SCREENING AND SAFETY IN IBOGAINE PATIENTS CLARE WILKINS-DIRECTOR,
22 Slides85.00 KB

SCREENING AND SAFETY IN IBOGAINE PATIENTS CLARE WILKINS-DIRECTOR, IBOGAINE ASSOCIATION

STRATEGIES Preparation Develop situational attention Stimulate team work Compensate for stressful factors
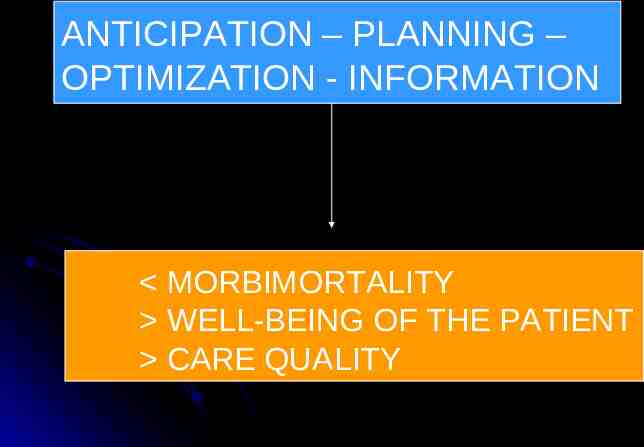
ANTICIPATION – PLANNING – OPTIMIZATION - INFORMATION MORBIMORTALITY WELL-BEING OF THE PATIENT CARE QUALITY

The cardiopulmonary function & the psychological state must be evaluated constantly

Objectives of the Evaluation: Relationship between doctor-patient: To be a comfortable experience; to be aware of all current illness and comorbidities MEDICAL HISTORY and PARACLINICALS (Laboratory and Electrocardiogram) Therapeutic plan as a team Obtain the informed consent of the patient

MAIN OBJECTIVE: SAFETY

SCREENING Contact by Phone & e-mail Medical Exam / Para-Clinicals Clinical history Anamnesis (medical intake) Psychological examination Physical examination Treatment plan

SCREENING Labor (work) Relatives. - obesity, CLINICAL HISTORY sedentarismo Habits: - alcoholism ( abstinence sydrome, liver disease). - nicotinism. - BZD, Opiáte’s, other drugs (tolerance, Sd abstinence). Allergies and adverse reactions to medicines: Allergic reactions -Medicines: antibiotics, NSAI, Antidepressants, Muscle Relaxants (succinilcolina), - Food

Screening Personal history Habits (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs) Use of medicines Illnesses (Cardiovascular and respiratory, UTI) Allergies and Cx (Surgeries) Pregnancy Acute Infections Family History HBP, Diabetes , Heart disease

Screening Illnesses that compromise cardiopulmonary function: HEART FAILURE , CORONARY HEART DISEASE , ARRHYTHMIAS (cardiac disorder), PULMONARY VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, VENOUS THROMBOSIS, RENAL FAILURE, ACTIVE INFECTIONS, PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHIES, THYROTOXICOSIS

PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Cardiovascular Thórax Distention Extremites Depth of respiratory movements and respiratory frequency Use of accesory muscles of respiration Respiratory sounds ( wheezing, crackles, rhonchi) Abdominal Arrhythmias Pulses and peripheral perfusión, circulation Probable vascular accesses swelling Neurological Mental state March and muscular force

General aspect Color (paleness, cianosis) Nutritional state Hydration Mental state

COMPLEMENTARY TESTS They detect disorders not suspected by the clinical history Individualized LABORATORY ELECTROCARDIOGRAM : The normality in EKG does not exclude coronary heart disease; there are some abnormalities that lack relevancy in asymptomatic patients.

LABORATORY They must be chosen according to the medical condition of the patient Recommendations for a healthy patient SMAC 21 PLUS AND CBC WBC (infection) RBC : Recent Hematocrito-hemoglobin (30 %) QS (glucose,cholesterol,trig) TGO, TGP, GGT (liver function) CREATININE , BUN , UREA (RENAL FUNCTION) TP,TPT (study of coagulation) CARDIAC ENZYMES URINE TEST
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM ECG ( over 40 years) ? EVERYONE Dx, Tx Used for the detection of arrhythmias, acute myocardial infarction, electrolytic imbalances and function of the pacemaker

TREATMENT PREPARATIONS BEFORE BEGINNING

FASTING The gastric emptying of clear liquids delay 1 hour and of solid 6 hours Stress, pain, anxiety and opioids delay the emptying

PREMEDICATION Prophylaxis for gastrointestinal symptoms: Omeprazol (Anti-Acid, Proton Inhibitor) 20 mg Oral Meclizine & Piridoxine (antiemetic) 25/50mg OA Metoclopramide (Anti-Emetic,Pro Kinetic)10 mg OA

Monitorization: The first and most important monitor is the human observer Constant Vitals : HR, Pulse, BP, Respirations. Medicate for nausea 60 minutes test dose 20-30 minutes full dose

Monitorization: Monitor during the following 12 hours, constantly Initiate with BP, pulse and saturation of O2 Note down pulse and saturation of oxygen first 4 hours every 30 minutes and check BP depending on clinical judgment Later, every 1hr up to completing 12 hours Check BP every 8 hrs up to finishing treatment

MONITOR CONSTANTLY Ventilation Oximetry A (saturation) saturation of 90 % can mean a Pao2 of 65 % mm Hg. To be trustworthy it needs a good peripheral perfusión pulse BP

Monitorization: Check for abstinence symptoms Rhinorrea, piloerection, mydriasis, yawning, lacrimation, tremors, hot or cold flashes, restlessness , vomiting, abdominal cramps, anxiety and muscle twitches