Stopping Attacks Before They Stop Business Jeff Vealey – Customer
45 Slides9.98 MB

Stopping Attacks Before They Stop Business Jeff Vealey – Customer Success Technical Advisor CyberArk Software 1
State of play There are only two types of companies: Those that have been hacked, and those that will be. Even that is merging in to one category; those that have been hacked and will be again. FBI Director Robert Mueller 2012 2
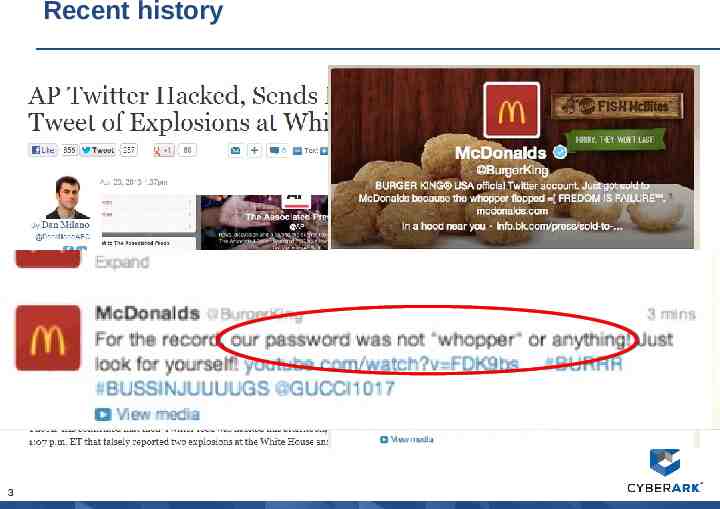
Recent history 3
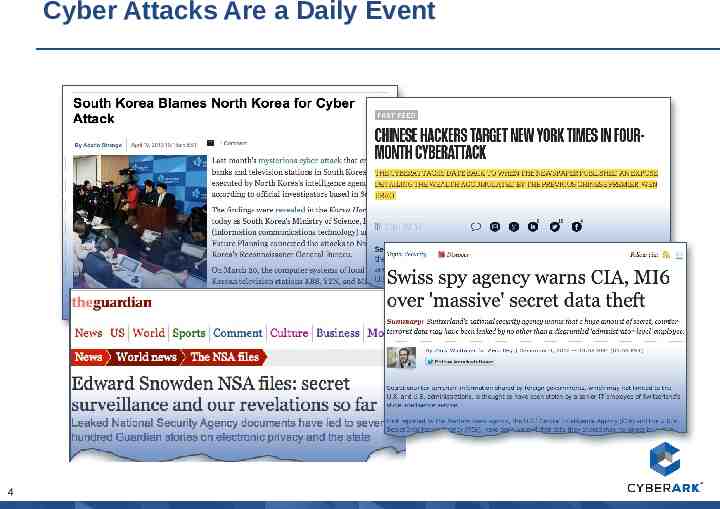
Cyber Attacks Are a Daily Event 4

Cyber Security and Privileged Access “ 100% “ 100% of data breaches breaches involved stolen stolen credentials.” credentials.” Mandiant, M-Trends and APT1 Report 5 “APT “APT intruders prefer intruders prefer to to leverage leverage privileged privileged accounts accounts where where possible, possible, such such as as Domain Domain Administrators, Administrators, service service accounts accounts with with Domain Domain privileges, privileges, local local Administrator Administrator accounts, accounts, and and privileged privileged user user accounts.” accounts.”
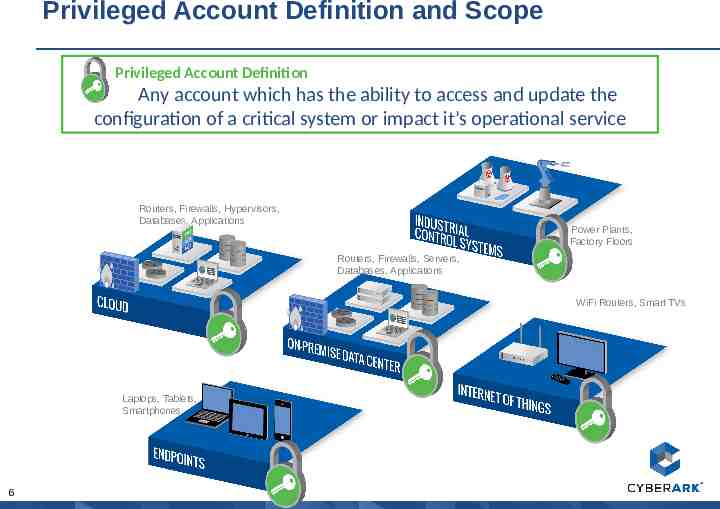
Privileged Account Definition and Scope Privileged Account Definition Any account which has the ability to access and update the configuration of a critical system or impact it’s operational service Routers, Firewalls, Hypervisors, Databases, Applications Power Plants, Factory Floors Routers, Firewalls, Servers, Databases, Applications WiFi Routers, Smart TVs Laptops, Tablets, Smartphones 6
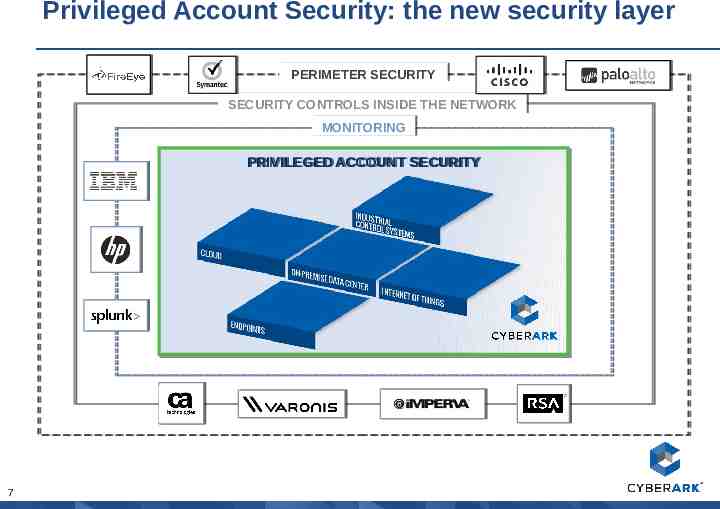
Privileged Account Security: the new security layer PERIMETER PERIMETER SECURITY SECURITY SECURITY SECURITY CONTROLS CONTROLS INSIDE INSIDE THE THE NETWORK NETWORK MONITORING MONITORING PRIVILEGED PRIVILEGED ACCOUNT ACCOUNT SECURITY SECURITY 7
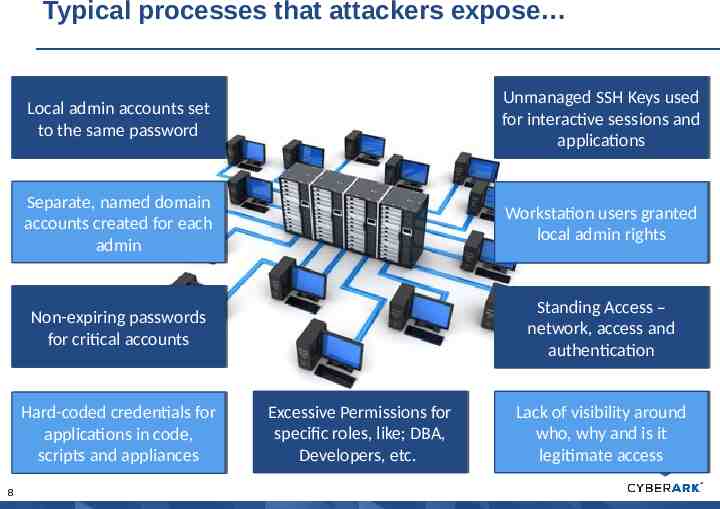
Typical processes that attackers expose Local Local admin admin accounts accounts set set to to the the same same password password Unmanaged Unmanaged SSH SSH Keys Keys used used for for interactive interactive sessions sessions and and applications applications Separate, Separate, named named domain domain accounts accounts created created for for each each admin admin Workstation Workstation users users granted granted local local admin admin rights rights Non-expiring Non-expiring passwords passwords for for critical critical accounts accounts Standing Standing Access Access –– network, network, access access and and authentication authentication Hard-coded Hard-coded credentials credentials for for applications applications in in code, code, scripts scripts and and appliances appliances 8 Excessive Excessive Permissions Permissions for for specific specific roles, roles, like; like; DBA, DBA, Developers, Developers, etc. etc. Lack Lack of of visibility visibility around around who, who, why why and and is is itit legitimate legitimate access access

Data Breaches - Real Life Example 9

How did the attackABC start? Company Step 2: Executive user with local admin Privilege discovered. Pass the hash attack starts Step 1: Attackers used Phishing Scam to detect local admin users. 10 Step 3: Hash of helpdesk user who remotely assisted executive 3 days prior extracted and used.
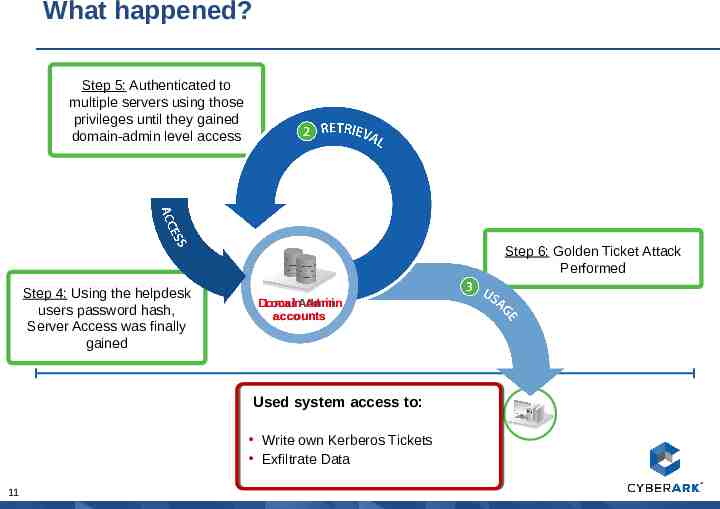
What happened? Step 5: Authenticated to multiple servers using those privileges until they gained domain-admin level access Step 6: Golden Ticket Attack Performed Step 4: Using the helpdesk users password hash, Server Access was finally gained Domain Local Admin Admin accounts Used system access to: Write own Kerberos Tickets Exfiltrate Data 11

Comprehensive Approach Required 12

Stats 13
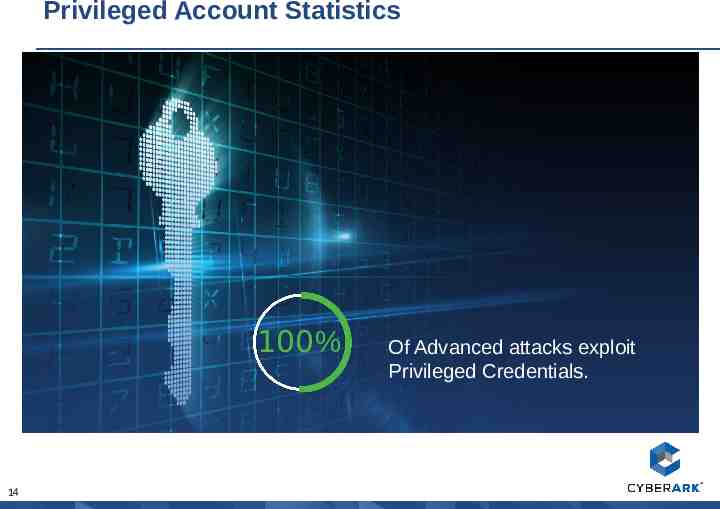
Privileged Account Statistics 100% 14 Of Advanced attacks exploit Privileged Credentials.
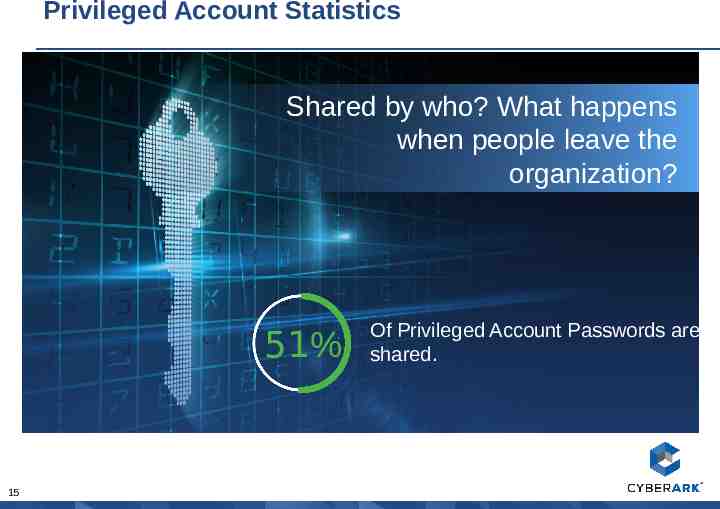
Privileged Account Statistics Shared by who? What happens when people leave the organization? 51% 15 Of Privileged Account Passwords are shared.

Privileged Account Statistics Current processes are making it easier for attackers to move around the infrastructure. 53% 16 Of Large Enterprises take 90 days or longer to change Privileged Passwords.

Privileged Account Statistics There is more than 1 way to underestimate this. Amount, Scope, Power, Same/Similar Passwords 86% 17 Of Large Enterprises do not know, or have underestimated the magnitude of their Privileged Account Security problem.

Privileged Account Statistics Remember the breach for a US health insurer? 70 million credit card details were stolen because of 1 unmanaged credential. 67% 18 Of Privileged Accounts across Enterprises are either unknown or un-managed
Privileged Account Statistics Truth? ?% 19 Are these numbers correct?
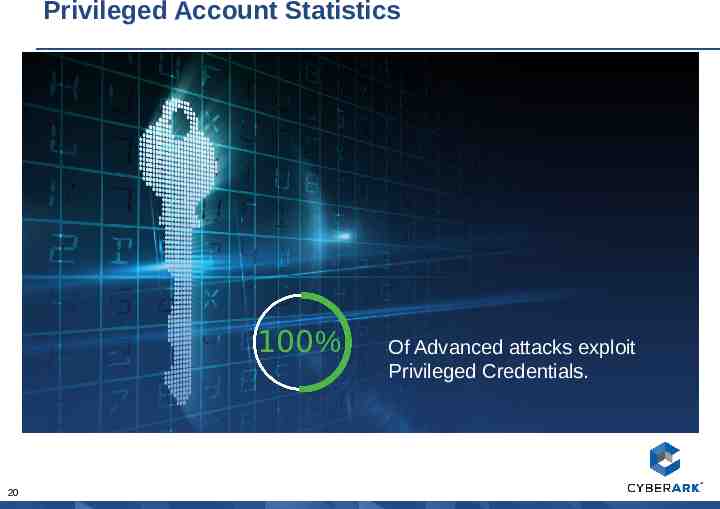
Privileged Account Statistics 100% 20 Of Advanced attacks exploit Privileged Credentials.

Compliance View 21

Compliance and Regulation PCI PCI SOX SOX 22

Reduce Risk of Privileged Account Exploits 23

Implement a standardized privileged access strategy For each layer: Why is Privileged Access needed? APPLICATION APPLICATION DATABASE DATABASE OPERATING OPERATING SYSTEM SYSTEM NETWORK NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE INFRASTRUCTURE 24 Who needs Privileged Access? Which entities are used to authenticate? Can approval workflows be enforced? What controls are in place right now?
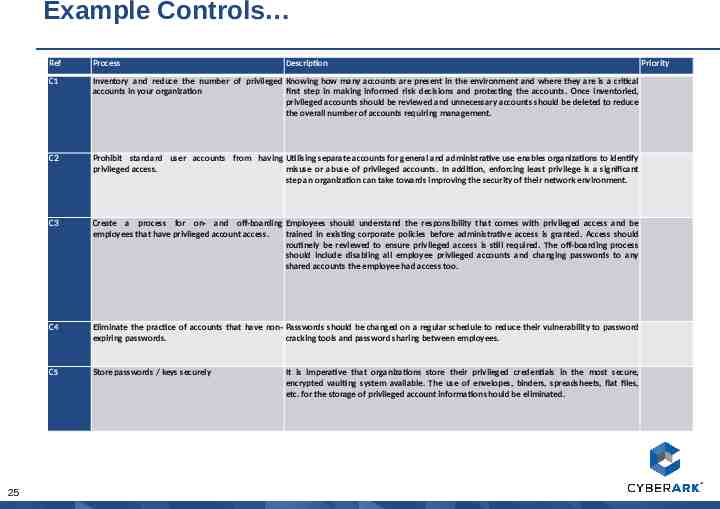
Example Controls 25 Ref Process Description C1 Inventory and reduce the number of privileged Knowing how many accounts are present in the environment and where they are is a critical accounts in your organization first step in making informed risk decisions and protecting the accounts. Once inventoried, privileged accounts should be reviewed and unnecessary accounts should be deleted to reduce the overall number of accounts requiring management. C2 Prohibit standard user accounts from having Utilising separate accounts for general and administrative use enables organizations to identify privileged access. misuse or abuse of privileged accounts. In addition, enforcing least privilege is a significant step an organization can take towards improving the security of their network environment. C3 Create a process for on- and off-boarding Employees should understand the responsibility that comes with privileged access and be employees that have privileged account access. trained in existing corporate policies before administrative access is granted. Access should routinely be reviewed to ensure privileged access is still required. The off-boarding process should include disabling all employee privileged accounts and changing passwords to any shared accounts the employee had access too. C4 Eliminate the practice of accounts that have non- Passwords should be changed on a regular schedule to reduce their vulnerability to password expiring passwords. cracking tools and password sharing between employees. C5 Store passwords / keys securely It is imperative that organizations store their privileged credentials in the most secure, encrypted vaulting system available. The use of envelopes, binders, spreadsheets, flat files, etc. for the storage of privileged account information should be eliminated. Priority
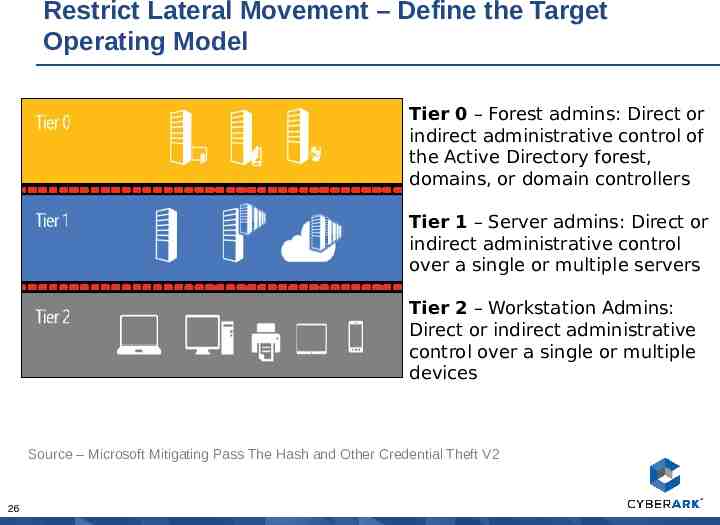
Restrict Lateral Movement – Define the Target Operating Model Tier 0 – Forest admins: Direct or indirect administrative control of the Active Directory forest, domains, or domain controllers Tier 1 – Server admins: Direct or indirect administrative control over a single or multiple servers Tier 2 – Workstation Admins: Direct or indirect administrative control over a single or multiple devices Source – Microsoft Mitigating Pass The Hash and Other Credential Theft V2 26

Privileged Account Security 27

Privileged Account Security - Critical Steps Discover all of your privileged accounts Protect and manage privileged account credentials Control, isolate and monitor privileged access to servers and databases Implement least privileges access for server and workstation access Use real-time privileged account intelligence to detect and respond to in-progress attacks 28
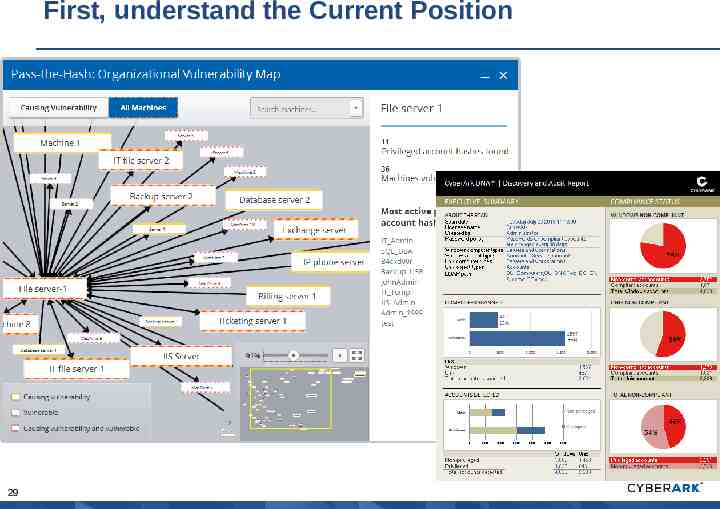
First, understand the Current Position 29
30

Protect and Manage Privileged Account Credentials Protect the Privileged Credentials – Secure Digital Vault Implement strong credential access workflows Simplify policy management - “master policy” function

Control, Isolate and Monitor Privileged Activity Establish a single point of control for privileged sessions Isolate malware from the target system Monitor and record command level activity
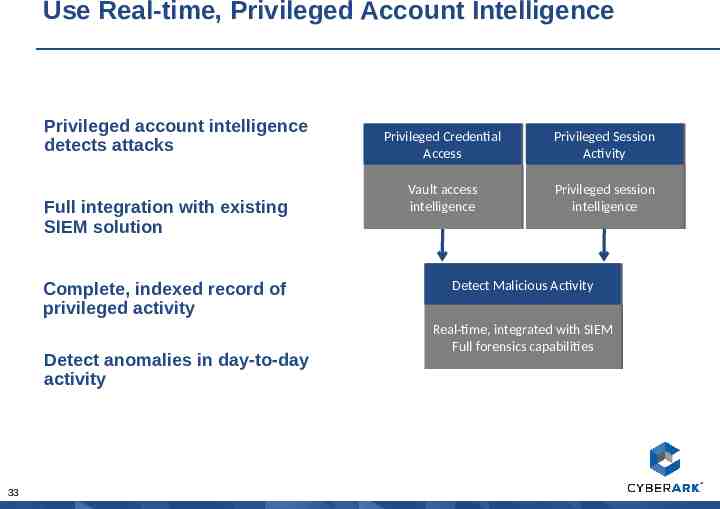
Use Real-time, Privileged Account Intelligence Privileged account intelligence detects attacks Full integration with existing SIEM solution Complete, indexed record of privileged activity Detect anomalies in day-to-day activity 33 Privileged Privileged Credential Credential Access Access Privileged Privileged Session Session Activity Activity Vault Vault access access intelligence intelligence Privileged Privileged session session intelligence intelligence Detect Detect Malicious Malicious Activity Activity Real-time, Real-time, integrated integrated with with SIEM SIEM Full Full forensics forensics capabilities capabilities
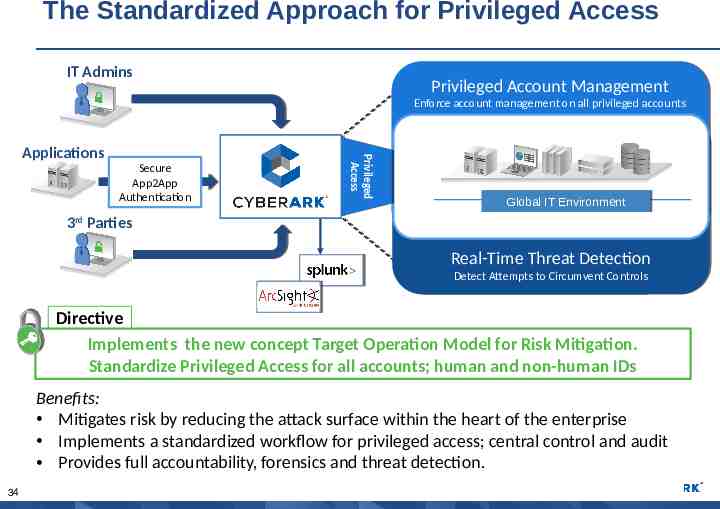
The Standardized Approach for Privileged Access IT Admins Privileged Privileged Account Account Management Management Enforce Enforce account account management management on on all all privileged privileged accounts accounts Secure App2App Authentication Privileged Access Applications Global Global IT IT Environment Environment 3rd Parties Real-Time Real-Time Threat Threat Detection Detection Detect Detect Attempts Attempts to to Circumvent Circumvent Controls Controls Directive Implements the new concept Target Operation Model for Risk Mitigation. Standardize Privileged Access for all accounts; human and non-human IDs Benefits: Mitigates risk by reducing the attack surface within the heart of the enterprise Implements a standardized workflow for privileged access; central control and audit Provides full accountability, forensics and threat detection. 34

So .in summary 35

36

37

38

39

40

41

42

43

44

Thank you 45






