Patrick An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 3/e Chapter
10 Slides188.50 KB

Patrick An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 3/e Chapter 6 PROTEINS AS DRUG TARGETS: RECEPTOR STRUCTURE & SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION Part 1: Sections 6.1 - 6.2 1

Contents Part 1: Sections 6.1 - 6.2 1. Receptor superfamilies 2. Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion channels) 2.1. General structure (3 slides) 2.2. Structure of protein subunits (4-TM receptor subunits) 2.3. Detailed structure of ion channel 2.4. Gating (2 slides) [9 slides] 1
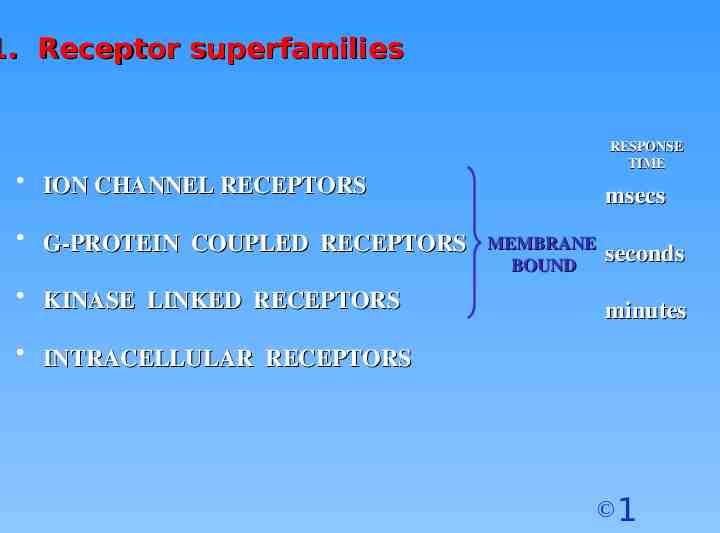
1. Receptor superfamilies RESPONSE TIME ION CHANNEL RECEPTORS G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS KINASE LINKED RECEPTORS msecs MEMBRANE BOUND seconds minutes INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS 1
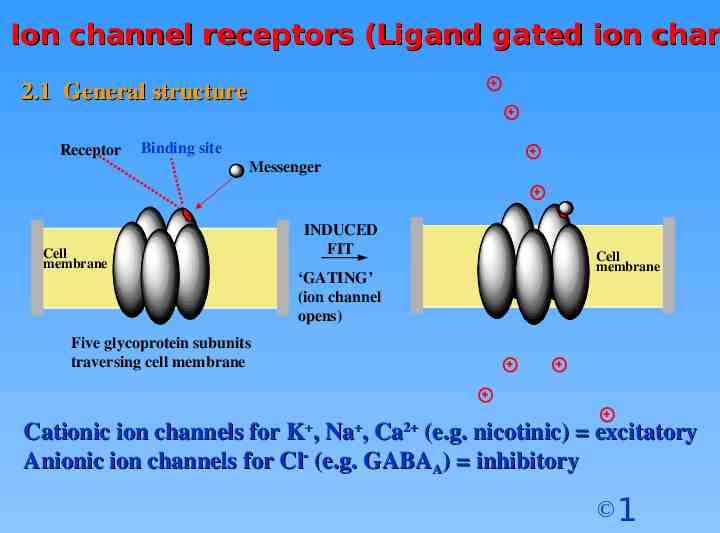
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan 2.1 General structure Receptor Binding site Messenger Cell membrane INDUCED FIT ‘GATING’ (ion channel opens) Cell membrane Five glycoprotein subunits traversing cell membrane Cationic ion channels for K , Na , Ca2 (e.g. nicotinic) excitatory Anionic ion channels for Cl (e.g. GABAA) inhibitory 1
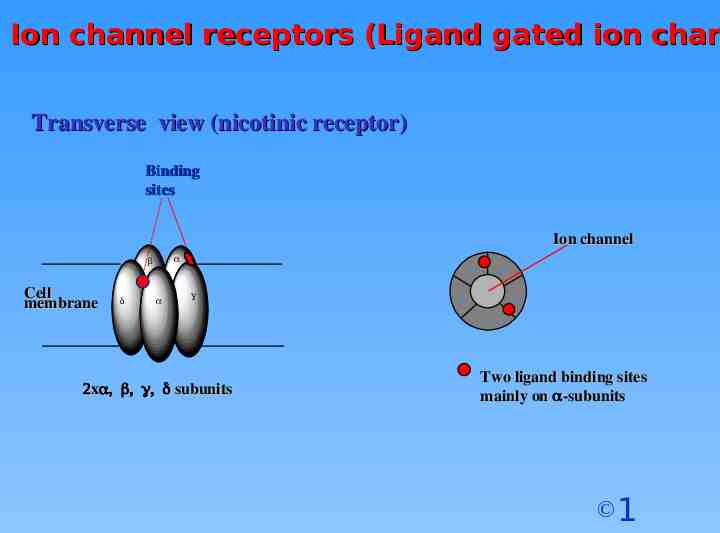
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan Transverse view (nicotinic receptor) Binding sites Ion channel Cell membrane x subunits Two ligand binding sites mainly on -subunits 1
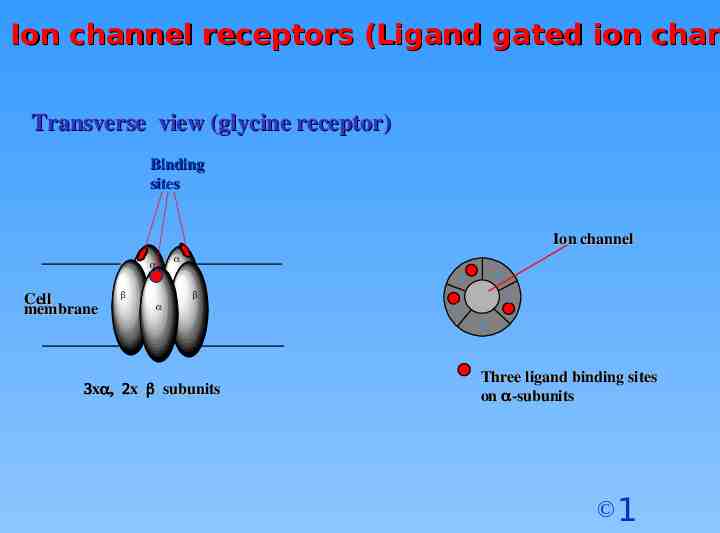
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan Transverse view (glycine receptor) Binding sites Ion channel Cell membrane x x subunits Three ligand binding sites on -subunits 1
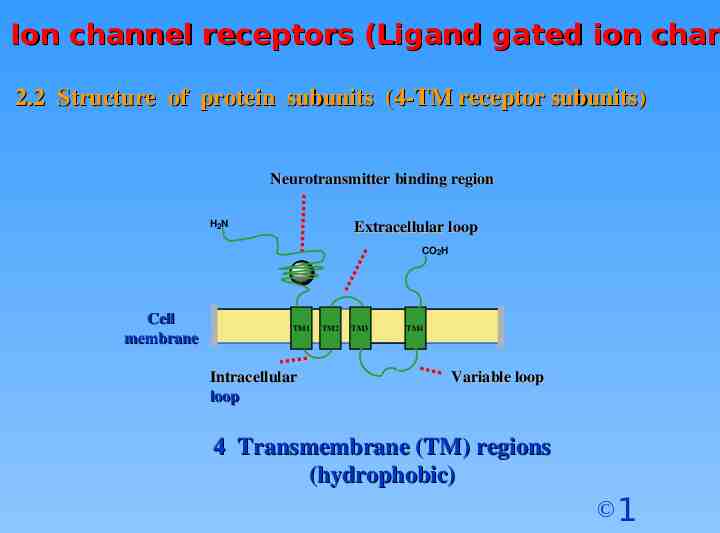
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan 2.2 Structure of protein subunits (4-TM receptor subunits) Neurotransmitter binding region H2N Extracellular loop CO2H Cell membrane TM1 Intracellular loop TM2 TM3 TM4 Variable loop 4 Transmembrane (TM) regions (hydrophobic) 1
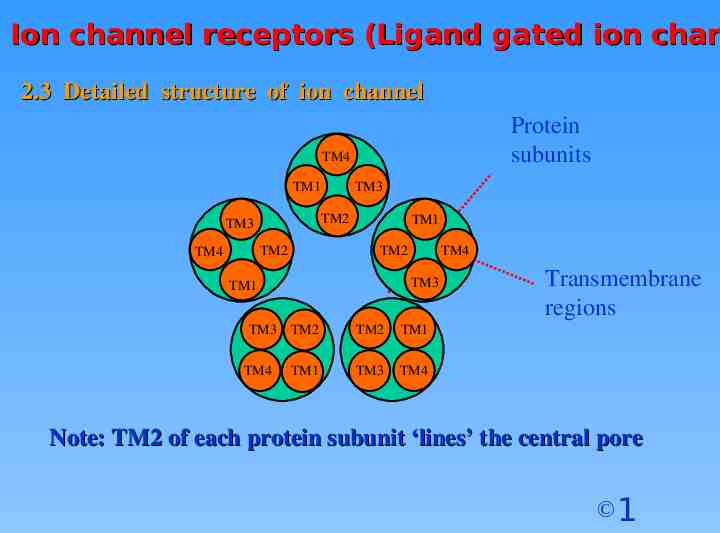
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan 2.3 Detailed structure of ion channel Protein subunits TM4 TM1 TM2 TM3 TM1 TM2 TM2 TM4 TM3 TM3 TM1 TM3 TM4 TM4 TM2 TM2 TM1 TM1 TM3 TM4 Transmembrane regions Note: TM2 of each protein subunit ‘lines’ the central pore 1
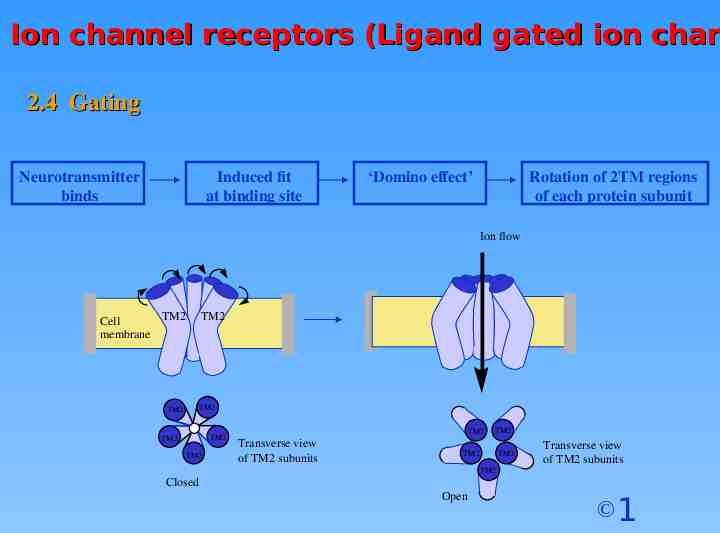
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan 2.4 Gating Neurotransmitter binds Induced fit at binding site ‘Domino effect’ Rotation of 2TM regions of each protein subunit Ion flow TM2 Cell membrane TM2 TM2 TM2 TM2 TM2 TM2 TM2 Transverse view of TM2 subunits TM2 TM2 TM2 Transverse view of TM2 subunits TM2 Closed Open 1
Ion channel receptors (Ligand gated ion chan 2.4 Gating Fast response measured in msec Ideal for transmission between nerves Binding of messenger leads directly to ion flows across cell membrane Ion flow secondary effect (signal transduction) Ion concentration within cell alters Leads to variation in cell chemistry 1






