Regulator Open Session – OCC Joel Miller Asset Management Group
42 Slides4.89 MB

Regulator Open Session - OCC Joel Miller Asset Management Group Leader Office of the Comptroller of the Currency April 29, 2009 1

Presentation Overview OCC – Asset Management Supervision Asset Management Risks Focus on Market Disruption Issues Managing Asset Management Risk Asset Management Examination Focus Conclusions Appendix I: OCC Guidance 2

OCC - Asset Management Supervision 3

OCC Asset Mgt. Supervision OCC regulates 1600 national banks and 70 limited purpose trust companies Range from large complex banks with global operations to community banks Approximately half of all national banks have fiduciary, retail brokerage, investment banking or advisory activities. About 150 OCC examiners with AM expertise perform on and off-site supervision. 4

OCC Asset Mgt. Supervision Supervision by Risk Objective: Assess a bank’s ability to identify, measure and monitor risk Risk Assessment System (RAS) – For nine risk categories, determine: Quantity of risk Quality level of risk management Direction FFIEC: Uniform Ratings System (CAMELS) FFIEC: Uniform Interagency Trust Ratings System (UITRS) – OCC focus: Composite Rating 5

OCC Asset Mgt. Supervision Integrated risk-based supervision Large Banks: EIC/AM Team Leader Mid-size Banks: EIC/Functional EIC-AM Community Banks: Portfolio Manager/AM Examiner Supported by five AM Lead Experts and Washington based AM Policy Group 6

Asset Management Risks 7

Asset Management Risk Areas Broad Risk Categories - Asset Management Activities Reputation Strategic Compliance Transaction (Operational) CAMELS: Management & Earnings Market Disruption – Has highlighted these risks, especially in certain products and activities 8

Asset Management Risk Areas Reputation and Litigation Risks Market disruption resulted in a substantial decline in the market value of fiduciary assets across almost all asset classes. Discretionary (managed) accounts and employee benefit accounts (e.g., 401-k), pose the greatest reputation and litigation risk to bank fiduciaries. Clients reassessing which asset managers best weathered the storm and moving assets accordingly. Client retention a key focus. 9

Asset Management Risk Areas Valuation of assets in illiquid markets Accounting guidance (FAS 157) requires fair value to represent current market conditions, but not the price that would be received in a forced or distressed sale. Pricing services dropped coverage of illiquid securities and bank asset managers and custodians had to seek other pricing sources. 10

Asset Management Earnings Why Focus on AM Earnings? Effects Earnings/CAMELS Significant losses can erode Capital Market disruption Firmwide high risk initiatives may be driven by earnings pressure Effective risk management in AM needed to avoid taking on excessive risk to compensate for lost earnings 11

Asset Management Risk Areas Market Sensitive Earnings Decline Asset base and administrative fees contract as market value of assets declines. Performance fees decline as many alternative investment strategies have turned negative. Flight to quality – investor movement away from higher profit margin business (equities) to lower margin cash/cash equivalents (MMMFs) – reduces management fees. EB Defined Contribution Plans Fees effected by: Reductions in employer match reductions Reductions in employee contributions as a result of layoffs or uncertainty 12

Asset Management Revenue AM revenue of 6.36 billion in 4Q08 comprised 25% of national banks’ noninterest income and 7% of operating income. National Bank AM revenue by Call Report category: Fiduciary Revenue 3.6 billion Securities Brokerage Revenue 1.3 billion Annuity Sales Revenue 95 million Investment Banking, Advisory and Underwriting Revenue 1.4 billion 13 Source: Call Report. Includes full-service national banks and limited-purpose national trust banks as of 12/31/08.
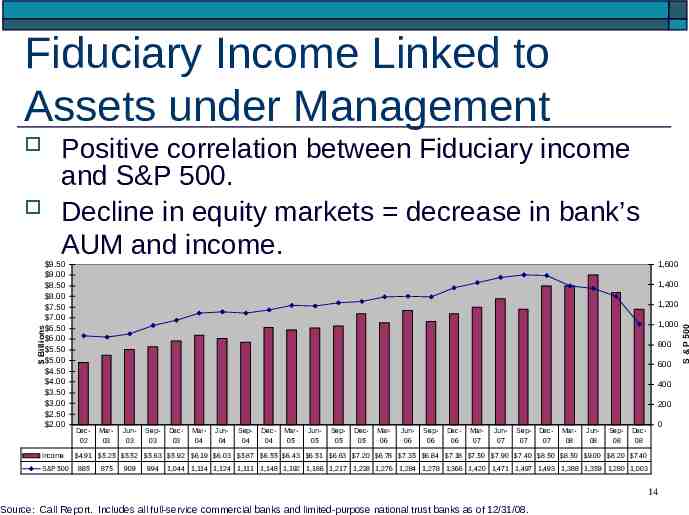
Fiduciary Income Linked to Assets under Management Positive correlation between Fiduciary income and S&P 500. Decline in equity markets decrease in bank’s AUM and income. Income S&P 500 1,600 1,400 1,200 1,000 Billions 9.50 9.00 8.50 8.00 7.50 7.00 6.50 6.00 5.50 5.00 4.50 4.00 3.50 3.00 2.50 2.00 800 600 400 200 Dec02 Mar03 Jun03 Sep03 Dec03 Mar04 Jun04 Sep04 Dec04 Mar05 Jun05 Sep05 Dec05 Mar06 Jun06 Sep06 Dec06 Mar07 Jun07 Sep07 Dec07 Mar08 Jun08 Sep08 Dec08 0 4.91 5.25 5.52 5.63 5.92 6.19 6.03 5.87 6.55 6.43 6.51 6.63 7.20 6.78 7.35 6.84 7.18 7.50 7.90 7.40 8.50 8.50 9.00 8.20 7.40 885 875 909 994 1,044 1,114 1,124 1,111 1,148 1,192 1,186 1,217 1,228 1,276 1,284 1,278 1,366 1,420 1,471 1,497 1,493 1,388 1,359 1,280 1,003 14 Source: Call Report. Includes all full-service commercial banks and limited-purpose national trust banks as of 12/31/08. S & P 500
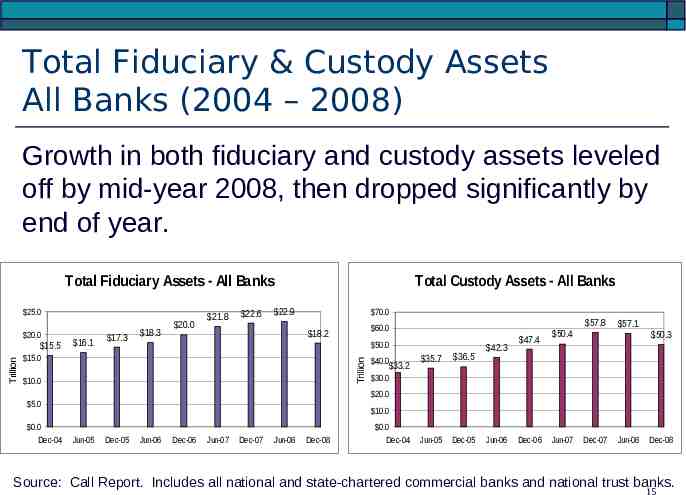
Total Fiduciary & Custody Assets All Banks (2004 – 2008) Growth in both fiduciary and custody assets leveled off by mid-year 2008, then dropped significantly by end of year. Total Fiduciary Assets - All Banks 25.0 20.0 16.1 18.3 21.8 22.6 22.9 70.0 57.8 60.0 18.2 50.0 15.0 Trillion Trillion 15.5 17.3 20.0 Total Custody Assets - All Banks 10.0 40.0 33.2 35.7 36.5 Jun-05 Dec-05 42.3 47.4 50.4 57.1 50.3 30.0 20.0 5.0 0.0 Dec-04 10.0 Jun-05 Dec-05 Jun-06 Dec-06 Jun-07 Dec-07 Jun-08 Dec-08 0.0 Dec-04 Jun-06 Dec-06 Jun-07 Dec-07 Jun-08 Dec-08 Source: Call Report. Includes all national and state-chartered commercial banks and national trust banks. 15

Asset Management Risk Areas AM products and services impacted by ongoing Market Disruption Hedge Funds Securities Lending Auction Rate Securities Collective Investment Funds Money Market Mutual Funds/STIFs 16

Asset Management Risk Areas Hedge Fund Issues Most strategies performing poorly in current market Performance and client liquidity needs lead to increasing redemption requests Which leads to gates raised/fund lock-ups Risks to bank fund managers. Decline in earnings potential due to industry contraction Litigation risk Reputation risk Banks are particularly vulnerable where they placed discretionary client assets in hedge funds and funds-of-funds that are now frozen or in liquidation. Bank custodians also vulnerable as clients seek out deep pockets to indemnify their hedge fund losses. 17

Asset Management Risk Areas Madoff Fraud Direct and Indirect Exposures Investments by individuals, foundations, endowments, and pension plans in Madoff “fund” – bank may be acting in a fiduciary capacity Indirect investments in fund-of-funds that invest a percentage of their assets in a Madoff “fund” Custodial relationships in which bank holds Madoff “fund” assets Lending exposure to clients who invested in Madoff “fund.” 18

Asset Management Risk Areas Securities Lending Issues Once viewed as low risk by clients and banks Decline in value of sec-lending pools (e.g. Lehman, AIG assets) holding reinvested cash collateral: Litigation and settlements Restrictions imposed on customers’ ability to withdraw assets Many customers now unwilling to take on additional risk and sec-lending opportunities dry up. For some banks, contraction has substantial decreased sec-lending business and earnings Banks perceived to be stronger in sec-lending have prospered in “flight to quality”. 19

Asset Management Risk Areas Auction Rate Securities Issues Regulatory actions - settlements with SEC, FINRA and state regulators that include buy-back schedules and CMPs. Voluntary ARS buybacks undertaken to preempt litigation. Both voluntary and involuntary buy-backs can be costly and saddle banks with illiquid securities with corresponding impact on bank earnings, capital and liquidity. Capital support agreements extended to affiliated funds holding these illiquid securities to buy time and keep ARS off the bank’s books. 20

Asset Management Risk Areas Collective Investment Fund Issues Funds holding illiquid assets such as RE facing flurry of redemption requests. Industry seeks to avoid liquidating fund assets at fire sale prices. Expect issuance of new Labor Department regulation, or Congressional action, that will compel substantial new fee and conflict disclosures for employee benefit assets. 21
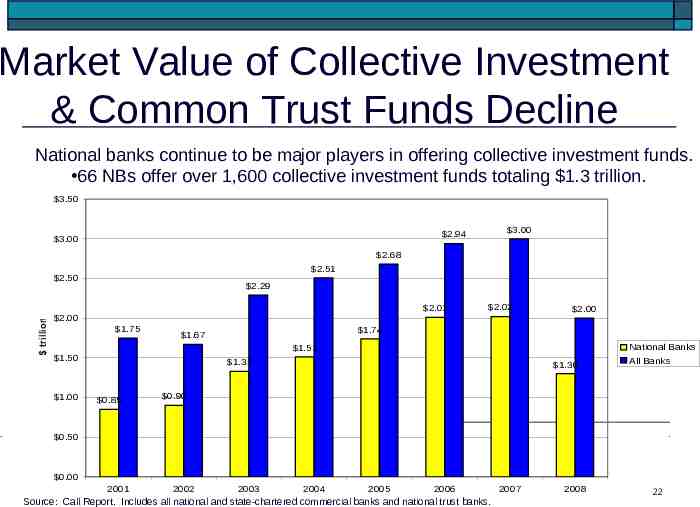
Market Value of Collective Investment & Common Trust Funds Decline National banks continue to be major players in offering collective investment funds. 66 NBs offer over 1,600 collective investment funds totaling 1.3 trillion. 3.50 3.00 2.94 3.00 2.68 2.51 2.50 2.29 trillion 2.01 2.02 2.00 1.75 2.00 1.74 1.67 1.51 1.50 1.00 1.33 0.85 1.30 National Banks All Banks 0.90 0.50 0.00 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source: Call Report. Includes all national and state-chartered commercial banks and national trust banks. 2007 2008 22

Asset Management Risk Areas MMMFs and Short Term CIF Issues Sponsors provide support to stabilize NAVs or unit values. (SIVs, Lehman ) “Flight to safety” from Prime funds to Treasury and Government funds. Low rates – waived fees Some funds closed or restricted Government Support Programs 23

Pledge Requirements – Reg 9.10 Enhanced FDIC insurance reduces trust pledge requirements: Coverage to 250,000 for certain retirement accounts Coverage expanded for irrevocable trusts Temporary coverage increase from 100K to 250K (through 12/31/09) for other accounts Temporary (through 12 /31/09) FDIC guarantee of certain non-interest bearing accounts FDIC insurance pass-through guidance applies to individual accounts held in covered non-interest bearing omnibus account. 24

Employee Benefits Deposit Prohibition – Problem Banks Banks that are no longer “well capitalized” or “adequately capitalized” are prohibited from accepting any employee benefit plan deposits. Federal Deposit Insurance Act as amended in 2006 (12 USC 1821(a)(1)(D)(ii)) imposes this prohibition. EB depositors still receive pass through coverage, but bank is in violation if it accepts EB deposits, including additions to existing accounts 25

Managing Asset Management Risk 26

Managing AM Risk Investment Management: Adhere to prudent investment standards Maintain effective and ongoing due diligence over external investment managers Maintain effective and ongoing due diligence over complex and alternative investments Properly conduct and document investment reviews 27

Managing AM Risk Effective valuation policies and oversight - Valuation of assets in illiquid markets Market disruption has made it difficult to value suddenly illiquid assets Pricing services dropped coverage of illiquid securities Accounting guidance (FAS 157) requires fair value on audited financial statements Improper valuations have been a key factor in disruption related litigation 28

Managing AM Risk Operational Focus: Potential increase in operating losses and trade errors associated with market volatility Potential stress on bank controls, operations, and risk management resulting from expense reduction Impact of loss of key personnel resulting from corporate-wide downsizing Need for due diligence over sub-custodians as highlighted by recent fraud disclosures 29

Asset Management Examination Focus 30

Asset Management Risk Areas GLBA/Regulation R Effective date for most banks - 1/1/09. Must ensure all securities activities conducted by a bank department, including the Treasury desk, comply with broker/dealer requirements. Bankers need to look across all lines within the bank (e.g., asset management, capital markets and commercial) to ensure compliance with the new regulatory requirements. Failure to comply could result in securities law violations and rescission of trades to the detriment of 31 the bank.

Recent OCC Issuances Conflicts of Interest Associated with Divestiture of Asset Mgt. Affiliates OCC Bulletin 2008-5 Annual Reg 9 Reviews OCC Bulletin 2008-10 Expectations Automated vs. Manual Reviews Unique Assets 32

AM Examination Observations Investments Effective annual reviews Process/oversight Documentation/Exceptions Understanding, due diligence and oversight of alternative investments (hedge funds) Oversight of third party investment advisors Proper authorization for use of affiliated funds or brokers Oversight of pricing for illiquid or thinly traded assets 33

AM Examination Observations Account Administration and Compliance Inadequate Compliance/Risk Management programs - testing Accepting direction from authorized parties EB administration/expertise Adequate/current policies and procedures Oversight of account overdrafts 34

AM Examination Observations Operations/Internal Controls/Audit Segregation of duties & dual control Controls over system access Corporate action processing automation BSA audit scope/trust activities Monitor 9.10 pledge requirements 35

Conclusions 36

Conclusions Earnings Pressures/Effective Risk Management Investment Management Due diligence/risks of complex investments Back to Basics Investment oversight Account Administration Operations 37

Appendix I: OCC Guidance 38

OCC Asset Management Handbooks & Guidance Retirement Plan Services Collective Investment Funds Asset Management Conflicts of Interest Custody Services Investment Management Services Personal Fiduciary Services Retail Nondeposit Investment Sales Insurance Activities A Guide to the National Banking System http://www.occ.treas.gov/nb/nbguide.pdf 39

OCC Handbooks & Guidance OCC 2008–10, Fiduciary Activities of National Banks: Annual Reviews of Fiduciary Accounts Pursuant to 12 CFR 9.6(c) OCC 2008-5, Conflicts of Interest: Risk Management Guidance – Divestiture of Certain Asset Management Businesses OCC 2007–42, Bank Securities Activities: SEC's and Federal Reserve's Final Regulation R OCC 2007-21, Supervision of National Trust Banks: Revised Guidance: Capital and Liquidity OCC 2007-7, Soft Dollar Guidance: Use of Commission Payments by Fiduciaries OCC 2007-6, Registered Transfer Agents: Transfer Agent Registration, Annual Reporting, and Withdrawal from Registration 40

OCC Handbooks & Guidance OCC 2006-24, Interagency Agreement on ERISA Referrals OCC 2004-2, Banks/Thrifts Providing Financial Support to Funds Advised by the Banking Organization or its Affiliates 41

QUESTIONS? Contact: Joel Miller, (202) 874-4493 [email protected] 42