CHAPTER 9 & 10 Customer Relationship Management Supply
21 Slides2.53 MB

CHAPTER 9 & 10 Customer Relationship Management Supply Chain Management

OUTLINE Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Definition Operational CRM Analytical CRM Supply Chain Management (SCM) Supply Chains IT Support for Supply Chain Management
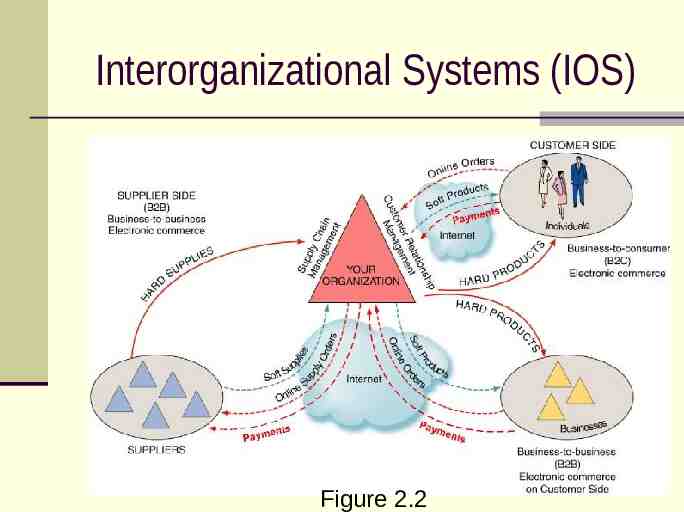
Interorganizational Systems (IOS) Figure 2.2

From Neighborhood Stores . Personal

To Today . Mobile population The Web Giant malls Impersonal
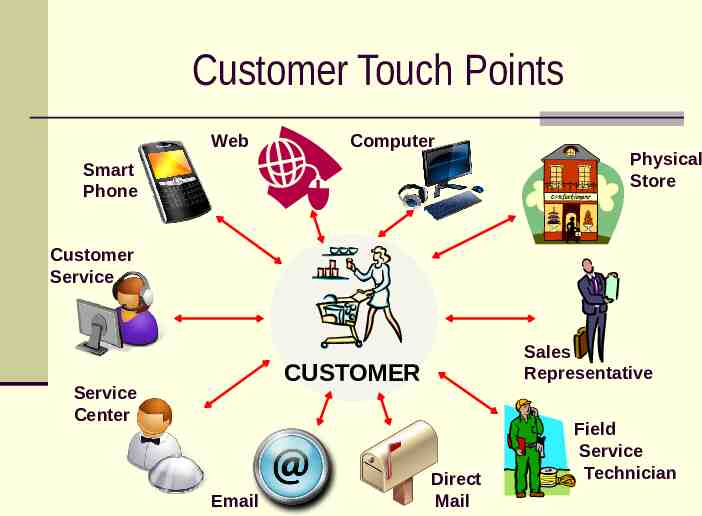
Customer Touch Points Web Computer Smart Phone Physical Store Customer Service Sales Representative CUSTOMER Service Center Email Direct Mail Field Service Technician

Customer Relationship Management: Motivations It costs six times more to sell to a new customer than to sell to an existing one. A typical dissatisfied customer will tell 8-10 people. By increasing the customer retention rate by 5%, profits could increase by 85%. 70% of complaining customers will remain loyal if their problem is solved

Principles of CRM A customer-centered organizational strategy “Treat different customers differently” Keep profitable customers and maximize lifetime revenue from them
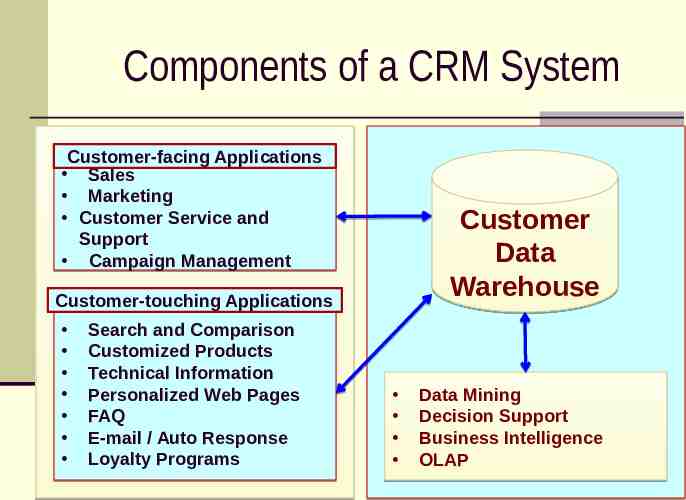
Components of a CRM System Customer-facing Applications Sales Marketing Customer Service and Support Campaign Management Customer Data Warehouse Customer-touching Applications Search and Comparison Customized Products Technical Information Personalized Web Pages FAQ E-mail / Auto Response Loyalty Programs Data Mining Decision Support Business Intelligence OLAP

Customer-Facing Applications Customer service and support Sales force automation Marketing Campaign management
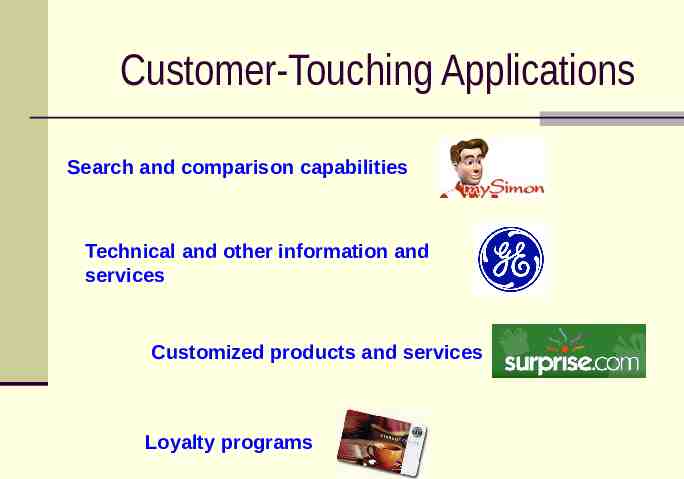
Customer-Touching Applications Search and comparison capabilities Technical and other information and services Customized products and services Loyalty programs
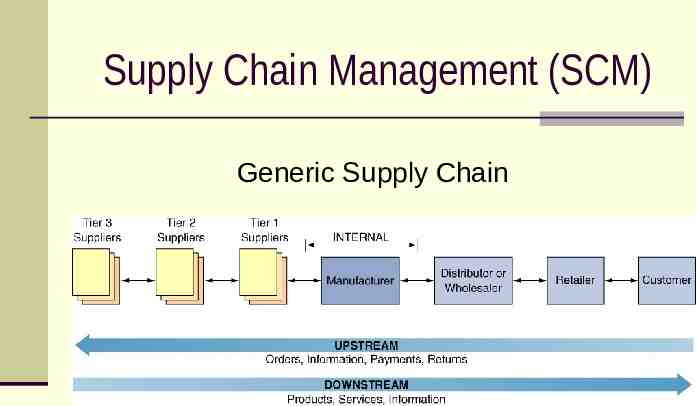
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Generic Supply Chain

Problems Along the Supply Chain Longer product development cycle Poor quality product Poor customer service High inventory costs Loss of revenues
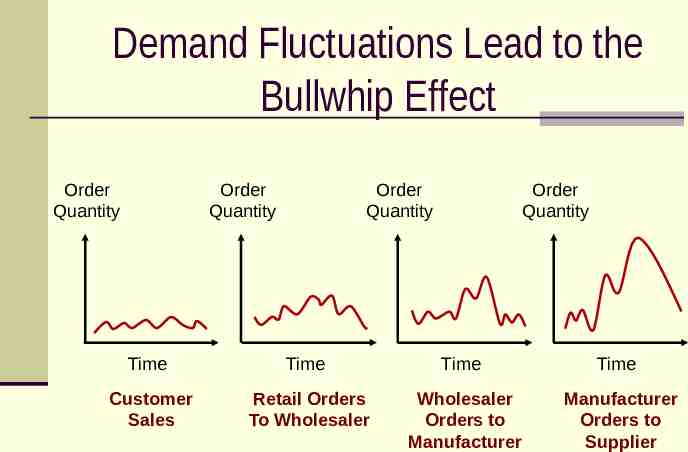
Demand Fluctuations Lead to the Bullwhip Effect Order Quantity Order Quantity Order Quantity Order Quantity Time Time Time Time Customer Sales Retail Orders To Wholesaler Wholesaler Orders to Manufacturer Manufacturer Orders to Supplier
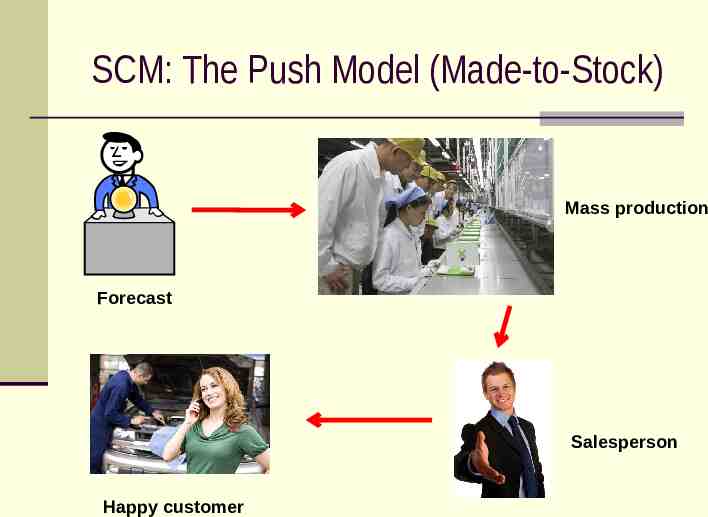
SCM: The Push Model (Made-to-Stock) Mass production Forecast Salesperson Happy customer
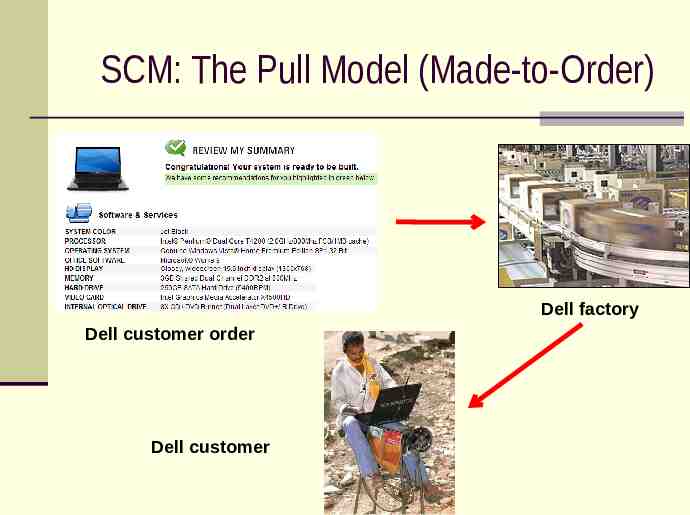
SCM: The Pull Model (Made-to-Order) Dell factory Dell customer order Dell customer

Solutions to Supply Chain Problems Removing excess inventory to expose hidden problems Just-in-time inventory (Toyota Production System) Information sharing Vendor-managed inventory (e.g., P&G)
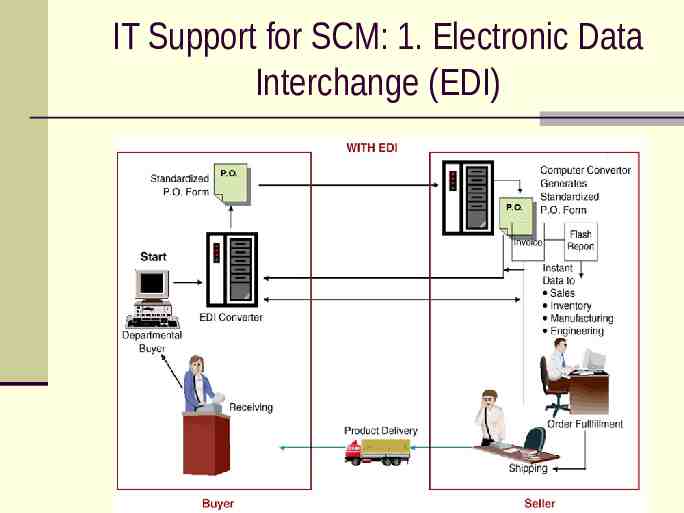
IT Support for SCM: 1. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)

IT Support for SCM: 2. Extranets The main goal of extranets is to foster collaboration between business partners. An extranet is open to selected B2B suppliers, customers and other business partners.
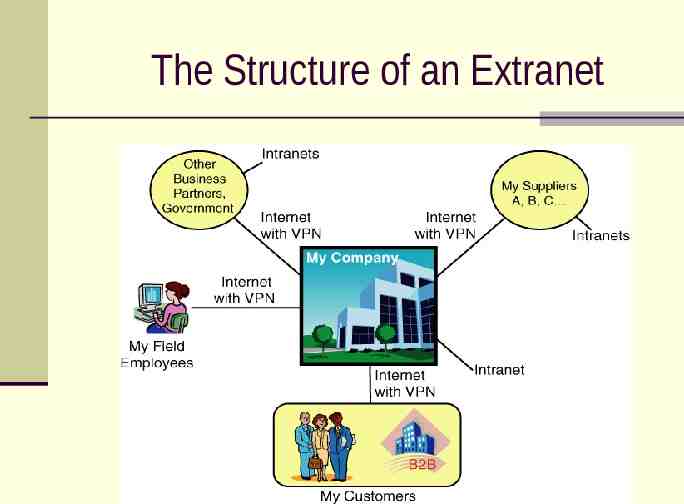
The Structure of an Extranet

Types of Extranets A company and its dealers, customers or suppliers An industry’s extranet Joint ventures and other business partnerships






