25th Executive Force Protection Board Alcohol Related
22 Slides570.29 KB

25th Executive Force Protection Board Alcohol Related Incident Screening Inspector General Assessment Overview Office of the Inspector General U.S. Marine Corps
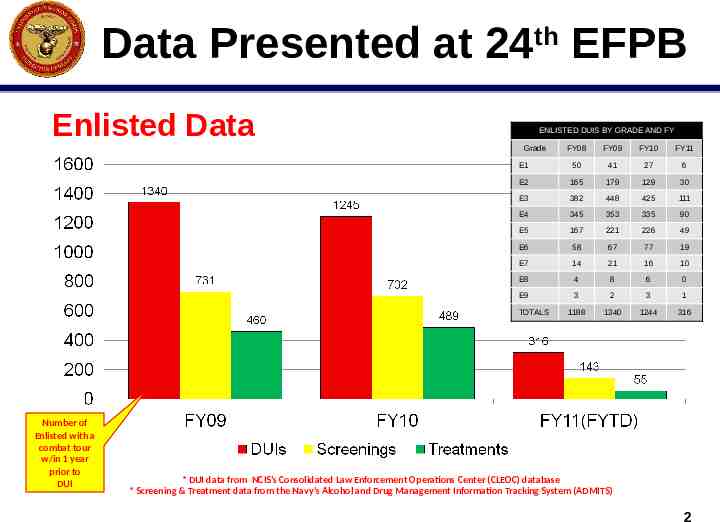
Data Presented at 24th EFPB Enlisted Data ENLISTED DUIS BY GRADE AND FY Grade FY08 FY09 FY10 FY11 E1 50 41 27 6 E2 165 179 129 30 E3 382 448 425 111 E4 345 353 335 90 E5 167 221 226 49 E6 58 67 77 19 E7 14 21 16 10 E8 4 8 6 0 E9 3 2 3 1 1188 1340 1244 316 TOTALS Number of Enlisted with a combat tour w/in 1 year prior to DUI * DUI data from NCIS’s Consolidated Law Enforcement Operations Center (CLEOC) database * Screening & Treatment data from the Navy’s Alcohol and Drug Management Information Tracking System (ADMITS) 2
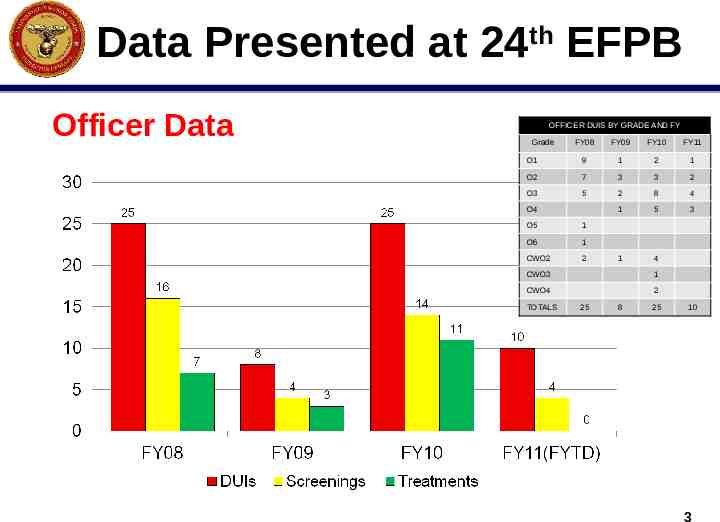
Data Presented at 24th EFPB Officer Data OFFICER DUIS BY GRADE AND FY Grade FY08 FY09 FY10 FY11 O1 9 1 2 1 O2 7 3 3 2 O3 5 2 8 4 1 5 3 1 4 O4 O5 1 O6 1 CWO2 2 CWO3 1 CWO4 2 TOTALS 25 8 25 10 3

IGMC Overview 24th EFPB Tasking Coordinate with M&RA and conduct an assessment of Substance Abuse Counseling Centers (SACC): Assess capacity issues, What causes delays between reported alcohol related incidents and individual screenings, What additional related problems negatively affecting timely evaluations. 4

Scope & Methodology Scope: Canvass the principal stakeholders within the substance abuse process in order to assess program compliance, capacity, related issues and review the current Marine Corps Order 5300.17. Commanding Officers (Ban/Sad Level) Substance Abuse Control Officer (SACO) Substance Abuse Counseling Center (SACC) Directors Behavioral Health Branch Personnel, M&RA (MF) Methodology: conducted focused survey, local site visit and interviews. Assessment conducted in two phases: Phase I MARADMIN 393/11 directed surveys for 15-25 Jul Three Anonymous Surveys 331 Commanding Officers (Bn/Sqdn level) 378 SACOs and Assistant SACOs All 16 SACC Directors Phase II Follow-on Interviews (1 Aug – 8 Sep) 11 Commanding Officers 13 SACOs 7 SACC Directors Behavioral Health Branch Personnel 5

IGMC Results Alcohol Related Incidents Screening Inspector General Assessment Overview Findings 22 Recommendations 9 6
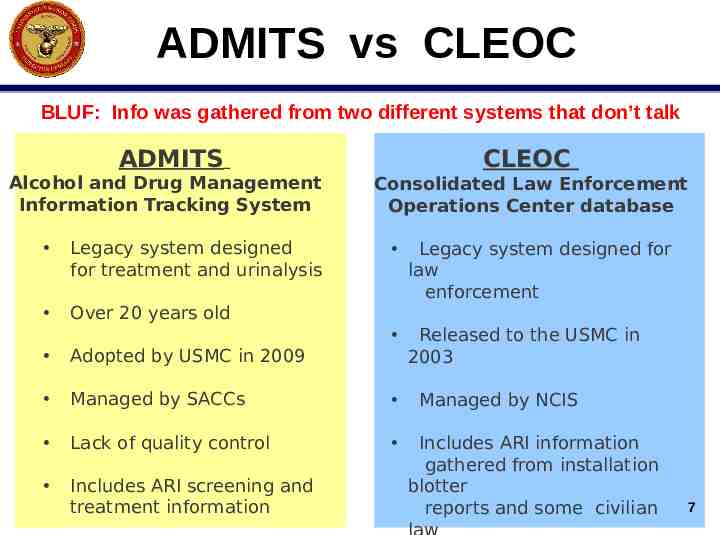
ADMITS vs CLEOC BLUF: Info was gathered from two different systems that don’t talk ADMITS Alcohol and Drug Management Information Tracking System Legacy system designed for treatment and urinalysis Over 20 years old CLEOC Consolidated Law Enforcement Operations Center database Legacy system designed for law enforcement Released to the USMC in 2003 Adopted by USMC in 2009 Managed by SACCs Lack of quality control Includes ARI screening and treatment information Managed by NCIS Includes ARI information gathered from installation blotter reports and some civilian 7
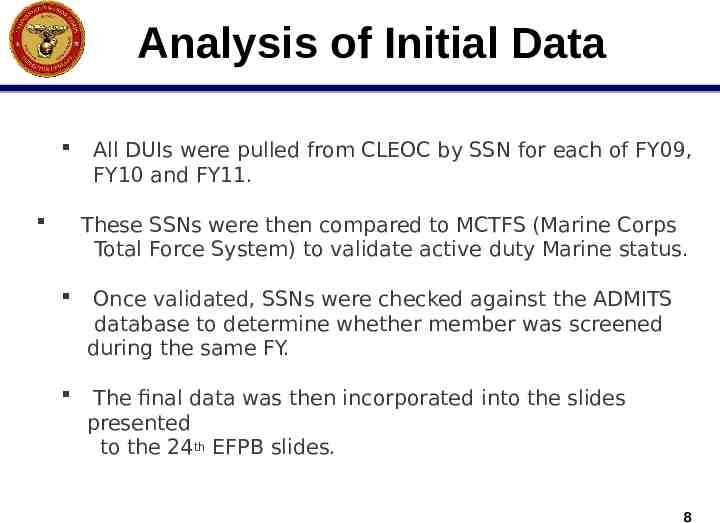
Analysis of Initial Data All DUIs were pulled from CLEOC by SSN for each of FY09, FY10 and FY11. These SSNs were then compared to MCTFS (Marine Corps Total Force System) to validate active duty Marine status. Once validated, SSNs were checked against the ADMITS database to determine whether member was screened during the same FY. The final data was then incorporated into the slides presented to the 24th EFPB slides. 8

Factors Contributing to Inaccuracy of Data CLEOC data was not checked against ADMITS data from previous or later FYs. Screening protocols vary by SACC. For example, not all SACCs create a new screening record if the member has been previously screened during the past two years. Information regarding Marines screened by Army or Air Force SACCs is not necessarily recorded in ADMITS. Members pending EAS are referred to VA not 9
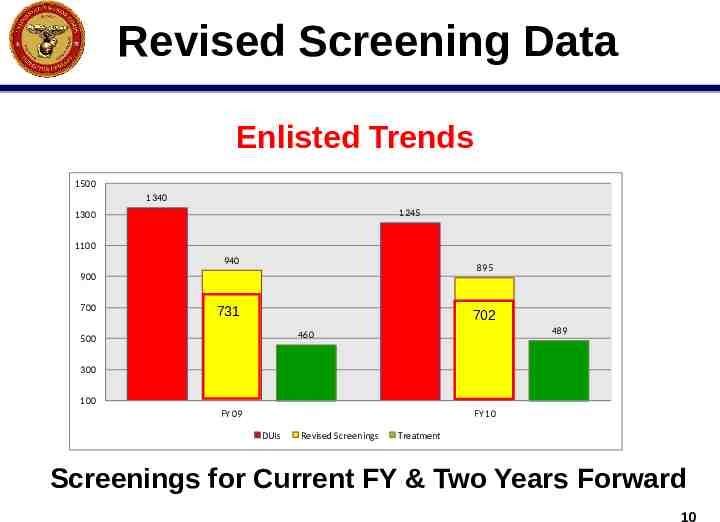
Revised Screening Data Enlisted Trends 1500 1340 1245 1300 1100 940 895 900 700 702 702 731 489 460 500 300 100 FY 09 FY 10 DUIs Revised Screenings Treatment Screenings for Current FY & Two Years Forward 10
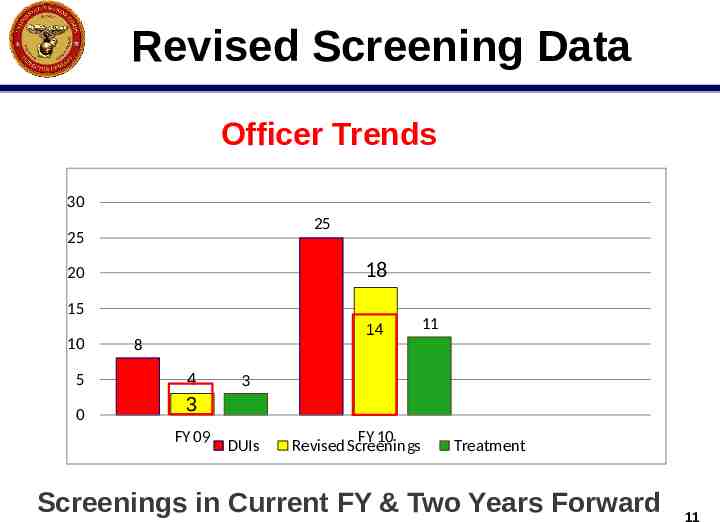
Revised Screening Data Officer Trends 30 25 25 18 20 15 10 5 0 14 8 4 11 3 3 FY 09 DUIs FY 10 Revised Screenings Treatment Screenings in Current FY & Two Years Forward 11

Findings 1. Not all ARIs are reported or result in screening. 2. No one entity is tracking ARIs and follow-on substance abuse screenings. 3. No single database exists for tracking ARIs and Command action, including screenings and treatment. 4. Pulling ARI screening/treatment data from existing databases is cumbersome and results in incomplete and unreliable data because existing CLEOC and ADMITS databases are not linked. 5. CLEOC is a law enforcement database that only includes certain ARIs reported to NCIS. On-base incidents. Some local civilian jurisdictions. 12

Findings 6. ADMITS is a legacy system that is not meeting the needs of the Marine Corps Substance Abuse Program in part due to inconsistent data input policies. 7. ADMITS doesn’t distinguish between types of ARIs. 8. Members are lost in the system due to deployments or PCS and don’t always receive screenings. 9. Blotter reports don’t include most civilian ARIs. 10. Not all SACC Directors receive blotter reports. 11. Not all SACC Directors who receive blotter reports act on reported information. 13

Findings 12. MCO 5300.17, Marine Corps Substance Abuse Program, doesn’t provide a uniformed approach to substance abuse screening and treatment. 13. All 16 SACCs continue to operate independently. Staff credentials and methods vary. Wait times for screenings vary. Screening protocols and treatment methods vary. 14. No uniform staffing T/O exists for SACCs. 68% of SACCs report they are understaffed (11 of 16 Directors) 14

Findings 15. Lack of transparency on SACC policies/procedures leads to unnecessary command frustration. SACCs triage cases causing extended wait times for some Marines sent for screenings. 16. Most SACOs are multi-tasked. 17. Some Commanders overload their SACOs with collateral duties. 18. SACOs are responsible for monitoring aftercare treatment programs, but aren’t adequately trained for the task. 19. From a command training perspective the substance abuse program is not adequately linked to other conditions (depression, PTSD, TBI) or suicide, spouse abuse, and sexual assault. 15

Findings 20. Junior leaders are not adequately trained on prevention and early intervention techniques. 21. Treatment for alcohol abuse is viewed as a punitive measure. 22. Due to the existing stigma, Marines are reluctant to self-report alcohol problems and seek treatment. 16

Reserve Component Problems Many Reservists lack easy access to SACCs, and must take time off from civilian work or school to obtain screening and treatment. Reservists experience long wait times when seeking SACC appointments because they seek to schedule these appointments during drill periods. Reservists reported problems related to the time and expense involved in obtaining transportation to the nearest SACC. 17 Reservists are not covered under TRICARE when they are

Recommendations 1. Direct Behavioral Health Branch (MFC) to: Establish Accreditation (develop a common level of practice, including uniform screening/treatment policies/procedures based on civilian industry best practices and standards). Create Model Staffing Template (T/O and T/E). Establish staff training standards. Establish industry standard credentials requirement and ensure uniform treatment. Establish quarterly MFC technical assistance visits. Establish regular communication (Sharepoint site or other means) for sharing MFC guidance and best practices. 18

Recommendations 2. Develop a central Case Management System that allows SACOs and Command Team members to open a case and input basic information. The system should allow varying levels of access based on the individual user’s “need to know”. 3. Update the Functional Area Checklist to ensure new Case Management System is regularly monitored for accuracy. 4. Make the SACC Directors responsible and accountable for monitoring ARIs in order to ensure successful screening and treatment. 19

Recommendations 5. Make SACCs responsible for monitoring After Care treatment programs. 6. Engage Marine leaders in undertaking a commanddriven Stigma Reduction Campaign that promotes prevention and early intervention. Existing programs to consider include: USAF Culture of Responsible Choices Campaign Confidential treatment and education (USA pilot) Early intervention – Prime for Life Program 20

Recommendations 7. Revise MCO 5300.17 as necessary to achieve agreedupon solutions. 8. Task MFC with developing a POA&M for achieving agreedupon solutions. 9. Provide necessary funding to complete agreed-upon solutions. 21

Questions ?






