MILITARY 101 A brief overview on the training, skills, and
34 Slides6.29 MB

MILITARY 101 A brief overview on the training, skills, and education of military Service members, as well as resources to assess the transferability of those skills to the civilian workforce. August 2020

What are the different branches of the military? What are the ranks in the U.S. Military? Discussion Topics What types of experience do Service members attain? What type of training and education do Service members receive? What tools are available to assess transferability of military skills and training? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 2

WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT BRANCHES AND COMPONENTS OF THE MILITARY? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 3

Army Mission: “To deploy, fight and win our nation’s wars by providing ready, prompt and sustained land dominance by Army forces across the full spectrum of conflict as part of the joint force.” The Army is the Nation’s oldest service, and as such, precedes all other services in matters of protocol SOLID, LLC - Military 101 4

Navy Mission: “The Department of the Navy will recruit, train, equip, and organize to deliver combat ready Naval forces to win conflicts and wars while maintaining security and deterrence through sustained forward presence.” Of all the services, the U.S. Naval Academy has produced the most astronauts, as well as the first American in space (Alan Shepard, Rear Admiral, USN, Ret.). SOLID, LLC - Military 101 5

Air Force The mission of the U. S. Air Force is to fly, fight and win . in air, space, and cyberspace. The Air Force was established with the National Security Act of 1947, along with the Central Intelligence Agency, and the National Security Council. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 6

Space Force The US Space Force “is a military service that organizes, trains, and equips space forces in order to protect U.S. and allied interests in space and to provide space capabilities to the joint force. ” The Space force motto Semper Supra means “Always Above.” SOLID, LLC - Military 101 7

Marine Corps “As America's expeditionary force in readiness since 1775, the U.S. Marines are forward deployed to win our Nation’s battles swiftly and aggressively in times of crisis. We fight on land, sea and air, as well as provide forces and detachments to naval ships and ground operations.” Famous Marines include Adam Driver, Gene Hackman, James Carville, and Bob Keeshan (a.k.a Captain Kangaroo) SOLID, LLC - Military 101 8

US Coast Guard The Coast Guard is the principal Federal agency responsible for maritime safety, security, and environmental stewardship in U.S. ports and waterways. As one of the five Armed Services of the United States, the Coast Guard is the only military branch within the Department of Homeland Security. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 9
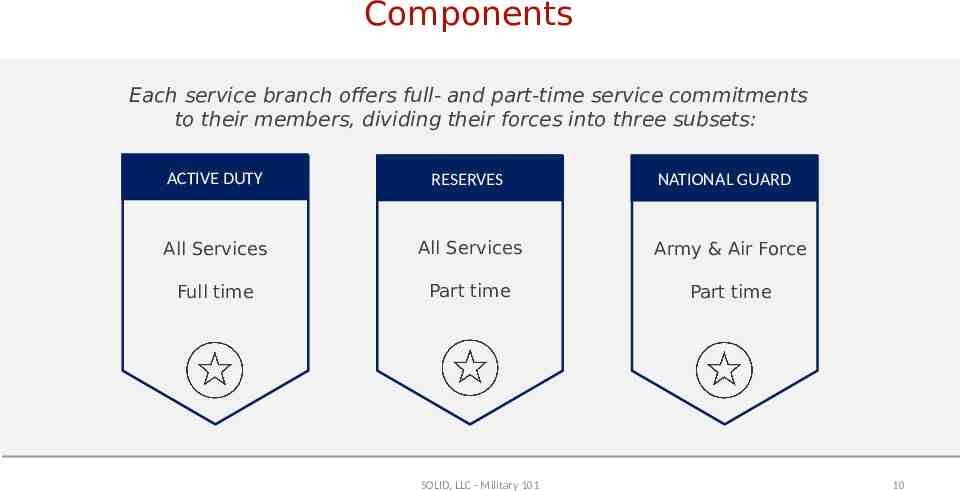
Components Each service branch offers full- and part-time service commitments to their members, dividing their forces into three subsets: ACTIVE DUTY RESERVES All Services All Services Army & Air Force Full time Part time Part time SOLID, LLC - Military 101 NATIONAL GUARD 10

Components – Active Duty Branches: Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, Space Force, and Coast Guard A person who is "active duty" is in the military full time, may live on a military base, and can be deployed at any time. To assist in their career development—as well as meet national security needs—most military personnel move frequently from one geographic duty location to another. On average, officers move every two to three years and enlisted personnel move every four years. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 11

Components Reserve Branches: Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard Each branch of the military has a Reserve component, which is under the command of their respective military branch (e.g., Army Reserve is under the command of the Army). The purpose of the Reserve is to provide and maintain trained, qualified units available for active duty when needed. This may be in times of war overseas, in a national emergency, or as the need occurs based on threats to national security. Historically, the primary job of the Reserve has been to fill gaps in stateside service positions when active duty forces ship overseas. In recent conflicts, Reserve units have deployed directly to overseas locations. At a minimum, members of the Reserve are required to participate in training drills (AKA "Drill") one weekend each month and two consecutive weeks per year. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 12

Components – National Guard Branches: Army and Air Force The National Guard consists of the Army National Guard and the Air Force's Air National Guard. Though federally funded, it is organized and controlled by the states under the authority of each state’s governor. In times of war or national crisis, the National Guard can become federalized and deployed by federal command authorities. During local emergencies, these units assist communities endangered by storms, floods, fires, and other disasters. Specialized units deployed overseas are prepared for and may see combat action, but traditionally Guard units are directed to work more in humanitarian relief or peacekeeping roles such as building schools and hospitals or training local peacekeepers. As with the Reserve, the National Guard requires training drills one weekend a month and two weeks per year at a minimum. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 13

WHAT ARE THE RANKS IN THE U.S. MILITARY? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 14
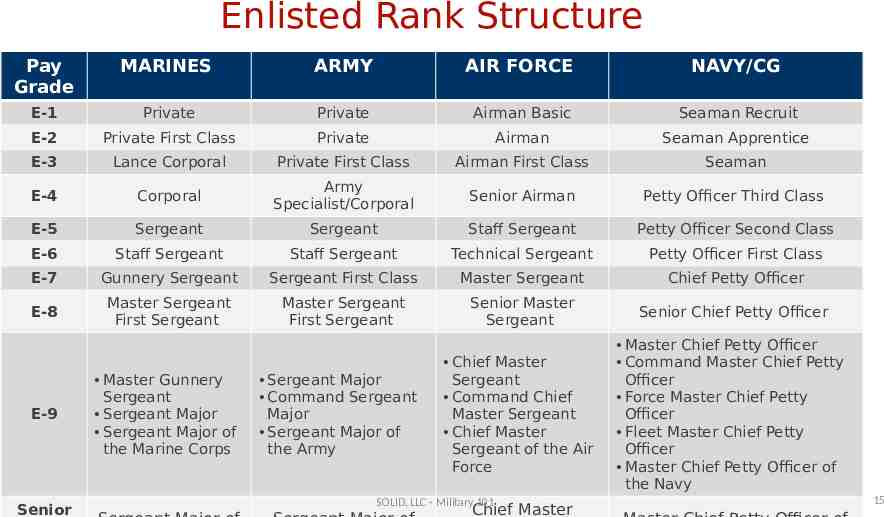
Enlisted Rank Structure Pay Grade MARINES ARMY AIR FORCE NAVY/CG E-1 Private Private Airman Basic Seaman Recruit E-2 Private First Class Private Airman Seaman Apprentice E-3 Lance Corporal Private First Class Airman First Class Seaman E-4 Corporal Army Specialist/Corporal Senior Airman Petty Officer Third Class E-5 Sergeant Sergeant Staff Sergeant Petty Officer Second Class E-6 Staff Sergeant Staff Sergeant Technical Sergeant Petty Officer First Class E-7 Gunnery Sergeant Sergeant First Class Master Sergeant Chief Petty Officer E-8 Master Sergeant First Sergeant Master Sergeant First Sergeant Senior Master Sergeant Senior Chief Petty Officer Chief Master Sergeant Command Chief Master Sergeant Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force Master Chief Petty Officer Command Master Chief Petty Officer Force Master Chief Petty Officer Fleet Master Chief Petty Officer Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy E-9 Senior Master Gunnery Sergeant Sergeant Major Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps Sergeant Major Command Sergeant Major Sergeant Major of the Army SOLID, LLC - Military 101 Chief Master 15
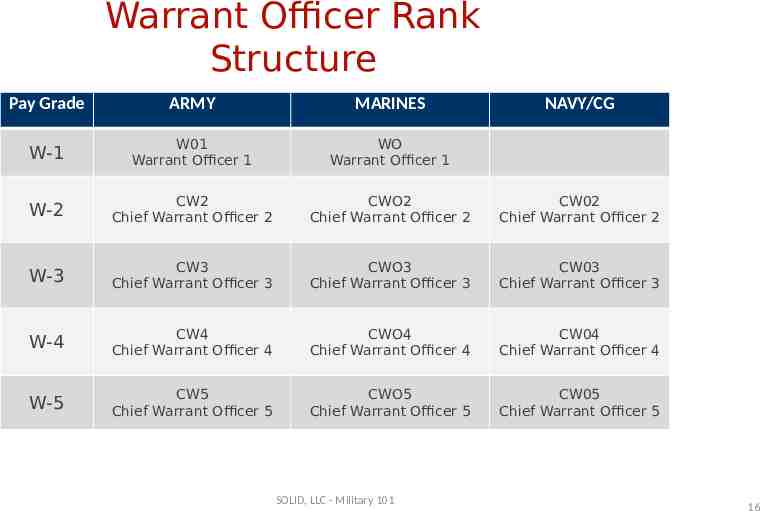
Warrant Officer Rank Structure Pay Grade ARMY MARINES W-1 W01 Warrant Officer 1 WO Warrant Officer 1 W-2 CW2 Chief Warrant Officer 2 CWO2 Chief Warrant Officer 2 CW02 Chief Warrant Officer 2 W-3 CW3 Chief Warrant Officer 3 CWO3 Chief Warrant Officer 3 CW03 Chief Warrant Officer 3 W-4 CW4 Chief Warrant Officer 4 CWO4 Chief Warrant Officer 4 CW04 Chief Warrant Officer 4 W-5 CW5 Chief Warrant Officer 5 CWO5 Chief Warrant Officer 5 CW05 Chief Warrant Officer 5 SOLID, LLC - Military 101 NAVY/CG 16
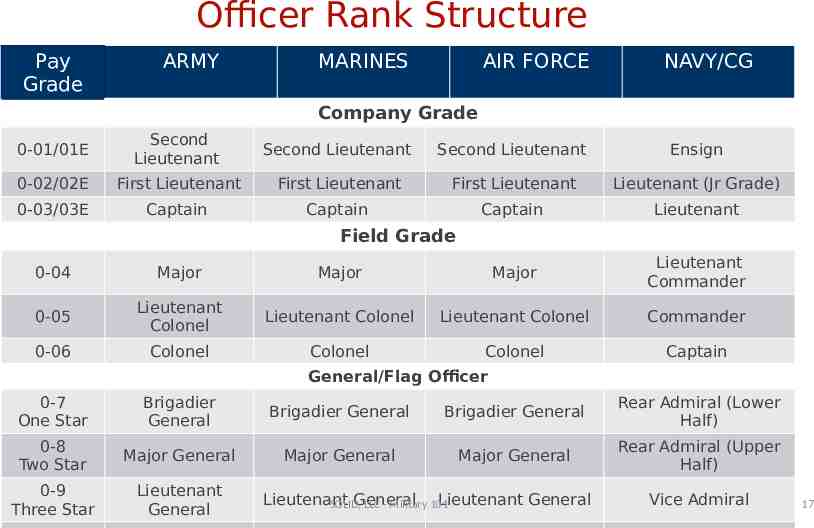
Officer Rank Structure Pay Grade ARMY MARINES AIR FORCE NAVY/CG Company Grade 0-01/01E Second Lieutenant Second Lieutenant Second Lieutenant Ensign 0-02/02E First Lieutenant First Lieutenant First Lieutenant Lieutenant (Jr Grade) 0-03/03E Captain Captain Captain Lieutenant Field Grade 0-04 Major Major Major Lieutenant Commander 0-05 Lieutenant Colonel Lieutenant Colonel Lieutenant Colonel Commander 0-06 Colonel Colonel Colonel Captain General/Flag Officer 0-7 One Star Brigadier General Brigadier General Brigadier General Rear Admiral (Lower Half) 0-8 Two Star Major General Major General Major General Rear Admiral (Upper Half) 0-9 Three Star Lieutenant General Lieutenant General Lieutenant General SOLID, LLC - Military 101 Vice Admiral 17

WHAT TYPES OF EXPERIENCE DO SERVICE MEMBERS ATTAIN? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 18
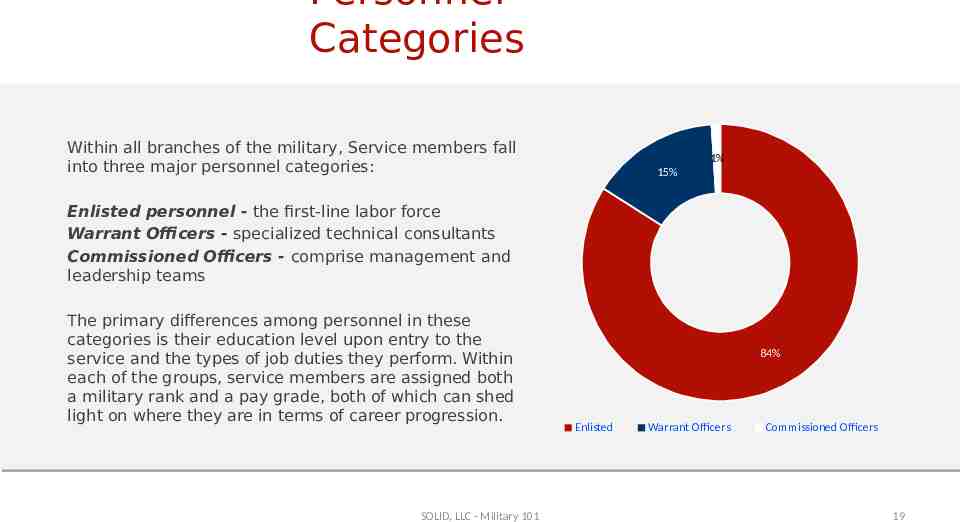
Personnel Categories Within all branches of the military, Service members fall into three major personnel categories: 1% 15% Enlisted personnel - the first-line labor force Warrant Officers - specialized technical consultants Commissioned Officers - comprise management and leadership teams The primary differences among personnel in these categories is their education level upon entry to the service and the types of job duties they perform. Within each of the groups, service members are assigned both a military rank and a pay grade, both of which can shed light on where they are in terms of career progression. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 84% Enlisted Warrant Officers Commissioned Officers 19

Military Career Options Enlisted Warrant Officer Officer Primary Duties Carry out fundamental operations of the military Highly specialized experts in their field and trainers Managers, leaders, problem solvers, planners Percentage of Armed Forces 84% 1% 15% Education Level Upon Entry High School Degree or Equivalent High School Diploma or Equivalent; College Degree College Degree Pay Grades E-1 to E-9 WO-1 TO WO-5 O-1 to O-10 Assessing Transferability of Skills Can be difficult due to unique military job titles, but skills are highly transferrable SOLID, LLC - Military 101 Not too difficult due to job title similarities and degrees held 20

Learning the Lingo: Military Occupations Service Army Navy/ CG Air Force Marine Corps Enlisted Warrant Officers Officers Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) Warrant Officer MOS (WO MOS) Area of Concentration (AOC) Rating Chief Warrant Officer (CWO) Designator, LDO, CG Specialty Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC) N/A AFSC Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) MOS (WO MOS) Looking for a Construction Laborer? Army – 51B – Carpentry and Masonry Specialist Navy – BU – Builder Air Force – 3E351 – Structural Journeyman Marines – 1371 – Operating Engineer Coast Guard – DC – Damage Controlman MOS SOLID, LLC - Military 101 21

Top 10 Occupational Areas of Transitioning Military Personnel o Aircraft Mechanics o Automotive Service Technicians and Mechanics o Computer Support Specialist/Operators/ Security Specialists o Cooks/Food Preparation Workers o Health Care Support Occupations o Police/Security Guard o Supply Chain (Shipping, Receiving/Traffic Clerks OR Stock Clerks/Order Filers/Logisticians) SOLID, LLC - Military 101 o Truck Driver o Military Specific 22

Military Occupations with No Civilian Job Equivalents Vast majority of military occupations have a direct civilian job equivalent Army and Marine Corps have largest numbers of enlisted Service members with no direct civilian job equivalent (e.g., Infantry, Mortar Man, Field Artillery) Lack of direct civilian occupational equivalent: Does not mean that the Service member lacks transferrable skills Does make it more difficult for Service members to document the transferability of their skills SOLID, LLC - Military 101 23

Civilian Credentialing Opportunities For transitioning service members, certifications and licenses are a means of demonstrating to civilian employers that their skills are on par with those of their civilian counterparts. Service members have a high success rate in attaining civilian credentials. High pass rates demonstrate the relevance of military training and experience to civilian jobs. CERTIFICATION AND LICENSURE EXAM PASS RATES 85% 70% One statistic from the Navy showed that its Service members have a pass rate of over 85 percent on certification and licensure exams, compared to industry average of 70 percent. SOLID, LLC - Military 101 24
Collateral Duties In addition to primary duties, Service members often have collateral duties that may correspond to civilian jobs or credentials. Command Fitness Leader Command Finance Specialist Correctional Custody Specialist Drug and Alcohol Counselor Equal Opportunity Advisor Instructor SOLID, LLC - Military 101 Information Assurance Senior Enlisted Leader Field Recruiter 25

WHAT TYPES OF TRAINING AND EDUCATION DO SERVICE MEMBERS RECEIVE? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 26

Military Training vs. Education Training Compensatory Mission-related Education VS Voluntary May or may not be military occupation- Formal and specific informal Career Roadmaps help guide Service members to training and education opportunities SOLID, LLC - Military 101 27

Military Training Boot Camp 7 to 12 weeks builds physical and mental stamina, develops team building skills, and orient recruits to the military mission, culture, and ethos Initial Technical Training Continued Training Throughout Career 8 weeks to one year intensive occupational training after basic training e.g., A-School or Advanced Individualized Training (AIT) Upon completion, qualified to hold their military occupational More advanced job training Leadership training Specialized Skills Training More than 60% of formal training qualifies as college credit SOLID, LLC - Military 101 28
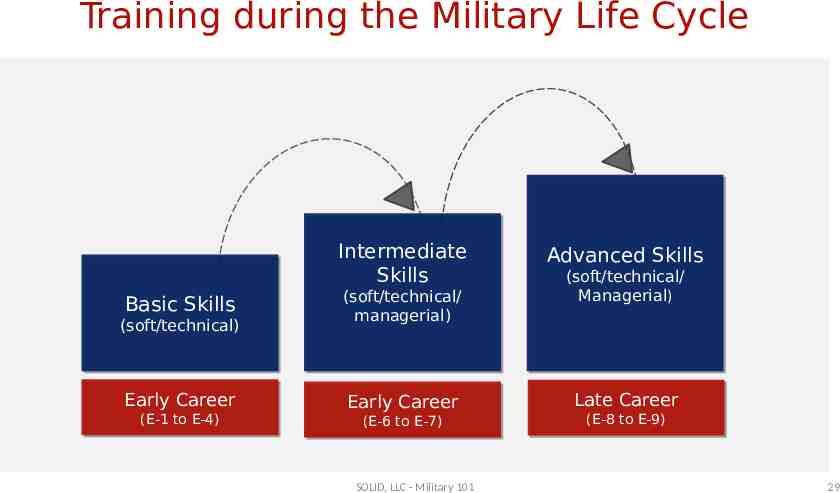
Training during the Military Life Cycle Intermediate Intermediate Skills Skills Advanced Advanced Skills Skills Basic Basic Skills Skills (soft/technical/ (soft/technical/ managerial) managerial) Early Early Career Career Early Early Career Career Late Late Career Career (soft/technical) (soft/technical) (E-1 (E-1 to to E-4) E-4) (E-6 (E-6 to to E-7) E-7) SOLID, LLC - Military 101 (soft/technical/ (soft/technical/ Managerial) Managerial) (E-8 (E-8 to to E-9) E-9) 29

Voluntary Education Provides variety of off-duty continuing education options Postsecondary Degree Programs Tuition Assistance Military Evaluations Program Credentialing Opportunities Each year about 300,000 Service members sign up for postsecondary courses leading to college degrees (approximately 1/3 of Service members). SOLID, LLC - Military 101 30
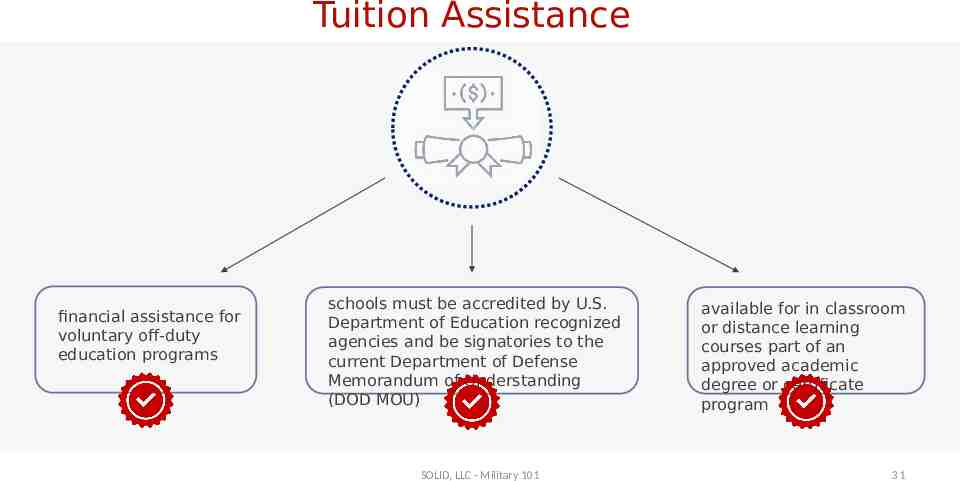
Tuition Assistance financial assistance for voluntary off-duty education programs schools must be accredited by U.S. Department of Education recognized agencies and be signatories to the current Department of Defense Memorandum of Understanding (DOD MOU) SOLID, LLC - Military 101 available for in classroom or distance learning courses part of an approved academic degree or certificate program 31

WHAT TOOLS ARE AVAILABLE TO EMPLOYERS TO ASSESS TRANSFERABILITY OF MILITARY SKILLS AND TRAINING? SOLID, LLC - Military 101 32

Tools to Assess Transferability of Military Skills The COOL (Credentialing Opportunities On-Line) Programs – map credentials to military occupations and federal civilian occupations. Access the COOL websites from the DoD COOL Portal SOLID, LLC - Military 101 33
Tools to Assess Transferability of Military Skills Additional tools MY NEXT MOVE FOR VETERANS CAREERS IN THE MILITARY www.careersinthemilitary.com A companion site to www.asvabprogram.com, houses public access to in-depth military career information DoD SKILLBRIDGE www.mynextmove.org/vets Includes interactive tools and data for 900 careers, including information on civilian careers with similar job skills to military occupations OCCUPATIONAL OUTLOOK HANDBOOK https://dodskillbridge.usalearning.gov The SkillBridge program allows Service members to get civilian work experience through industry training, apprenticeships, and internships during last 180 days of service SOLID, LLC - Military 101 Job Opportunities for Armed Forces Includes details for military occupations, including duties, job outlook, pay, similar occupations, and work environment 34






