NIPP 2013: Partnering for Critical Infrastructure Security and
18 Slides2.87 MB

NIPP 2013: Partnering for Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience 3/29/23

Table of Contents Strategic Drivers, Vision, Goals The Critical Infrastructure Environment Overview and Core Tenets Collaborating to Manage Risk Call to Action Next Steps Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 2
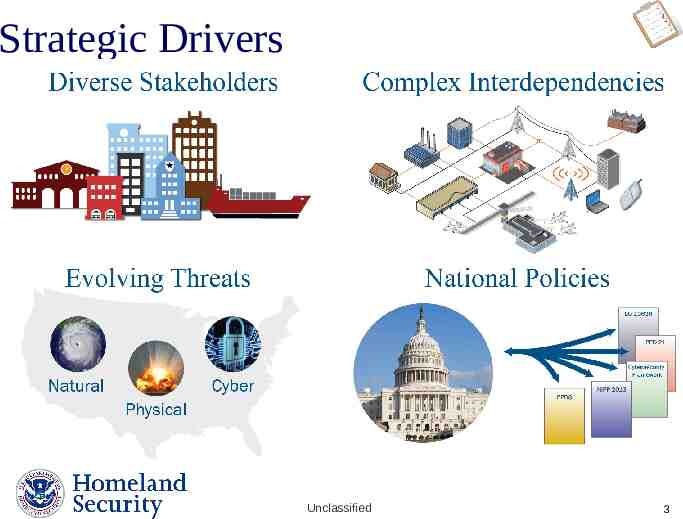
Strategic Drivers Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 3

NIPP 2013 Vision A Nation in which physical and cyber critical infrastructure remain secure and resilient, with vulnerabilities reduced, consequences minimized, threats identified and disrupted, and response and recovery hastened Security: Reducing the risk to critical infrastructure by physical means or defensive cyber measures to intrusions, attacks, or the effects of natural or manmade disasters Resilience: The ability to prepare for and adapt to changing conditions, and withstand and recover rapidly from disruptions Unclassified 4 Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 4

NIPP 2013 Goals Assess and analyze critical infrastructure threats, vulnerabilities and consequences to inform risk management Address multiple threats through sustainable efforts to reduce risk; account for costs and benefits of security investments Enhance critical infrastructure resilience; minimize the adverse consequences of incidents as well as conduct effective responses Share actionable and relevant information across the critical infrastructure community to build awareness and enable risk-informed decision making Promote learning and adaptation during and after exercises and incidents Unclassified 5 Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 5

Critical Infrastructure Today Critical Infrastructure defined: “Assets, systems, and networks, whether physical or virtual, so vital to the United States that their incapacitation or destruction would have a debilitating effect on national security, economic security, national public health or safety, or any combination thereof.” 16 Critical Infrastructure Sectors Chemical Commercial Facilities Communications Critical Manufacturing Dams Defense Industrial Base Emergency Services Energy Unclassified Financial Services Food & Agriculture Government Facilities Healthcare and Public Health Information Technology Nuclear Reactors, Materials and Waste Transportation Systems Water & Wastewater Systems Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 6

Today’s Risk Landscape America remains at risk from a variety of threats including: Acts of Terrorism Cyber Attacks Extreme Weather Pandemics Accidents or Technical Failures NIPP 2013 offers a distributed approach for addressing the diverse and evolving risk environment. Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 7

National Policies President Obama announced two policies related to critical infrastructure security and resilience in February 2013: Presidential Policy Directive 21: Presidential Policy Directive 21: Critical Infrastructure Security and Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience Resilience “The Nation's critical infrastructure provides the essential services that underpin American society. Proactive and coordinated efforts are necessary to strengthen and maintain secure, functioning, and resilient critical infrastructure that are vital to public confidence and the Nation's safety, prosperity, and well-being.” – Presidential Policy Directive (PPD) 21 Executive Order 13636: Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 8

Many Stakeholders, Many Strengths Comparative Advantage Engaging in collaborative processes Applying individual expertise Bringing resources to bear Building the collective effort Enhancing overall effectiveness Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 9

Core Tenets Coordinated and comprehensive risk identification and management Cross-sector dependencies and interdependencies Enhanced information sharing Comparative advantage in risk mitigation Regional and SLTT partnerships Cross-jurisdictional collaboration Security and resilience by design Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 10

Evolution from 2009 NIPP Security and Resilience Elevates security and resilience as the primary aim of critical infrastructure homeland security planning efforts Cyber-Physical Integration Integrates cyber and physical security and resilience efforts into an enterprise approach to risk management Partnership Structure Focuses on establishing a process to set critical infrastructure national priorities determined jointly by the public and private sector International Affirms that critical infrastructure security and resilience efforts require international collaboration Risk Management Updates the critical infrastructure risk management framework and addresses alignment to the National Preparedness System, across the prevention, protection, mitigation, response, and recovery mission areas Regional and Local Partnerships Supports execution of the National Plan and achievement of the National Preparedness Goal at both the national and community levels, with focus on leveraging regional collaborative efforts Call to Action Presents a detailed Call to Action with steps that will be undertaken, shaped by each sector’s priorities and in collaboration with critical infrastructure partners, to make progress toward security and resilience Unclassified 11 Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 11
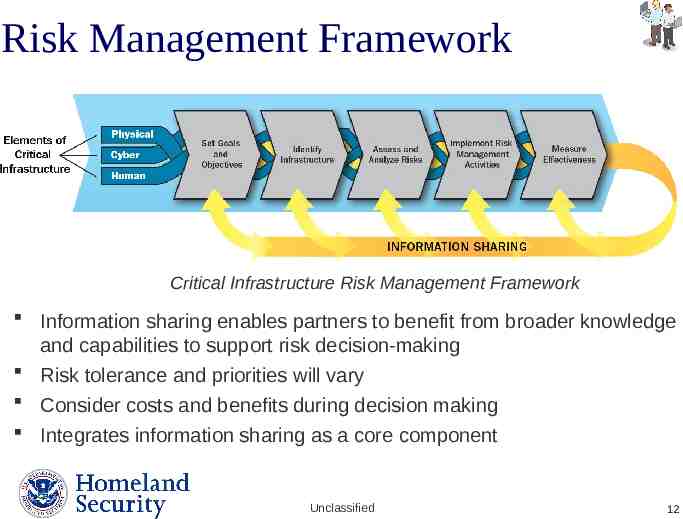
Risk Management Framework Critical Infrastructure Risk Management Framework Information sharing enables partners to benefit from broader knowledge and capabilities to support risk decision-making Risk tolerance and priorities will vary Consider costs and benefits during decision making Integrates information sharing as a core component Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 12
Call to Action A whole of community approach to advancing the national effort Build on Existing Partnerships Innovate in Managing Risk Unclassified Focus on Outcomes Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 13

Call to Action Build upon Partnership Efforts Set National Focus through Joint Priority Setting Determine Collective Actions through Joint Planning Efforts Empower Local and Regional Partnerships to Build Capacity Nationally Leverage Incentives to Advance Security and Resilience Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 13

Call to Action Innovate in Managing Risk Enable Risk-Informed Decision-Making through Enhanced Situational Awareness Analyze Infrastructure Dependencies, Interdependencies, and Associated Cascading Effects Rapidly Identify, Assess, and Respond to Cascading Effects During and Following Incidents Promote Infrastructure, Community, and Regional Recovery Strengthen Coordinated Technical Assistance, Training, and Education Improve Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience by Advancing R&D Solutions Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 13

Call to Action Focus on Outcomes Evaluate Achievement of Goals Learn and Adapt During and After Exercises and Incidents Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 13

Resources and Training Visit www.dhs.gov/nipp for links to the full NIPP 2013 and the NIPP Supplements and critical infrastructure training: NIPP Supplements Connecting to the NICC and NCCIC Executing a Critical Infrastructure Risk Management Approach Incorporating Resilience into Critical Infrastructure Projects NPPD Resources to Support Vulnerability Assessments Critical Infrastructure Partnership Courses IS 913 Achieving Results through Critical Infrastructure Partnership and Collaboration IS 921 Implementing Critical Infrastructure Protection Programs and CI TOOLKIT Security Awareness Series Courses IS 906 Workplace Security IS 907 Active Shooter IS 912 Retail Security Awareness IS 914 Surveillance Awareness: What you can do IS 915 Protecting Critical Infrastructure Against Insider Threat IS 916 Critical Infrastructure Security: Theft and Diversion – What You Can Do Unclassified Presenter’s Name June 17, 2003 17