M K T G, 13 e Chapter 1: An Overview of Marketing 2021
44 Slides6.99 MB

M K T G, 13 e Chapter 1: An Overview of Marketing 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. notscanned, be scanned, copied duplicated,ororposted posted to a publicly website, in whole or inorpart. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May May not be copied or or duplicated, publiclyaccessible accessible website, in whole in part. 1

Learning Outcomes At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Define the term marketing. 2. Describe four marketing management philosophies. 3. Discuss the differences between sales and market orientations. 4. Describe several reasons for studying marketing. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2

Icebreaker The term marketing means different things to different people. What is the first definition that comes to mind when you hear the term marketing? 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 3

1-1 What is Marketing? 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 4

1-1 What Is Marketing? (1 of 3) Marketing – the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large Marketing has two facets: 1. It is a philosophy, an attitude, a perspective, or a management orientation that stresses customer satisfaction. 2. It is an organizational function and a set of processes used to implement this philosophy. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 5

1-1 What Is Marketing? (2 of 3) Marketing: Entails processes that focus on delivering value and benefits to customers Uses communication, distribution, and pricing strategies to provide customers and other stakeholders with the goods, services, ideas, values, and benefits they desire when and where they want them Involves building long-term, mutually rewarding relationships when these benefit all parties concerned Entails an understanding that organizations have many connected stakeholder “partners,” including employees, suppliers, stockholders, distributors, and others 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 6

1-1 What Is Marketing? (3 of 3) Exchange – people giving up something in order to receive something else they would rather have An exchange can take place only if the following five conditions exist: 1. There must be at least two parties. 2. Each party has something that might be of value to the other party. 3. Each party is capable of communication and delivery. 4. Each party is free to accept or reject the exchange offer. 5. Each party believes it is appropriate or desirable to deal with the other party. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 7

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 8

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (1 of 10) The following philosophies influence an organization’s marketing processes: 1. Production orientation 2. Sales orientation 3. Market orientation 4. Societal marketing orientation 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 9

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (2 of 10) Production Orientation Production orientation – a philosophy that focuses on the internal capabilities of the firm rather than on the desires and needs of the marketplace 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 10

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (3 of 10) What can we do best? What can our engineers design? What services are most convenient for the firm to offer? What is easy to produce, given our equipment? Where do our talents lie? 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 11

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (4 of 10) A production orientation can fall short if it does not consider whether the goods and services that the firm produces most efficiently also meet the needs of the marketplace. Sales Orientation Sales orientation – the belief that people will buy more goods and services if aggressive sales techniques are used and that high sales result in high profits The fundamental problem with a sales orientation is a lack of understanding of the needs and wants of the marketplace. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 12

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (5 of 10) 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 13

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (6 of 10) Market Orientation Marketing concept – the idea that the social and economic justification for an organization’s existence is the satisfaction of customer wants and needs while meeting organizational objectives The marketing concept includes the following: Focusing on customer wants and needs so that the organization can distinguish its product(s) from competitors’ offerings Integrating all the organization’s activities, including production, to satisfy customer wants Achieving long-term goals for the organization by satisfying customer wants and needs legally and responsibly 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 14

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (7 of 10) Market orientation – a philosophy that assumes that a sale does not depend on an aggressive sales force but rather on a customer’s decision to purchase a product; it is synonymous with the marketing concept Achieving a market orientation involves: Obtaining information about customers, competitors, and markets Examining the information from a total business perspective Determining how to deliver superior customer value Implementing actions to provide value to customers Understanding your competitive arena and competitors’ strengths and weaknesses is a critical component of a market orientation. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 15

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (8 of 10) Societal Marketing Orientation Societal marketing orientation – the idea that an organization exists not only to satisfy customer wants and needs and to meet organizational objectives but also to preserve or enhance individuals’ and society’s long-term best interests 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 16
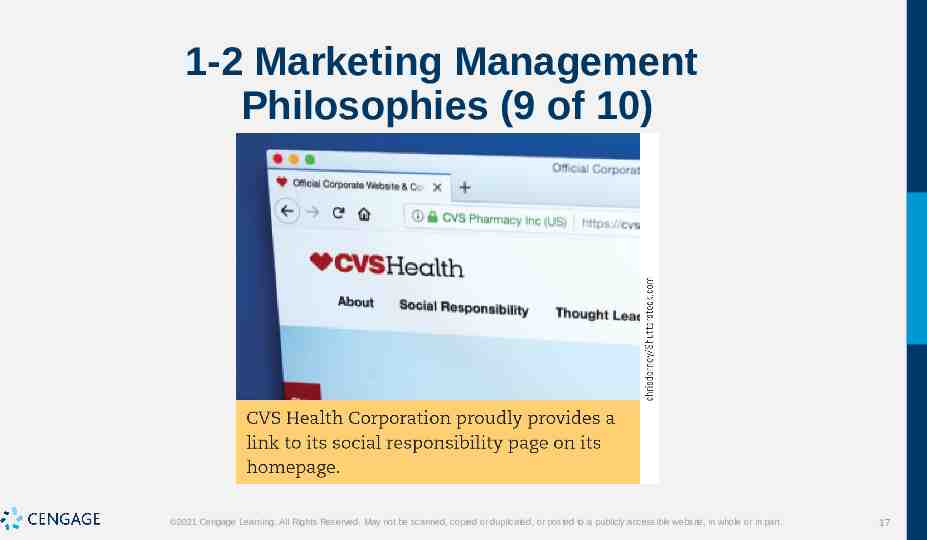
1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (9 of 10) 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 17

1-2 Marketing Management Philosophies (10 of 10) Who Is in Charge? The Internet and the widespread use of social media have accelerated the shift in power from manufacturers and retailers to consumers and business users. “The customer is boss.” — Former Procter & Gamble C E O A. G. Lafley 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 18

Group Activity 1 1. Form a team with four other students. 2. Choose three firms from Fortune’s list of “World’s Most Admired Companies.” 3. Go to the website of each firm and acquire as much information as possible on the company’s social responsibility efforts. 4. Prepare a five-minute oral presentation on your findings. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 19

Group Activity 1 Debrief What information did your group find regarding the social responsibility efforts of the company? What were the challenges your group faced during this activity? (For example, were their any companies that did not include any information about their social responsibility efforts on their websites?) 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 20

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 21

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (1 of 18) Sales and market orientations can be compared in terms of five characteristics: 1. The organization’s focus 2. The firm’s business 3. Those to whom the product is directed 4. The firm’s primary goal 5. The tools used to achieve the organization’s goals 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 22

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (2 of 18) The Organization’s Focus Many of the historic sources of competitive advantage—technology, innovation, and economies of scale—allowed sales-oriented companies to focus their efforts internally and prosper. Today, many successful firms derive their competitive advantage from an external, market-oriented focus. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 23
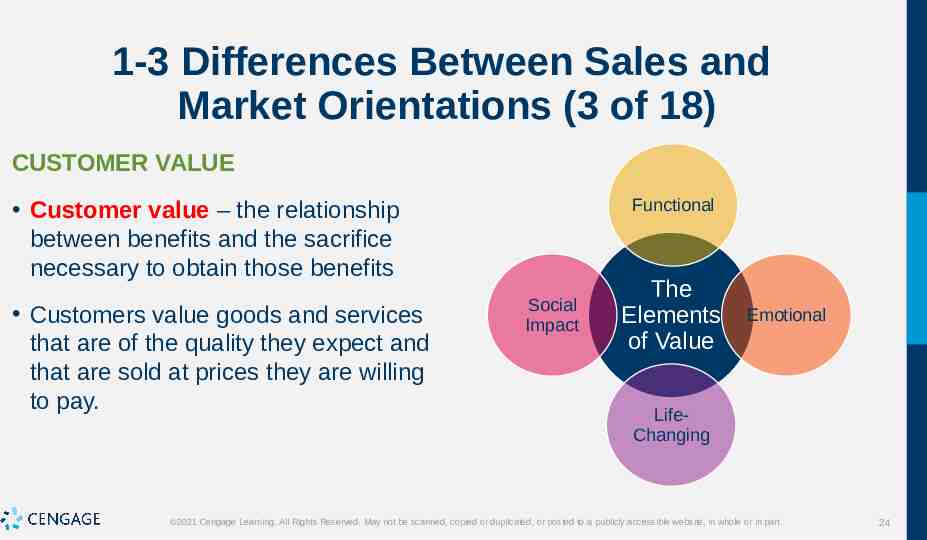
1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (3 of 18) CUSTOMER VALUE Functional Customer value – the relationship between benefits and the sacrifice necessary to obtain those benefits Customers value goods and services that are of the quality they expect and that are sold at prices they are willing to pay. Social Impact The Elements of Value Emotional LifeChanging 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 24

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (4 of 18) CUSTOMER SATISFACTION Customer satisfaction – customers’ evaluation of a good or service in terms of whether it has met their needs and expectations 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 25

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (5 of 18) BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Relationship marketing – a strategy that focuses on keeping and improving relationships with current customers Most successful relationship marketing strategies depend on: Customer-oriented personnel Effective training programs Employees with the authority to make decisions and solve problems Teamwork 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 26

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (6 of 18) Customer-Oriented Personnel For an organization to be focused on building relationships with customers, employees’ attitudes and actions must be customer oriented. Any person that is not customer oriented weakens the positive image of the entire organization. Customer-oriented personnel come from an organizational culture that supports its people. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 27

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (7 of 18) The Role of Training Leading marketers recognize the role of employee training in customer service and relationship building. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 28

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (8 of 18) Empowerment Empowerment – delegation of authority to solve customers’ problems quickly— usually by the first person the customer notifies regarding a problem Empowered employees: Manage themselves Are more likely to work hard Account for their own performance and that of the company Take prudent risks to build a stronger business and sustain the company’s success 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 29

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (9 of 18) Teamwork Teamwork – collaborative efforts of people to accomplish common objectives Teamwork improves: Job performance Company performance Product value Customer satisfaction 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 30

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (10 of 18) The Firm’s Business A sales-oriented firm defines its business (or mission) in terms of goods and services. A market-oriented firm defines its business in terms of the benefits its customers seek. People who spend their money, time, and energy expect to receive benefits, not just goods and services. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 31

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (11 of 18) Answering the question “What is this firm’s business?” in terms of the benefits customers seek, instead of goods and services, offers at least three important advantages: 1. It ensures that the firm keeps focusing on customers and avoids becoming preoccupied with goods, services, or the organization’s internal needs. 2. It encourages innovation and creativity by reminding people that there are many ways to satisfy customer wants. 3. It stimulates an awareness of changes in customer desires and preferences so that product offerings are more likely to remain relevant. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 32

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (12 of 18) 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 33

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (13 of 18) Those to Whom the Product Is Directed A sales-oriented organization targets its products at “everybody” or “the average customer.” The fallacy of developing products directed at the average user is that relatively few average users actually exist. A market-oriented organization aims at specific groups of people. A market-oriented organization recognizes that different customer groups want different features or benefits. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 34

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (14 of 18) CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Customer relationship management (C R M) – a company-wide business strategy designed to optimize profitability, revenue, and customer satisfaction by focusing on highly defined and precise customer groups C R M is accomplished by: Organizing the company around customer segments Establishing and tracking customer interactions with the company Fostering customer-satisfying behaviors Linking all processes of the company from its customers through its suppliers Companies that adopt C R M systems are almost always market-oriented. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 35

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (15 of 18) Big Data – the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data On-demand marketing – delivering relevant experiences, integrated across both physical and virtual environments, throughout the consumer’s decision and buying process As technology evolves and becomes more sophisticated, consumer expectations of their decision- and buying-related experiences have risen. For on-demand marketing to be successful, companies must deliver high-quality experiences across all touch points with the customer, including sales, service, product use, and marketing. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 36

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (16 of 18) The Firm’s Primary Goal A sales-oriented organization seeks to achieve profitability through sales volume and tries to convince potential customers to buy, even if the seller knows that the customer and product are mismatched. The ultimate goal of most market-oriented organizations is to make a profit by: Creating customer value Providing customer satisfaction Building long-term relationships with customers 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 37

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (17 of 18) 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 38

1-3 Differences Between Sales and Market Orientations (18 of 18) A Word of Caution Promotion is the means by which organizations communicate with present and prospective customers about the merits and characteristics of their organization and products. Effective promotion is an essential part of effective marketing. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 39

Knowledge Check Suppose that the Coca-Cola Company has decided to no longer use its iconic polar bear in its holiday season advertising and that the company has asked its employees to submit ideas for replacement mascots. Which of the following is this an example of? a. Relationship marketing b. Co-creation c. Empowerment d. Teamwork 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 40

1-4 Why Study Marketing? 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 41

1-4 Why Study Marketing? There are several important reasons to study marketing. Marketing plays an important role in society. Marketing is important to businesses. Marketing offers outstanding career opportunities. Marketing affects your life every day. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 42

Group Activity 2 1. Form a team with three other students. 2. Choose a career in the marketing industry. 3. Use the Internet to find as much information about this career as possible, such as typical duties, work environment, educational requirements, salary, job outlook, and so forth. 4. Prepare a five-minute oral presentation on your findings. 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 43

Group Activity 2 Debrief What information did your group find regarding their chosen career in marketing? Was there anything you learned about the career that surprised you? (For example, did you expect the salary to be higher or lower? Did you think the demand for future employment would be higher or lower?) Did any information supplied by the other groups affect your decision about pursuing a career in a certain area of marketing? 2021 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 44






