Figure 1. National Drug-Involved Overdose Deaths* Number Among All
10 Slides1.09 MB
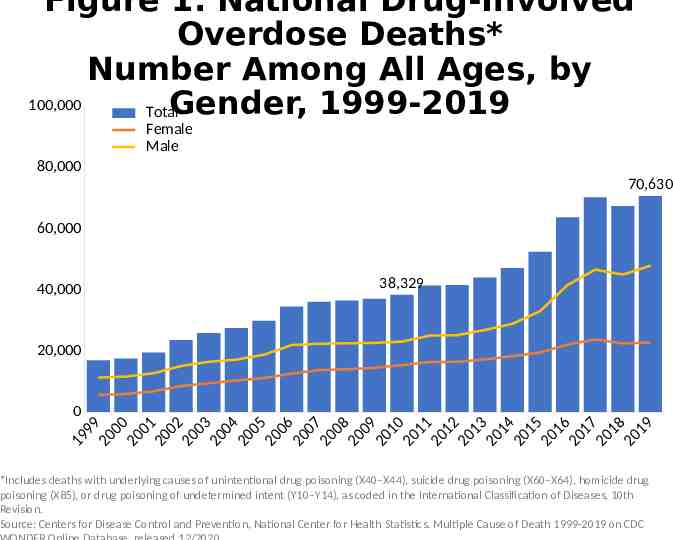
Figure 1. National Drug-Involved Overdose Deaths* Number Among All Ages, by 100,000 Gender, 1999-2019 Total Female Male 80,000 70,630 60,000 40,000 38,329 20,000 0 9 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 03 00 4 0 0 5 0 06 00 7 0 0 8 0 0 9 01 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 0 13 01 4 01 5 0 16 01 7 01 8 0 1 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Includes deaths with underlying causes of unintentional drug poisoning (X40–X44), suicide drug poisoning (X60–X64), homicide drug poisoning (X85), or drug poisoning of undetermined intent (Y10–Y14), as coded in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC
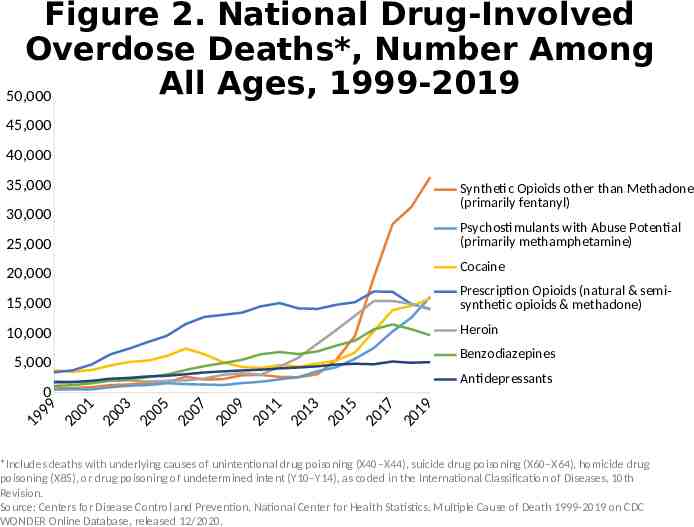
Figure 2. National Drug-Involved Overdose Deaths*, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 50,000 45,000 40,000 35,000 Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone (primarily fentanyl) 30,000 Psychostimulants with Abuse Potential (primarily methamphetamine) 25,000 Cocaine 20,000 15,000 Prescription Opioids (natural & semisynthetic opioids & methadone) 10,000 Heroin Benzodiazepines 5,000 1 0 9 99 Antidepressants 0 20 1 0 20 3 0 20 5 0 20 7 0 20 9 1 20 1 1 20 3 1 20 5 1 20 7 1 20 9 *Includes deaths with underlying causes of unintentional drug poisoning (X40–X44), suicide drug poisoning (X60–X64), homicide drug poisoning (X85), or drug poisoning of undetermined intent (Y10–Y14), as coded in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
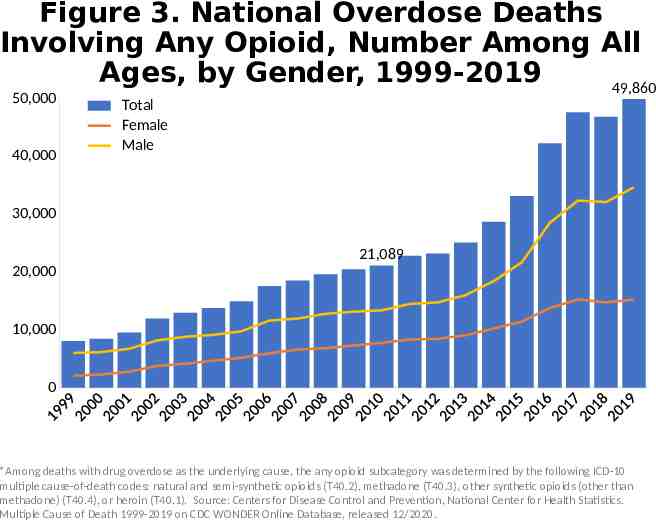
Figure 3. National Overdose Deaths Involving Any Opioid, Number Among All Ages, by Gender, 1999-2019 49,860 50,000 40,000 Total Female Male 30,000 21,089 20,000 10,000 0 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the any opioid subcategory was determined by the following ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death codes: natural and semi-synthetic opioids (T40.2), methadone (T40.3), other synthetic opioids (other than methadone) (T40.4), or heroin (T40.1). Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
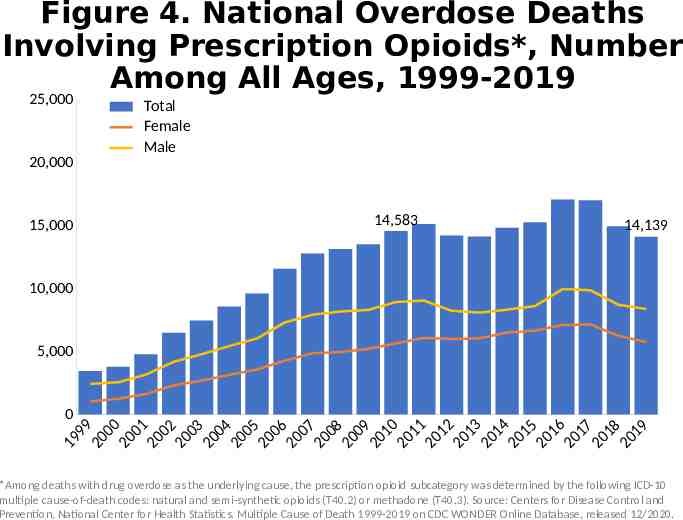
Figure 4. National Overdose Deaths Involving Prescription Opioids*, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 25,000 20,000 15,000 Total Female Male 14,583 14,139 10,000 5,000 0 9 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 02 00 3 0 0 4 0 05 00 6 00 7 0 08 0 09 0 1 0 01 1 01 2 0 1 3 0 1 4 01 5 0 1 6 0 17 0 18 01 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the prescription opioid subcategory was determined by the following ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death codes: natural and semi-synthetic opioids (T40.2) or methadone (T40.3). Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
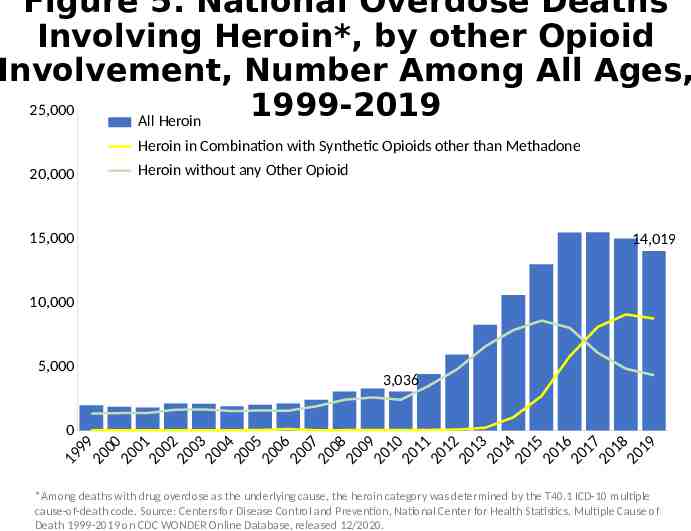
Figure 5. National Overdose Deaths Involving Heroin*, by other Opioid Involvement, Number Among All Ages, 25,000 1999-2019 All Heroin Heroin in Combination with Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone 20,000 Heroin without any Other Opioid 15,000 14,019 10,000 5,000 3,036 0 9 9 0 00 0 0 1 00 2 0 0 3 00 4 0 0 5 0 06 0 0 7 00 8 0 0 9 01 0 0 1 1 01 2 0 1 3 0 14 0 15 01 6 0 1 7 01 8 0 1 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the heroin category was determined by the T40.1 ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death code. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
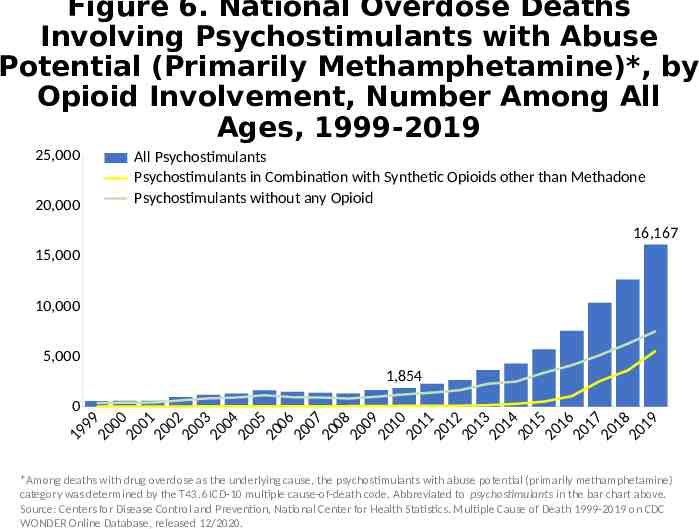
Figure 6. National Overdose Deaths Involving Psychostimulants with Abuse Potential (Primarily Methamphetamine)*, by Opioid Involvement, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 25,000 20,000 All Psychostimulants Psychostimulants in Combination with Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone Psychostimulants without any Opioid 16,167 15,000 10,000 5,000 1,854 0 9 9 00 0 0 0 1 00 2 0 0 3 00 4 0 0 5 00 6 0 0 7 00 8 00 9 01 0 01 1 01 2 01 3 01 4 01 5 01 6 01 7 01 8 01 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the psychostimulants with abuse potential (primarily methamphetamine) category was determined by the T43.6 ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death code. Abbreviated to psychostimulants in the bar chart above. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
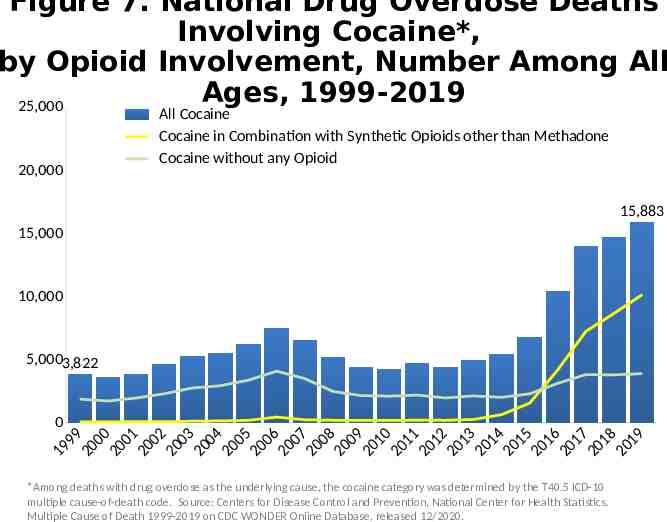
Figure 7. National Drug Overdose Deaths Involving Cocaine*, by Opioid Involvement, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 25,000 20,000 All Cocaine Cocaine in Combination with Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone Cocaine without any Opioid 15,883 15,000 10,000 5,0003,822 0 9 9 00 0 0 01 0 0 2 00 3 00 4 00 5 0 06 0 0 7 00 8 0 0 9 0 1 0 0 11 0 1 2 01 3 0 1 4 0 1 5 0 16 0 1 7 01 8 0 1 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the cocaine category was determined by the T40.5 ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death code. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
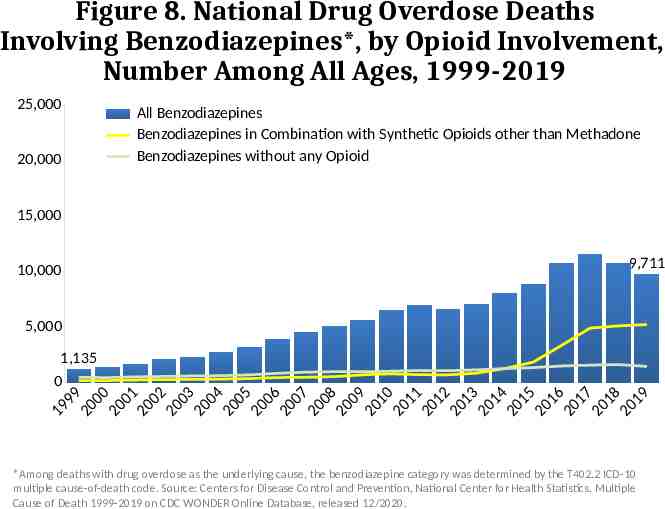
Figure 8. National Drug Overdose Deaths Involving Benzodiazepines*, by Opioid Involvement, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 25,000 20,000 All Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines in Combination with Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone Benzodiazepines without any Opioid 15,000 10,000 9,711 5,000 1,135 0 9 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 0 04 0 05 0 0 6 0 0 7 0 0 8 0 0 9 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 01 3 01 4 0 1 5 0 1 6 0 1 7 0 1 8 0 1 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the benzodiazepine category was determined by the T402.2 ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death code. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
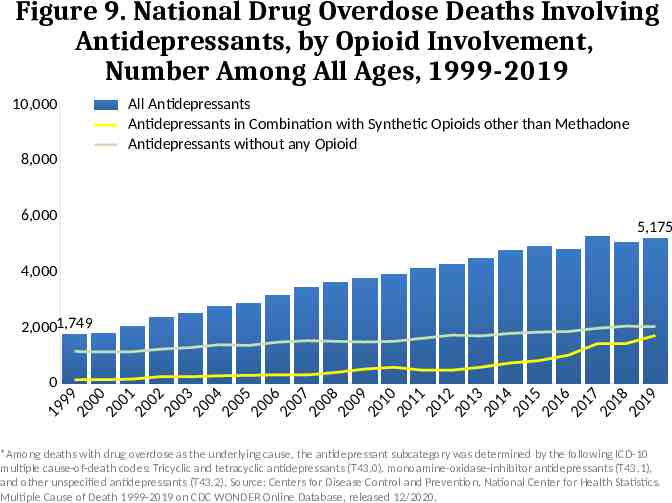
Figure 9. National Drug Overdose Deaths Involving Antidepressants, by Opioid Involvement, Number Among All Ages, 1999-2019 10,000 8,000 6,000 All Antidepressants Antidepressants in Combination with Synthetic Opioids other than Methadone Antidepressants without any Opioid 5,175 4,000 2,0001,749 0 9 9 00 0 0 0 1 00 2 00 3 0 04 0 05 0 0 6 00 7 0 08 0 0 9 01 0 01 1 0 12 0 13 0 1 4 01 5 0 16 0 1 7 01 8 01 9 9 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 *Among deaths with drug overdose as the underlying cause, the antidepressant subcategory was determined by the following ICD-10 multiple cause-of-death codes: Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants (T43.0), monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor antidepressants (T43.1), and other unspecified antidepressants (T43.2). Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Multiple Cause of Death 1999-2019 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released 12/2020.
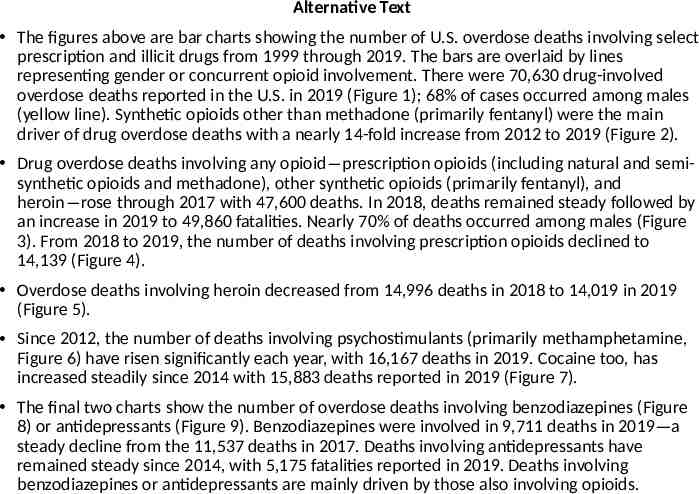
Alternative Text The figures above are bar charts showing the number of U.S. overdose deaths involving select prescription and illicit drugs from 1999 through 2019. The bars are overlaid by lines representing gender or concurrent opioid involvement. There were 70,630 drug-involved overdose deaths reported in the U.S. in 2019 (Figure 1); 68% of cases occurred among males (yellow line). Synthetic opioids other than methadone (primarily fentanyl) were the main driver of drug overdose deaths with a nearly 14-fold increase from 2012 to 2019 (Figure 2). Drug overdose deaths involving any opioid―prescription opioids (including natural and semisynthetic opioids and methadone), other synthetic opioids (primarily fentanyl), and heroin―rose through 2017 with 47,600 deaths. In 2018, deaths remained steady followed by an increase in 2019 to 49,860 fatalities. Nearly 70% of deaths occurred among males (Figure 3). From 2018 to 2019, the number of deaths involving prescription opioids declined to 14,139 (Figure 4). Overdose deaths involving heroin decreased from 14,996 deaths in 2018 to 14,019 in 2019 (Figure 5). Since 2012, the number of deaths involving psychostimulants (primarily methamphetamine, Figure 6) have risen significantly each year, with 16,167 deaths in 2019. Cocaine too, has increased steadily since 2014 with 15,883 deaths reported in 2019 (Figure 7). The final two charts show the number of overdose deaths involving benzodiazepines (Figure 8) or antidepressants (Figure 9). Benzodiazepines were involved in 9,711 deaths in 2019—a steady decline from the 11,537 deaths in 2017. Deaths involving antidepressants have remained steady since 2014, with 5,175 fatalities reported in 2019. Deaths involving benzodiazepines or antidepressants are mainly driven by those also involving opioids.