How I Passed the CISSP Test: Lessons Learned in Certification
24 Slides6.33 MB

How I Passed the CISSP Test: Lessons Learned in Certification Presented by Kirk A. Burns, CISSP

Admin Data Emergency Exits Breaks Phones Other Admin Data

Introduction Instructor What is this class going to provide me? What should I expect to get out of this class?

Class Structure Broken up into 12 parts Part 1: introduction Parts 2 – 11: will be the domains Part 12: will be examples of types of questions you might see. THESE ARE NOT copies of the questions from the exam

What is (ISC)²? (ISC)² International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium Non-profit organization which specializes in information security education and certifications Often described as the “world’s largest IT security organization” Based in Palm Harbor, Florida, USA Offices in London, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Vienna, Virginia Over 85,000 certified professionals in 135 countries http://www.isc2.org

(ISC)² Code of Ethics Preamble: The safety and welfare of society and the common good, duty to our principals, and to each other, requires that we adhere, and be seen to adhere, to the highest ethical standards of behavior. Code of Ethics Canons: Protect society, the common good, necessary public trust and confidence, and the infrastructure Act honorably, honestly, justly, responsibly, and legally Provide diligent and competent service to principals Advance and protect the profession

BENEFITS OF (ISC)² MEMBERSHIP Member Benefits Continuing Education Security Leadership Series events Discounts Worldwide receptions, conferences, RSA, InfoSec, SecureAmerica Face-to-Face Networking Virtual Networking Career Tools, InterSeC

BENEFITS OF (ISC)² MEMBERSHIP Industry Awards Resources InfoSecurity Professional Magazine Information Security Perspective journal Member submitted security awareness materials Volunteer Opportunities http://staysafeonline.org

What is CISSP? Certified Information Systems Security Professional Governed by (ISC)² Worldwide recognition of competence Practical understanding of information security issues and solutions ANSI accreditation based on the ISO/IEC 17024:2003 standard (obtained in June 2004) Awareness of security challenges As of November 2013, reported to have 90,198 members worldwide in 149 countries

ROLE OF THE CISSP CISSPs often hold job functions such as: Security Consultant Security Manger IT Director/Manager Security Auditor Security Architect Security Analyst Security Systems Engineer Chief Information Security Officer Director of Security Network Architect

ROLE OF THE CISSP Develops and oversees the implementation of the organization’s information security policies and procedures Provide advice on implementation of information security solutions and technologies Monitoring compliance with regulatory bodies and employees, contractors, alliances and other 3rd parties

COMMON BODY OF KNOWLEDGE CBK The (ISC)² CBK is a compendium of topics relevant to information security professionals around the world. The (ISC)² CBK is the accepted standard in the industry, the subject of many books written on information security, and the core of the university information assurance programs around the globe. The CBK continues to be updated annually by (ISC)² CBK Committees comprised of members from many industries and regions around the world, to reflect the most current and relevant topics required to practice in the field. (ISC)² uses the CBK domains to assess a candidate’s level of mastery of information security.

How to Get Your CISSP Certification 1) Obtain the Required Experience a) must have a minimum of five (5) years cumulative paid full-time work experience in two (2) or more of the ten (10) domains. b) May receive a one year experience waiver with a four-year college degree, or regional equivalent OR additional credential from the (ISC) approved list (requiring four (4) years of direct full-time professional security work experience in two or more of the ten domains) 2) Study for the Exam 3) Schedule the Exam 4) Pass the Exam 5) Complete the Endorsement Process 6) Maintain the CISSP Certification

CISSP EXAM The CISSP exam 250 questions 6 hours To pass must get 700 points out of 1000 BE ON TIME!!!!!! Bring admission letter Must have government issued Photo ID Bring pencil and eraser 500

ENDORSEMENT PROCESS What is needed for the Endorsement Process Provide a recent resume Complete the Examination Registration Form Submit a completed and executed Endorsement Form

MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS To maintain the CISSP certification and remain in “good standing” with (ISC)², you are required to: Pay the Annual Maintenance Fee (AMF) of 85 USD at the end of each certification year Earn and submit 120 credits over three years. A minimum of 20 CPEs must be posted during each year of the three year certification cycle

THE DOMAINS Access Control Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning Cryptography Information Security Governance and Risk Management Legal, Regulations, Investigations, and Compliance Operations Security Physical (Environmental) Security Security Architecture and Design Software Development Security Telecommunications and Network Security

Golden Rule 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. People Safety First Management buy-is is Critical Everyone is responsible for Security Training is Essential Policy is the Key to (nearly) everything

What If I Don’t Have The Experience? For those who don’t have the experience, there is the Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Only need 1 year of experience Domains covered: Access Controls Cryptography Malicious Code and Activity Monitoring and Analysis Networks and Communications Risk, Response and Recovery Security Operations and Administration

Access Control

Domain Objectives Provide definitions and key concepts Identify access control categories and types Discuss access control threats Review system access control measures Understand Intrusion Detection and Intrusion Prevention systems Understand Access Control assurance methods

Access Control Is the basic foundation of information security Implemented differently depending on whether the are of implementation is physical, technical or administrative. Categories include: Preventive Detective Corrective Deterrent Recovery Directive Compensating Often used in combination

Access Control A comprehensive threat analysis will identify the areas that will provide the greatest cost-benefit impact. The field of access control is constantly evolving. Organizations need to know what is available and what methods will best address their issues. Data and system access control are NOT the same. User might have access to a system but not to the data. Think “need-to-know” Access control assurance addresses the due diligence aspect of security. Implementing a control is part of due care, but due diligence involves regularly checking to ensure that the control is working as expected.
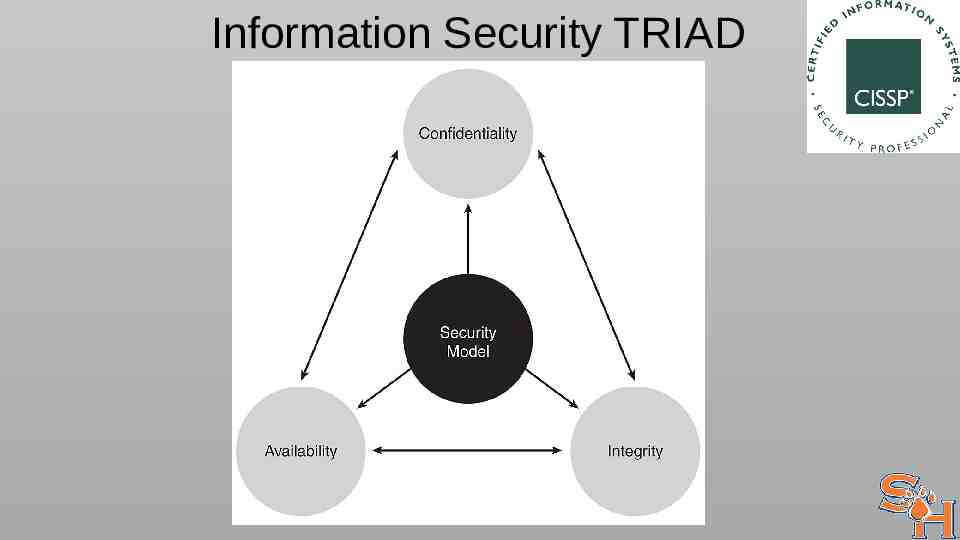
Information Security TRIAD






