Cash and Receivables Sid Glandon, DBA, CPA Assistant Professor
19 Slides146.50 KB

Cash and Receivables Sid Glandon, DBA, CPA Assistant Professor of Accounting

Cash and Cash Equivalents Cash coin and currency demand deposits Cash equivalents Short-investments (90 days) Money market funds Treasury bills Commercial paper

Internal Controls Separation of duties Checking accounts Petty cash funds Physical protection of cash Protection of the accounting information system records Bank reconciliations

Bank Reconciliation Three steps Reconciliation per bank Reconciliation per book Adjusting journal entries

Items Not Considered Cash Overdraft without the right of offset Restricted cash accounts Investments Post dated checks from customers Loans to employees

Restricted Cash Not available to cover current liabilities Bond sinking funds Compensating balances

Receivables Accounts receivable (Trade) Notes receivable Nontrade receivables Advances to officers and employees Advances to subsidiaries Deposits Dividends and interest receivable Claims against others

Initial Valuation Converted into cash within operating cycle Initial valuation at the amount expected to be received Trade discounts Selling price less than normal list price Cash or sales discounts Incentive for paying invoice on time gross method net method

Subsequent Valuation Sales Returns Uncollectible accounts Allowance method Balance sheet approach Income statement approach

Balance Sheet Approach Prepare a schedule of agee accounts receivable Determine amount or percentage that will likely not be collected Adjust the allowance account to reflect the computed amount by Journalize Bad debt expense-debit Allowance for doubtful accounts-credit

Journal Entry: Balance Sheet Approach ACCOUNT DEBIT CREDIT Bad debt expense XXX Allowance for doubtful accounts XXX To adjust the allowance for doubtful accounts

Income Statement Approach Determine net credit sales Calculate estimated percentage of bad debt expense against net credit sales Journalize Bad debt expense-debit Allowance for doubtful accounts-credit

Journal Entry: Income Statement Approach ACCOUNT DEBIT CREDIT Bad debt expense XXX Allowance for doubtful accounts XXX To record bad debt expense for the year

Transactions Using the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Beginning balance Write-off of uncollectible accounts Reinstate accounts previously written-off Analyze ending balance and adjust based on the analysis of year end aged accounts receivables

ACCOUNT Allowance for doubtful accounts Accounts receivable To write-off an uncollectable account DEBIT CREDIT XXX XXX ACCOUNT DEBIT CREDIT Accounts receivable XXX Allowance for doubtful accounts XXX To reinstate an account previously written-off ACCOUNT DEBIT CREDIT Cash XXX Accounts receivable XXX To record the collection of the reinstated account
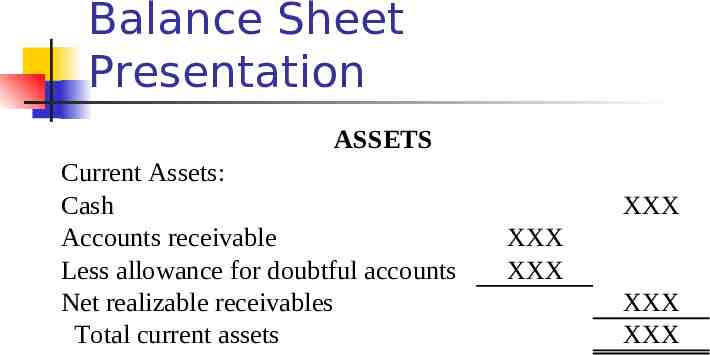
Balance Sheet Presentation ASSETS Current Assets: Cash Accounts receivable Less allowance for doubtful accounts Net realizable receivables Total current assets XXX XXX XXX XXX XXX

Recognition of Notes Receivable Interest-bearing notes Note issued at face value Noninterest-bearing notes Zero-interest-bearing notes Interest is Imputed and the note is sold at a discount

Financing with Receivables Secured borrowing Sales of receivables Assigned or pledged Factoring Securitization Sales without recourse Sales with recourse

Discounting a Note Sale of note to a financial institution Discount rate (banks market interest rate) is applied to the maturity value The seller receives cash of the maturity value less the discount






