Hardware and Software Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Information Syst
57 Slides1.38 MB

Hardware and Software Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 1

Principles and Learning Objectives Information system users must work closely with information system professionals to define business needs, evaluate options, and select the hardware and software that provide a cost-effective solution to those needs. – Identify and discuss the role of the essential hardware components of a computer system. – List and describe popular classes of computer systems and discuss the role of each. – Outline the role of the operating system and discuss how operating systems have evolved over time. – Identify and briefly describe the functions of the two basic kinds of software. Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 2

Principles and Learning Objectives Organizations do not develop proprietary application software unless doing so will meet a compelling business need that can provide a competitive advantage. – Discuss how application software can support personal, workgroup, and enterprise business objectives. – Identify three basic approaches to developing application software. Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 3

Principles and Learning Objectives End users and IS professionals use a programming language whose functional characteristics are appropriate to the task at hand. – Outline the overall evolution of programming languages and highlight the differences between programming languages used by end users and IS professionals. Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 4

Principles and Learning Objectives The information system industry continues to undergo constant change; users need to be aware of recent trends and issues in software licensing to be effective in their business and personal life. – Identify several key issues and trends in licensing that have an impact on organizations and individuals. Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 5
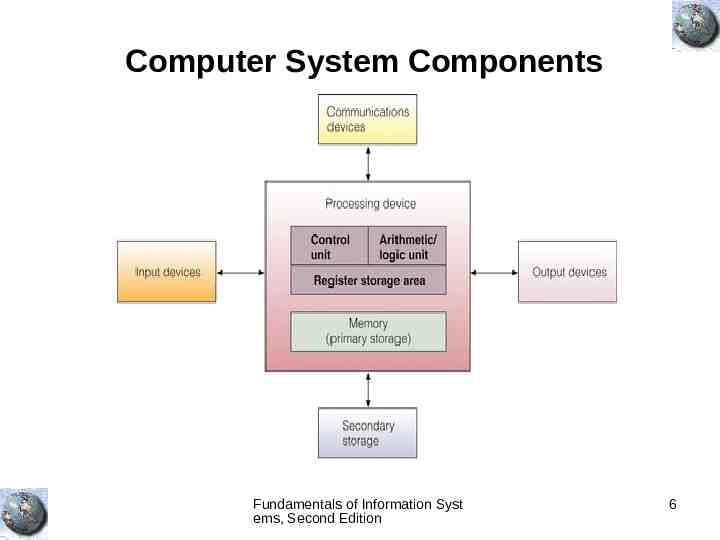
Computer System Components Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 6

Hardware Components in Action Instruction phase – Step 1: Fetch instruction – Step 2: Decode instruction Execution phase – Step 3: Execute the instruction – Step 4: Store the results Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 7
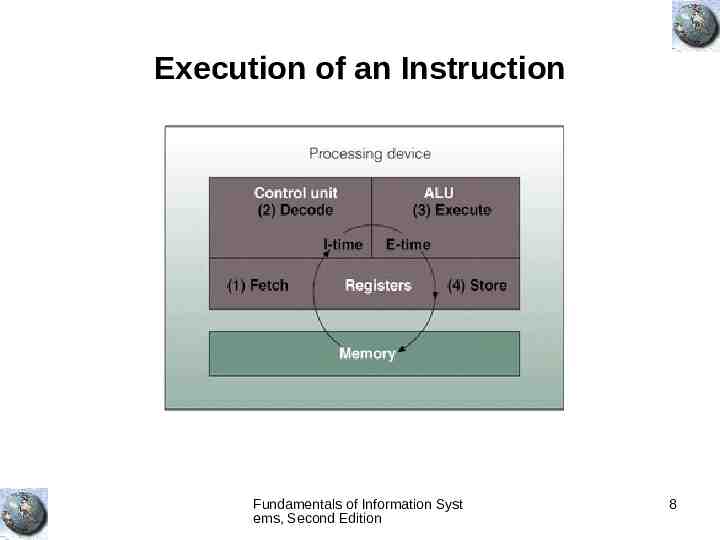
Execution of an Instruction Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 8
Processing and Memory Devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 9
Processing Characteristics and Functions Machine cycle time Clock speed Wordlength Superconductivity Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 10
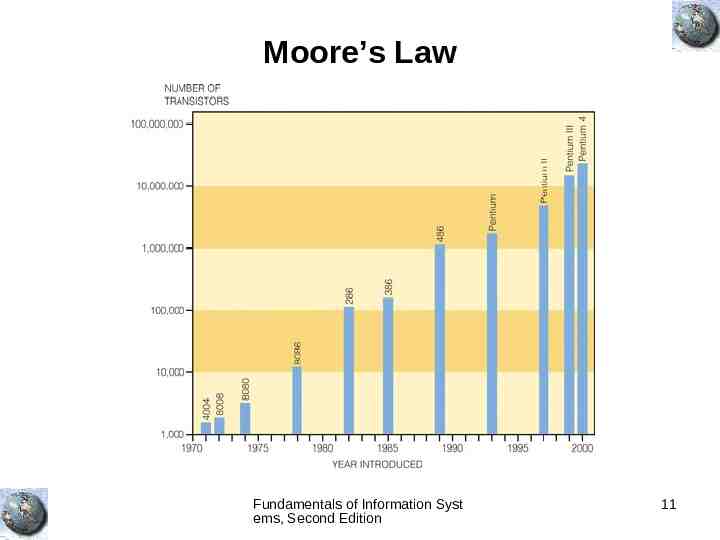
Moore’s Law Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 11
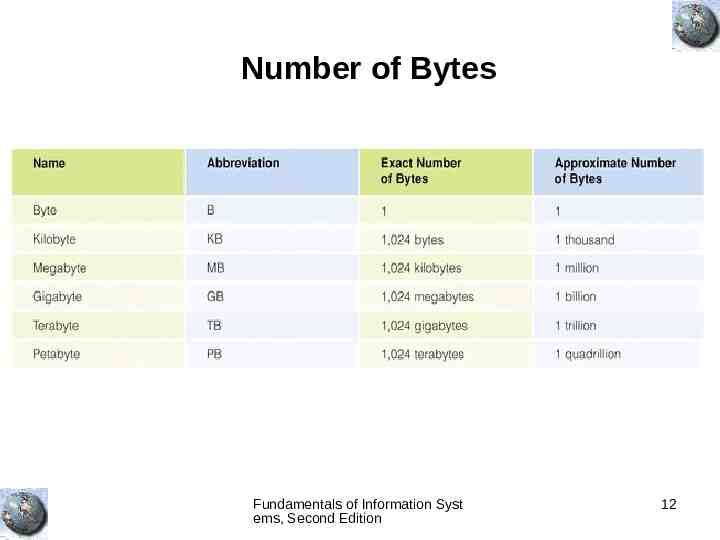
Number of Bytes Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 12
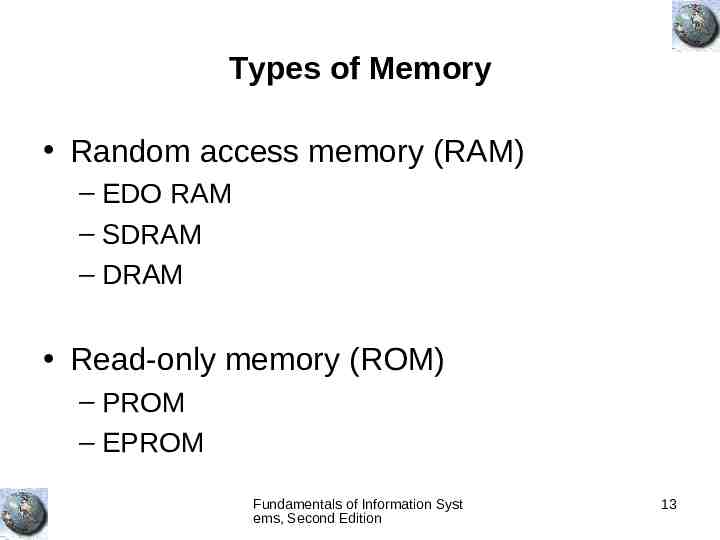
Types of Memory Random access memory (RAM) – EDO RAM – SDRAM – DRAM Read-only memory (ROM) – PROM – EPROM Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 13
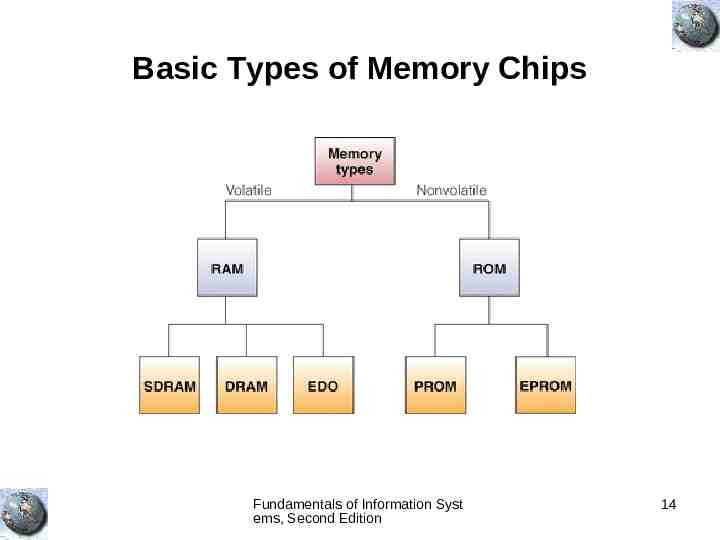
Basic Types of Memory Chips Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 14

Secondary Storage and Output Devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 15
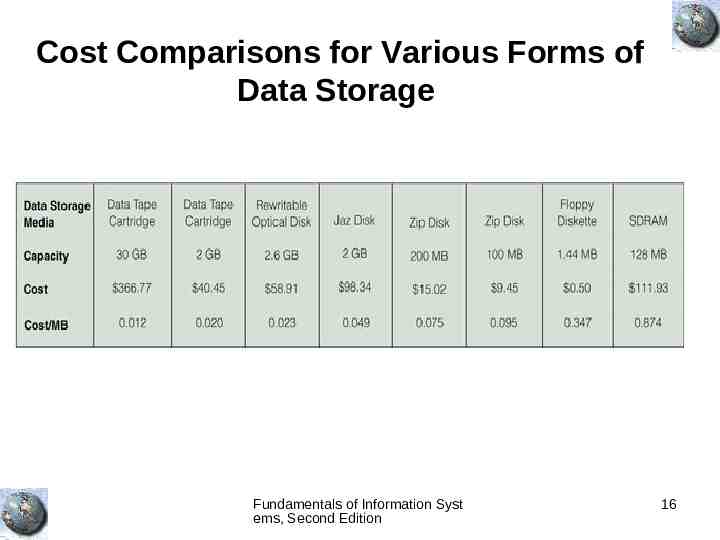
Cost Comparisons for Various Forms of Data Storage Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 16

Secondary Storage Access Methods Sequential access Direct access Sequential access storage devices Direct access storage devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 17

Secondary Storage Devices Magnetic tapes Magnetic discs RAID SAN Optical discs Magneto-optical discs Digital versatile discs Memory cards Expandable storage Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 18

Types of Secondary Storage Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 19

Hard Disc Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 20
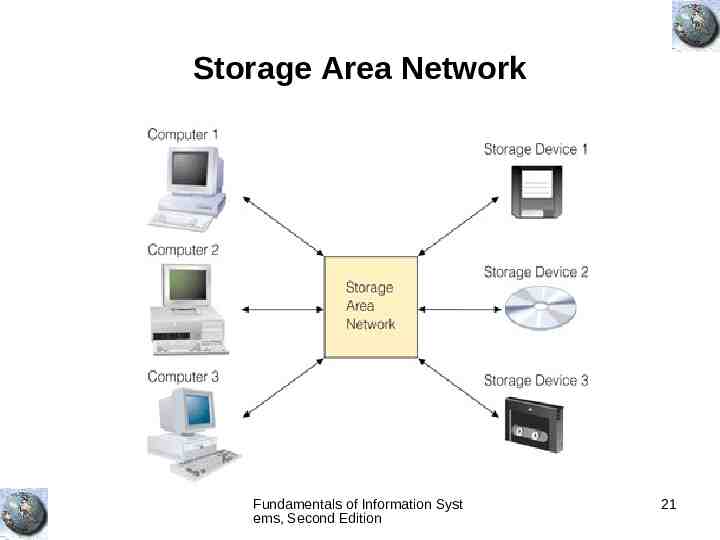
Storage Area Network Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 21

Digital Versatile Disc Player Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 22

Expandable Storage Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 23
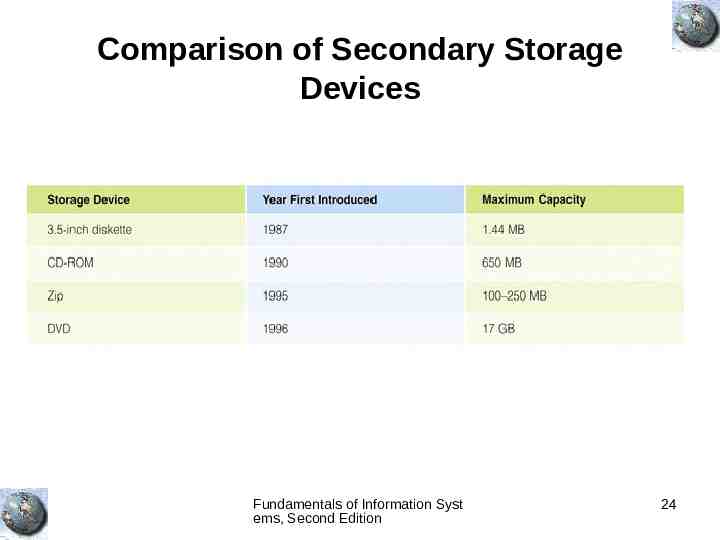
Comparison of Secondary Storage Devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 24

Input Devices Personal computer input devices Voice-recognition devices Digital computer cameras Terminals Scanning devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 25

A PC Equipped with a Computer Camera Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 26
Output Devices Display Monitors Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) Printers and Plotters Music Devices Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 27

Laser Printer Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 28
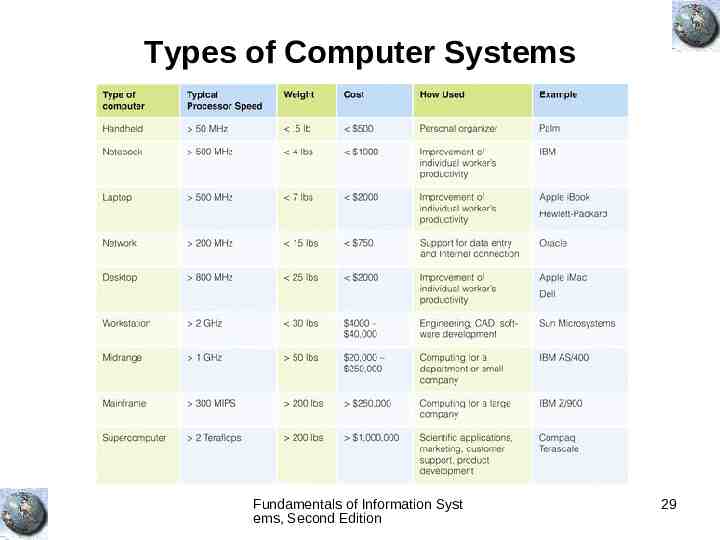
Types of Computer Systems Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 29

Overview of Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 30

Overview of Software Computer programs Documentation Systems software Computer system platform Application software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 31
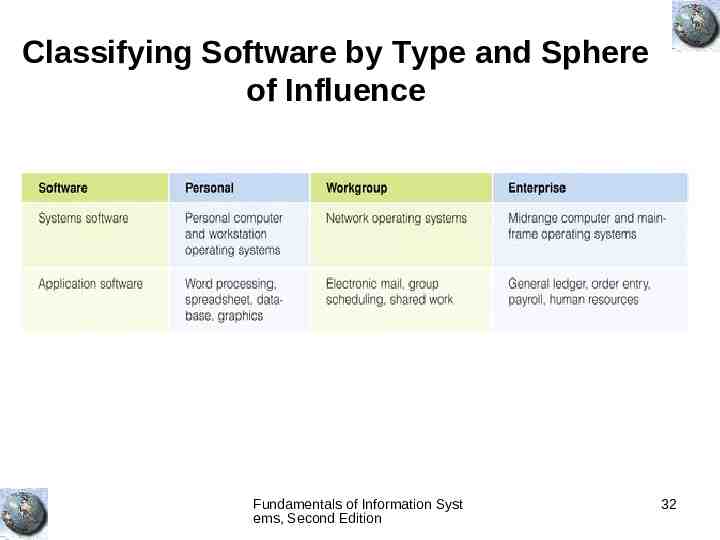
Classifying Software by Type and Sphere of Influence Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 32

Systems Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 33

Operating Systems Perform common computer hardware functions Provide a user interface Provide a degree of hardware independence Manage system memory Manage processing tasks Provide networking capability Control access to system resources Manage files Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 34
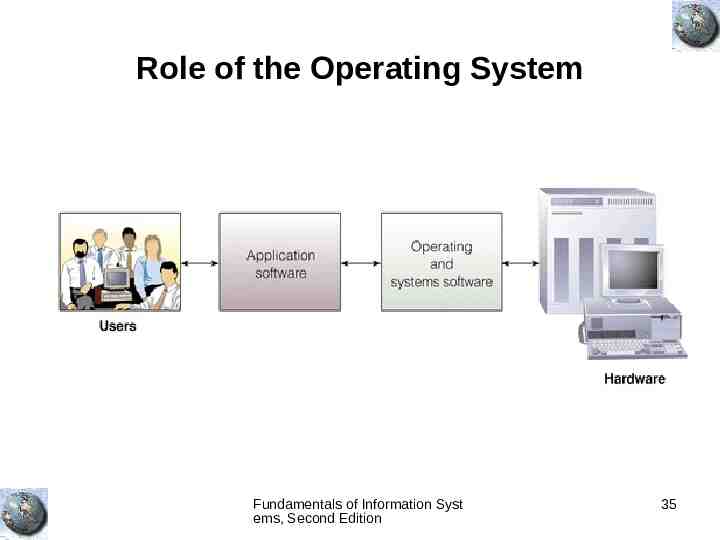
Role of the Operating System Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 35
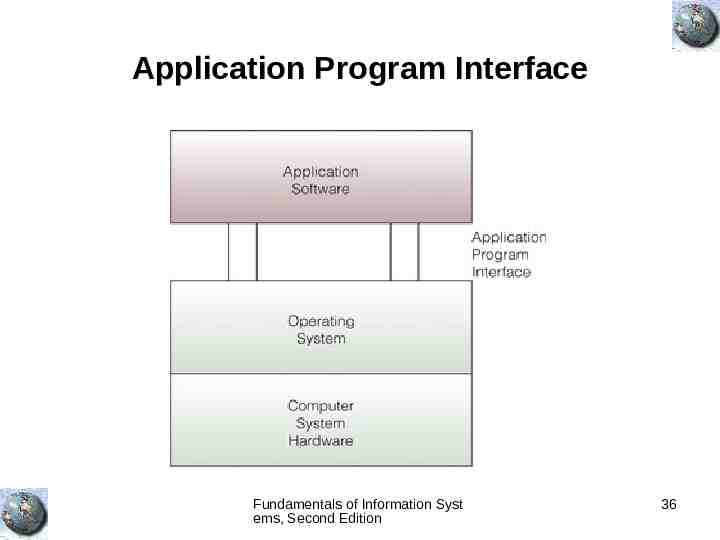
Application Program Interface Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 36
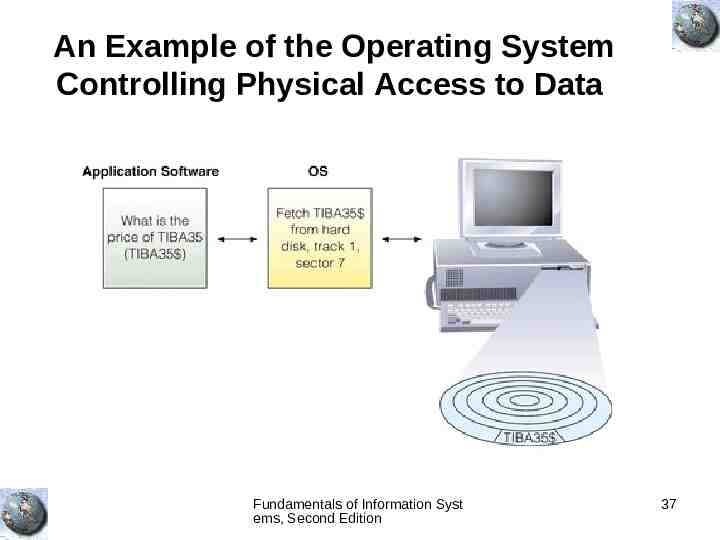
An Example of the Operating System Controlling Physical Access to Data Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 37
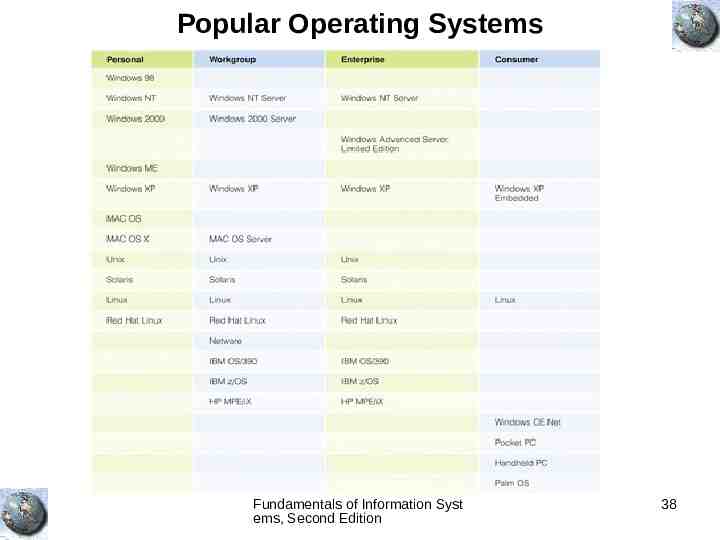
Popular Operating Systems Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 38

Workgroup Operating Systems Windows 2000 Server Unix Netware Red Hat Linux Mac OS X Server Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 39
Consumer Appliance Operating Systems Windows CE .NET Windows XP Embedded Handheld PC Pocket PC Palm OS Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 40

Nokia 7650 Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 41

Application Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 42
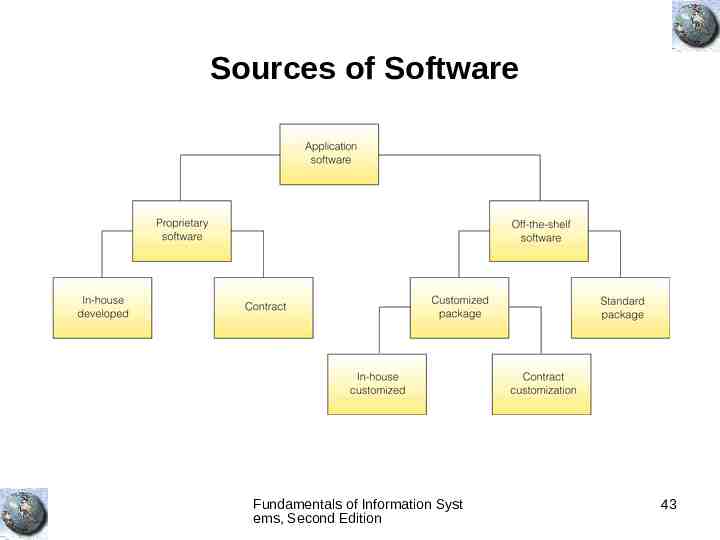
Sources of Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 43
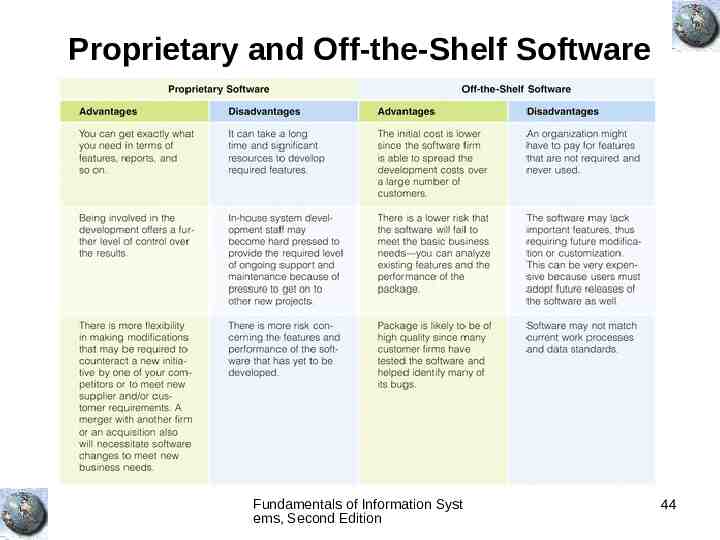
Proprietary and Off-the-Shelf Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 44
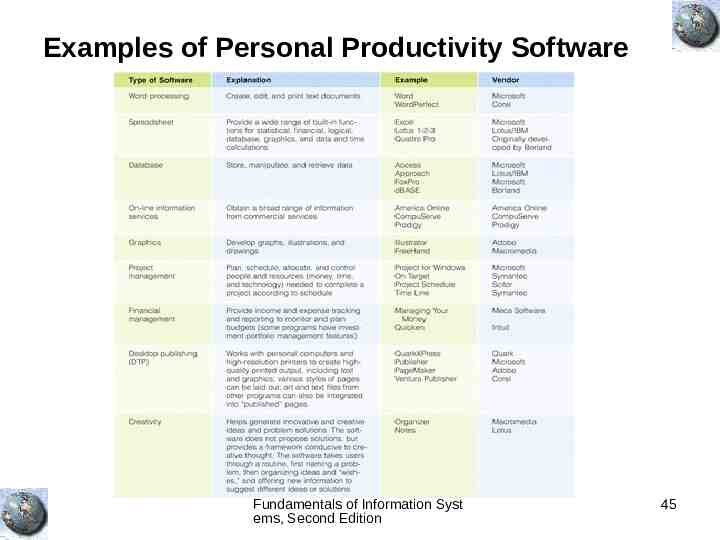
Examples of Personal Productivity Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 45
TurboTax Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 46
Quicken Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 47
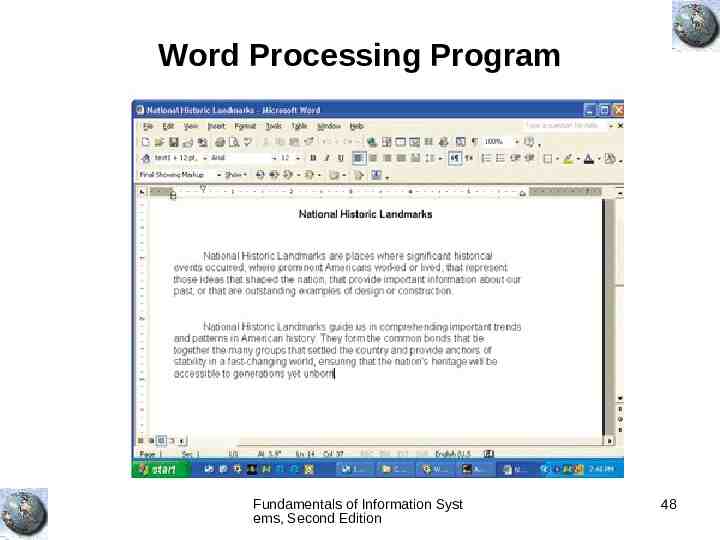
Word Processing Program Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 48
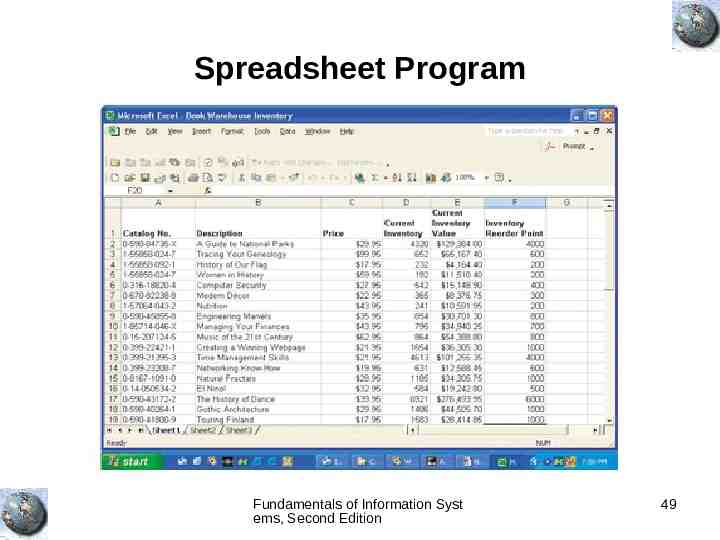
Spreadsheet Program Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 49
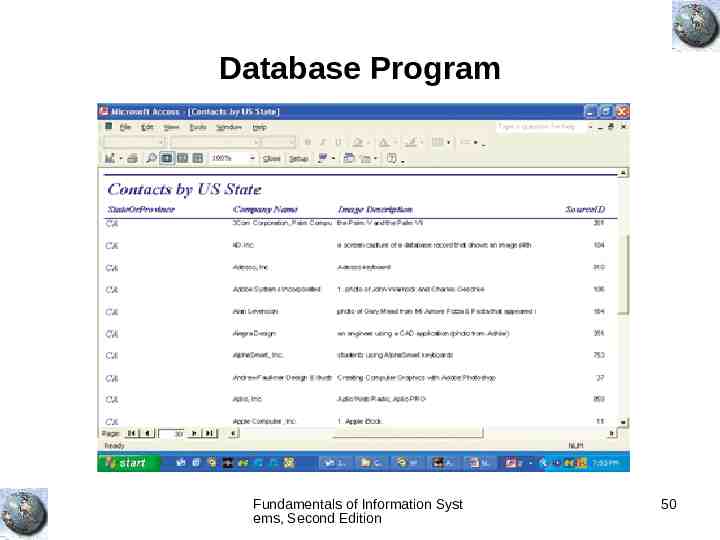
Database Program Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 50
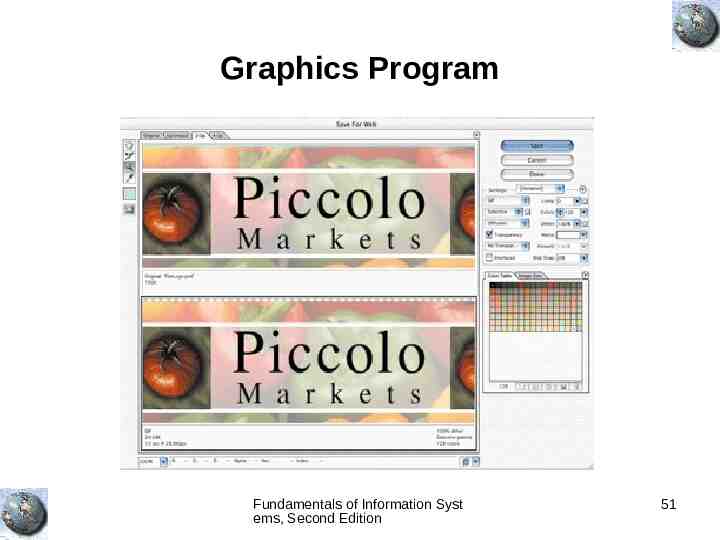
Graphics Program Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 51
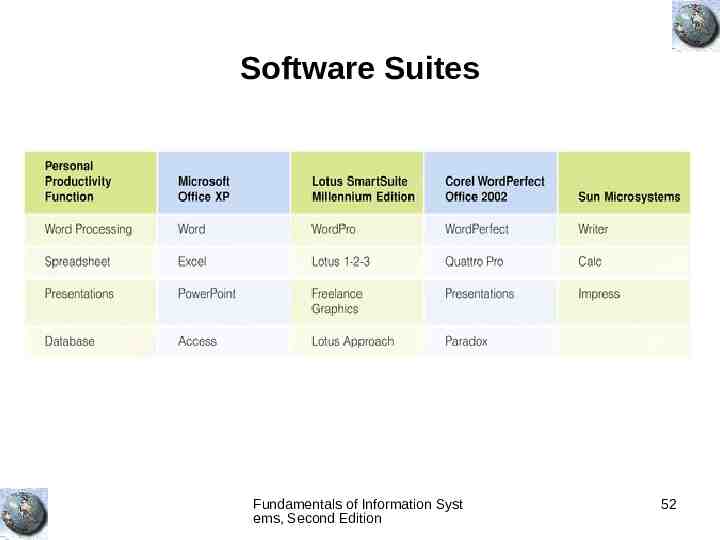
Software Suites Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 52
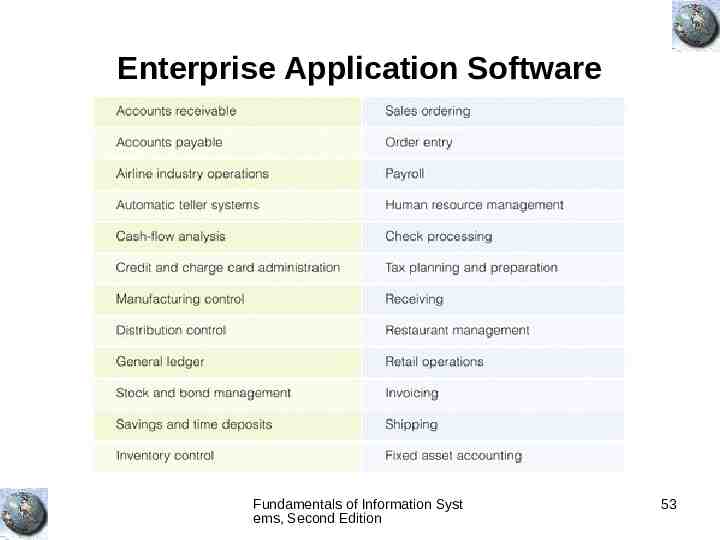
Enterprise Application Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 53
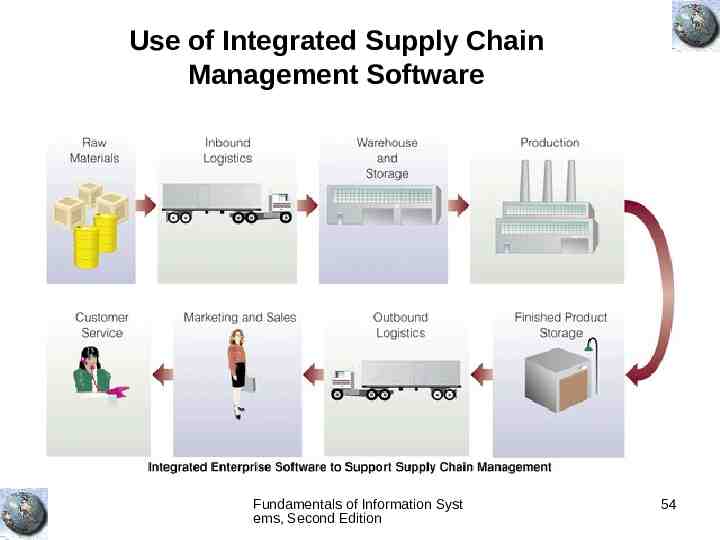
Use of Integrated Supply Chain Management Software Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 54

Selected Enterprise Resource Planning Vendors Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 55
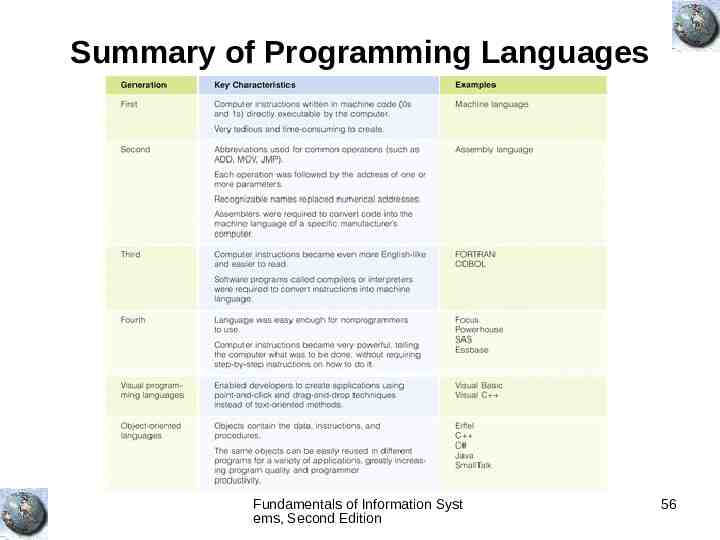
Summary of Programming Languages Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 56

Summary Hardware devices work together to perform input, processing, data storage, and output. There are two main categories of software: systems software and application software. An operating system (OS) is a set of computer programs that controls the computer hardware to support users’ computing needs. Application software may be proprietary or off-the-shelf. There are five generations of programming languages, plus objectoriented programming languages. Fundamentals of Information Syst ems, Second Edition 57





