Trading Strategies Involving Options ── 選擇權交易策略 1
49 Slides563.50 KB

Trading Strategies Involving Options 選擇權交易策略 1

Hypothesis The underlying asset is a stock Other underlying assets can apply to similar results The options used in the strategies are European American option may probably be exercised early that leading to different profit outcome Ignore the time value of money To Simplify the exposition 2

Hypothesis Initial cost premium( 權利金 )-long side margin( 保證金 )-short side 3

Types of Strategies Hedge holding single option on a stock and the stock itself Spread taking a position in two (or more) options of the same type. Combination Taking a position in both calls and puts on the same stock 4

Hedge strategy Covered call( 備兌買權 ) Protective call( 保護性買權 ) Protective put ( 保護性賣權 ) Covered put ( 備兌賣權 ) holding single option on a stock and the stock itself 5

Put – Call Parity S P C Ke-r*T D S : stock price ; P : the price of put ; C : the price of call ; K : strike price / exercise price ; r : risk-free interest rate ; T : the time to maturity ; D : the present value of the dividends 6

Covered call long a stock & short a call S-C Ke-rf*T D–P Profit S C C K-C K ST -C -(K-C) 7

Protective call short a stock & long a call -S C -Ke-rf*T-D P Profit C K-C K-C ST K -C C -S 8

Protective put long a stock & long a put S P Ke-rf*T D C Profit S ST K -P P 9

Covered put short a stock & short a put -S-P -Ke-rf*T-D-C Profit P -P ST K -S 10

Spread trading strategy Bull Spreads( 多頭價差 ) Bear Spreads( 空頭價差 ) Box Spreads( 箱形價差 ) Butterfly Spreads( 蝶形價差 ) Calendar Spreads( 時間價差 / 行事曆價差 / ) Diagonal Spreads( 對角價差 ) taking a position in two (or more) options of the same type (i.e., two calls or two puts) 11

Definition Type: two types—call & put Option series: 1.options of the same type 2.different expiration dates, the same strike price; different strike prices, the same expiration date. 12

Bull spread Both options have the same expiration date Hoping that the stock price will be up Limit both the upside profit potential and the downsi de risk i.e. limiting both sides Three types of bull spreads can be distinguished 1. both calls are initially out of the money 2. one call is initially in the money ; the other call is initially out of the money 3. both calls are initially in the money 13

Bull Spread Using Calls Buy a call with a lower strike price and sell a call with a higher strike price Profit C K1 ST K2 -C 14

Payoff from a bull spread created using calls Stock price range Payoff from long Payoff from call option short call option Total payoff ST K2 ST - K1 -(ST – K2) K2 - K1 K1 ST K2 ST - K1 0 ST - K1 ST K1 0 0 0 15

Example An investor buys for 3 a call with a strike price of 30 and sells for 1 a call with a strike price of 35 The profit is therefore as follows: Stock price range Profit ST 30 -2 30 ST 35 ST – 32 ST 35 3 16

Bull Spread Using Puts Buy a put with a lower strike price and sell a put with a higher strike price Profit -P K1 K2 ST P 17

Bear Spreads Both options have the same expiration date Hoping that the stock price will decline Limit both the upside profit potential and the d ownside risk 18

Bear Spread Using Puts Sell a put with a lower strike price and buy a put with a higher strike price Profit -P K1 K2 ST P 19

Payoff from a bear spread created using puts Stock price range Payoff from long Payoff from put option short put option Total payoff ST K2 0 0 0 K1 ST K2 K2 - ST 0 K2 - ST ST K1 K2 - ST -(K1 – ST) K2 - K1 20

Example An investor buys for 3 a put with a strike price of 3 5 and sells for 1 a put with a strike price of 30 The profit is therefore as follows: Stock price range Profit ST 30 3 30 ST 35 33 - ST ST 35 -2 21

Bear Spread Using Calls Sell a call with a lower strike price and buy a cal l with a higher strike price Profit c K1 K2 ST -c 22

Box Spread A combination of a bull call spread with strike prices k1 and k2 and a bear put spread with th e same two strike prices If all options are European a box spread is worth the present value of the difference between the strike prices( (K2 - K1)e-rT ) ; If they are American this is not necessarily so. 23

Box Spread 24

Box Spread If the market price of the box spread is too lo w(high),it is profitable to buy(sell) the box,called “long box” or “short box” Commissions are important to be considered when implementing this strategy coz the small profit may be easily offset by commissions Alligator spread 25

Butterfly Spread Involves positions in options with three differe nt strike prices K1 : a relatively low strike price K3 : a relatively high strike price K2 : halfway between K1 and K3 , close to the current stock price Large stock price moves are unlikely 26

Butterfly Spread Using Calls Buy a call option with a relatively low K1 , buy a call option with a relatively high K3 , and sell two call options with K2 Profit C C K1 K2 K3 ST -C 27

Payoff from a butterfly sprea d Stock price Payoff from f Payoff from sec Payoff from range irst long call ond long call short calls Total payoff ST K1 0 0 0 0 K1 ST K2 ST - K1 0 0 ST - K1 K2 ST K3 ST - K1 0 -2(ST – K2) K3 - ST ST K3 ST - K1 S T - K3 -2(ST – K2) 0 28

Example The stock price is 61.An investor buys for 10 a cal l with a strike price of 55, 5 a call with a strike price of 65 and sells for 7 two puts with a strike price of 60 The profit is therefore as follows: Stock price range Profit ST 55 -1 55 ST 60 ST - K1 -1 60 ST 65 K3 - ST -1 ST 65 -1 29

Butterfly Spread Using Puts Buy a put option with a relatively low K1 , buy a put option with a relatively high K3 , and sell two put options with K2 Profit -P K1 K2 K3 ST P P 30

Calendar Spread The options have the same strike price and different expiration dates Neutral calendar spread : A strike price close to the current stock price is chosen Bullish calendar spread : Involves a higher strike pri ce Bearish calendar spread : Involves a lower strike pri ce Reverse calendar spread : Buys a short-maturity opt ion and sells a long-maturity option 31

Calendar Spread Using Calls Buy a longer-maturity call option and Sell a call o ption with the same strike price Profit C K ST -C 32
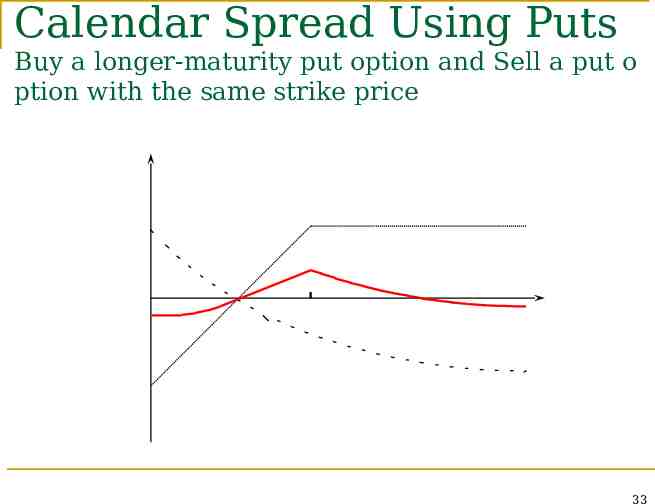
Calendar Spread Using Puts Buy a longer-maturity put option and Sell a put o ption with the same strike price Profit -P K ST P 33

Brief Summary Bull and Bear spreads: different strike prices and the same expiration date Calendar spreads: the same strike price and different expiration date 34

Diagonal Spread Both the expiration date and the strike price of the calls are different Increases the range of profit patterns that are possible 35
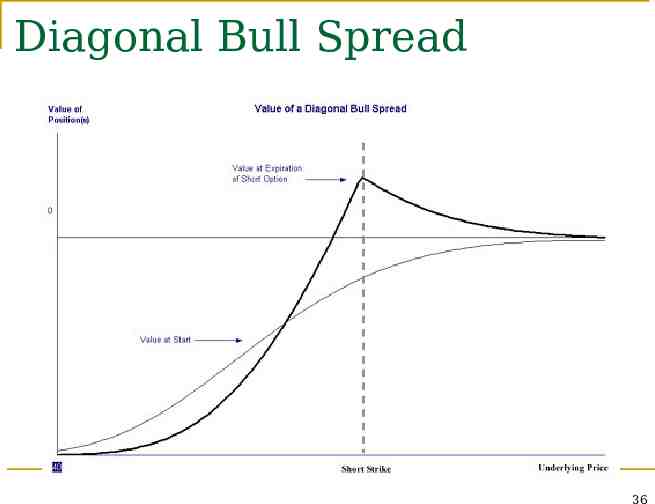
Diagonal Bull Spread 36

Diagonal Bear Spread 37

Combinations Taking a position in both calls and puts on the same stock Straddle( 跨式價差 ) Strips( 紙帶價差 ) Straps( 皮帶價差 ) Strangles( 勒式價差 ) 38

Straddle Bottom straddle (straddle purchase) : Buying a call and put with the same strike price and expiration date ; expecting a large move in a stock price but does not know in which directi on the move will be Top straddle (straddle write) : Selling a call and put with the same strike price and expiration date ; large stock price moves are unlikely 39

Bottom straddle Profit C K ST P 40

Payoff from a bottom straddle Stock price range Payoff from long call Payoff from long put Total payoff ST K 0 K - ST K - ST ST K ST - K 0 ST - K 41

Strip & Strap Strip : Buy one call and two puts with the same strike price and expiration date ; Considers a decrease in the stock price to be a more likely than an increase Strap : Buy two calls and one put with the same strike price and expiration date ; Considers a increase in the stock price to be a more likely than an decrease 42

Strip & Strap call put Strip 1 2 Strap 2 1 43

Strip & Strap Profit Profit K Strip ST K ST Strap 44

Strangle Bottom vertical combination : Buy a put and a call with the same expiration date and different strike prices Top vertical combination : Sell a put and a call with the same expiration date and different strike prices The stock price has to move farther in a strangle than in a straddle for the investor to make a profit ; The downside risk is less than a straddle 45

Bottom vertical combination Profit C K1 K2 ST P 46

Profit The stock price has to move farther in a strangle than in a straddle for the investor to C make a profit ; K1 K2 ST The downside risk is less than P a straddle Strangle Profit C K ST P Straddle 47

Payoff from a bottom vertical combination Stock price range Payoff from long Payoff from long call put Total payoff ST K1 0 K1 - ST K1 - ST K1 ST K2 0 0 0 ST K2 ST - K2 0 ST - K2 48

Other Payoffs All payoff functions (at time T) can be found: if Euro options can expire (at time T) with every single possible strike price Profit K1 K2 K3 ST 49