Soil Taxonomy and Classification
47 Slides4.48 MB

Soil Taxonomy and Classification

Soil Taxonomy Hierarchy Order 12 Suborder 63 Great group 250 Sub group 1400 Family 8000 Series 19,000 Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species

Diagnostic Surface Horizons Epipedons Mollic Umbric Ochric Histic Melanic Plaggen Anthropic Very common “specialized” Human-derived
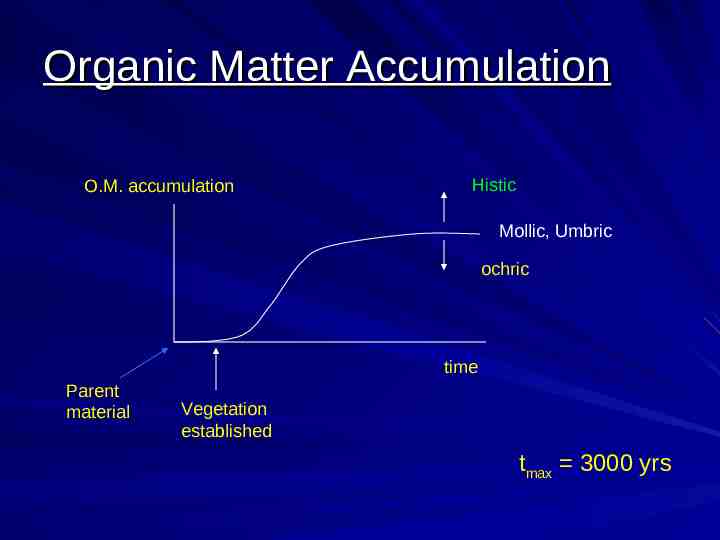
Organic Matter Accumulation O.M. accumulation Histic Mollic, Umbric ochric time Parent material Vegetation established tmax 3000 yrs

Diagnostic Sub-surface Horizons

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Formation Translocation Transformation Clays Organic Matter Oxides
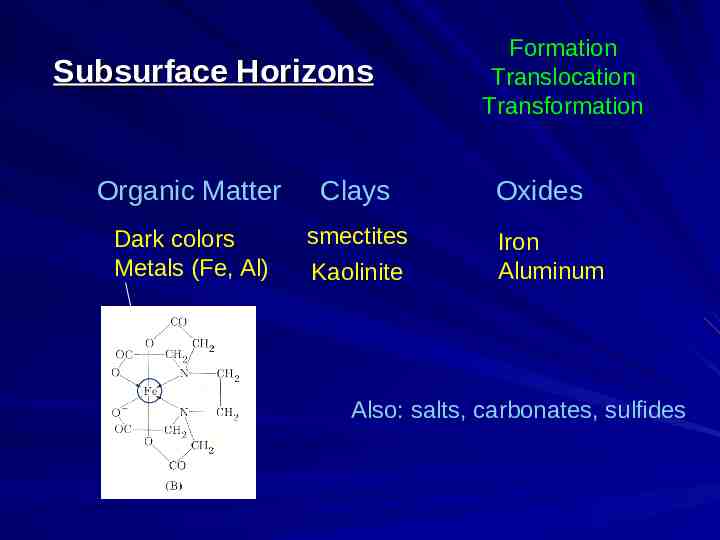
Subsurface Horizons Organic Matter Clays Dark colors Metals (Fe, Al) smectites Kaolinite Formation Translocation Transformation Oxides Iron Aluminum Also: salts, carbonates, sulfides

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Albic Argillic Spodic Oxic Kandic Cambic Sombric sulfuric Natric Agric Calcic Gypsic Salic Duripan Fragipan Placic Subordinate Distinctions

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Albic (white) Horizon Light-colored (Value 6 moist ) Elluvial (E master horizon*) Low in clay, Fe and Al oxides Generally sandy textured Low chemical reactivity (low CEC) Typically overlies Bh or Bt horizons *not all E horizons are albic horizons albic

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Argillic Horizon Illuvial accumulation of silicate clays Illuvial based on overlying horizon Clay bridges Clay coatings Bt horizon

Diagnostic Subsurface Clay Horizons Argillic Horizon High Necessary Kandic Horizon Activity of Clays Illuviation of clay Low Not Necessary

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Spodic Horizon Illuvial accumulation of organic matter and aluminum ( /- iron) Dark colored (value, chroma 3) Low base saturation (acidic) Formed under humid acid conditions Bh horizon Spodic

Elluviation and Illuviation Elluviation (E horizon and A horizons) Organic matter Clays A A E E Bh horizon Bt horizon Bt Bh Spodic horizon Argillic horizon

Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons Oxic horizon Highly weathered (high temperatures, high rainfall) activity - High in Fe, Al oxides - High in low-activity clays (kaolinite smectite vermiculite) Bo horizon

Diagnostic Horizons Surface Horizons: Mollic- thick, dark colored, high %B.S., structure Umbric – same, but lower B.S. Ochric – pale, low O.M., thin Histic – High O.M., thick, wet, dark Sub-Surface Horizons: Argillic – illuvial accum. of clay (high activity) Kandic – accum. of clay (low activity) Spodic – Illuvial O.M. accumulation (Al and/or Fe) Oxic – highly weathered, kaolinite, Fe and Al oxides Albic – light colored, elluvial, low reactivity

Soil Taxonomy Diagnostic Epipedons Diagnostic Subsurface horizons Moisture Regimes Temperature Regimes Age Texture Depth
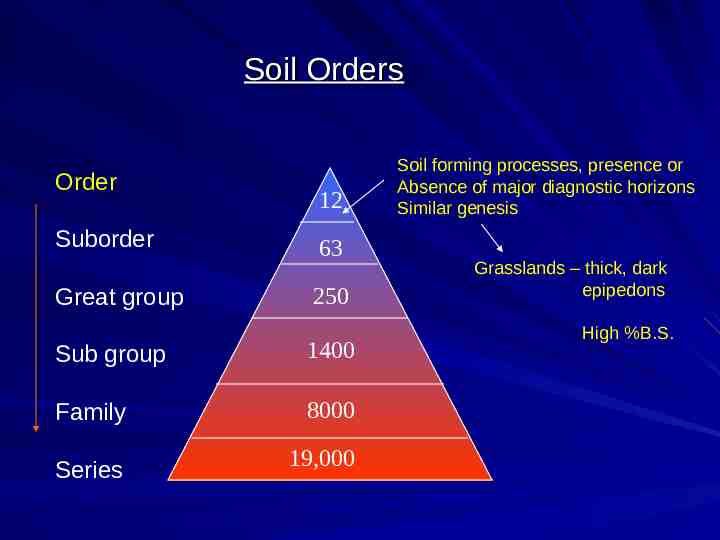
Soil Orders Order Suborder Great group 12 63 250 Sub group 1400 Family 8000 Series 19,000 Soil forming processes, presence or Absence of major diagnostic horizons Similar genesis Grasslands – thick, dark epipedons High %B.S.

Soil Orders Entisols Histosols Inceptisols Andisols Gelisols Alfisols Mollisols Ultisols Spodosols Aridisols Vertisols Oxisols

Soil Orders Entisol Histosol Inceptisol Alfisol Ultisol Spodosol Mollisol EntHistInceptAlfUltSpodMoll- Recent Histic (organic) Inception Television alien Ultimate Spodos (wood ash) Mollis (soft) Oxisol Andisol Gelisol Aridisol Vertisol OxAndGelAridVert- oxide Ando (black) Gelid (cold) Arid (dry) Verto (turn)
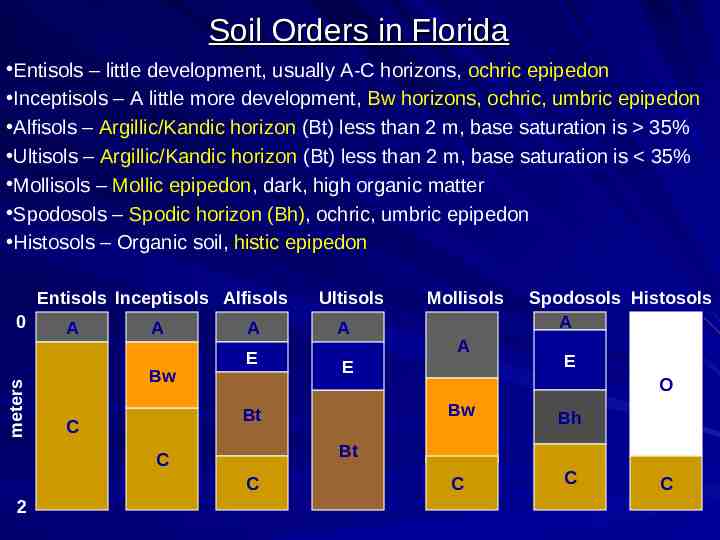
Soil Orders in Florida Entisols – little development, usually A-C horizons, ochric epipedon Inceptisols – A little more development, Bw horizons, ochric, umbric epipedon Alfisols – Argillic/Kandic horizon (Bt) less than 2 m, base saturation is 35% Ultisols – Argillic/Kandic horizon (Bt) less than 2 m, base saturation is 35% Mollisols – Mollic epipedon, dark, high organic matter Spodosols – Spodic horizon (Bh), ochric, umbric epipedon Histosols – Organic soil, histic epipedon Entisols Inceptisols Alfisols meters 0 A A Bw A E A C Mollisols A E Bt Spodosols Histosols A E O Bw Bh C C Bt C C 2 Ultisols C

Entisols Young Soils Weaklly developed Sandy or clayey Ochric Epipedon A – C profiles
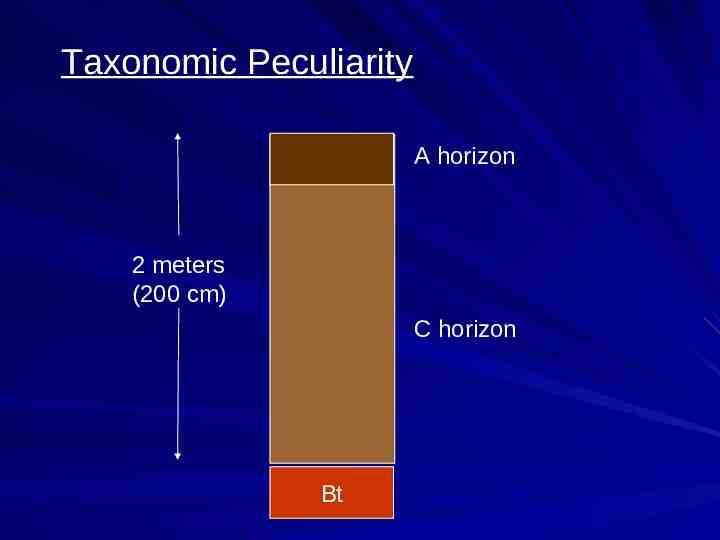
Taxonomic Peculiarity A horizon 2 meters (200 cm) C horizon Bt

Entisols

Inceptisols Ap horizon Little Development Ochric, Histic, or Umbric epipedon One or more subsurface horizons Weakly developed Contains many unweathered minerals Bw horizon C horizon

Histosols Peat or muck 20% organic matter Agriculturally valuable Sometimes used as fuel Often over impermeable material

Histosols
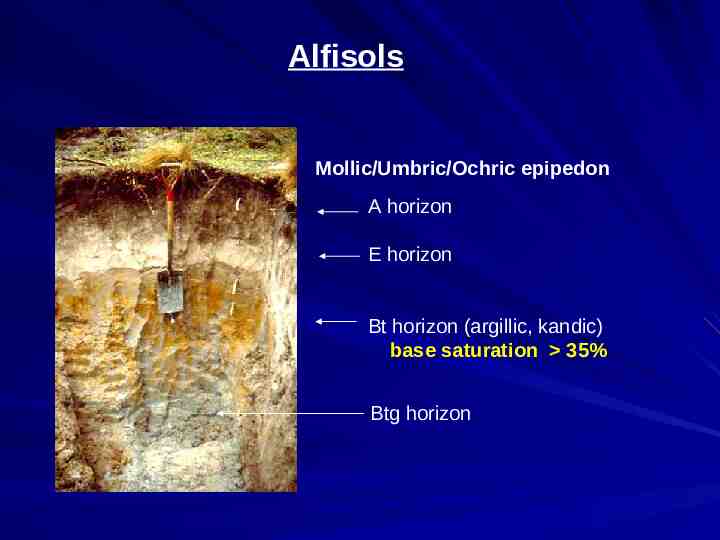
Alfisols Mollic/Umbric/Ochric epipedon A horizon E horizon Bt horizon (argillic, kandic) base saturation 35% Btg horizon

Ultisols A horizon E horizon Bt horizon Mollic/umbric/Ochric epipedon Argillic or Kandic horizon Base saturation 35%

Ultisols and Alfisols Mixed Hardwood Forests

Spodosols Associated with acidic vegetation Subsoil accumulation of organic matter with aluminum and/or iron Formed under Wet acidic conditions Poorly or Very poorly drained Pine Flatwoods State Soil of Florida

Spodosols Pine Flatwoods (wet, acidic)

Mollisols Mollic Epipedon High organic matter Thick surface horizon Highly productive Many with argillic Poorly-drained Surface % B.S. 50%

Mollisols Grasslands

Soil Orders Weathering and development slight Entisols Histosols Inceptisols Andisols Gelisols Aridisols Vertisols Alfisols Mollisols Ultisols Spodosols Strong Oxisols
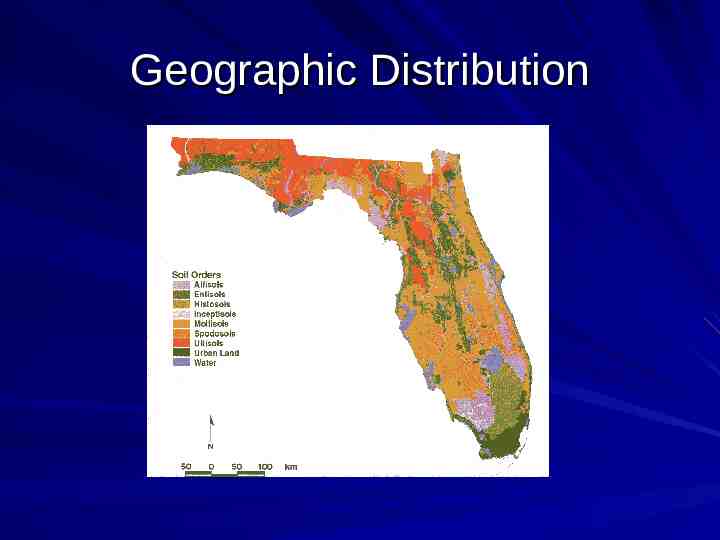
Geographic Distribution
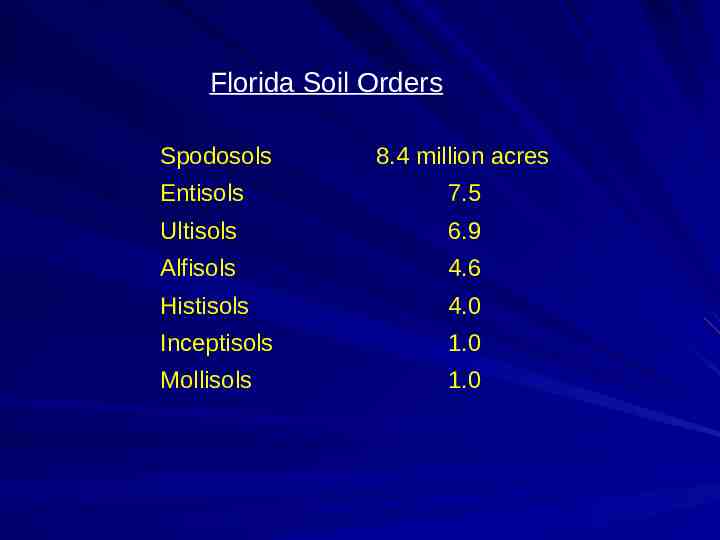
Florida Soil Orders Spodosols 8.4 million acres Entisols 7.5 Ultisols 6.9 Alfisols 4.6 Histisols 4.0 Inceptisols 1.0 Mollisols 1.0

Soil Taxonomy Order 12 Soil forming processes / diagnostic horizons Suborder 63 Great group 250 Sub group 1400 Family 8000 Series 19,000 Genetic similarity: Wetness, climate, vegetation
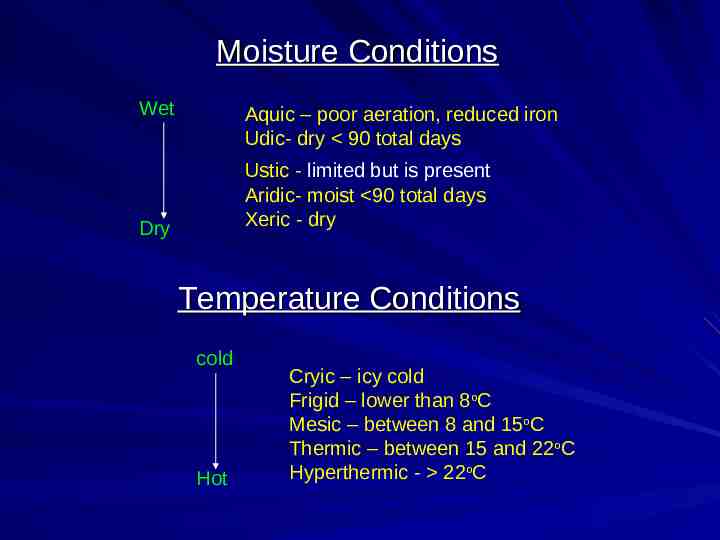
Moisture Conditions Wet Aquic – poor aeration, reduced iron Udic- dry 90 total days Ustic - limited but is present Aridic- moist 90 total days Xeric - dry Dry Temperature Conditions cold Hot Cryic – icy cold Frigid – lower than 8oC Mesic – between 8 and 15oC Thermic – between 15 and 22oC Hyperthermic - 22oC

Suborders Temperature, moisture, diagnostic horizons Suborder Examples Aquod Udult Udoll Xeroll Ochrept Umbrept alboll very wet spodosol wet ultisol wet mollisol dry mollisol

Soil Taxonomy Order 12 Suborder 63 Great group 250 Sub group 1400 Family 8000 Series 19,000 Soil forming processes / diagnostic horizons Soil moisture conditions, diagnostic horizon Arrangement of Diagnostic horizons

Great Groups Based on diagnostic horizons and their arrangements or other features like age, color, texture Arg - argillic horizon present Pale - old Kand - kandic horizon present Hapl - minimum horizonation quartzi – quartz sand Hum - humid

Greater Specificity Order Suborder Great Group Ultisol Udult paleudult Mollisol Aquoll argiaquoll Alfisol Udalf paleudalf Ultisol Udult hapludult

Sub group Expresses the core concept of the great group Moisture, sandiness, depth, color Typic Arenic Grossarenic Aquic shallow sand deeper sand deep sand Typic hapludult Grossarenic quartzipsamment Subgroup Great group suborder order

Families Properties important to growth of plant roots Particle size mineralogy Sandy Loamy Fine loamy Clayey Siliceous Kaolinitic Smectitic Oxidic temperature oC Frigid 8 Mesic 8-15 Thermic 15-22 Hyperthermic 22

Series Horizon number, order, thickness, texture, structure, Color, Organic matter, pH, accumulations Order Mollisol Sub-order G. Group Aquoll Argiaqoll Sub-group typic Argiaquoll Family Series typic argiaquoll Brookston loamy siliceous Cordova Westland

Alachua County Apopka loamy, siliceous, hyperthermic grossarenic paleudult Ledwith fine, smectitic, hyperthermic mollic albaqualf Surrency loamy, siliceous, thermic, arenic paleaquult Pomona sandy, siliceous, hyperthermic, ultic, haplaquod paleudult order Suborder great group sub-group family albaqualf paleaquult haplaquod
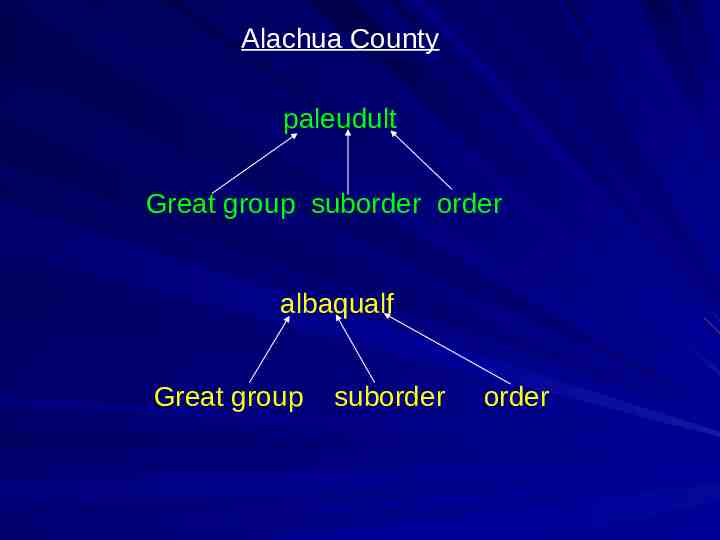
Alachua County paleudult Great group suborder order albaqualf Great group suborder order