The Kentucky Teacher Internship Program for Interdisciplinary
58 Slides3.27 MB

The Kentucky Teacher Internship Program for Interdisciplinary Early Childhood Education 2016

Advanced Organizer Introductions What is your role on the Intern Committee? What is your experience with young children? Training assumptions and objectives The nature of early childhood Early childhood in Kentucky Interdisciplinary Early Childhood Education (IECE) KTIP IECE Resources

Training Assumptions Participants will already: have completed KTIP training. understand how their role as coach and mentor contributes to the success of the intern. be familiar with the KTIP materials. have an understanding of how to gather performance evidence and score intern performance.

KTIP Committee Qualifications Resource Teacher (RT) At least 4 years of teaching experience; least Rank 2 At Classroom teacher KTIP Training Principal (PR) Public School – school principal with principal certification Private schools – those serving in principal role regardless of certification Assistant principal can serve when there are more than 2 interns. KTIP Training Teacher Educator (TE) Whoever the university assigns KTIP Training

Order of RT Assignment Priority shall be given to resource teachers in the following order: 1. Teachers with the same certification in the same school; 2. Teachers with the same certification in the same district; 3. Teachers in the same school; 4. Teachers in the same district; and 5. Teachers in an adjacent school district.

Training Objectives Participants will: describe the diversity of early childhood settings. identify features of appropriate early childhood curriculum, instruction and assessment. describe the multiple roles of early childhood educators. demonstrate the ability to use the IECE Teacher Standards in the KTIP process.

Working in Pairs describe what an early childhood environment looks like What are the children doing? What does the physical environment look like? What is included in the daily routine / schedule? What is the teacher doing? What are the other adults in the environment doing? How do we know children are learning? How are all children included in all activities? How are the families included?

Group Discussion What are the children doing? What does the physical environment look like? What is included in the daily routine / schedule? What is the teacher doing? What are the other adults in the environment doing? How do we know children are learning? How are all children included in all activities? How are the families included?

Professional Resources for Early Childhood Education

The National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) Website: www.naeyc.org Mission: NAEYC's mission is to serve and act on behalf of the needs, rights and well-being of all young children with primary focus on the provision of educational and developmental services and resources. NAEYC defines early childhood as birth through age 8.

NAEYC Position on Developmentally Appropriate Practice As NAEYC defines it, developmentally appropriate practice (DAP) is a framework of principles and guidelines for best practice in the care and education of young children, birth through age 8. It is grounded both in the research on how young children develop and learn and in what is known about education effectiveness. The principles and guidelines outline practice that promotes young children's optimal learning and development. http://www.naeyc.org/DAP

Developmentally Appropriate Practice in Early Childhood Programshttp://www.naeyc .org/store/DAP-and-Basicsof-DAP-Set (3rd edition) (Copple & Bredekamp, 2009) http://www.naeyc.org/stor e/DAP-and-Basics-of-DAPSet Basics of Developmentally Appropriate Practice An Introduction for Teachers of Infants and Toddlers (Gonzalez-Mena, Copple & Bredekamp, 2013) Basics of Developmentally Appropriate Practice: An Introduction for Teachers of Kindergartners (Phillips & Scrinzi, 2013) Basics of Developmentally Appropriate Practice: An Introduction for Teachers of Children 3 to 6 (Copple & Bredekam, 2006)

The developmentally appropriate classroom environment is one where children most often: Lead.rather than follow the teacher. Create.rather than duplicate. Move.rather than wait. Make the lines.rather than color in the lines. Speak.rather than listen passively. Initiate.rather than imitate. Raise questions.rather than answer the teacher's questions. Solve their own problems.rather than the teacher's problems. Make art.rather than do crafts. Emphasize the process.rather than the product. Use authentic skills.rather than drill and practice. Make books.rather than fill in workbooks. Decide.rather than submit. Choose wisely.rather than being told. Make a plan.rather than follow the teacher's plan. Try again.rather than fail. Crosser, S. (n.d.). The butterfly garden: Developmentally appropriate practice defined. Early Childhood News. Retrieved June 19, 2008, from http://www.earlychildhoodnews.com/earlychildhood/article view.aspx?ArticleId 115

Age-specific DAP Resources for Teachers http://www.naeyc.org/DAP/resourc es

The Division for Early Childhood of the Council for Exceptional Children (DEC) Website: http://www.dec-sped.org Mission: The Division for Early Childhood promotes policies and advances evidence-based practices that support families and enhance the optimal development of young children who have or are at risk for developmental delays and disabilities. DEC defines early childhood as birth through age 8.

DEC Position on Developmental Delay DEC believes: in the uniqueness of the young child that services and interventions must be responsive to the child’s needs and patterns of development that disability categories are often inappropriate for children birth through 8 years and that developmental delay can be a more appropriate designation of disability for special education eligibility. http://www.dec-sped.org/

DEC Recommended Practices in Early Intervention/Early Childhood Special Education (2014) http://dec.membershipsoftwar e.org/recommendedpractices

Interdisciplinary Early Childhood Education in Kentucky

The Early Childhood Age Range in KY KY agrees with DEC and NAEYC that the early childhood age range is birth through 8 years. The IECE certification was established as birth through kindergarten since KY already had a certification addressing the primary years. The IECE certification age range is consistent with DEC’s and NAEYC’s recommendations that preservice programs focus on two of the 3 age ranges: infant/toddler, preschool, and primary. The KY Early Childhood Standards focus on birth through 4 years as KY has standards for K-12.

KY IECE Certification From 16 KAR 2:040 Section 4 found at http://www.lrc.state.ky.us/kar/016/002/040.htm (1) The professional certificate for interdisciplinary early childhood education, birth to primary, shall be valid for teaching children from birth to entry into the primary program, including teaching children in kindergarten or another program for five (5) year old children if the program is operated separately from the primary program. (2) A person holding this certificate shall serve as a primary developer and implementer of an individual program for children with or without disabilities including an individual education plan (IEP) and individual family service plan (IFSP) with consultation and support from a specialist according to the needs of the child.

Kentucky Department of Education Definition of Preschool Kentucky's preschool education programs are available for all four-year-old children whose family income is no more than 160% of poverty; all three and four-year-old children with developmental delays and disabilities, regardless of income; and other four-year- old children as placements are available based on district decision. The preschool program is designed to be developmentally appropriate for young children. "Developmentally appropriate" is defined in law to mean that the program focuses on the child's physical, intellectual, social and emotional development, including interpersonal, intrapersonal, and socialization skills. From http://education.ky.gov/educational/pre/Pages/default.aspx

Kentucky Preschool Regulations Let’s take a look at Kentucky Preschool Regulations

KY Early Childhood Standards

KY Early Childhood Standards The entire “Building A Strong Foundation for School Success” includes : Early Childhood Standards Continuous Assessment Guide Quality Self Study Additionally, there are Parent Guides for the Standards and now the application document of who to “use” the Standards . “road map” http:// kidsnow.ky.gov/School%20Readiness/Pages/Early-Childhood-Stand ards-2013.aspx

Building a Strong Foundation for School Success Kentucky’s Early Childhood Standards (KY ECS) Kentucky's Continuous Assessment Guide Kentucky Early Childhood Quality Self Study http://kidsnow.ky.gov/Improving-Early-Care/Pages/Tools-and-Resources.a spx

Building a Strong Foundation for School Success Parent Guides http://kidsnow.ky.gov/engaging-fa milies/Pages/Parent-Guides.aspx Field Guides http://kidsnow.ky.gov/Improving-E arly-Care/Pages/Tools-and-Resourc es.aspx

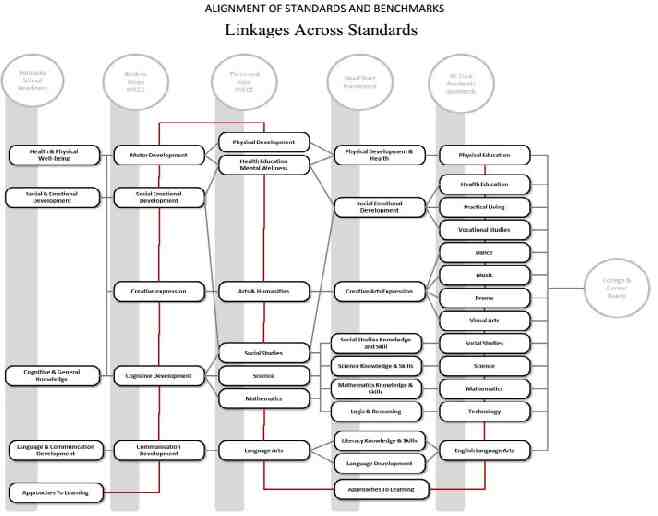
KY ECS The main goals of the KY ECS were to (1) ensure a linkage of early childhood standards and Kentucky Core Academic Standards across the Birth – Four age span; and (2) ensure linkage of early childhood standards and Kentucky Core Academic Standards with the Kentucky Program of Studies, K-12.

The guiding principles of the KY ECS Ensure the use of developmentally appropriate practices Support and enhance quality in early care and education settings Address a range of developmental needs Ensure attention to social/emotional needs Reflect cultural sensitivity Reflect an understanding of the ecological nature of early childhood

The KY ECS are broken down into Standards Benchmarks Developmental Example Continuum Behaviors **Take note of the KY Core Academic Standards and Head Start Outcomes**

Activity with the KY ECS In small groups or pairs, identify the Standard, Benchmark and Developmental Continuum that is being addressed in the provided scenario. Let’s Next, discuss our findings as a large group. we’ll see how the KY ECS align with the KY Core Academic Standards
KY Core Academic Standards http://education.ky.gov/districts/legal/Docu ments/Kentucky%20Core%20Academic%20 Standards%20June%202013.pdf

NAEYC Position on KY Core Academic Standards http://www.naeyc.org/topics/common-core

KY Core Academic Standards Learning Goals Goal 1 -Basic Communication and Mathematics Skills Goal 2- Application of Core Concepts Goal 3 - Developing Self-Sufficiency Goal 4 - Responsible Group Membership Goal 5 - Think and Solve Problems Goal 6 - Connect and Integrate Knowledge

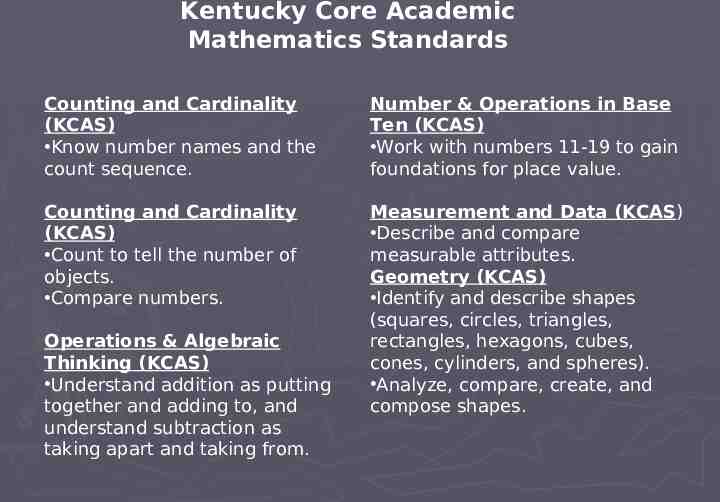
Kentucky Early Childhood Standard (KYECS) aligned to Kentucky Core Academic Kindergarten Standards (KYCAS) Mathematics

Kentucky Core Academic Mathematics Standards Counting and Cardinality (KCAS) Know number names and the count sequence. Number & Operations in Base Ten (KCAS) Work with numbers 11-19 to gain foundations for place value. Counting and Cardinality (KCAS) Count to tell the number of objects. Compare numbers. Measurement and Data (KCAS) Describe and compare measurable attributes. Geometry (KCAS) Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). Analyze, compare, create, and compose shapes. Operations & Algebraic Thinking (KCAS) Understand addition as putting together and adding to, and understand subtraction as taking apart and taking from.
Kentucky Early Childhood Standards MATHEMATICS (3S AND 4S) Standard 1: Demonstrates general skills and uses concepts of mathematics. Benchmark 1.1: Demonstrates an understanding of numbers and counting. Benchmark 1.2: Recognizes and describes shapes and spatial relationships. Benchmark 1.3: Uses the attributes of objects for comparison and patterning. Benchmark 1.4: Uses nonstandard and/or standard units to measure and describe

Kentucky Early Childhood Standard 3s and 4s (KYECS) aligned to Kentucky Core Academic Kindergarten Standards (KYCAS) English/Language Arts

Kentucky Core Academic English/Language Arts Standards Reading Literature Key Ideas and Details Craft and Structure Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity Reading Informational Texts Key Ideas and Details Craft and Structure Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity Foundational Skills Print Concepts Phonological Awareness Phonics and Word Recognition Fluency Writing Text Types and Purposes Production and Distribution of Writing Research to Build and Present Knowledge Range of Writing Speaking and Listening Comprehension and Collaboration Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas Language Conventions of Standard English Knowledge of Language Vocabulary Acquisition and Use

Kentucky Early Childhood Standards – English/Language Arts (3S AND 4S) English/Language Arts Standard 1: Demonstrates general skills and strategies of the communication process. Benchmark 1.1: Uses non-verbal communication for a variety of purposes. Benchmark 1.2: Uses language (verbal, signed, symbolic) for a variety of purposes. Benchmark 1.3: Communicates with increasing clarity and use of conventional grammar. English/Language Arts Standard 2: Demonstrates general skills and strategies of the listening and observing processes. Benchmark 2.1: Engages in active listening in a variety of situations. Benchmark 2.2: Observes to gain information and understanding. English/Language Arts Standard 3: Demonstrates general skills and strategies of the reading process. Benchmark 3.1: Listens to and/or responds to reading materials with interest and enjoyment. Benchmark 3.2: Shows interest and understanding of the basic concepts and conventions of print. Benchmark 3.3: Demonstrates knowledge of the alphabet. Benchmark 3.4: Demonstrates emergent phonemic/phonological awareness. Benchmark 3.5: Draws meaning from pictures, print, and text. Benchmark 3.6: Tells and retells a story. English/Language Arts Standard 4: Demonstrates competence in the beginning skills and strategies of the writing process. Benchmark 4.1: Understands that the purpose of writing is communication. Benchmark 4.2: Produces marks, pictures, and symbols that represent print and ideas.

IECE Teacher Standards

KY IECE Teacher Standards Standard I: Designs/Plans Instruction Standard II: Creates/Maintains Environments Standard III: Implements Instruction Standard IV: Assesses & Communicates Learning Results Standard V: Reflects/Evaluates Professional Practices Standard VI: Collaborates with Colleagues/Families/Others Standard VII: Engages in Professional Development Standard VIII: Supports Families Standard IX: Demonstrates Implementation of Technology Standard X: Provides Leadership within School/Community/Profession

KY IECE Teacher Standards Let’s take time for review of the Standards and Indicators What is unique in the IECE Standards? How do these standards reflect the environment being created? Review the information you shared on the charts and compare to the IECE Standards.

KTIP IECE

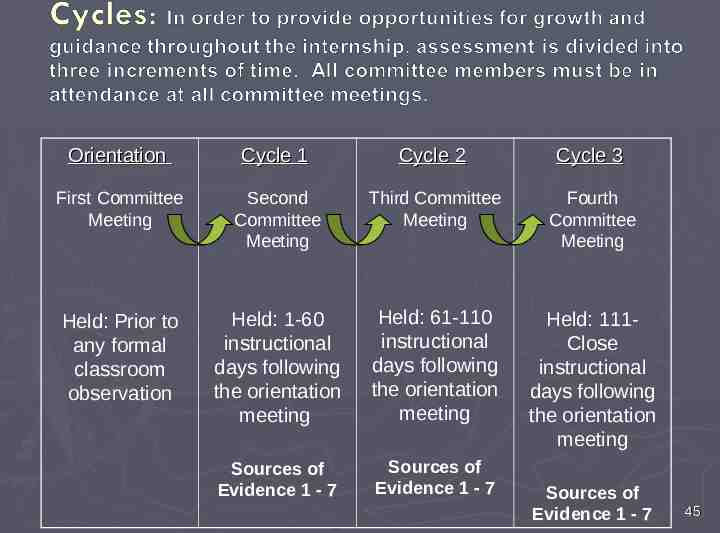
Orientation Cycle 1 Cycle 2 Cycle 3 First Committee Meeting Second Committee Meeting Third Committee Meeting Fourth Committee Meeting Held: Prior to any formal classroom observation Held: 1-60 instructional days following the orientation meeting Held: 61-110 instructional days following the orientation meeting Held: 111Close instructional days following the orientation meeting Sources of Evidence 1 - 7 Sources of Evidence 1 - 7 Sources of Evidence 1 - 7 45
Source of Evidence Professional Growth Self-Assessment of Performance See page 18 in KTIP Handbook Prior to orientation meeting: Intern completes self-assessment Intern reviews self-assessment with resource teacher Resource teacher asks guided questions At orientation meeting: Discuss results of self-assessment 46

Lesson Plan When Plan? does the intern complete Lesson Before each lesson being observed. Review each of the requirements of Lesson Plan on pages 8-9 of your KTIP Handbook. 47

Lesson Plan What are the children doing? Are the activities developmentally appropriate? What does the physical How will the environment be used environment look like? in teaching and learning? What is included in the daily routine How does the intern plan for / schedule? transition? What is the teacher doing? How does the intern plan for her/his teaching? What are the other adults in the How does the intern plan for the environment doing? other adults to participate in teaching? How do we know children are Are the assessments appropriate? learning? How are all children included in all Is intern planning for individual activities? needs? How are the families included? How does the lesson plan reflect family collaboration?

Demonstrate Teaching Skills During Observation Using the Lesson Plan that you have developed, discuss how that observation may look. For example: What are the children doing? What will the environment look like? What is included in the daily routine/schedule? What is the teacher doing? What are the other adults in the environment doing? How do we know children are learning? How are all children included in all activities? How are families included? 49 49

The Post-Observation Conference All committee members conduct a post observation conference prior to the committee meeting. The post-observation conference should take place as soon as possible after the observation. 50

Post Observation and Reflection Analysis of student performance data and reflection on the impact of instruction are critical to improve teaching. Review pages 10 - 11 of the KTIP Handbook. Must be completed no later than two days after each observed lesson. Discuss with a shoulder partner mentoring suggestions. 51

Professional Growth The Professional Growth Source of Evidence is a critical source of documentation that shows the intern has been afforded due process during the internship. When assisting the intern in choosing professional development activities, it is important to direct the intern to activities that will specifically address priority growth needs. 52

Student Voice Is NOT required for IECE interns

Professional Involvement Log Records and Communication

Introduction to the IPR In pairs / small group, review the IPR. Again, identify what you find as unique about IECE.

Resources Kentucky Preschool Guidance (PGES) http://education.ky.gov/teachers/pges/tpges/documents/ tpges%20guidance%20for%20preschool.pdf Kentucky Department of Education http://education.ky.gov/Pages/default.aspx KDE Preschool Education Programs for Teachers/Administrators http://education.ky.gov/curriculum/conpro/prim-pre/ Pages/default.aspx Building a Strong Foundation for School Success http://kidsnow.ky.gov/Improving-Early-Care/Pages/Toolsand-Resources.aspx

Resources First Steps – Kentucky’s Early Intervention System http://chfs.ky.gov/dph/firststeps.htm National Association for the Education of Young Children http://www.naeyc.org/ Division of Early Childhood http://www.dec-sped.org/ Center in the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning http://csefel.vanderbilt.edu/ Technical Assistance Center on Social Emotional Intervention http://www.challengingbehavior.org/ CONNECT Modules http://community.fpg.unc.edu/ Kentucky Autism Training Center http://louisville.edu/education/kyautismtraining

Resources Transition One Stop http://www.transitiononestop.org/ The National Early Childhood Technical Assistance Center http://ectacenter.org/ Early Childhood Standards: 2013 http://kidsnow.ky.gov/School%20Readiness/Pages/EarlyChildhood-Standards-2013.aspx IECE Brochure http://education.ky.gov/educational/pre/Documents/IECE Brochure.doc