Technical Report Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks
24 Slides515.02 KB

Technical Report Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion

INTRODUCTION WiMax Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access IEEE 802.16 standards IEEE 802.16d - 2004 IEEE 802.16e - 2005 IEEE 802.16m - TBA Last Mile Broadband Access Wireless alternative to cable and DSL Deployment Sprint 4G network Clearwire ISP
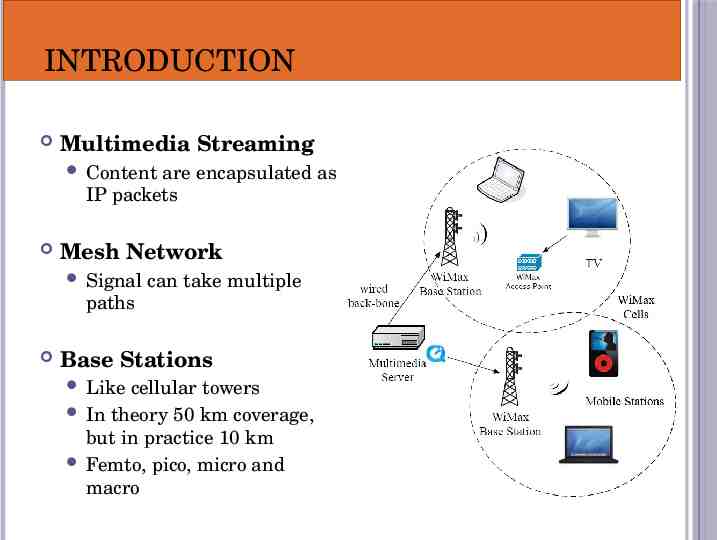
INTRODUCTION Multimedia Streaming Content are encapsulated as IP packets Mesh Network Signal can take multiple paths Base Stations Like cellular towers In theory 50 km coverage, but in practice 10 km Femto, pico, micro and macro

INTRODUCTION Subscriber Stations Client devices Built-in laptop or multimedia devices Standalone access point Mobile Stations Mobile version of SS Battery powered, power saving is important

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion

PROTOCOL LAYERS Two Layers MAC and PHY layers Integrates into OSI Data Link and Physical layers Media Access Control (MAC) Layer Interfaces with upper layer protocols Allows Wimax to be build on top of multimedia applications. Provides Packets fragmentation Security Quality of Service (QoS)
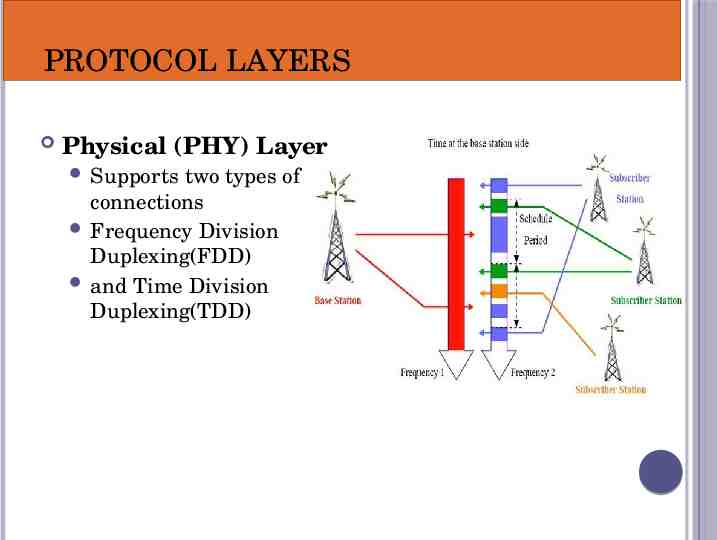
PROTOCOL LAYERS Physical (PHY) Layer Supports two types of connections Frequency Division Duplexing(FDD) and Time Division Duplexing(TDD)

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion

MULTIMEDIA FEATURES Multicast Broadcast Service (MBS) Provides multimedia broadcast services Dedicated MBS frame or piggyback with unicast Supports macro diversity and mobility Mechanisms for delivery during sleep-mode Forward Error Correction (FEC) Convolutional codes is required Encoding is apply at the PHY layer

MULTIMEDIA FEATURES Power Saving Support for sleep mode is mandatory in BS Optional on receiver 3 Power saving classes Type 1: fixed length, each sleep window is twice the last Type 2: equal sleep and listen windows Type 3: single sleep and listen windows, the BS controls the start and end time. Recommended for multicast services.

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion
QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) Service Flows (SF) Defines by the MAC layer Maps QoS to each connection Packets scheduling not defined by standard 5 QoS Classes Each connection is assigned to a class Assign by the BS Request by the clients / subscriber stations Can be on-demand Details of each class in Tech Report

QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) Voice over IP (VoIP) Request for Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) Explicit bandwidth grant, BS grants bandwidth as needed Streaming Video Real-Time Polling Service (rtPS) BS provides unicast poll, the SS can request for additional bandwidth Requires more overhead than UGS
QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) Bandwidth Requests Initiates by the SS In Broadcast service it affects all SS Can be on a per connection basis Piggyback with another packet Bandwidth Grants Grants are given out on a per connection or per subscriber station Grants per subscriber requires a scheduler at the SS

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion

EXISTING WORKS IPTV over WiMax WiMax as last mile TV channels are encapsulated No mentioning of ESG WiMax as extension to DVB-H Complement coverage for DVB-H Provides services where satellite coverage is not possible (indoor). End users equip with WiMax receiver instead of DVB-H

EXISTING WORKS Video Delivery Proposed new sublayer Uses MBS framework Channels are mapped to connections SVC Streaming Leverage multiple connections feature Uses Report Periods to request target bit rates Additional connections to improve reliability

EXISTING WORKS SVC Streaming with MIMO Uses multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technique Separate video bitstream into important (Iframes) and opportunistic bits (B and Pframes) I-frames are given higher code gain Results in better peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR)

Multimedia Streaming Over WiMax Networks Introduction Protocol Layering Multimedia Features Quality of Service (QoS) Existing Works Enhanced MBS Conclusion

E-MBS Enhanced Multicast Broadcast Service (EMBS) IEEE 802.16m draft Support for switching between broadcast and unicast services Connections can switch between broadcast and unicast mode Strict Requirements for Interruption Times 1 to 1.5 seconds

CONCLUSION WiMax is an ideal medium for multimedia streaming Standard features Multicast Broadcast Service (MBS) Quality of Service (QoS) Real-time bandwidth grants Enhanced version of MBS (E-MBS) Improves multimedia streaming over WiMax

REFERENCES [1] R. Hamzaoui, V. Stankovic, and Z. Xiong, Multimedia Over IP AND Wireless Networks: Compression, Networking, and Systems, 1st ed. AP, 2007. [2] J. Andrews, A. Ghosh, and R. Muhamed, Fundamentals of WiMAX: Understanding Broadband Wireless Networking, 1st ed. Prentice Hall, 2008. [3] A. Sayenko, V. Tykhomyrov, H. Martikainen, and O. Alanen, “Performance analysis of the ieee 802.16 arq mechanism,” in MSWiM ’07: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Symposium on Modeling, analysis, and simulation of wireless and mobile systems, Chania, Crete Island, Greece, 2007, pp. 314 322. [4] F. Ohrtman, WiMAX Handbook: Building 802.16 Wireless Networks., 1st ed. McGraw-Hill, 2005. [5] I. Uilecan, C. Zhou, and G. Atkin, “Framework for delivering iptv services over wimax wireless networks,” in Proc.

REFERENCES [6] G. Gur, S. Bayhan, F. Alagoz, and A. Jamalipour, “Framework for delivering iptv services over wimax wireless networks,” in Proc. IEEE International Workshop on Satellite and Space Communications, 2008 (IWSSC ’08), Legans, Madrid, Spain, October 2008, pp. 326–330. [7] J. Wang, M. Venkatachalam, and Y. Fang, “System architecture and cross-layer optimization of video broadcast over wimax,” Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 712–721, May 2007. [8] H. Juan, H. Huang, C. Y. Huang, and T. Chiang, “Cross-layer system designs for scalable video streaming over mobile wimax,” in Proc. WCNC 2007, Hong Kong, China, March 2007, pp. 1862 – 1866. [9] J. Chui and A. Calderbank, “Multilevel diversity-embedded space-time codes for video broadcasting over wimax,” in Proc. International Symposium on Information Theory, 2008 (ISIT ’08), Toronto, Canada, July 2008, pp. 1068–1072. [10] C. Cicconetti, L. Lenzini, E. Mingozzi, and C. Eklund, “Quality of service support in ieee 802.16 networks,” IEEE Network, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 50–55, March/April 2006.