A Scalable content-addressable network Presenter: Baoning Wu
15 Slides1,007.50 KB

A Scalable content-addressable network Presenter: Baoning Wu

Motivation Many peer-to-peer systems appear, but most of them are not scalable. – Napster needs a central server to store index of all files. – Gnutella floods request with a certain scope. Can we have a scalable p2p file distribution system?

CAN (content-addressable network) Scalable indexing mechanism is crucial in scalable p2p systems. Hash table is used! (key, value) pair Each CAN node stores a chunk(zone) of the entire hash table

Design D-dimensional Cartesian co-ordinate space Map key to a point P with a determined hash function Routing the request if the point P is not owned by the requesting node or its immediate neighbors.
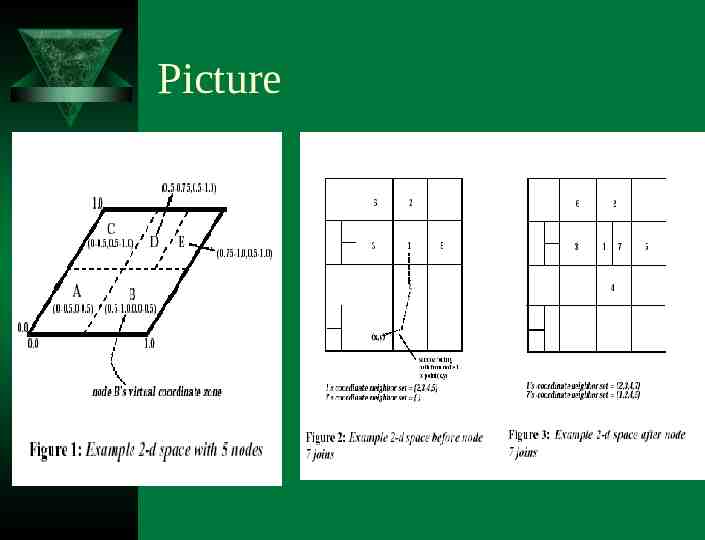
Picture

Routing detail Each CAN node maintains coordinate routing table that holds the IP address and virtual coordinate zone of its neighbors. Routing a message towards its destination by simple greedy forwarding to the neighbor with coordinated closest to the destination coordinates.
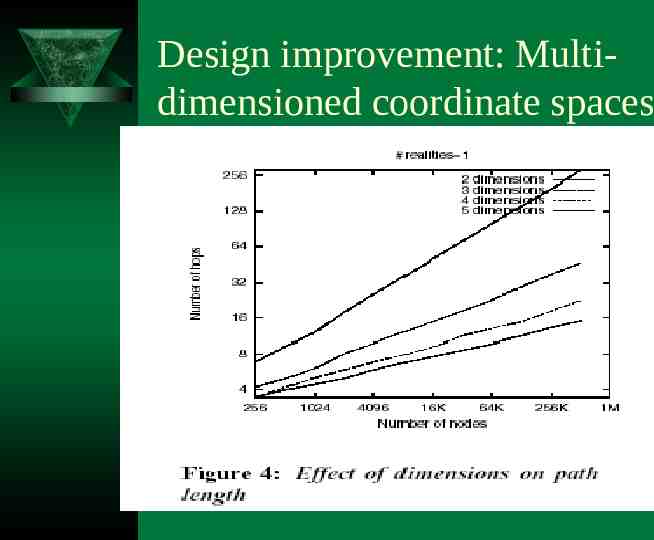
Design improvement: Multidimensioned coordinate spaces
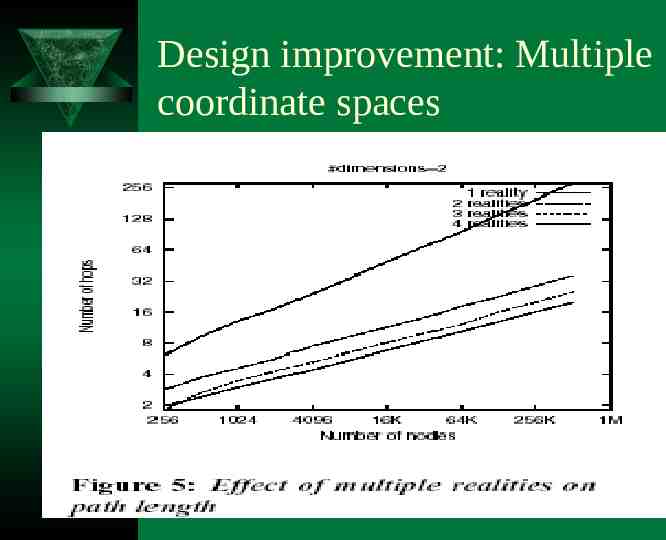
Design improvement: Multiple coordinate spaces
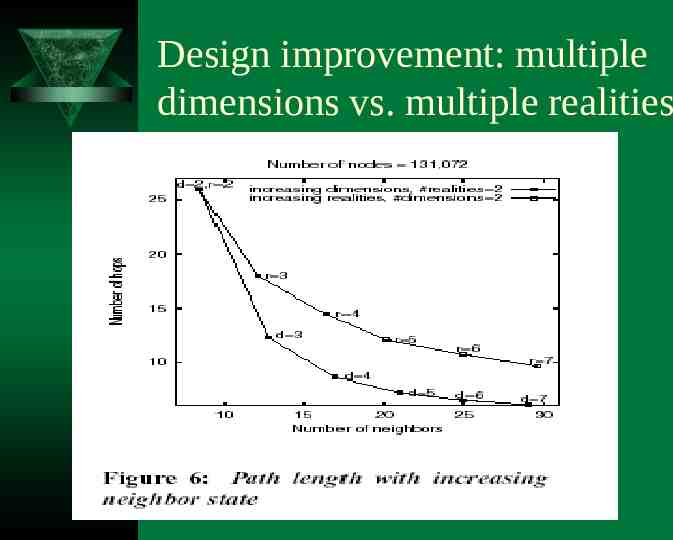
Design improvement: multiple dimensions vs. multiple realities

Design improvement: RTT weighted routing
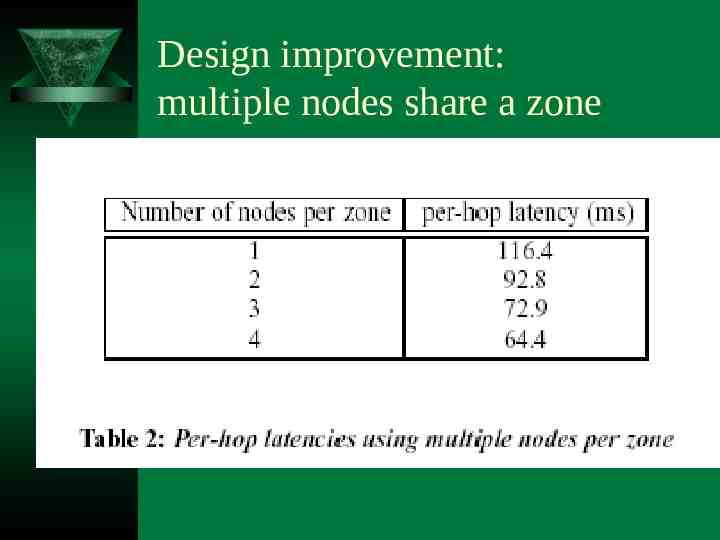
Design improvement: multiple nodes share a zone
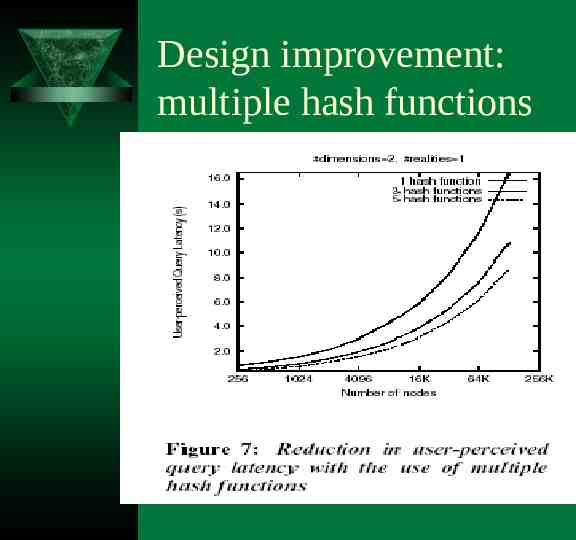
Design improvement: multiple hash functions
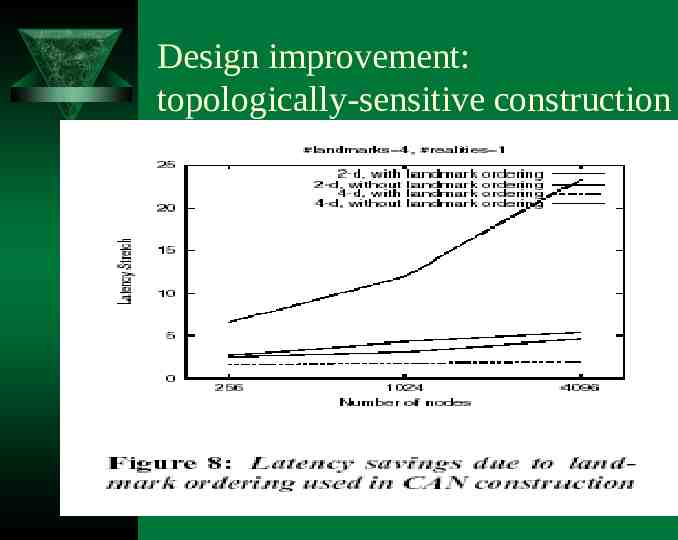
Design improvement: topologically-sensitive construction

Review Dimensionality Number of realities Number of peer nodes per zone Number of hash functions Use of RTT weighted routing metric Use of topologically-sensitive construction

QUESTIONS?






