No Data Left Behind: Federal Student Aid A Case History Holly Hyland,
39 Slides1.29 MB

No Data Left Behind: Federal Student Aid A Case History Holly Hyland, Federal Student Aid Lisa Elliott, Federal Student Aid

Agenda Federal Student Aid Overview Data Strategy Initiative Enterprise Data Management Program Description of the End Game Lessons Learned DAMA Impact Questions 2

Who We Are The Higher Education Amendments of 1998 established Federal Student Aid as the federal government’s first Performance Based Organization (PBO) to modernize the delivery of the Department’s Title IV federal student aid programs. As specified in the authorizing legislation, the purposes of the PBO are to: Increase accountability Improve service to students and parents Integrate business processes and information systems Strengthen program integrity Reduce costs 3

Who We Are As a PBO, Congress grants Federal Student Aid certain limited managerial flexibilities over its human capital management, budget and procurement activities Our focus is on: Delivering world-class customer service Developing award-winning products and services that are of value to our customers Effectively managing the programs to ensure fair, effective and appropriate oversight, and service delivery at the lowest cost without sacrificing service levels or quality 4

Our Mission Our federal grant and loan programs represent the largest sources of student aid in the United States, annually providing approximately 74B to more than 11M students/parents, including nearly 13B in Pell Grants to the most needy students. We provide this aid through and with the nearly 10,000 program participants. We oversee (directly and indirectly) the management of the 402B loan portfolio of 80M loans to more than 26M borrowers. 6,130 Schools 35 Guaranty Agencies 5 3,200 Lenders 45 3rd-Party\ Servicers 36 Secondary Markets

Our Critical Functions Federal Student Aid is responsible for a range of critical functions that include, among others: Processing millions of student financial aid applications Disbursing billions of dollars in aid funds to students through schools Enforcing financial aid rules and regulations Partnering with schools, financial institutions and guaranty agencies to prevent fraud, waste and abuse Educating students and families about the process of obtaining aid Servicing millions of student loan accounts Securing repayment from borrowers who have defaulted on their loans Operating information technology systems and tools that manage billions in student aid dollars 6

Our Environment FSA's technology environment is understandably complex: 21 different information systems provide services. 140 internal exchange points across FSA’s computing environment, and 175 external exchange points entering into our environment. 60 million FAFSA’s processed a year – 97% on-line applications Different identifiers are used to identify partners based upon particular system and type of business transaction. Multiple procedures required to enroll and register for access to FSA systems. FSA systems require different user credentials and enforce different policies using different User ID formats. 7

Our Integration Challenge The Higher Education Act (HEA) legislation of 1998 specifically called on Federal Student Aid to integrate, and defined three principal goals with respect to integration of Federal Student Aid’s information systems: To integrate the information systems supporting the Federal student financial assistance programs. To implement an open, common, integrated system for the delivery of student financial assistance under Title IV. To develop and maintain a student financial assistance system that contains complete, accurate, and timely data to ensure program integrity. 8
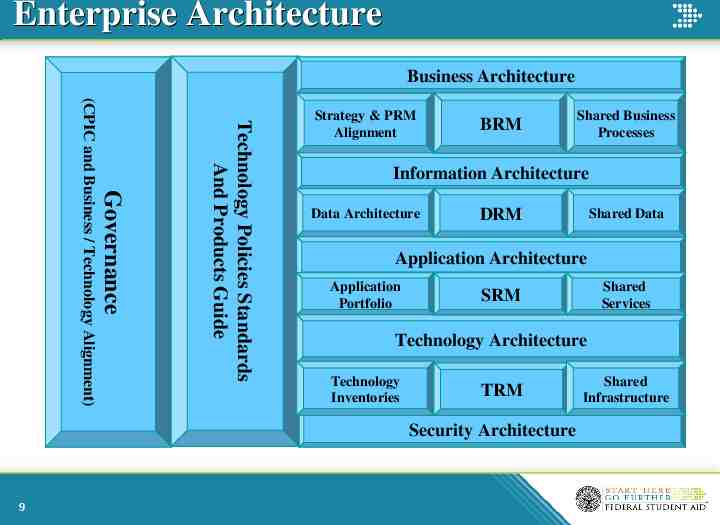
Enterprise Architecture Business Architecture Technology Policies Standards And Products Guide Governance (CPIC and Business / Technology Alignment) Strategy & PRM Alignment BRM Information Architecture Data Architecture DRM Shared Data Application Architecture Application Portfolio Shared Services SRM Technology Architecture Technology Inventories TRM Security Architecture 9 Shared Business Processes Shared Infrastructure
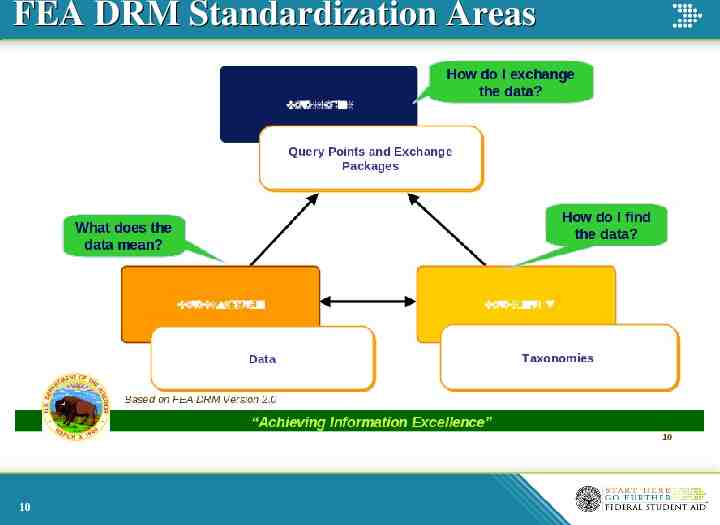
FEA DRM Standardization Areas 10
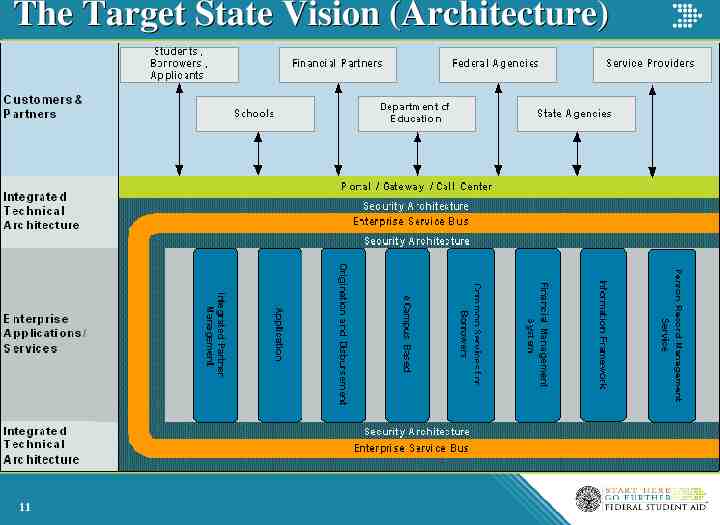
The Target State Vision (Architecture) 11
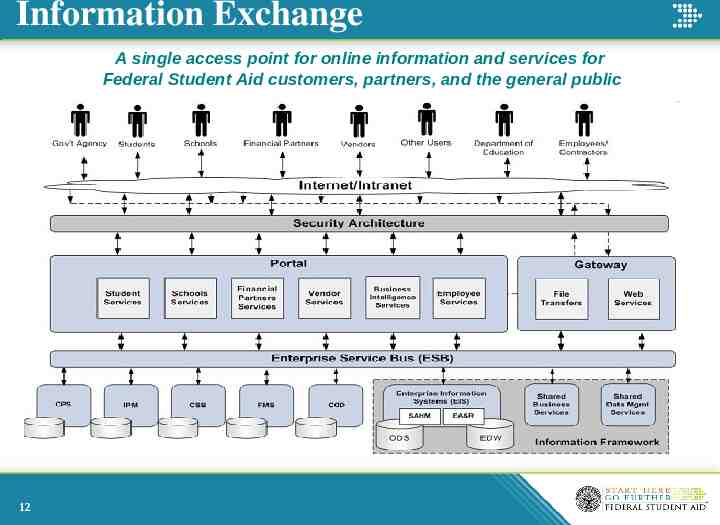
Information Exchange A single access point for online information and services for Federal Student Aid customers, partners, and the general public 12
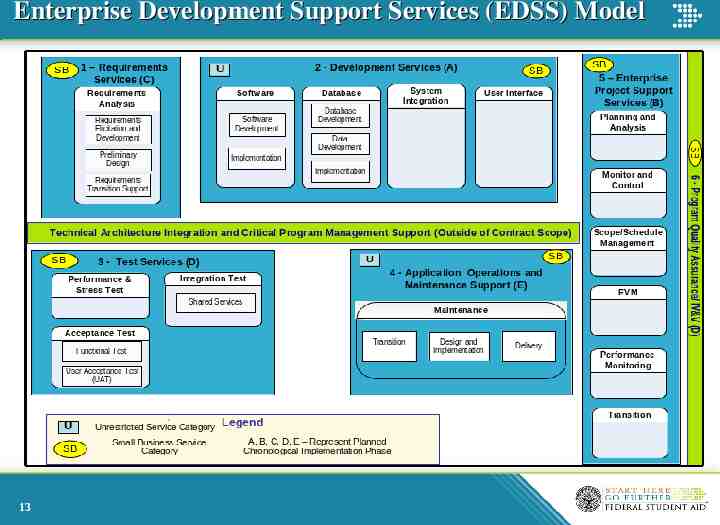
Enterprise Development Support Services (EDSS) Model 13

Getting to the Data 2000 Modernization Blueprint – “the wall” 2003 Terry Shaw (former COO) – “the data is missing” Representatives from all business areas “vision without constraint” to determine how things should work. Bumblebee Chart (Integration Vision Framework) Target State Vision (TSV) 2004 Data Strategy 2006 Enterprise Data Management 14
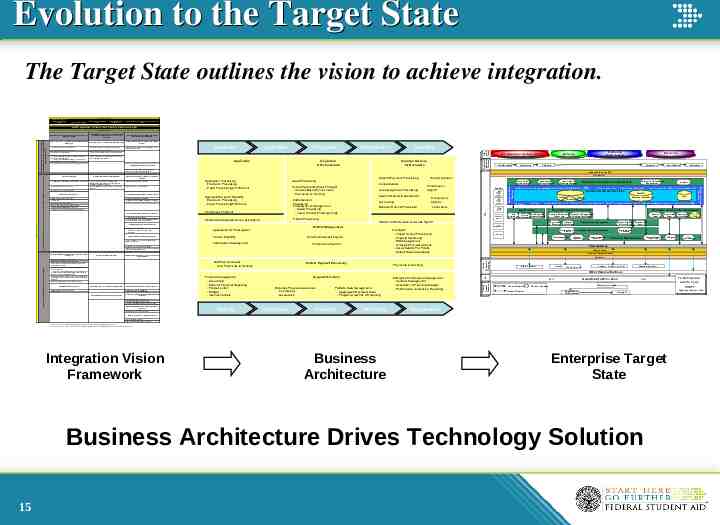
Evolution to the Target State The Target State outlines the vision to achieve integration. FSA Strategic Objectives Integrate FSA systems and provide new technology solutions Improve program integrity Reduce program administrative costs Improve human capital management Improve products and services to provide better customer service Core Business Driver Find the Right Balance Between Efficient Delivery & Effective Oversight Core Business Outcomes -Enterprise (cross-functions) information and analysis -RID implementation across the lifecycle -Better common loan identification -RID implementation across the lifecycle -Customer centric buildup for schools across the lifecycle -Provide an integrated, cross-lifecycle, web-delivered customer view that is system independent -Customer centric buildup for students across the lifecycle -Delivery partner access to information to support selfmonitoring and decision making Run the Business to Enable Right Actions, Right Transactions to the Right People Ability to proactively inform regulatory and statutory changes -Simplify programs through proactive informing to policy and legislative processes Application Origination Application -Provide information to prospective students Disbursement Servicing Origination & Disbursement Actionable data to drive decision making Common Services for Borrowers Aid Awareness & Application Aid Education Submission Institution Participation Delivery Repayment -Clear indication of aid status displayed throughout the enterprise -Support analytic approach to oversight/problem identification, decision making, policy and legislation through data, information and tools -Timely delivery/deployment of systems -Provide enrollment status via the web -Support audit functions to track access to FSA systems and data. -Analytic approach to system changes Application Processing - Electronic Processing - Paper Processing & Fulfillment Award Processing School Payments (Pass-Through) - Student Based Pymnt Calcs - Payments & Tracking -Maximize access to available resources Automated business processes Clearly defined ownership and management of data -Uniform business rules across systems -Common edits -Ownership and definition of shared data -Define data related standards (including XML standards) -Automate internal/system interfaces -Single, secure external gateway for file exchange -Automate identity and management processes -Configure security to minimize and simplify user interfaces Consistent and accurate data across the enterprise -Continuous data quality verification -Establish and follow common data definitions to facilitate the exchange of data internally and externally Flexible standards, technologies and services -Balance between COTS procurement and enterprise technology standards Applicant/Recipient Eligibility - Electronic Processing - Paper Processing/Fulfillment Disbursement Processing Funding Level Management - Award Processing - Calc & Monitor Funding Chngs Performance Mgmnt* P-Note Processing Student Authentication & Access Mgmnt Case Tracking (Ombudsman) Consolidations Loan Assignment Processing Death, Disability & Bankruptcy Accounting Borrower Refund Processing Performance Mgmnt* Enablers EAI Enterprise Application Integration Delinquency Mgmnt ITA Integrated Technical Architecture Collections VDC Recommend Policy Changes Application for Participation Partner Eligibility Oversight - Closed School Processing - Ongoing Monitoring - Risk Management - Oversight Reviews/Actions - Accountability For Funds - Default Rate Calculations Performance Mgmnt* SSIM Logic Standardized business processes Streamlined processes for routine oversight functions -Uniform business rules across functions -Common edits Actionable information to inform business processes -Include customer input and feedback -Analytic approach to process changes Timely identification of risk-based non-compliance Effectively & efficiently manage organizational financial well-being -Easier financial internal exchange -Smarter contracting for customer service -Strategic contracting/acquisition strategy supporting business objectives Right skilled/trained workforce aligned with business processes -Maximize access to available resources Enterprise Performance Management Process Promissory Notes Analytics Servicing Reporting (FFEL & Campus Based) SSCR NSLDS FMS Warehouse/Data Marts Partner Payment Calculation/PrePopulation CDR Match Against CDA (FAH) Distribute Eligibility Computation Edits - EFCRID Mappings Authentication & Access Management Common Services for Borrowers Application Origination & Disbursement Authentication & Access Tools Establish Aid Eligibility Aid Awareness Person Record Determination Award & DisbursementSchool Aid Payments & Funding Level Mgmt Processing Application Process Service Loans Partner Enrollment Trading Partner Management Partner Payment Admin Partner Payment Management Consolidate Recovery & Loans Resolution Payment State Agency Processing Funding Ancillary Services AR Management Process Payments Funds & Internal Controls Financial Management External Financial Reporting Budgeting Schools Portal Financial Management - Accounting - External Financial Reporting - Funds Control - Budget - Internal Controls Eligibility Payments & Tracking Financial Partners Portal Support Functions Business Process Awareness - Counseling - Awareness Participation Portfolio Data Management - Aggregated Recipient Data - Program Analytics & Reporting Oversight Monitoring Enterprise Performance Management - Contract Management - Acquisition & Planning Strategy - Performance Analytics & Reporting Trading Partners & Servicers Partner Payment Processing State Agencies Schools ( School Servicers) Lenders (Lender Servicers) Guaranty Agencies Other External Partners Department of Education FMSS Internal Transfer External Transfer GAPS Partner Application Business Function Origination & Disbursement Management Assumption 1: It is presumed an Enterprise Plan will be in place to support the vision (resource allocation, budgeting, training, QA processes). Assumption 2: Customers are defined as Students, Schools, Financial Partners, DoED, FSA Employees, External/Internal Audit Groups, Delivery Partners and Budget Services. Business Architecture To-Be Financial Aid Life Cycle DRAFT High-Level Business View Oversight Maximize effectiveness of program based goals Enterprise Target State Business Architecture Drives Technology Solution 15 GL Accounting FSA Gateway -Greatest return in collections -Effectively deliver financial aid to recipients Integration Vision Framework CSB Partner Eligibility Relationship & Oversight Mgmt Help Desk Bulk Payment Calcs - ACA Payments to Schools -Reduce reporting requirements (use the data we have) Transfer Monitoring Trading Students Partners Transactions Edit Checks Tailored and relevant business services for all customer lifecycle activities -Easier for FSA to support customers by providing views across the person and entity -Establish a common method and process for transition that is easy and accurate for administering trading partner enrollment and access to FSA systems and resources -Defined roles and responsibilities of FSA in supporting delivery partners driven by what they need, what should be provided and how/priority Audit History Virtual Data Center ED Effective and balanced oversight Enterprise Analytics and Research Common Data Architecture Business Intelligence Tools Enrollment/Access Mgmnt Participation Management Acquisition & Planning Strategy Send/Receive from Matching Agencies Generate/Distribute ISIR/SAR Credit Check Student Authentication & Access Mgmnt Partner Management -Define data access authorization standards -Infrastructure capacity that is secure, scalable and flexible to meet the changing needs of FSA -Right time data exchange between systems -Right time data exchange with delivery partners -Easier and more accurate external exchanges that meet the needs of delivery partners Collections Call Centers Default Aversion Maintain appropriately secured information -Defined, secure access points -Right access to right person/entity at right point in time Consolidation Student Aid on the Web Inbound Payment Processing Enterprise Shared Functions Deployment of technology solutions to meet program objectives FSA Efficient, automated oversight capabilities Servicing Eligibility -Right data available at right time and organizational agreement about what is required and when Self-service capabilities System-independent, integrated services to customers across the lifecycle Improve & Integrate Business Processes Into Delivery Solutions Awareness Lifecycle Phase -CSID implementation across the lifecycle Applicant/ Borrower Process Easy customer access to required information throughout the Easy and timely access to required oversight information delivery cycle Trading Partner Process Core Business Enablers Maintain Right & Effective Levels of Oversight Through Combination of Enhanced Tools & Customer SelfMonitoring Enterprise Shared Functions Provide the Right Security, Tools, Systems, Architecture & Technology to Enable the Business to Achieve its Outcomes Support Effective & Informed Decision Making by Making the Right Information Available at the Right Time to the Right People Provide Easier Access to Make it Easier for Our Customers to do Business With Us
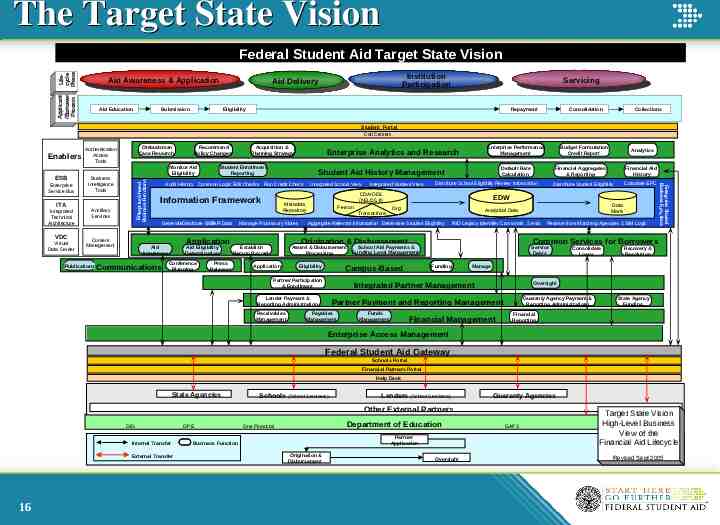
The Target State Vision Lifecycle Phase Federal Student Aid Target State Vision Applicant /Borrower Process Aid Awareness & Application Aid Education Institution Participation Aid Delivery Submission Servicing Eligibility Repayment Consolidation Collections Student Portal Call Centers ESB ITA Integrated Technical Architecture VDC Virtual Data Center Monitor Aid Eligibility Business Intelligence Tools Ancillary Services Content Management Publications Recommend Policy Changes Student Enrollment Reporting Information Framework Application Aid Awareness Communications Aid Eligibility Determination Conference Planning Manage Promissory Notes Person Transactions Org Award & Disbursement Processing Application Partner Participation & Enrollment Receivables Management Common Services for Borrowers Funding Funds Management Consolidate Loans Recovery & Resolution Manage Oversight Guaranty Agency Payment & Reporting Administration Partner Payment and Reporting Management Payables Management Receive from Matching Agencies SSIM Logic Service Debts Integrated Partner Management Lender Payment & Reporting Administration Data Marts RID Legacy Identifier Crosswalk Send/ School Aid Payments & Funding Level Management Campus-Based Eligibility Distribute Student Eligibility Analytical Data Aggregate Relevant Information / Determine Student Eligibility Financial Aid History Calculate EFC EDW / Origination & Disbursement Establish Person Record Press Releases Integrated Student View Distribute School Eligibility / Review Information CDA/ODS (NSLDS II) Metadata Repository / Generate / Distribute ISIR / SAR Data Integrated School View Analytics Financial Aggregates & Reporting Default Rate Calculation Student Aid History Management Audit History Common Logic Edit Checks Run Credit Check Budget Formulation Credit Report Enterprise Performance Management Enterprise Analytics and Research Enterprise Shared Business Fu nc tions Enterprise Service Bus Ombudsman Case Research Authentication Access Tools Enterpr ise Shared Business Functio ns Enablers Acquisition & Planning Strategy Financial Management State Agency Funding Financial Reporting Enterprise Access Management Federal Student Aid Gateway Schools Portal Financial Partners Portal Help Desk State Agencies Schools (School Servicers) Lenders (School Servicers) Guaranty Agencies Other External Partners OIG Internal Transfer External Transfer 16 OPE Department of Education One Financial Partner Application Business Function Origination & Disbursement Oversight GAPS Target State Vision High-Level Business View of the Financial Aid Lifecycle Revised Sept 2005

Data Strategy Purpose Develop an overall approach towards data to ensure that accurate and consistent data is available to and exchanged between Federal Student Aid and our customers, partners, and compliance and oversight organization. Get the Right Information To the Right Person At the Right Place and Time At the Right Cost 17

Data Strategy Initiatives Data Strategy evolved into the integration of five core initiatives: Data Framework As-Is and Target State Data Flows Refine Target State Vision Data Quality Mad Dog Develop Quality Assurance Strategy Implement Data Quality Assurance Strategy XML Framework Develop XML ISIR Develop XML Registry / Repository Production Deployment of XML Registry / Repository 18 Common Identification Standard Student Identification Method Routing ID Trading Partner Enrollment and Access Enrollment and Access Management Technical Strategies Data Storage, Web Services, Web Usage, and FSA Gateway Web Consolidation Options Enterprise Analytics Architecture CDA Operating Guidelines

Data Strategy Key Findings The Data Strategy team confirmed several key findings: Data should be organized by business process, not by system. Providing data access to business experts is the key component of improving the enterprise’s ability to make informed business decisions. Need to develop a single enterprise solution for all trading partner/person identification and access. “As-Is” data flow discussions have facilitated a broader understanding of end-to-end business processes across all Federal Student Aid program areas. 19
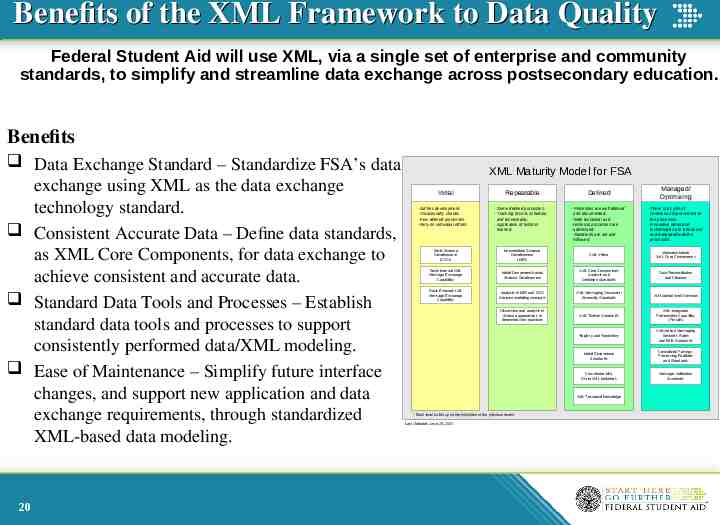
Benefits of the XML Framework to Data Quality Federal Student Aid will use XML, via a single set of enterprise and community standards, to simplify and streamline data exchange across postsecondary education. Benefits Data Exchange Standard – Standardize FSA’s data exchange using XML as the data exchange technology standard. Consistent Accurate Data – Define data standards, as XML Core Components, for data exchange to achieve consistent and accurate data. Standard Data Tools and Processes – Establish standard data tools and processes to support consistently performed data/XML modeling. Ease of Maintenance – Simplify future interface changes, and support new application and data exchange requirements, through standardized XML-based data modeling. 20 XML Maturity Model for FSA Initial - Ad-hoc development. - Occasionally chaotic. - Few defined processes. - Rely on individual efforts. Repeatable Defined Managed/ Optimizing - Some defined processes. - Tracking of cost, schedule, and functionality. - Application of lessons learned. - Processes are well defined and documented. - Both functional and technical processes are addressed. - Standards are set and followed. - There is a cycle of continuous improvement to the processes. - Innovative ideas and technologies are introduced and integrated with the processes. Basic Schema Development (COD) Intermediate Schema Development (ISIR) XML Vision Maintain/Update XML Core Components Basic Internal XML Message Exchange Capability Initial Component-based Schema Development XML Core Components Analysis and Definition Standards Data Reconciliation and Cleanup Basic External XML Message Exchange Capability Analysis of ISIR and COD Schema modeling concepts XML Messaging Document Assembly Standards XML-based Web Services Discussion and analysis of Schema approaches to determine best practices XML Toolset Standards XML-integrated Presentation Capability (Portals) Registry and Repository XML-based Messaging Business Rules and Edits Standards Initial Governance Standards Centralized Parsing / Processing Facilities and Standards Coordinate With Other XML Initiatives Message Validation Standards XML Technical Knowledge * Each level builds upon the principles of the previous levels. Last Updated: June 25, 2003

Enterprise Data Management Formalized October, 2006 Building off of the work that we’ve been doing informally for the last four years with PESC and adding formal discipline with the Data Management Body of Knowledge (DMBOK) EDM is a service to the business with the following goals: Support the improvement of enterprise analytics and Decrease the cost of and improve the quality of new development projects Focus on data as an enterprise asset. 21

Enterprise Data Management Three year strategy: Concentrate on fundamentals and foundation/communication materials. Start an Enterprise Data Governance Workgroup and improve and expand Metadata Management. Develop and implement Data Quality policies and procedures (started in year two). 22
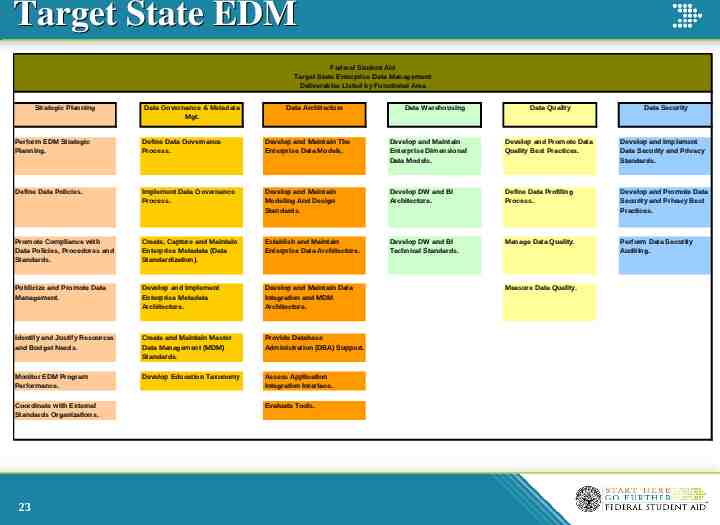
Target State EDM Federal Student Aid Target State Enterprise Data Management Deliverables Listed by Functional Area Strategic Planning Data Governance & Metadata Mgt. Data Architecture Data Warehousing Data Quality Data Security Perform EDM Strategic Planning. Define Data Governance Process. Develop and Maintain The Enterprise Data Models. Develop and Maintain Enterprise Dimensional Data Models. Develop and Promote Data Quality Best Practices. Develop and Implement Data Security and Privacy Standards. Define Data Policies. Implement Data Governance Process. Develop and Maintain Modeling And Design Standards. Develop DW and BI Architecture. Define Data Profiling Process. Develop and Promote Data Security and Privacy Best Practices. Promote Compliance with Data Policies, Procedures and Standards. Create, Capture and Maintain Enterprise Metadata (Data Standardization). Establish and Maintain Enterprise Data Architecture. Develop DW and BI Technical Standards. Manage Data Quality. Perform Data Security Auditing. Publicize and Promote Data Management. Develop and Implement Enterprise Metadata Architecture. Develop and Maintain Data Integration and MDM Architecture. Identify and Justify Resources and Budget Needs. Create and Maintain Master Data Management (MDM) Standards. Provide Database Administration (DBA) Support. Monitor EDM Program Performance. Develop Education Taxonomy Assess Application Integration Interface. Coordinate with External Standards Organizations. 23 Evaluate Tools. Measure Data Quality.

Data Policy and Strategic Planning Defines EDM strategic direction and promotes compliance with EDM policies, procedures and standards. Drafted of an EDM Strategic Plan. Developed an EDM Concept of Operations. Drafted Enterprise Data Policies. Developed EDM Language for inclusion into Contracts. Maintained EDM Business Case. Published Performance Metrics. 24
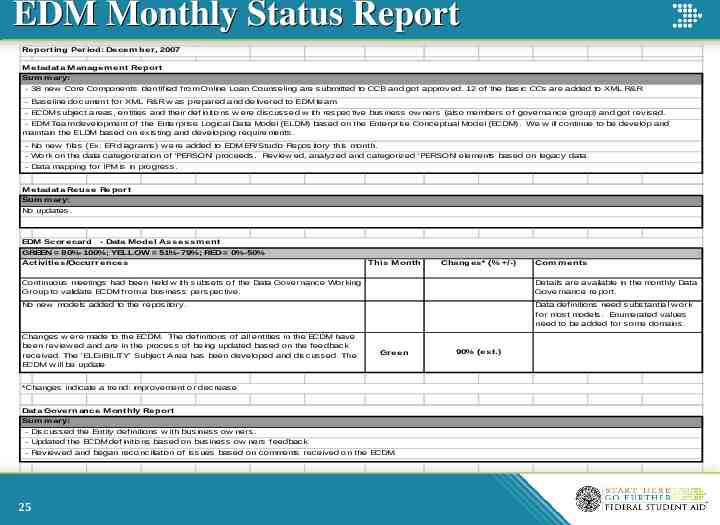
EDM Monthly Status Report Re porting Period: De ce m be r, 2007 Me tadata M anage m e nt Re port Sum m ary: - 38 new Core Components identif ied f rom Online Loan Counseling are submitted to CCB and got approved. 12 of the basic CCs are added to XML R&R - Baseline document f or XML R&R w as prepared and delivered to EDM team. - ECDM subject areas, entities and their def initions w ere discussed w ith respective business ow ners (also members of governance group) and got revised. - EDM Team development of the Enterprise Logical Data Model (ELDM) based on the Enterprise Conceptual Model (ECDM). We w ill continue to be develop and maintain the ELDM based on existing and developing requirements. - No new f iles (Ex: ER diagrams) w ere added to EDM ER/Studio Repository this month. - Work on the data categorization of 'PERSON' proceeds. Review ed, analyzed and categorized 'PERSON' elements based on legacy data. - Data mapping f or IPM is in progress. Me tadata Re us e Re port Sum m ary: No updates. EDM Score card - Data M odel As s e s s m e nt GREEN 80%-100%; YELLOW 51%-79%; RED 0%-50% Activitie s /Occurre nce s This Month Change s * (% /-) Com m e nts Continuous meetings had been held w ith subsets of the Data Governance Working Group to validate ECDM f rom a business perspective. Details are available in the monthly Data Governance report. No new models added to the repository. Data def initions need substantial w ork f or most models. Enumerated values need to be added f or some domains. Changes w ere made to the ECDM. The def initions of all entities in the ECDM have been review ed and are in the process of being updated based on the f eedback received. The 'ELIGIBILITY' Subject Area has been developed and discussed. The ECDM w ill be update Gre e n *Changes indicate a trend: improvement or decrease Data Gove rnance M onthly Re port Sum m ary: - Discussed the Entity def initions w ith business ow ners. - Updated the ECDM def initions based on business ow ners f eedback. - Review ed and began reconciliation of issues based on comments received on the ECDM. 25 90% (e s t.)

Data Governance Implements data governance processes to maintain standardized data definitions and associated metadata. Started two years ago with a Data Governance Pilot tackling – Enterprise Address. Developed Data Standardization Policies and Procedures. Developed Data Dictionary Standards. Developed Data Governance Plan. Formed Enterprise Data Governance Workgroup. Business people agreed to learn basic to intermediate data modeling concepts. Joint development of data-related artifacts with business and technical staff. 26
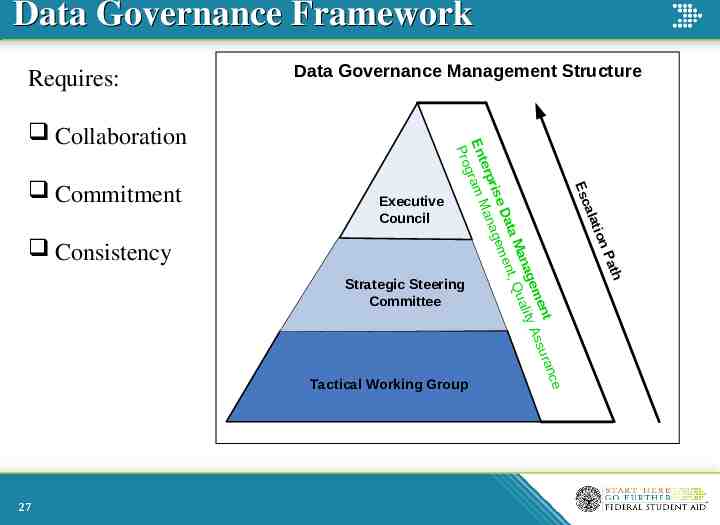
Data Governance Framework Requires: Data Governance Management Structure h 27 ce Tactical Working Group Pat Strategic Steering Committee n atio Consistency Executive Council al Esc Commitment n ent ssura gem ty A ana Quali aM t, Dat men rise anage erp Ent ram M g Pro Collaboration
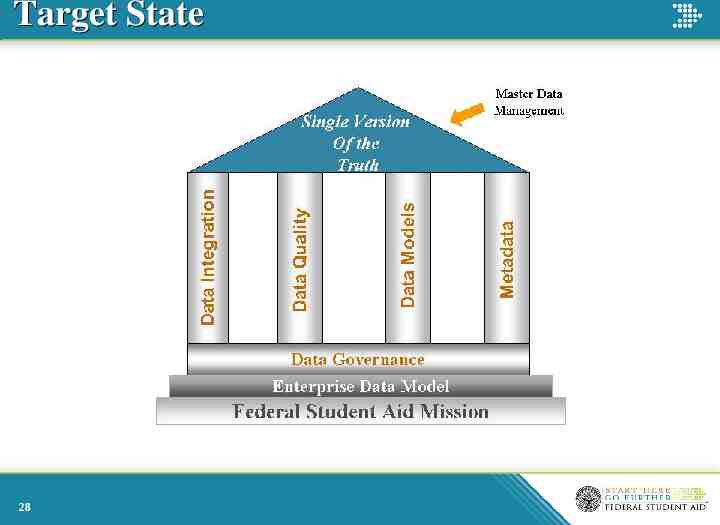
Target State 28

Metadata Management Uses metadata to guide, control and integrate data activities and products. Donated metadata registry, the XML Registry and Repository for the Education Community, to the Education Community of Interest. www.fsaxmlregistry.ed.gov Published as Open Source on SourceForge. http://sourceforge.net/projects/fsaxmlregistry/ Classification scheme extends beyond that used by Federal Student Aid. Promotes use of common standards across the Education Community of Interest. 29
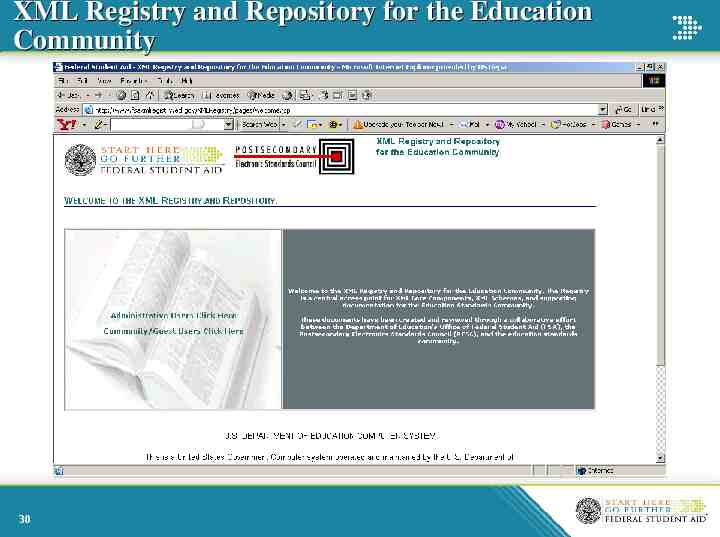
XML Registry and Repository for the Education Community 30

Metadata Management Uses metadata to guide, control and integrate data activities and products. Developed Enterprise Metadata Inventory. Developing Master Data Management. Purchased and testing IBM Information Server. 31
Data Architecture Promotes sharing of database assets, the use of an integrated architecture to support enterprise-wide data movement, access to common data, data transformation and migration. Developed an Enterprise Conceptual Data Model (signed off by the business areas). Developing Enterprise Logical Data Model. Data Modeling Standards and Procedures. Developed Naming Standards. Developed Data Model Registration Policies and Procedures. Developed Data Migration Roadmap: A Best Practice Summary. Developed Data Synchronization Policies and Procedures. Researched Data Integration Services Best Practices and Recommendation. 32

Data Quality Institutionalizes a set of repeatable processes to continuously monitor data and improve data accuracy, completeness, timeliness and relevance. Developed Enterprise Data Quality Scorecard Building upon previous work (Data Quality Assurance Strategy) to promote reuse Developing Data Quality Policies and Procedures Planning a Data Quality service for the for business areas (data profiling services, etc) 33

Future Areas of Focus The US Department of Education Develop US Dept of ED Enterprise Conceptual Data Model – created from the business areas. Form US Dept of ED Data Governance Workgroup. Encourage PK12 and Postsecondary data alignment. Encourage and contribute to PK 20 Data Standardization and Education Taxonomy. 34

When We’ll Be Done Federal Student Aid is a proactive organization with sophisticated enterprise analytics that are used to inform Congress and help determine new policy. An Education Taxonomy is not a misunderstood word. Enterprise Data Artifacts are complete, of high-quality and used by the business areas often. Federal Student Aid “owns” its data and it’s organized by Business Capability Area, Business Function, and Data. This information is in the SOW for development projects and creates high-quality, lower cost development. 35

Lessons Learned If it’s not in business (plain) language and/or it’s not clear how it supports the business – EDM doesn’t pay for it. True change takes time. Period. The technology is not the hard part – the people part is the hard part. Have someone who’s really, really good with the soft skills at the table. Luck is not a good business strategy. Little and often. It really does help when you have consistency of staff. Collaboration is so worth the time it takes. Business areas and Technologists can work together and develop really, really good work. 36
DAMA Impact Changed CONOPS after researching DMBOK. Developed data definition standards after attending “The Dictionary: Heart of Data Quality.” Felt better about EDM coming from a business area after attending “Mastering Master Data.” Prioritized Data Quality work from year three to year two after attending “Introduction to Data Quality Tools and Technologies.” Purchased “Data Modeling Made Simple” for members of Data Governance Workgroup. Changed data models after attending “Make Your Data Model Diagram Really Communicate.” 37

Closing Remark As you can gather from our presentation, Federal Student Aid’s data work did not begin as a mature Enterprise Data Management Program; in fact, it began in chaos. However, over time: 38 Opportunities were identified, Huge goals were set, Communities of interest were engaged Purpose was communicated Strategic decisions were made Crazy ideas were tried and evaluated Best practices were researched Mistakes were made and course corrections were implemented Baby steps were accomplished Everyone was heard and valued

Questions We appreciate your feedback and comments. Holly Hyland; Phone: 202-377-3710 Email: [email protected] Lisa Elliott; Phone: 202-377-4454 Email: [email protected] 39






