New Senior Secondary History Curriculum (Secondary 4-6) Understanding
20 Slides329.00 KB

New Senior Secondary History Curriculum (Secondary 4-6) Understanding and Interpreting the Curriculum

Background The NSS History Curriculum framework was formulated alongside the report on the New Academic Structure for Senior Secondary Education and Higher Education – Action Plan for Investing in the Future of Hong Kong It is one of the six elective subjects in the PSHE KLA It shares all the generic skills involved in the study of humanities subjects, such as critical thinking and enquiry, and aims to develop in students the essential skills of historical investigation during the three years of study

Interface with Junior Secondary Education The study of History at senior secondary level is based on knowledge of history that students should have acquired at junior secondary level as well as the understanding of the patterns of development in historical periods of national and world history that student acquired in taking other related PSHE curricula such as “Integrated Humanities” and “ History and Culture”.

It also builds on the skills of chronological thinking, historical comprehension, empathy, enquiry, critical thinking and communication that students should have developed at junior secondary level. It also enables the students to further develop an enquiring mind, an attitude of respect for and tolerance of different opinions, and a sense of balanced judgment and objectivity, which should have been cultivated through the study of History or other related PSHE curricula at junior secondary level.

Interface with Post-secondary Pathways The study of History provides prospective university students with a sound conceptual framework and knowledge of the 20th Century world It provides them with skills needed for studying subjects of their personal interests in the fields of humanities, social sciences or even business management. It also provides them with research skills to sign up courses in heritage studies, archaeology and anthropology in their university studies.

Understanding the Curriculum The compulsory part of the curriculum takes the form of themes subdivided into topics. It focuses on the study of local, national, regional and global developments of the 20th century world. It evolves from the existing S4-5 History curriculum with an introductory part constitutes approximately 10 contact hours on the ‘Introduction to the Making of the Modern World” to make the curriculum more integral. It constitutes two-third of the curriculum and occupies approximately 190 contact hours.

The Electives of the curriculum aims to introduce to students other approaches to history that could be more relevant to their needs, interests and ability level. It constitutes one-third of the curriculum and occupies approximately 40 contact hours. Another 25 contact hours will be allocated to other learning activities e.g. field visits or museum visits. Students are require to choose from ONE of the three Electives

Elective 1 : Comparative studies focus on related aspects and course of development in different countries or regions to promote generalization of trends or patterns in history stimulating enquiries into the uniqueness of specific events.

Elective 2 : Issue-based studies Enables students to demonstrate their understanding of key historical concepts and their mastery of major skills of an area that interests them An issue-based approach helps promote students’ reflective thinking and awareness of communal and world issues and to enhances their commitment to resolving these issues.

Elective 3 : Local and Heritage Study cater for students who have developed interest in our local community and heritage education prepare students for job-related studies or employment in areas relating to heritage or tourism.

A Diagrammatic Presentation of NSS History Curriculum Framework and Assessment Compulsory Part The Making of the Modern World Elective Part Values and attitude Modernisation and Transformation in 20th cent ury Asia Conflicts and Cooperation in 20th century Worl d Chronological thinking Historical comprehension and analysis Historical interpretation Organization and communication 1. Comparative studies 2. Issue-based studies 3. Local and heritage studies Historical thinking Skills Historical enquiry (one of the following) Assessment : Internal assessment Public assessment SBA Assessment: Internal assessment Public Assessment – SBA Public Examination Organization and communication

Progression of Studies In order to give students a chance to explore their interest in History at S4, teachers should provide students with a “taster” of this course. Basic historical concepts such as chronology, cause and effect, and continuity and change are introduced in the introductory part of the curriculum i.e. “Introduction to the Making of the Modern World” Teachers will have the discretion to decide whether to start with Theme A or Theme B in S4, as the study of either Theme can help students to develop the skills of detecting bias, analyzing and interpreting historical information, and formulation opinions on historical issues.

By the end of S4, students should be able to present logical and coherent arguments, and to apply basic historical knowledge and skills in everyday life. They will then decide whether to continue studying History or not. Those who decide to continue studying History and complete the Compulsory Part of the curriculum can apply the knowledge, concepts and skills that they have acquired to the study of an elective based on their personal interests and / or needs.
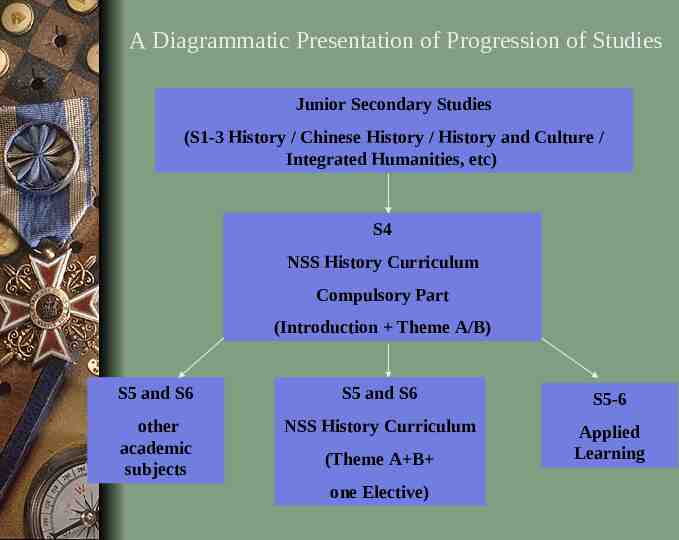
A Diagrammatic Presentation of Progression of Studies Junior Secondary Studies (S1-3 History / Chinese History / History and Culture / Integrated Humanities, etc) S4 NSS History Curriculum Compulsory Part (Introduction Theme A/B) S5 and S6 S5 and S6 S5-6 other academic subjects NSS History Curriculum Applied Learning (Theme A B one Elective)

Interpreting the Curriculum Compulsory Part “Introduction : The Making of Modern World” to introduce to students the historical background to the modernization and transformation of Asia in the 20th Century. to promote the understanding of the conflicts and cooperation in the 20th Century world among students through examining the relationships among the major Western powers in the 19th Century.

Note: This part of the curriculum forms an essential background to the understanding of the 20th Century history but will not constitute as one of the area to be examined during the public examination.

Elective 1 & 2 Comparative studies and Issue-based studies focus on different approaches to history topics could be derived from either Theme A or Theme B

Elective 3 Local and heritage studies cater for students who have special interest in the history of our local community and / or in heritage studies. prepare students for further studies in the fields of culture , heritage and museum management

Note : Schools offering the NSS History Curriculum have to offer the three Electives to all students. Students will have the choice of opting either ONE of the Electives.

http://www.edb.gov.hk/index.asp x?langno 2&nodeid 3206#3219






