Protecting Confidential Client Data! Presented by: [Insert Your
61 Slides2.21 MB

Protecting Confidential Client Data! Presented by: [Insert Your Name Here]

Agenda Background Sizing Up the Problem The Fix! Human Aspects Technology Local Remote Sharing Disposing of Old Data

Background:

Sensational Headlines daily! Cyber-thieves shift nearly 450,000 from Carson,CA city coffers (May 2007) using keylogger software. T.J. Maxx data theft (some 45 million credit and debit card numbers) likely due to wireless ‘wardriving‘, i.e. thief with a laptop, a telescope antenna, and a wireless LAN adapter (December 2006).

Sensational Headlines Daily! Veterans Administration announces confidential information of 26.5 million service personnel was stolen when employee’s home laptop was stolen (June 2006). Over 600,000 laptop thefts occurred in 2004, totaling an estimated 720 million in hardware losses and 5.4 billion in theft of proprietary information.

The Times are a Changing Over the next 3 years employees equipped with Notebooks or Tablet PCs will grow from 35% to 50% 95% will be wirelessly enabled. Knowledge workers will be mobile 50% of the time working from home, office, hotels, airports, customer sites, etc. Iny 2008 75% of business cell phones will be smart phones (Blackberry, Treo, Communicator, etc.) Most have removable memory cards. In their present state they do not offer adequate security (file encryption, “device kill”, firewalling, authentication, tracking and logging).

The Times are a Changing Increase in mobility with devices “roaming wild” will cause a major upsurge in breaches: Breaches may go undetected or undiscovered for long periods of time. Problem could easily become overwhelming (identity theft will look like child’s play).

Information Security Management “Short List” Router/IP addressing Firewall Patches Anti Virus Spam Spyware Passwords / Passphrases Unprotected Shares Personal Firewall Web-based e-mail/ file sharing Wireless Physical Access Backups

Goals of IT Security Confidentiality Data is only available to authorized individuals Integrity Data can only be changed by authorized individuals Availability Data and systems are available when needed

OVERALL GOAL: Reduce Risk to an Acceptable Level Just because it can happen doesn’t mean it will. Put threats into perspective by assessing: Probability of attack Value of business assets put at risk Business cost and consequence of attack REMEMBER – no policy, procedure, or measure can provide 100% security

Sizing Up the Problem:

What’s Confidential? Social Security # Credit/debit card numbers Driver’s license number Bank account numbers Birth dates PIN codes Medical records Mother’s maiden name?

Where Is Confidential Data Stored? In-House Systems Physically secure? Network access restricted to only authorized individuals? Backup Media Physical location? Format? Remote Users Laptops, home computers & memory sticks?

Who Has Access? Data access restricted to authorized individuals? Shared passwords shared data and no accountability Wide open network information free-forall

The Fix:

The Fix! In short Restrict access and/or Make it unreadable Data is made “unreadable” using encryption technology.

The Fix! Encryption Process of transforming information to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special key (to decrypt). Ciphers Algorithm or code used to encrypt/decrypt information.

The Fix! Encryption Ciphers Ciphers Classical Substitution Rotor Machines Transposition Stream Modern Private Key Public Key Block

The Fix! Things to remember about encryption Use modern, public standards! Longer key lengths are always better (increased computing power has made shorter keys vulnerable to cracking in shorter time) Private keys are optimal

Human Aspects Policy Who is allowed access? When is access allowed? What users are allowed to do? Where is data permitted to be Accessed from (devices & locations?) Stored Network servers Desktops Laptops (data is now mobile) Thumb drives

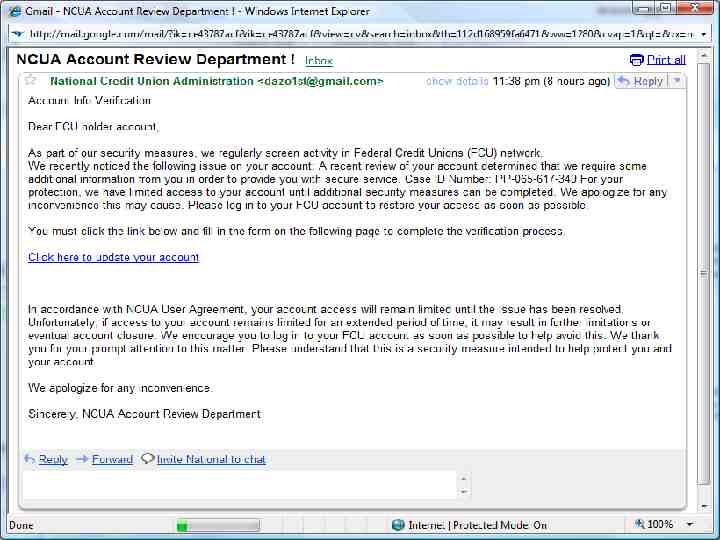
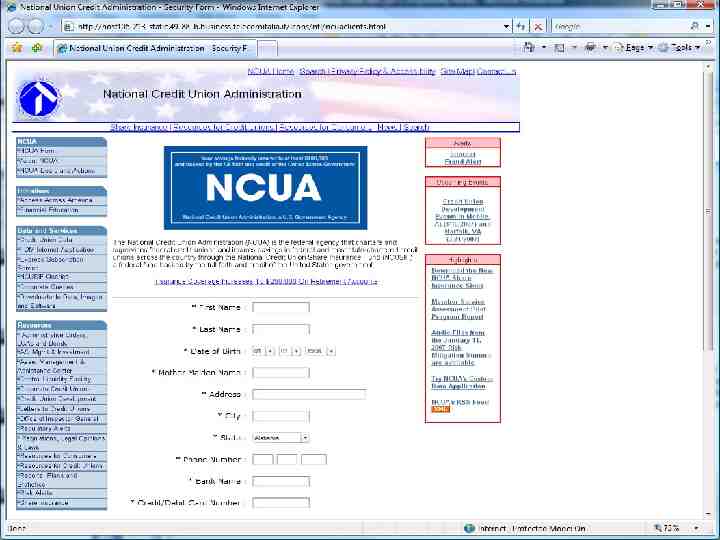
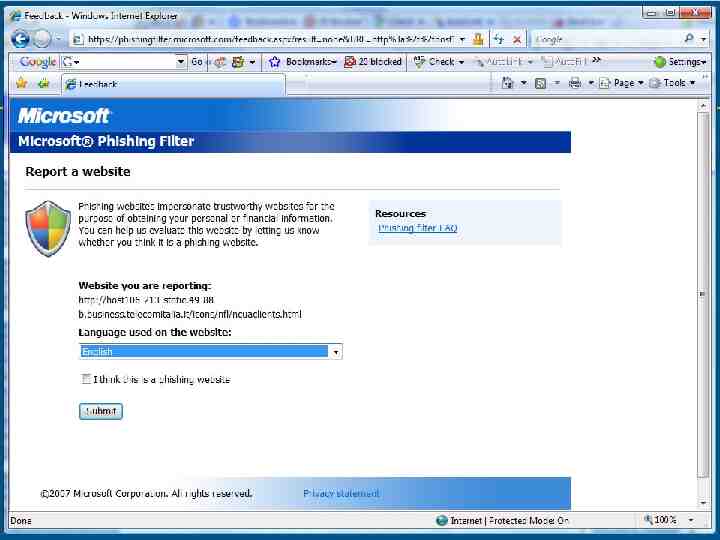
Human Aspects – Mitigating Risk Acceptable Use Policies Business data access rules: who, where, when and what Supported mobile devices and operating systems Required security measures and configurations Process for usage monitoring, auditing and enforcement (check your state and local laws) Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDA)? Training & Communication – regular and often? Social Engineering “Click here” to download key logger! Phishing attacks are still highly effective for stealing Personal information Login information – can then be used to access systems contain confidential data
Technology – Local Physical security Sensitive data located on secure systems Locked server room Locker server cage(s)
Storage Media Hard drive encryption – Software-based Windows Encrypting File System (EFS) Supported on NTFS volumes (W2K, XP & Vista) Encrypt/decrypt files and/or folders in real time Uses certificate issued by Windows
Storage Media Hard drive encryption – Software-based Vista BitLocker Encrypts entire Windows Operating System volume Available with: Vista Ultimate Vista Enterprise Third party, commercial encryption software TrueCrypt PGP Desktop Home

Storage Media Hard drive encryption – Hardware-based Seagate Technology Momentus 5400 FDE.2 laptop drive features built-in (hardware) encryption (March 2007) Heart of the new hardware-based system is a special chip, built into the drive, that will serve to encode and decode all data traveling to or from the disk. Requires password to boot machine Disk is useless/inaccessible to others

Storage Media “Phone home” software Software that monitors machines and notifies system administrators regarding: Who is using Where machine is located What hardware and/or software changes are made Example: CompuTrace

Storage Media USB Thumb Drives Most older drives completely insecure If you want to store/transfer secure data on USB thumb drive, look for device that can Encrypt data Authenticate user

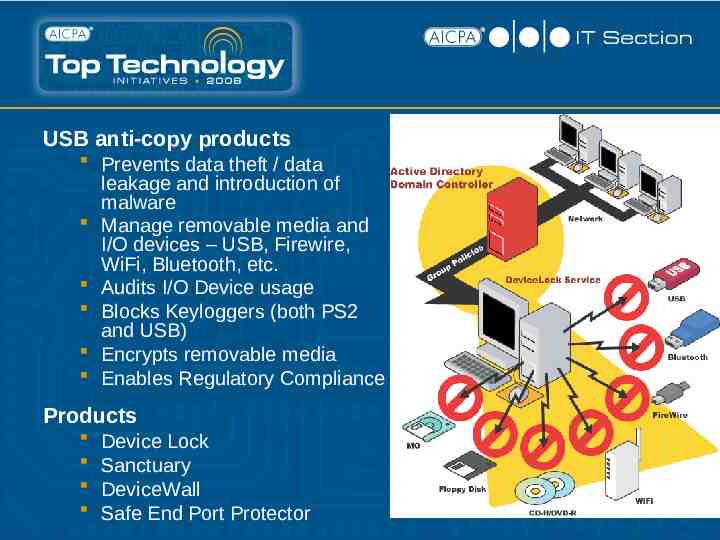
USB anti-copy products Prevents data theft / data leakage and introduction of malware Manage removable media and I/O devices – USB, Firewire, WiFi, Bluetooth, etc. Audits I/O Device usage Blocks Keyloggers (both PS2 and USB) Encrypts removable media Enables Regulatory Compliance Products Device Lock Sanctuary DeviceWall Safe End Port Protector

Authentication Authentication Factors What you know – Passwords/passphrases What you have – Tokens, digital certificates, PKI Who you are – Biometrics (finger, hand, retina, etc.) Two factor authentication will become increasingly important.

Authentication APC BIOMETRIC PASSWORD MANAGER fingerprint reader - USB by APC ( 35 - 50) Hundreds of devices like this ranging from 25 300.
Application Software In general, application passwords are poor protection (since most can be broken) e.g. Passware (www.lostpassword.com) Unlock 25 different applications including Windows, Office, Quick Books, Acrobat, Winzip, etc.

Mitigating Unsafe User Behavior Managed services – key piece of security puzzle Spam, virus, content management and filtering, spyware, etc. Benefits Easier on the user Easier on IT Mobile devices should be periodically reviewed: Currency of software and patches Health of machine User logs Recommendation: Quarterly or Trimester

VPN (Virtual Private Network) A VPN is a private network that uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect remote sites or users together. Instead of using a dedicated, real-world connection such as leased line, a VPN uses "virtual" connections routed through the Internet from the company's private network to the remote site or employee.

Overview

VPN (Virtual Private Network) Benefits Extend geographic connectivity Reduce transit time and transportation costs for remote users Provide telecommuter support Improve security Reduce operational costs versus traditional WAN Improve productivity Direct printing to office Direct connect to network drives

VPN Use 3rd-party VPN service, e.g. HotSpotVPN, JiWire Spot Lock, Public VPN or WiTopia Personal VPN
Host-Based Computing Remote Control GoToMyPC - 14-34/month LogMeIn Symantec pcAnywhere VNC

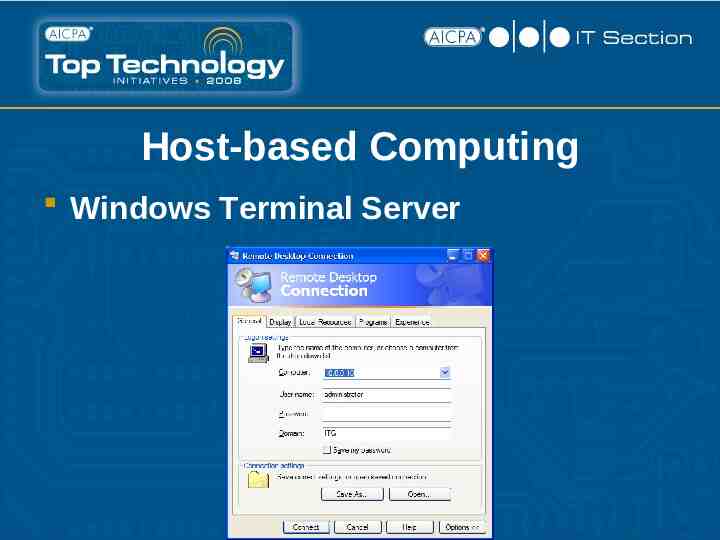
Host-based Computing Windows Terminal Server

Digital Certificates Implement digital certificates for internally hosted corporate web resources or webpresence, e.g. E-mail, CRM, B2? site, etc. This allows all traffic to be encrypted via SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). Pad lock indicates traffic is being encrypted and the web site owner’s identity can be verified (by certificate authority).

Wireless Security – Network Side DON’T do a plug-n-play install! Password protect administrative setup Encryption: WEP (good) – remember to change keys regularly WPA (better) WPA2 (best) Enter authorized MAC addresses on WAP Use VPN or IPSec to encrypt all traffic Walk perimeter to determine whether rogue WAPs are active
Wireless Security - End Users No unprotected shares – all shares turned off Ensure all mobile devices are updated with the latest security patches Only use SSL websites when sending/entering sensitive data (credit cards and personal identity information) Digitally sign data to make it difficult for hackers to change data during transport Encrypt documents that contain sensitive data that will be sent over the Internet

Wireless Security - End Users As a general rule (while not always possible) use WiFi for Internet surfing only Disable or remove wireless devices if they are not being used. This includes: WiFi – 802.11a/b/g/n Bluetooth Infrared Cellular Avoid hotspots where it is difficult to tell who is connected Ad-hoc/peer-to-peer setting should be disabled

WiFi Security - End Users WiFi Best Practices Use broadband wireless access (EvDO, 3G/GPRS, EDGE, UMTS) to make wireless connections: Verizon and Sprint Broadband services are very fast - 59.99/month – unlimited access Wireless carriers offer fairly good encryption and authentication

Wireless Recommendations Consider using specialized security software to help mobile users detect threats and enforce company policies Example - http://www.airdefense.net

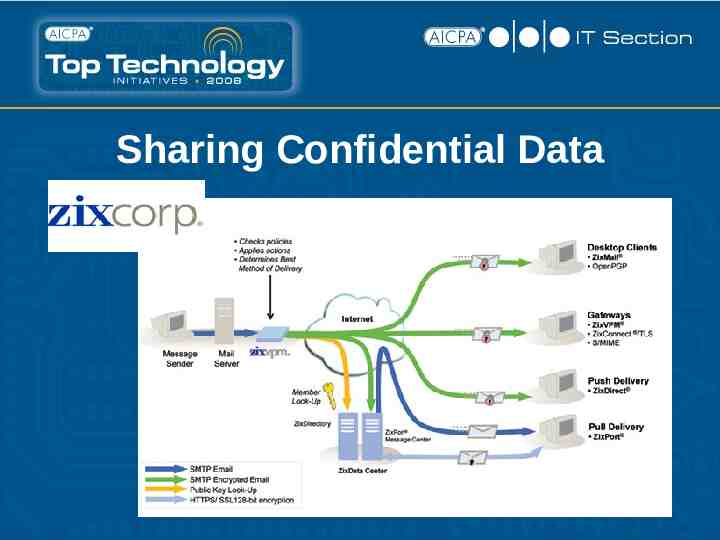
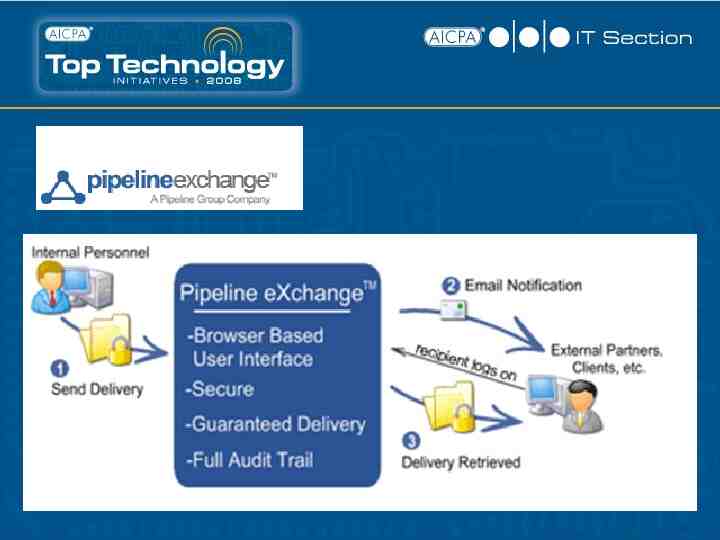
Sharing Confidential Data Options: E-mail FTP / Secure FTP Secure transmission programs Customer portal / extranet 3rd Party Hosted Data Exchange Digital Rights Management (DRM)

Sharing Confidential Data E-mail As a general rule, e-mail is insecure! In order to secure: Digital Certificates / PKI PGP Verisign

Sharing Confidential Data Secure FTP Secure FTP utilizes encryption to transfer files in a secure manner. Can use a number of different strategies/approaches to accomplish. Due to complexity, not often utilized for sharing data with clients.

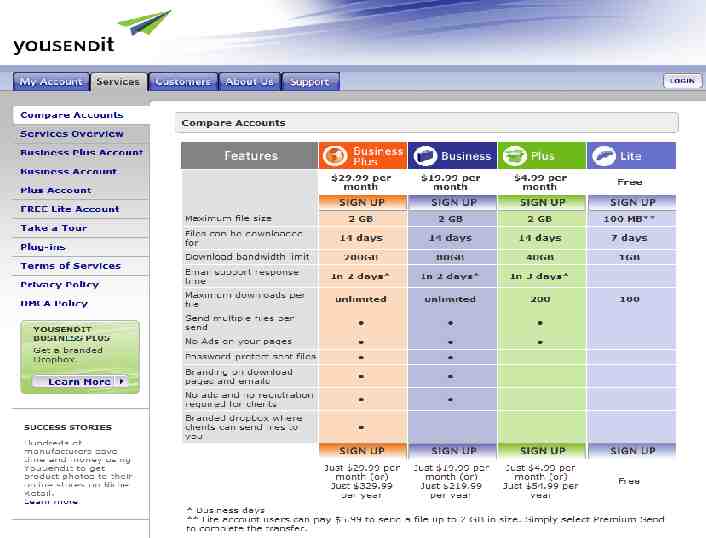
Sharing Confidential Data Client Extranets Internal Hosted e.g. ShareFile Branded! 100/mo. 30 employees Unlimited clients

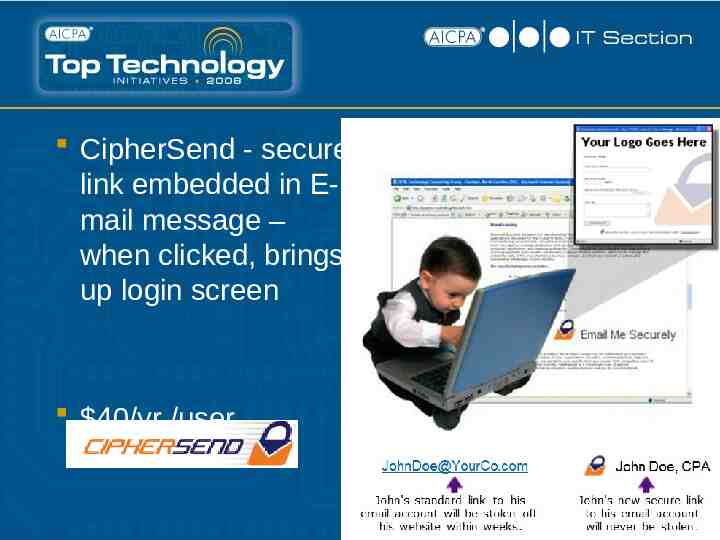
CipherSend - secure link embedded in Email message – when clicked, brings up login screen 40/yr./user

Sharing Confidential Data
Digital Rights Management Evolving strategy utilizes a combination of technologies in order to control access to content. Incorporates Encrypted files – file is locked until permission to access is granted by DRM Server. Digital Rights Management Server – provides webbased permission to View/Edit/Copy/Print an encrypted document. Access granted based on date, version, user, etc. Content can be shared freely & openly since access is separately governed by DRM Server.
Disposing of Confidential Data Remove media! Wipe media Software to overwrite drive multiple times Permanent magnet Destroy media Semshred – www.semshred.com

Conclusion:
Keys to Implementing a Successful Security Strategy for Confidentiality Define the scope Users Devices (don’t forget PDA’s and smart phones) Locations Define your usage policies Communicate Get buy in (if they don’t agree you won’t be successful) Enforce with management tools Don’t over engineer
Contact Information [Insert Your Name] [Insert Firm Name Here] [Insert Address] [Insert Phone No.] [Insert email address]