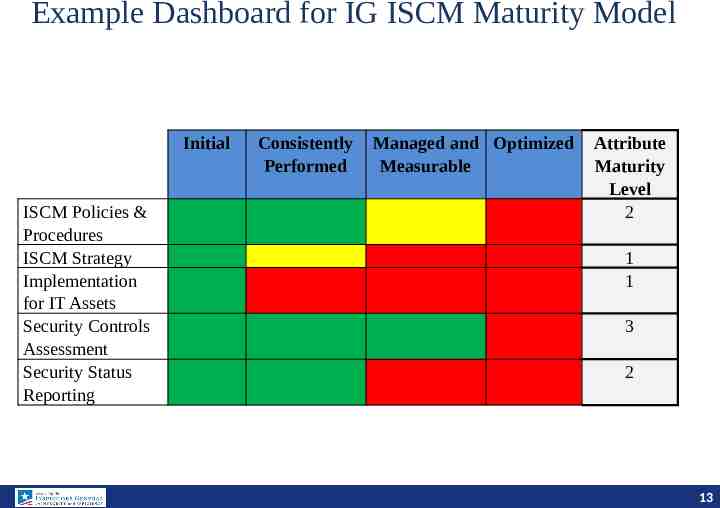
Example Dashboard for IG ISCM Maturity Model Initial ISCM Policies & Procedures ISCM Strategy Implementation for IT Assets Security Controls Assessment Security Status Reporting Consistently Performed Managed and Optimized Measurable Attribute Maturity Level 2 1 1 3 2 13

Progress to Date Discussed maturity model approach with members of the FAEC IT Committee, which includes representatives from 38 OIGs – Formed maturity model workgroup consisting of representatives from 7 OIGs – Treasury, FDIC, Transportation, TIGTA, Interior, CNCS, and FRB – Initial focus is on developing an IG FISMA reporting maturity model for ISCM (1 of 11 areas IGs are required to review as part of their annual FISMA evaluations) Maturity Model workgroup held its first brainstorming session on March 13th – Working sessions held April 3, 17, and 24 to refine maturity level criteria and attributes for the different maturity levels for continuous monitoring Met with OMB and DHS on April 25 and subsequently with GAO, NIST, Senate staffer, and CIO Council – Received positive feedback and overall support 14

Next Steps Continue technical development of maturity model for continuous monitoring: subgroup on ISCM attributes, and another subgroup on integrating model with NIST framework for critical infrastructure cybersecurity Test drive/pilot with participating IGs by end of 2014/early 2015 Make any needed tweaks for inclusion in 2015 OIG FISMA metrics Goal of working with DHS to develop a FISMA maturity model reporting framework for all 11 information security areas 15

References 16

References NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-53, Rev. 4, Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations SP 800-137, Information Security Continuous Monitoring for Federal Information Systems and Organizations OMB Memorandum M-14-03, Enhancing the Security of Federal Information and Information Systems United States Government Concept of Operations for Information Security Continuous Monitoring 17

2014 NIST Framework for Improving CyberSecurity Functions Categories Subcategories Identify Risk Assessment System inventory, categorization Protect Identification & Authentication; Security Awareness and Training PIV card; awareness and rolebased training Detect Continuous Monitoring Strategy, scanning Respond Incident Response Detection and reporting Recover Contingency Planning BIA, backups Implementation Tiers Tier 1 - Partial Tier 2 – Risk informed Tier 3 Repeatable Tier 4 - Adaptive 18
Additional NIST Guidance on Maturity Models NIST Program Review for Information Security Management Assistance outlines five maturity levels – polices, procedures, implementation, test, and integration NIST maturity model for information security performance measurement 19
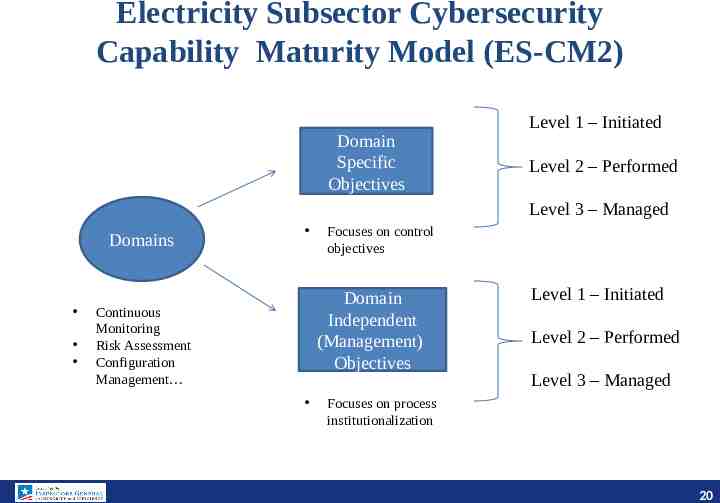
Electricity Subsector Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (ES-CM2) Domain Specific Objectives Level 1 – Initiated Level 2 – Performed Level 3 – Managed Domains Focuses on control objectives Domain Independent (Management) Objectives Continuous Monitoring Risk Assessment Configuration Management Level 1 – Initiated Level 2 – Performed Level 3 – Managed Focuses on process institutionalization 20
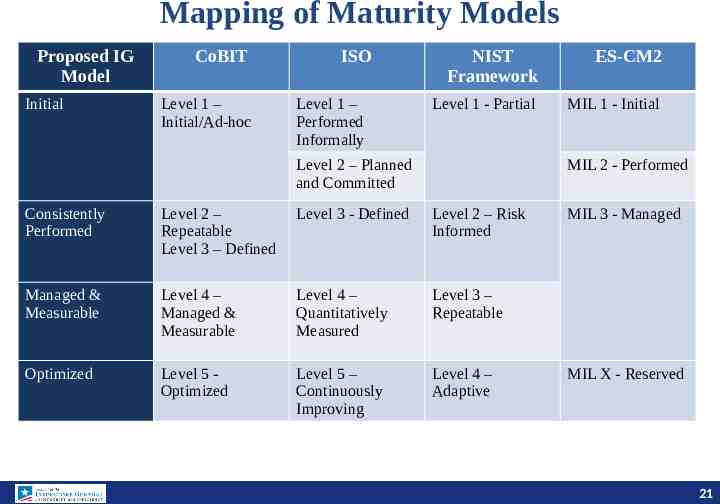
Mapping of Maturity Models Proposed IG Model Initial CoBIT Level 1 – Initial/Ad-hoc ISO Level 1 – Performed Informally NIST Framework ES-CM2 Level 1 - Partial MIL 1 - Initial Level 2 – Planned and Committed MIL 2 - Performed Consistently Performed Level 2 – Repeatable Level 3 – Defined Level 3 - Defined Level 2 – Risk Informed Managed & Measurable Level 4 – Managed & Measurable Level 4 – Quantitatively Measured Level 3 – Repeatable Optimized Level 5 Optimized Level 5 – Continuously Improving Level 4 – Adaptive MIL 3 - Managed MIL X - Reserved 21