iRGD, a tumor-penetrating peptide for tumor-specific drug delivery
36 Slides8.76 MB

iRGD, a tumor-penetrating peptide for tumor-specific drug delivery Tatiana Hurtado de Mendoza Casaus Sanford Burnham Medical Research Institute

Current problems in cancer treatment Some drugs affect not only the cancer cells but also the healthy cells in the body- Toxic side effects – Need for specific delivery of the drugs to the tumor Poor penetration of drugs into the tumor- Affects efficacy of the therapy – Need to improve amount of drug that gets inside the tumor Metastasis – Need to prevent metastasis from happening

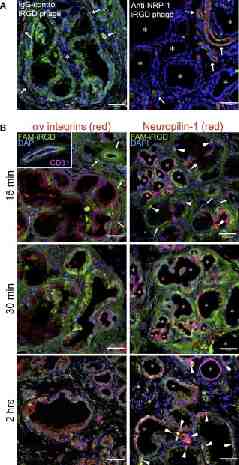
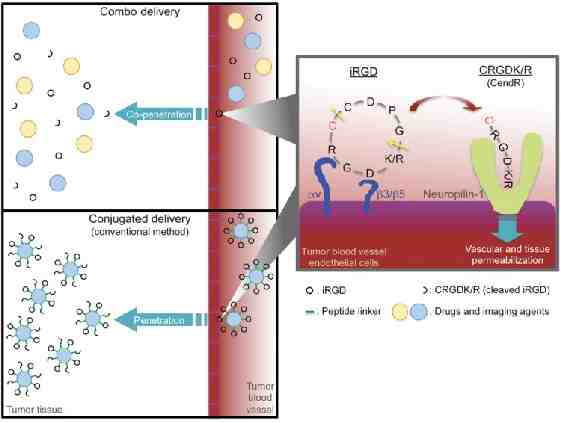
Tumor penetrating peptide iRGD iRGD (CRGDKGPDC) is a peptide discovered by phage display screening for peptides that recognized tumor blood vessels in a human prostate cancer model With its RGD motif is able to bind integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 present only in tumor vasculature It also contains a CendR motif (R/KXXR/K) that mediates cell penetration through the Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) receptor The CendR motif is exposed after cleavage of the peptide by a cell surface associated protease present in the tumor environment The interaction of its CendR motif with NRP1 induces vascular permeability- Bystander effect
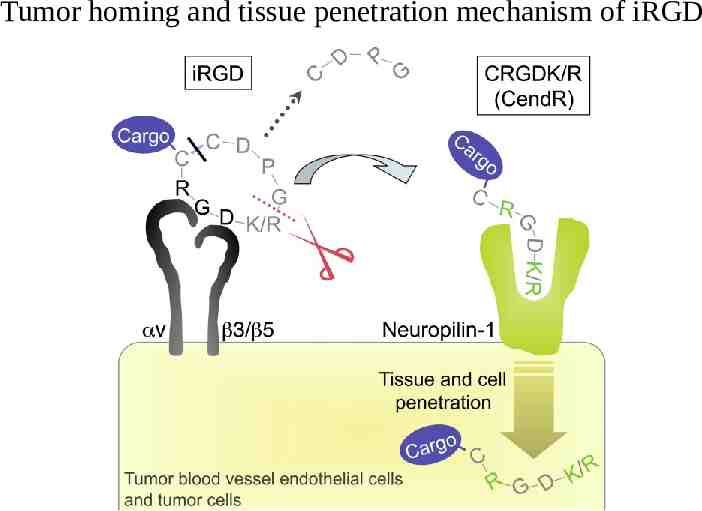
Tumor homing and tissue penetration mechanism of iRGD

Presentation Overview iRGD specifically homes to tumors and penetrates deep into tumor tissue iRGD can carry therapeutic drugs to tumors and increase their efficacy iRGD-Drug conjugates iRGD and co-injected drug – Bystander effect Systemic and intraperitoneal administration iRGD prevents metastasis

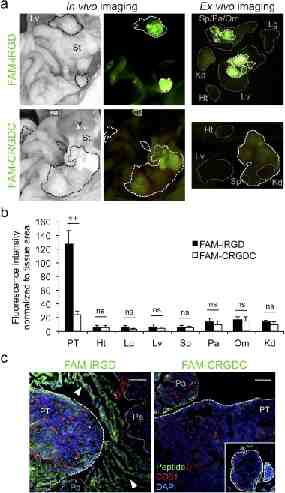
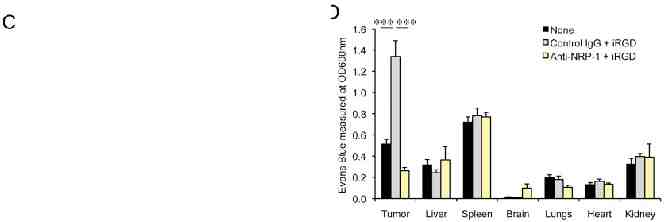
Tumor homing and treatment experiments Tumor models: – BT474- Breast Cancer – 22RV1-Prostate Cancer – KPC mice- Pancreatic Cancer Tumor Homing: – Intravenous (iv) injection of FAM labeled iRGD – Circulation time 1-2h – Examine the organs under UV ilumination – Imunofluorescence tissue sections Treatment studies: – IV injection of iRGD-drug conjugate or iRGD free drug – Drugs: Small molecules- Doxorubicine Nanoparticles- Abraxane Monoclonal antibodies- Trastuzumab – Evaluation of the amount of drug in tumor and other tissues – Evaluation of tumor weight or tumor volume
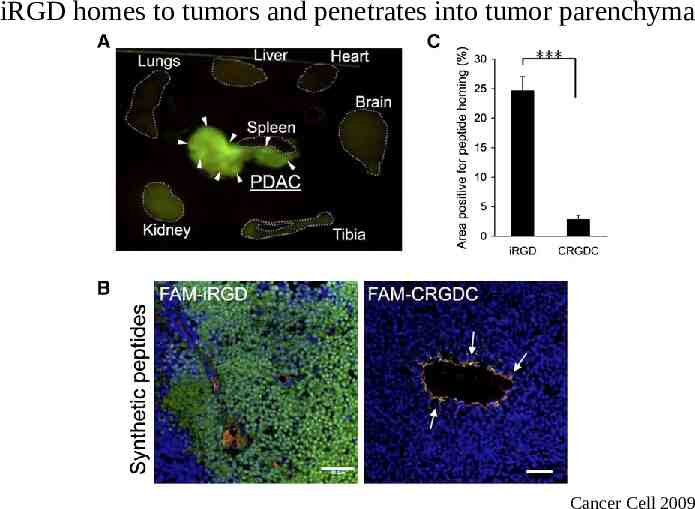
iRGD homes to tumors and penetrates into tumor parenchyma Cancer Cell 2009
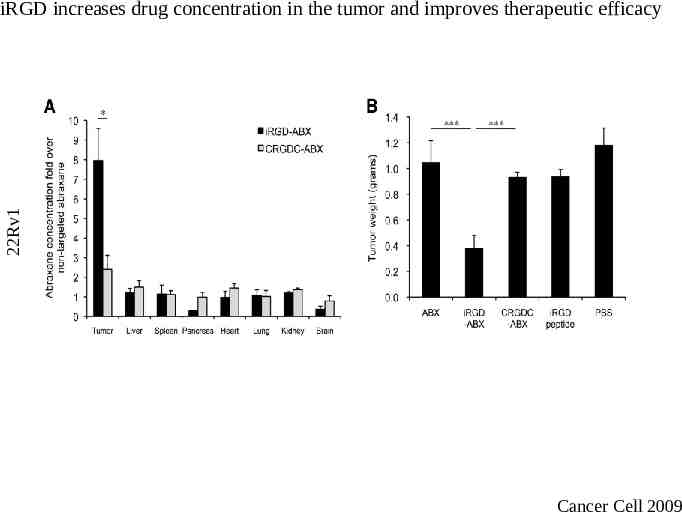
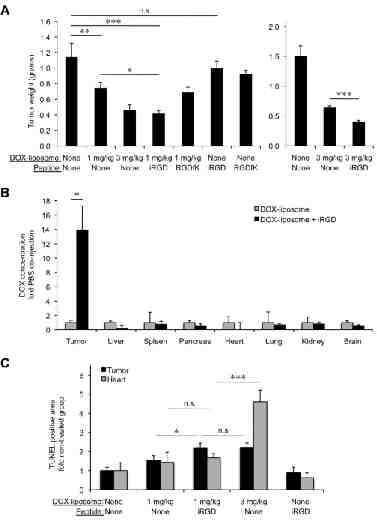
22Rv1 iRGD increases drug concentration in the tumor and improves therapeutic efficacy Cancer Cell 2009
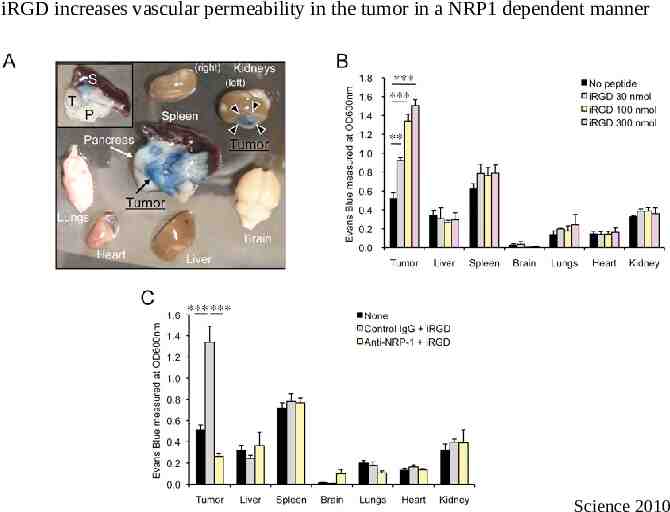
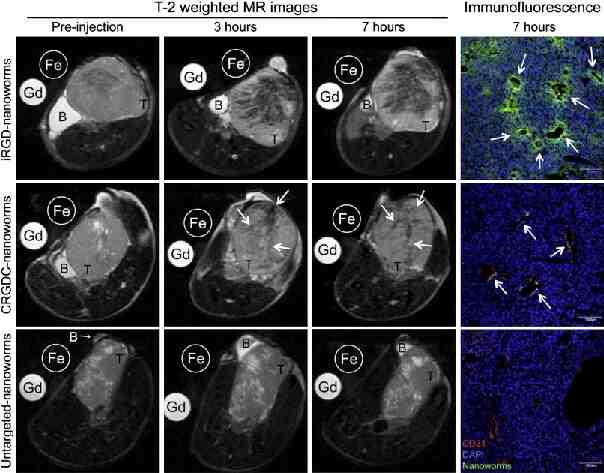
iRGD increases vascular permeability in the tumor in a NRP1 dependent manner Science 2010
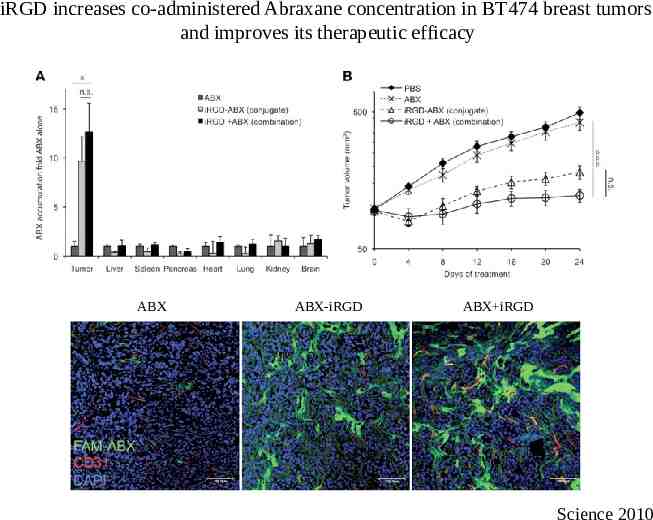
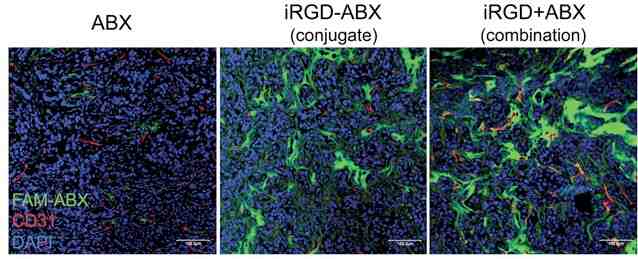
iRGD increases co-administered Abraxane concentration in BT474 breast tumors and improves its therapeutic efficacy ABX ABX-iRGD ABX iRGD Science 2010
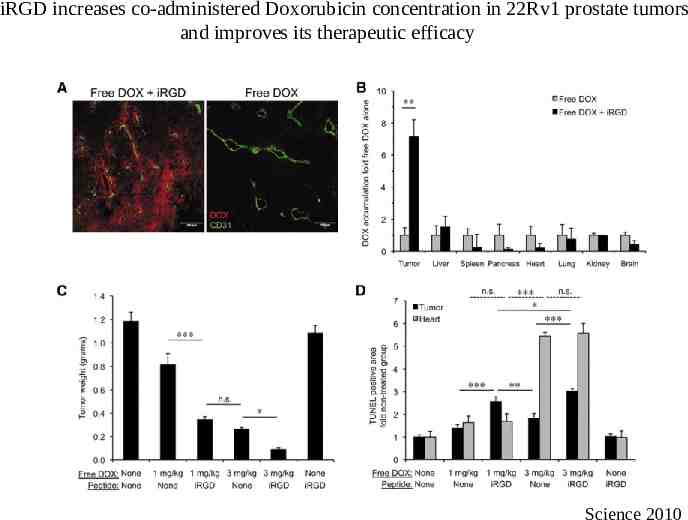
iRGD increases co-administered Doxorubicin concentration in 22Rv1 prostate tumors and improves its therapeutic efficacy Science 2010
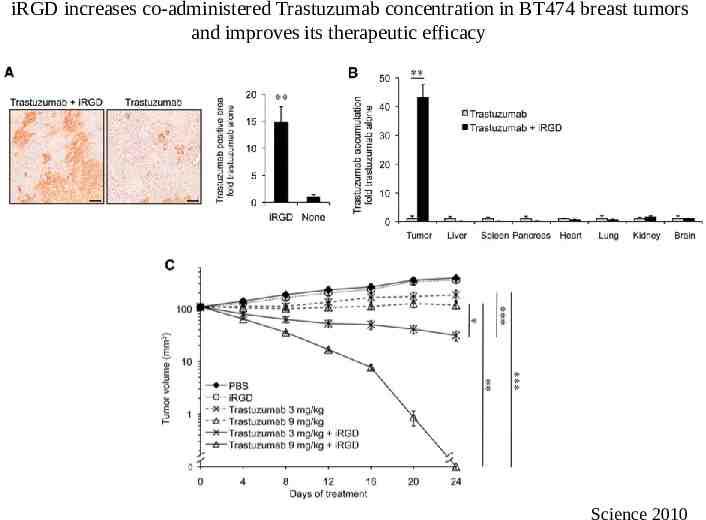
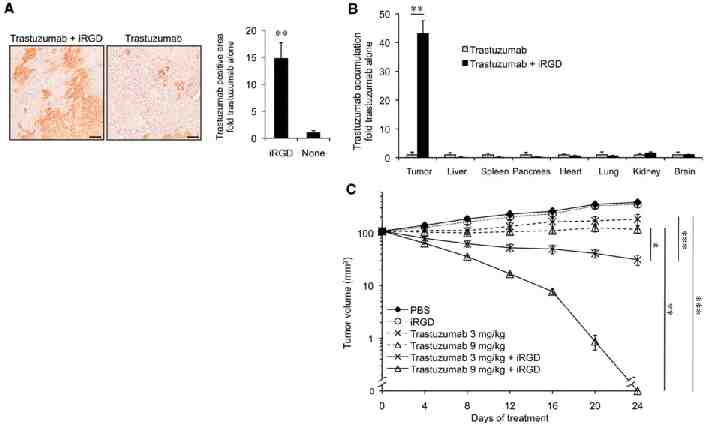
iRGD increases co-administered Trastuzumab concentration in BT474 breast tumors and improves its therapeutic efficacy Science 2010

Peritoneal administration of iRGD Systemically administered drugs partially enter the peritoneal fluid Drug concentration is too low to have significant therapeutic effects Tested iRGD tumor penetration and co-administration of Doxorubicin by intraperitoneal (ip) injection Models: – MKN45P- Gastric cancer – Lovo-6- Colon Cancer – Tumor cells express high levels of αv integrins and NRP1 Tested iRGD penetration into human metastasis explants
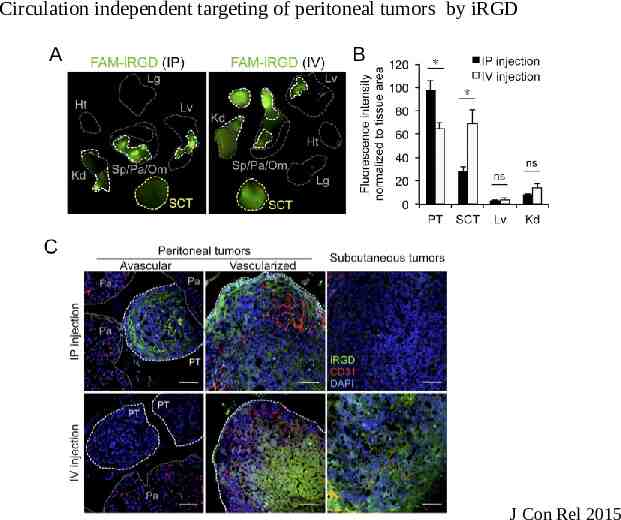
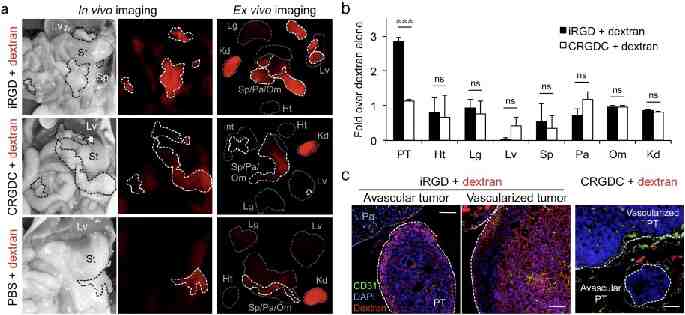
Circulation independent targeting of peritoneal tumors by iRGD A B J Con Rel 2015
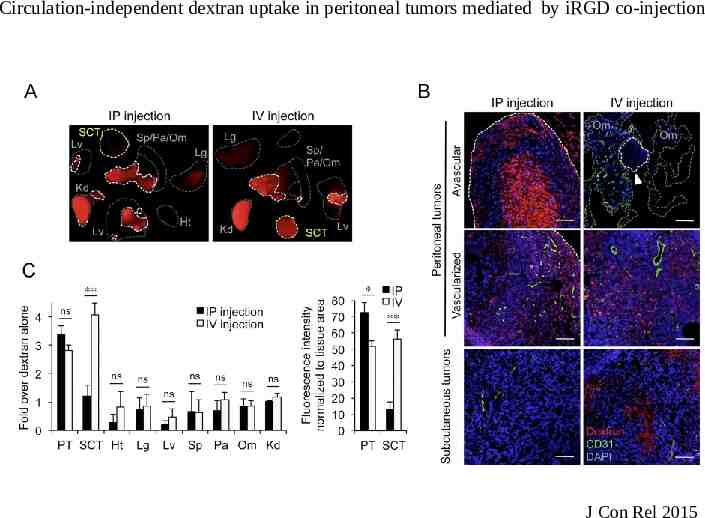
Circulation-independent dextran uptake in peritoneal tumors mediated by iRGD co-injection A B J Con Rel 2015
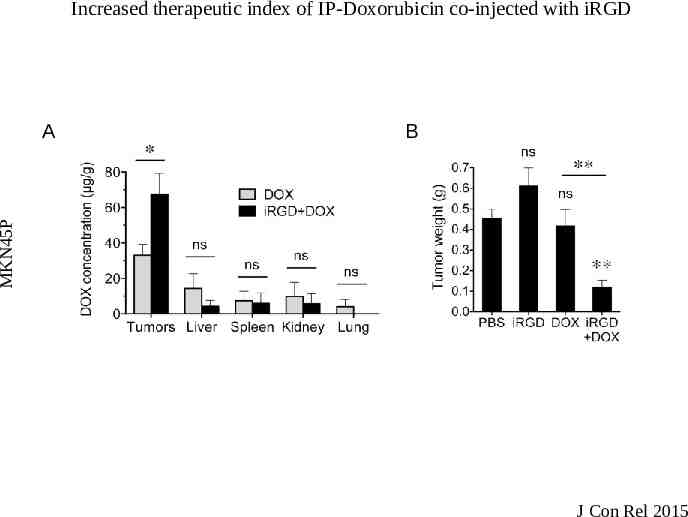
Increased therapeutic index of IP-Doxorubicin co-injected with iRGD B MKN45P A J Con Rel 2015
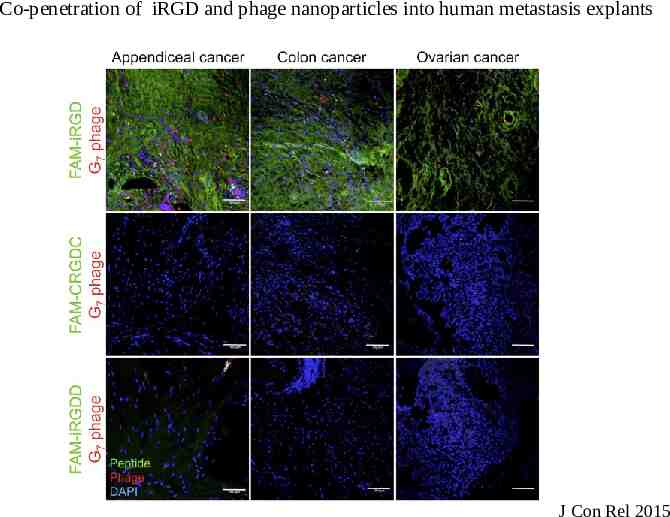
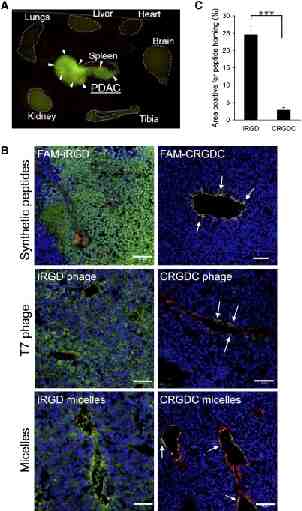
Co-penetration of iRGD and phage nanoparticles into human metastasis explants J Con Rel 2015

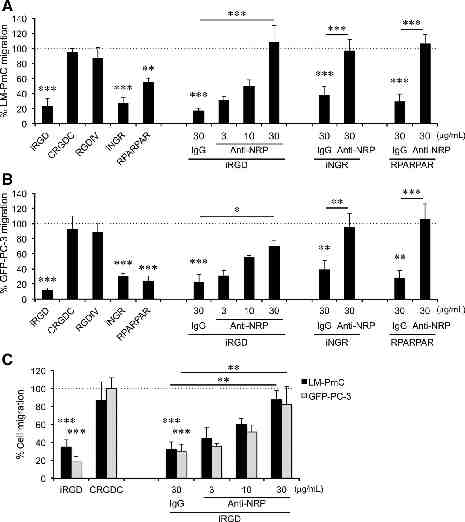
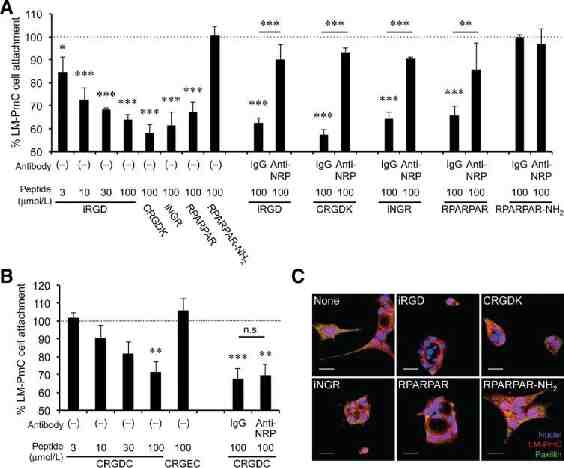
iRGD inhibits spontaneous metastasis iRGD treatment in two models of spontaneous metastasis – PC3- human prostate cancer (GFP labeled) – LMP- mouse pancreatic cancer (mCherry labeled) Mechanism of metastatic inhibition – RGD or CendR motif dependent – Cell attachment – Cell migration
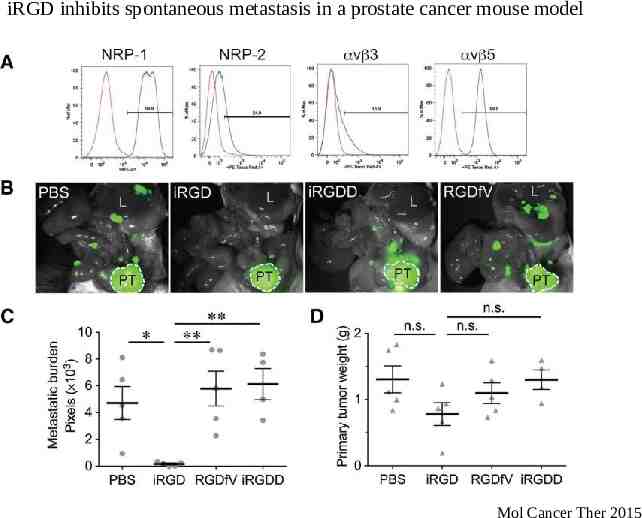
iRGD inhibits spontaneous metastasis in a prostate cancer mouse model Mol Cancer Ther 2015
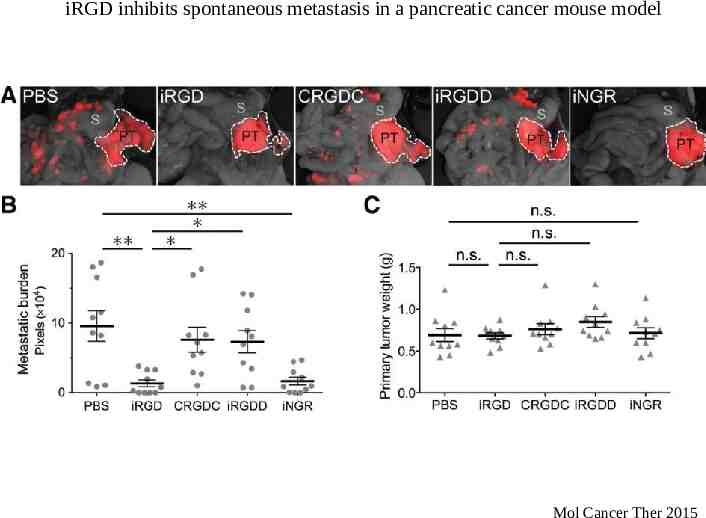
iRGD inhibits spontaneous metastasis in a pancreatic cancer mouse model Mol Cancer Ther 2015
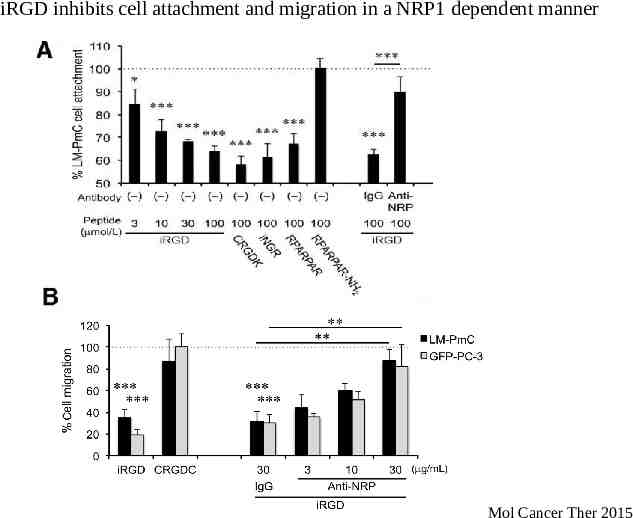
iRGD inhibits cell attachment and migration in a NRP1 dependent manner Mol Cancer Ther 2015

Summary and Future Perspective iRGD specifically targets tumors and penetrates deep into tumor parenchyma iRGD-drug conjugation or co-administration increases therapeutic efficacy iRGD can be used for tumor imaging (iRGD-iron oxide nanoworms for MRI) iRGD can be used for treatment of peritoneal tumors by ip administration iRGD prevents spontaneous metastasis Perform toxicology studies Clinical Trials

Acknowledgements Kazuki Sugahara Tambet Teesalu Erkki Ruoslahti Gary Braun Pablo Scodeller Andrew Lowy (UCSD Moores Cancer Center)
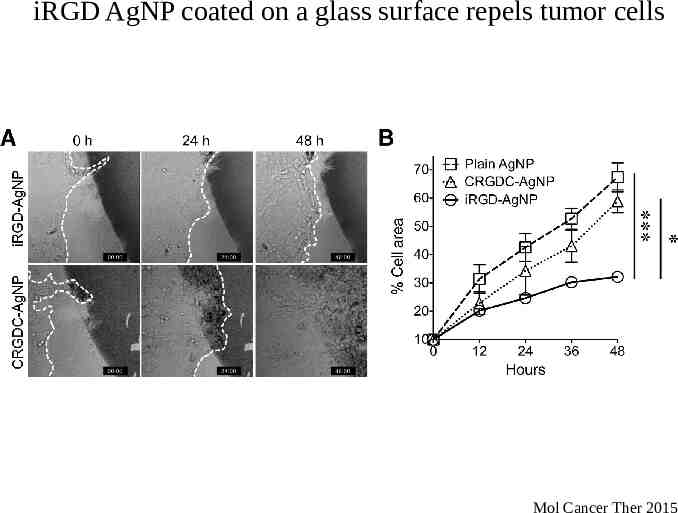
iRGD AgNP coated on a glass surface repels tumor cells Mol Cancer Ther 2015