HL7 2.X Conformance Tutorial January 2001 Ioana Singureanu,
73 Slides554.00 KB

HL7 2.X Conformance Tutorial January 2001 Ioana Singureanu, Eversolve Mary Ann Juurlink, Killdara 1

Speakers Ioana Singureanu, CEO Eversolve [email protected] Mary Ann Juurlink, Healthcare Product Architect, Killdara [email protected] 2

Also thanks to Kathy Blyler, [email protected] Bas van Poppel, [email protected] 3

Part 1 : Conformance Concepts Overview of HL7 2.x Conformance Conformance Concepts Use case derived message profiles Ioana Singureanu Sample Conformance documentation Mary Ann Juurlink 4

Part 2: Hands-on tutorial Hands-on message profiling exercise Real-life scenarios See the specification and tool in action ! 5

Part 1 : Conformance Concepts Overview of HL7 2.x Conformance Conformance Concepts Use case derived message profiles Ioana Singureanu 6

The problem. Interoperability standard for clinical application – uptake The standard combines the collective experience of many vendors Multiple business requirement sets combined but not enough specificity for any given implementation: optionality. Optional message elements had encouraged standard uptake but created difficulties in establishing standard conformance Z-segments, Z-triggers, optional fields and segments are all allowed by the standard. LACK OF UNIFORM SEMANTICS 7

The solution. V3 Add specificity to existing messages and identify the specific scenarios/use cases Identify, document, and bridge semantic differences Eliminate optionality (“implementable”) UML- Unified Methodology Language (just like V3) RIM V2.X Collective Experience MDF Common equivalent Message Message Type Type Requirements Message Type Requirements Message Profile 8

Conformance SIG HL7 Conformance has two objectives: – Interoperability Implementable message profiles – Certification Conformance Statement Informative Documentation – Specification for Message Profile Content Tutorial - education You are invited 9

Glossary Message Profile Conformant Message Profile Message profile id Conformance Statement Compatibility Consistency Registration Certification Validation 10

Message Profile Message specification indicating a precise, unambiguous use of message constructs (segments, fields, data types) for exchanging information based on a messaging standard. A message specification where “optional” are disallowed and repeatable constructs will be bound by maximum cardinality specifications. developed by vendors to describe their applications’ interoperability developed by healthcare providers to describe their interoperability needs. 11

Message Profiles specify Use Case Model (UML) and Vocabulary (field semantics, code sets, user-defined value sets) Static message profile – Message,segment, field, data type Dynamic interaction – Initiating message, response message 12

Conceptual Overview Message Profile Static Profile Dynamic Profile Initiating Message Response Message Critical Care Unit A/D/T System Initiating Message Clinical Data Repository 13

Static Message Profile HL7(1).HL7(1).v2 2(4).static-profile(1).ADT(3).A01(1).NULL(0).NULL(0).1(1) ADT A01 Message Profile HL7 Message Structure MSH MSH EVN EVN PID PID Segments/Segment Groups: - Cardinality (min, max) NK1 NK1 NK1 NK1 NK1 NK1 NK1 . PV1 NK1 NK1 . PV1 . . PV2 PV2 OBX OBX AL1 AL1 . NK1 . Fields/Components: - Field Usage (Optionality) (R, RE, C, CE, X) - Cardinality (max repeats) - Value Sets/Coding system 14 - Descriptions

Message Profile Specification HL7(1).HL7(1).v2 2(4).static-profile(1).ADT(3).A01(1).NULL(0).NULL(0).1(1) Specification of Min, Max Cardinality ADT A01 MSH EVN PID [ { NK1 PV1 PV2 [ { OBX [ { AL1 [ { DG1 [ { PR1 [ { GT1 [ { IN1 [ IN2 [ IN3 } ] [ ACC ] [ UB1 ] [ UB2 ] ADT Message } } } } } } ] ] 1.1 1.1 1.1 ] 1.3 1.1 1.1 ] 0.0 ] 1.* ] 0.0 ] 0.0 ] 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 Chapter Message Header Event Type Patient Identification Next of Kin Visit Info Visit - additional info Observation/Result Allergy Information Diagnosis Information Procedures Guarantor Information 2 3 3 3 3 3 7 3 6 6 6 Insurance Information Insurance Information - Addit. Info. Insurance Information - Cert. 6 6 6 Accident Information Universal Bill Information Universal Bill 92 Information 6 6 6 15
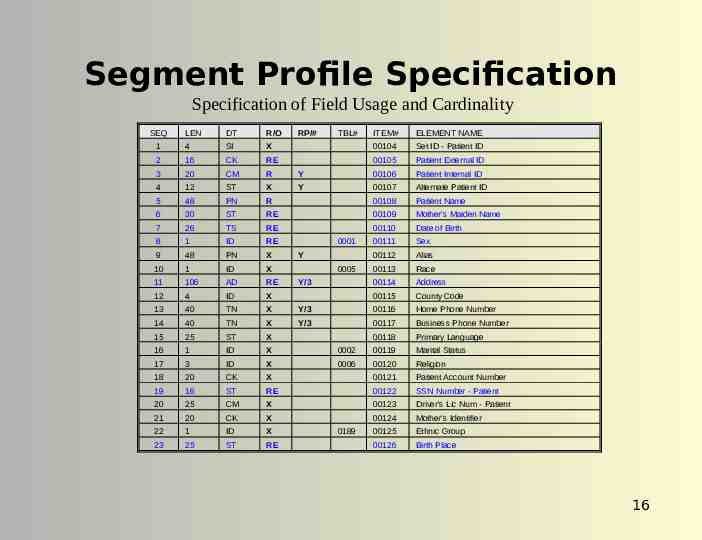
Segment Profile Specification Specification of Field Usage and Cardinality SEQ LEN DT R/O 1 4 SI 2 16 CK 3 20 CM R 4 12 ST X 5 48 PN 6 30 7 26 8 9 RP/# TBL# ITEM# ELEMENT NAME X 00104 Set ID - Patient ID RE 00105 Patient External ID Y 00106 Patient Internal ID Y 00107 Alternate Patient ID R 00108 Patient Name ST RE 00109 Mother's Maiden Name TS RE 00110 Date of Birth 1 ID RE 00111 Sex 48 PN X 00112 Alias 10 1 ID X 00113 Race 00114 Address 00115 County Code 0001 Y 0005 11 106 AD RE 12 4 ID X Y/3 13 40 TN X Y/3 00116 Home Phone Number 14 40 TN X Y/3 00117 Business Phone Number 15 25 ST X 00118 Primary Language 16 1 ID X 0002 00119 Marital Status 17 3 ID X 0006 00120 Religion 18 20 CK X 00121 Patient Account Number 19 16 ST RE 00122 SSN Number - Patient 20 25 CM X 00123 Driver's Lic Num - Patient 21 20 CK X 00124 Mother's Identifier 22 1 ID X 00125 Ethnic Group 23 25 ST RE 00126 Birth Place 0189 16

Field/Component Profile Specification 1.1.1 OBX-8 Abnormal flags (ID) 00576 Definition: This field is used to indicate the normalcy status of the result. This field will be specified with a repeat count of three (3). The first repetition will specify the abnormal flag. The second repetition will specify the delta flag. The third repetition will specify the microbial susceptibilities. Values from HL7 table #0078: - abnormal flags alpha {N,A,AA,CNM} numeric {L,H,LL,HH,CNM, , } - delta flags alpha {B,W} numeric {U,D} Field Descriptions – In cases where HL7 2.x fields descriptions are unclear or ambiguous, supply a more precise semantic definition. - microbial susceptibility flags {S,R,I,MS,VS} Only the most extreme flag for each repetition of the field should be specified. Note that the value “CNM” (Could Not Measure) has been added to HL7 table #0078. 17

Field/Component Profile Specification PID-26 Citizenship (ID) 00129 Definition: indicates the patient's country of citizenship. Refer to user-defined table 0171 country code for suggested values or to ISO 3166. This vendor profile specification uses ISO 3166 Alpha-3 codes. Vendor defined tables: – HL7 2.2 definition of PID-26 refers to Table #0171 which is undefined – HL7 suggests using ISO-3166 – ISO 3166 has 3 different coding schemes - Alpha-2, Alpha-3, Numeric – A vendor/provider may choose ISO-3166 - Alpha-3 18

Message Profile Hierarchy Registration Authority HL7(1) HL7(1) Organization Version v2 2(4) Profile Type ADT(3) A01(1) static-profile(1) Message Type Trigger Event A02 (2) ORM(21) ORU(23) O01(92) R01(112) Structure NULL (0) NULL (0) DIAG(1) DIET(2) . NULL (0) Use Model NULL (0) NULL (0) NEW(1) CANCEL(4). NEW(1) CANCEL(4) . LAB(1) DEVICE(2) Data Version 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 1(1) 19

Dynamic Interaction Receiver Responsibility MSH-15,16 ED1 OFF B BED1 OFF BE D 1OF F BED1 OFF BED1 O FF BE D 1OF F BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BE D 1OF F BED1 OFF POTASSIUM3.5-5.0 POTASSIUM3.5-5.0 BE D 1OF F POTASSIUM3.5-5.0 POTASSIUM3.5-5.0 BED1 OFF POTASSIUM3.5-5.0 BED1 OFF ED1 OFF B BED1 OFF ED1 OFF B Accept App ACK Vectr a XU 5/90C Critical Care Unit HIS/CIS No ACK A/D/T System BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF Accept Ack BED1 OF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF BED1 OFF POTASSIUM3.5 -5 .0 POTASSIUM3.5-5 .0 BED1 OFF POTASSIUM3.5- 5 .0 POTASSIUM3 .5 -5 .0 BED1 OFF POTASSIUM3.5- 5 .0 BED1 OFF ED1 OFF B BED1 O FF BED1 OFF Vectra XU 5/ 90C Order Filling Application Clinical Data Repository 20

Message Profile Summary Well-defined process for developing Message Profiles. A Message Profile is a pre-negotiated agreement: – Static (data contents) – Dynamic (application interaction) Registered by a unique identifier. 21

Message Profiles are used for Describing the content of inbound and outbound interfaces – Conformance statement Certifying conformance Validating messages Simplifying interoperability – Not plug-and-play but close 22

HIS Sample System Application Use Case Radiology System Application Use Case Patient Management Oncology System Sender Receivers Message Profile Admission {1 1 3 . 3 1} Transfer {1 1 3 . 5 1} Discharge {1 1 3 . 7 1} 23

Message Profiles are HL7 Conformant A message profile which meets the HL7 standard requirements: all the required segments and fields are specified and all fields are using the appropriated HL7 data types as specified in the Chapter 2 of the HL7 standard Only conformant profiles will be registered 24

HL7 Message Profile Identification A unique identifier is assigned to a message profile submitted by a vendor or a healthcare provider Assigned when the profile is registered with HL7 (Registration tool) ASN.1 Generated by the message profile registration tool (HL7 provided to members) Unique – OID – ASN.1(American Symbolic Notation) Object Identifier Conformance SIG 25

OID OID root for Registered Conformance Profiles is: 2.16.840.1.113883.9. 2 ISO 16 840 113883 HL7 9 Profile Samples: 2.16.840.1.113883.9.1 2.16.840.1.113883.9.2 2.16.840.1.113883.9.3 2.16.840.1.113883.9.4 26

Purpose of OID Unique identifier Registration – For cataloging message profiles registered by HL7 Used to specify the conformance statement of an application – References to OIDs 27

Conformance Statement A document describing the HL7 interoperability characteristics as a use case model (UML) of an application and the message profiles implemented by that application. Describes overall interoperability requirements along with the message profiles. Basis for compliance certification 28

Message Profile Registry Oncology System Conformance Statement Reference to Use Case Model {1 1 3 . 3 0} {1 1 3 . 3 1} {1 1 3 . 4 1} {1 1 3 . 5 1} Radiology System Conformance Statement Use Case Model {1 1 3 . 6 1} {1 1 3 . 7 1} {1 1 3 . 7 2} {1 1 3 . 8 1} ASN.1 identifiers29 Application Conformance Statement

Compatibility Relationship between an outbound and an inbound message profile such that, despite differences, they can interoperate Outbound message profile will be richer in content than an inbound profile. 30

ADT Message Profile Compatibility Example Hospital Registration System (producer) Radiology system (receiver) Oncology system (receiver) Nursing System (receiver) 31

Consistency Characteristic of all message profile specifications registered with HL7. – XML documents following a pre-defined DTD Consistent documentation of message profiles will ensure that vendors and providers will be able to easily integrate applications. Encourages reuse, comparison, differences – Simplifies interoperability 32

Application Role The set of messages (message types) an application can send or received as part of its operation. Applications with similar interoperability needs are expected to use the same application profile. – Part of HL7 Version 3 33

Registration A conformant message profile document will be registered with HL7 and be granted a unique message profile identifier. 34

Certification The process by which an application’s conformance claim in verified against the actual application implementation. Certification is a very important part of conformance Conducted by providers, national or regional health organizations – Not conducted by HL7 35

Verification The process by which a message instance (one message) is verified against the message profile on which it is based. 36

XML Considerations /XML XML Message – It represents an XML document and it contains data and meta-data (tags) as described by its schema/DTD. XML DTD/Schema – Contains the rules (structure, content, data types, cardinality) for constructing and validating an XML document. Message document Version 2.XML specification from XML Sig (informative - normative) 37

Conformance Benefits Consistent documentation Reuse of specification – Convergence on use cases Lower cost of integration – Tool for comparing specifications Similar to Version 3 – Conformance SIG is developing Implementation guide Chaos - order 38

Conformance Support in the HL7 Standard Version 2.4, 2.5 – MSH:21 – Profile identifier – OID data type for ASN.1 identifiers – Conformance Chapter – Implementation Guide Version 3 – At the core of the Message Development Process – Chapter 8 of MDF – Implementation Guide 39

Overview of HL7 2.x Conformance Conformance Concepts Use case derived message profiles Sample Conformance documentation 40

Use Case Analysis UML – Language for describing requirements Use Case Analysis Use Case Models Conceptual Interoperability Model – Expressed in the user’s terms Information Model 41

Use Case derived Message Profiles Specification for Message Profile Content – See the HL7 web site Use cases, static profile, dynamic specification, profile identifiers Allows clinical site and application vendors to specify their standard conformance XML DTD/schemas for describing profiles – Profiling tool 42

Vendor Message Profiles Conformance Statements Contract between vendor and customers – It will enable clinical sites to make better purchasing decisions and clearly evaluate the capabilities of various software products. Unambiguous, registered, backed by design and analysis 43

Site Message Profiles Supports specific needs Required of third-party application vendors RFP Simplifies introduction/acquisition of new applications 44

HL7 Registry of Profiles Search/browse Unique profile identifiers Consistent Profile Documentation DTD/Schema representation of the profile Indicates who is using a profile Version 3 application roles 45

Version 3 Deliverables (for a given domain) Version 3 Conformance (for a given application) Actors Profiled App Domain Use Case Analogous to V2.x Profiling Leaf-level Use Cases Use Case Model Role1Role1 Role1 Role1 Sends Receives Receives -------- Sends --------Sends Receives --------Sends -------- ------------------------------ Receives ----------------------- ------------------------------ --------------- ----------------------- -------- --------------- -------- Application Profile HMD Sends ---------------------- Receives ---------------------- Static Message Structures Interaction Model 46

Overview of HL7 2.x Conformance Conformance Concepts Use case derived message profiles Ioana Singureanu Sample Conformance documentation Mary Ann Juurlink 47

The Goal To enable healthcare organizations to better communicate with their partners by sharing data electronically To facilitate Healthcare integration efficiently and cost effectively To use and promote open systems and standards 48

Existing Infrastructure Hospital Registration System Clinical information system support messaging (VPN) no support for secure communication (Internet) Remote Lab system Remote Physician’s Office cannot send/receive messages easily 49

How do we achieve the goal? By developing profiles for applications By encouraging vendors to create their own profiles and register them with HL7 By creating a transition path (V2.x V3.0) based on conformance profile development 50

Message Profiling Specification Use case model Vocabulary – Coding – Value sets – Field semantics Static Definition of an HL7 v2.x message – Message Level Profile – Segment Level Profile – Field Level Profile Dynamic Definition of HL7 v2.x message – Interaction Model 51

Register a Patient ADT A04 Scenario 40 year old female Diabetes Community hospital Arrives by ambulance Message Description A registration event (ADT A04) signals that a patient has arrived or checked in but is not assigned a bed. 52

Use Case Actors Hospital registration System Is responsible for notifying all appropriate systems Remote Lab System Receives the messages and sends results Remote Physicians Office Receives the message 53

Use Case Model routes message FiveSight sends message Care Data Systems Patient Registration ADT A04 receives message Intrinsiq receives message Killdara 54

Use Case Description Preconditions The patient is ready for clinical attention and demographic information is supplied Flow of events The patient is registered and the appropriate system is notified Post Conditions The appropriate system has been notified 55

Dynamic Interaction 1. Sequence Diagram : Care Data Systems : FiveSight : Killdara : Intrinsiq RegisterPatientADT A04( ) RegisterPatientADT A04( ) RegisterPatientADT A04( ) 2. Receiver responsibility AcceptNever, Application Never 56

Static Definition 1. 2. ADT A04 MSH EVN PID [{ NK1 }] PV1 PV2 [{ AL1 }] Segment Level Profile PID (1) – Patient Demographics SEQ 1 2 3 4 5 DT SI CK CM ST PN R/O RP/# ITEM# TBL# RE 00104 RE 00105 R Y 00106 RE Y 00107 R 00108 6 7 8 9 10 11 ST TS ID PN ID AD RE RE RE 00001 RE Y RE RE Y/3 Message Level Profile ELEMENT NAME SetID – Patient ID Patient External ID Patient Internal ID Alternate Patient ID3. Patient Name 00109 00110 00111 Sex 00112 00005 00113 00114 Mother’s Maiden . Date Of Birth Alias Race Address Cardinality Message Description [1,1] Message Hea [1,1] Event Type [1,1] Patient Demo [0, ] Next of Kin [1,1] Admit Visit Inf [1,1] More Admit V [0, ] Allergy Info Field Level Profile Patient Internal ID (00106) Components: patient ID (NM) check digit (NM) check digit scheme (ID) assigning facility ID (ST) type (ID) Patient Name (00108) Components: family name given name middle initial or name suffix (e.g., JR or III) prefix (e.g., DR) degree (e.g., MD) Name is standard format described in Chapter 2, HL7 Standard. 57

ADT A04 XML Conformance Profile produced using the Message Work Bench report XML Spec Field Name "Patient ID (Internal ID) " Description "" Optionality "R" Repeatable "Y" Sequence "3" Primitive "T" Datatype "CM" Length "20" QuantLo "1" QuantHi "0" DataValues ExValue "" ConstantValue "" DBName "" DataSet "" FieldName "" ValueSourceType "ODBC"/ /Field Field Name "Alternate Patient ID " Description "" Optionality "NS" Repeatable "N" Sequence "4" Primitive "T" Datatype "ST" Length "12" QuantLo "0" QuantHi "0" DataValues ExValue "" ConstantValue "" DBName "" DataSet "" FieldName "" ValueSourceType "ODBC"/ /Field Field Name "Patient Name" Description "" Optionality "R" Repeatable "N" Sequence "5" Primitive "F" Datatype "PN" Length "48" QuantLo "1" QuantHi "0" Component Name "family name" Description "" Optionality "O" Repeatable "N" Sequence "1" Primitive "T" Datatype "ST" Length "0" QuantLo "0" QuantHi "0" DataValues ExValue "" ConstantValue "" DBName "" DataSet "" FieldName "" ValueSourceType "ODBC"/ /Component Component Name "given name" Description "" Optionality "O" Repeatable "N" Sequence "2" Primitive "T" Datatype "ST" Length "0" QuantLo "0" QuantHi "0" DataValues ExValue "" ConstantValue "" DBName "" DataSet "" FieldName "" ValueSourceType "ODBC"/ /Component 58

HL7 Conformance Profile DTD V2.X This is the result of associating the dtd with the ADT A04 Conformance Profile All profiles registering with HL7 must be validated against this dtd One dtd per version !-- PID - Patient Identification section -- !ELEMENT PID (PID.3 , PID.5, PID.27* ) !ELEMENT PID.3 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5 (PID.5.1?, PID.5.2?, PID.5.3?, PID.5.4?, PID.5.5?, PID.5.6? ) !ELEMENT PID.5.1 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5.2 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5.3 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5.4 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5.5 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.5.6 (#PCDATA) !ELEMENT PID.27 (#PCDATA) 59

The Most Common ADT HL7 Message Profiles Hospital Registration System ADTA01 AdmitPatient ADTA02 TransferPatient ADTA03 DischargePatient ADTA04 RegisterPatient ADTA05 PreadmitPatient ADTA08 UpdatePatientInfo ADTA11 CancelAdmit Clinical Information System Patient Management Register Patient Pre-admit Patient Update Patient Information Transfer Patient Admit Patient Cancel Admit Discharge Patient 60

The Most Common Order/Result HL7 Message Profiles Ordering System Filler System triggersOrder ORMO01 NewDiagnosticStudyOrder ORRO02 DiagnosticStudyOrderAccepted ORRO02 UnableToAcceptDiagnosticStudyOrder ORRO02 DiagnosticStudyOrderCancelled ORMO01 CancelDiagnosticStudyOrder ORRO02 DiagnosticStudyOrderCancelledAsRequeste ORRO02 UnableToCancelDiagnosticStudyOrder receivesOrder Diagnostic Study Order Cancel Diagnostic Study Order New Diagnostic Study Order Diagnostic Study Order Cancelled Diagnostic Study Order Accepted Diagnostic Study Order Cancelled (by Filler) Unable to Accept Diagnostic Study Order as Requested Unable to Cancel Diagnostic Study Order 61

HL7 V3 Message Development Lifecycle Requirements Requirements Analysis Analysis Application Application Design Design Analysis Analysis Domain Domain Analysis Analysis Interaction Interaction Design Design Message Message Design Design 2-nd 2-nd Order Order 11 choice choice of of 0-n Drug 0-n Drug 0-1 0-1 Nursing Nursing C Code a art b blue c color Use UseCase Case Model Model (UCM) (UCM) c Code Information Information Model Model&& Vocabulary Vocabulary (RIM) (RIM) Interaction Interaction Model Model (IM) (IM) Hierarchical Hierarchical Message Message Descriptions Descriptions (HMD) (HMD) Messaging Messaging Documents Documents Medical Medicallogic logic TYPE MPSLOC TYPE MPSLOC CONTAINS { CONTAINS { IID id[id].TYPE !ENTITYIID %DT MPSLOC id[id].TYPE nm[name].TYPE ST%DT MPSLOC !ENTITY “MPSLOC.id, nm[name].TYPE ST data: ad[addr].TYPE XAD “MPSLOC.id, data: MPSLOC.name?, ad[addr].TYPE XAD location of action ph[phon].TYPE XTN MPSLOC.name?, location of action MPSLOC.addr?, ph[phon].TYPE XTN : READ LAST email address MPSLOC.addr?, : MPSLOC READ LAST MPSLOC.phon?, email address [emlAdr].TYPE XTN MPSLOC; ; MPSLOC.phon?, MPSLOC.emlAdr?" [emlAdr].TYPE XTN ‘ {patient } MPSLOC.emlAdr?" ‘ {patient } location} location} Message MessageTypes Types for use with Document for use with Document XML, ER7, etc for Variable XML, Types ER7, etc Types for Variable (MET) HL7 PRA definition (MET) HL7 PRA for definition for (DTD) Arden syntax (DTD) Arden syntax (AVD) (AVD) Reference Model Repository 62

Deliverables Some form of the “Technical Committee Documentation Template” Domain interaction model Leaf level interaction model Common message types (HMD) So now what do we do with all of this? How to we apply our specific user requirement? 63

Starting point for Conformance Profiling Encounter manager : AR Encounter manager Encounter tracker : AR Encounter tracker Encounter archivist : AR Encounter archivist interaction #1, message structure A Trigger Event: Schedule Encounter interaction #2, message structure B Trigger Event: Delete Scheduled Encounter interaction #3, message structure C interaction #4, Message Structure C Trigger Event: Admit Patient interaction #5, message structure D Hierarchichal Message Description for Trigger Event "Admit Patient", Sending Application Role "Encounter Manager" Information Model Mapping 1 root Patient encounter Message Structures Message Elements 1 1 ENC C 1 D M 1 status cd 1 CE status cd 1 26 M 1 M 1 encounter classification cd 1 CE encounter classification cd 2 12 M 1 M 1 id 1 id 3 M 1 M 1 end dttm 1 VTS end dttm 4 R 1 R 1 expected insurance plan qty 1 NM expected insurance plan qt y 5 R 1 R 1 first similar illness dt patient classification cd 1 VTS 1 CE first similar illness dt patient classification cd 6 7 R R 1 1 R R 1 1 start dttm 1 VTS start dttm 8 M 1 M 1 ST ENC 3 13 4 M 1 3 64

Hierarchical Message Definition Information Model Mapping Classes and attributes of the R-MIM, describes a “walk” through. Message Element Describes elements and types, set up as a hierarchy General constraints Describes specific constraints for the message element defined in the row 65

0.1 1.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.* 1 0.1 ORD M ED unassigned R R R Cardinality Conformance Update mode set Default Update Mode Default Default R Default Value (#) Default Default "NI" Constraint/Note # Mandatory Coding Strength (default CWE) Domain Specification (#) Cardinality Constraints based on application requirements M R 66

Message Profiling Specification for Version 3 Use case model Vocabulary – Coding – Value sets – Field semantics Static Definition of an HL7 V3 message – Message Level Profile – Segment Level Profile – Field Level Profile Dynamic Definition of HL7 3 message – Interaction Model – application role 67

Version 3 vs. Version 2.X V3 V2.X Analysis, Design i.e Collective Experience RIM Interaction model HMD Message Common Specific disambiguate Profile Profile 68

Benefits of Message Profiling Conformance statement Describes a standard implementation by coupling events, data elements and messages Improves clarity and precision Profiles may be registered with HL7 Approaches plug and play Conformance testing Messages can be validated against the message profile 69

ROI Benefits of Hl7 Conformance Reduces the overhead of integrating applications EFFICIENCY Able to meet the needs of the clinicians for access to information, when and where they need it QUALITY OF COMMUNICATION Clinical sites can evolve yet maintain their infrastructure SAVINGS 70

Conformance Tool Available! The Messaging Workbench tool is available free of charge It is open source It is supported within the VA for the foreseeable future 71

Contacts We in the Conformance sig are interested in your feedback and suggestions for improvement of the tool The Conformance sig list server is a good source for general information For conformance tool information: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected] [email protected] 72

Q&A 73






